Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer 2
Uploaded by
Rosie CuasitoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reviewer 2
Uploaded by
Rosie CuasitoCopyright:
Available Formats
BON qualifications M masters in NSG A- accredited nsg org (PNA) S seven (1 chairman, 6 members) I immediately resign upon appointment
ent N not convicted of any crime P pecuniary interest, absence of T 10 yrs experience (last 5 years hr in RP) C citizen & resident of RP
Ex. Papavarine Hcl Prophantheline Bromide (Profanthene) c.) Vasodilator NTG d.) Antacid Maalox e.) H2 receptor antagonist -Ranitidin(Zantac) to decrease pancreatic stimulation f.) Ca gluconate to decrease pancreatic stimulation
DEAN qualification Chief nurse & Director > RN + MAN + 5 yrs experience in nsg
Nurse Licensure Exam 1. Cert of Good Moral Char (Optional) 2. Proof holder of Fil citizenship Birth cert. 3. Proof BSN degree Transcript with scanned picture done by reg
2. Withold food & fluid aggravates pain (total NPO) 3. Assist in Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) or hyperalimentation Complications of TPN Infectionmaintain a strict aseptic technique Pulmonary Embolismcheck all connection to system Hyperglycemia Hyperkalemia 4. Institute stress mgt tech a.) DBE b.) Biofeedback 5. Comfy position -Knee chest or fetal lie position 6. If pt can tolerate food, give increase CHO, decrease fats, and moderate CHON 7. Complications: Chronic hemorrhagic pancreatitis, Peritonitis, Septicemia, Shock
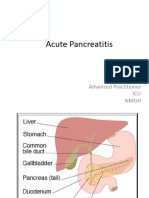
PANCREATITIS
acute or chronic inflammation of pancreas leading to pancreatic edema, hemorrhage & necrosis due to auto digestion (self-digestion). Bleeding of pancreas - Cullens sign on umbilical area PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE (PUD) excoriation / erosion of submucosa & mucosal lining due to: a.) Hyper secretion of acid pepsin b.) Decrease resistance to mucosal barrier Incidence Rate: 1. Men 40 55 yrs old 2. Aggressive persons/ type A personality 3. Hereditary Predisposing factors: 1. Hereditary 2. Emotional 3. Smoking vasoconstriction GIT ischemia 4. Alcoholism stimulates release of histamine = Parietal cell release Hcl acid = ulceration 5. Caffeine tea, soda, chocolate 6. Irregular diet 7. Rapid eating 8. Ulcerogenic drugs NSAIDS, aspirin, steroids, indomethacin, ibuprofen Indomethacin -S/E corneal cloudiness. Needs annual eye check up. NSAID and steroids= gastropathy 9. Gastrin producing tumor or gastrinoma Zollinger Ellisons syndrome 10. Microbial invasion helicobacter pylori. Metronidazole (Flagyl)
Predisposing factors: 1. Chronic alcoholism 2. Hepatobilary disease 3. Obesity 4. Hyperlipidemia 5. Hyperparathyroidism 6. Drugs Thiazide diuretics,aspirin, pills, Pentamidine HCL (Pentam) for clients with AIDS, 7. Diet increase saturated fats S/Sx: 1. Severe Midepigastrium epigastric pain radiates from back & flank area (left upper quadrant) -24-48 hrs. Aggravated by heavy meals/eating, accompanied by DOB 2. N/V 3. Tachycardia 4. Palpitation due to pain (abdominal guarding) 5. Dyspepsia /indigestion (rigid board like abdomen) 6. Decrease bowel sounds 7. (+) Cullens sign -ecchymosis of umbilicus hemorrhage 8. (+) Grey Turners spots ecchymosis of flank area 9. Hypocalcemia Diagnosis: Serum amylase & lipase increase Urine lipase increase Serum Ca decrease Nursing Mgt: 1. Meds a.) Narcotic analgesic -Meperidine Hcl (Demerol) Dont give Morphine SO4 will cause spasm of the sphincter of ODDI. b.) Smooth muscle relaxant/ anticholinergic
SITE PAIN
GASTRIC ULCER Antrum or lesser curvature > 30 min 1 hr after eating > epigastrium > gaseous & burning >not usually relieved by food & antacid >Eating leads to pain Normal gastric acid secretion common hematemesis Wt loss a. stomach cancer b. hemorrhage
DUODENAL ULCER Duodenal bulb >2-3 hrs after eating >mid epigastrium >cramping & burning pain >usually relieved by food & antacid >12 MN 3am pain >Eating lessens pain Increased gastric acid secretion Not common Melena Wt gain a. perforation
HYPERSECRETION VOMITING HEMORRHAGE WT COMPLICATIONS
Diagnosis: Endoscopic exam Stool from occult blood (+) Gastric analysis Gastric Ulcer: normal gastric acid secretion Duodenal: increased gastric acid secretion GI Series-confirm presence of ulceration Nursing Mgt: 1. Diet bland, non irritating, non spicy 2. Avoid caffeine & milk/ milk products > Increase gastric acid secretion 3. Administer meds Antacids > ACA Aluminum containing antacids Magnesium containing antacids H2 receptor antagonist: o Ranitidine (Zantac) SE: fever o Cimetidine (Tagamet)hastens the effect of oral anticoagulants o Famotidine (Pepcid) SE: fever -Avoid smoking decrease effectiveness of drug Nursing Mgt: Administer antacid & H2 receptor antagonist (Cimetidine) 1hr apart Cemetidine decrease antacid absorption & vise versa Cytoprotective agents o Sucralfate (Carafate) -Provides a paste like subs that coats mucosal lining of stomach o Misoprostol (Cytotec) SE: menstrual spotting Sedatives/ Tranquilizers -Valium, lithium Anticholinergics / Antispasmodic o Atropine SO4 o Prophantheline Bromide (Profanthene) NOTE: Pt has history of hpn crisis with peptic ulcer disease. Rn should not administer alka seltzer-has large amount of Na. Surgery: subtotal gastrectomy -Partial removal of stomach. Billroth I (Gastroduodenostomy) Removal of of stomach & anastomoses of gastric stump to the duodenum Billroth II (Gastrojejunostomy) Removal of -3/4 of stomach & duodenal bulb & anastomostoses of gastric stump to jejunum. Before surgery for BI or BII -Do vagotomy (severing of vagus nerve) & pyloroplasty (drainage) first.
Nursing Mgt: Monitor NGT output or drainage immediately post op-bright red o Immediately post op should be Bright Red o Within 36-48h output is yellow green o After 48h output is Dark Red due to HCl acid Administer meds: o Analgesic o Antibiotic o Antiemetics Maintain patent IV line VS, I&O & bowel sounds Complications: o Hemorrhage hypovolemic shock Late signs anuria o Peritonitis o Paralytic ileus most feared o Hypokalemia o Thrombophlebitis o Pernicious anemia o Septicemia
Dumping syndrome
common complication rapid gastric emptying of hypertonic food solutions CHYME leading to hypovolemia. Sx of Dumping syndrome: 1 Dizziness 2 Diaphoresis 3 Diarrhea 4 Palpitations Nursing mgt: o Avoid fluids in chilled solutions, sweets (fluids must be taken after meals) o Small frequent feedings-6 equally divided feedings o Diet decrease CHO, moderate fats & CHON o Flat on bed 15 -30 minutes after q feeding
prevent infection
Type 1 (IDDM) Juvenile onset type Brittle disease Predisposing Factors Hereditary (total destruction of pancreatic cells) Related to viruses Drugs o Lasix o Steroids Related to carbon tetrachloride toxicity Signs and Symptoms Polyuria Polydypsia Polyphagia Glycosuria Weight loss Anorexia nausea and vomiting Blurring of vision Increase susceptibility to infection Delayed/poor wound healing Treatment Insulin therapy Diet Exercise Complication: Diabetic Ketoacidosis - due to severe hyperglycemia leading to severe CNS depression Mgt for Complication > Assist in mechanical ventilation > Administer 0.9 NaCl followed by .45 NaCl (hypotonic solutions) to counteract dehydration and shock > Monitor strictly vital signs, intake and output and blood sugar levels > Administer medications as ordered Insulin therapy (regular acting insulin/rapid acting insulin peak action of 2 4 hours) Sodium Bicarbonate to counteract acidosis Antibiotics to
Type 2 (NIDDM) Adult onset Maturity onset type Obese over 40 years old Predisposing Factors Obesity because obese persons lack insulin receptor binding sites Signs and Symptoms Usually asymptomatic Polyuria Polydypsia Polyphagia Glucosuria Weight gain Treatment Oral Hypoglycemic agents Diet Exercise Complications : HYPER OSMOLAR NON KETOTIC COMA - Hyperosmolar: increase osmolarity (severe dehydration) - Non ketotic: absence of lypolysis (no ketones) Mgt for Complication > Assist in mechanical ventilation > Administer 0.9 NaCl followed by .45 NaCl (hypotonic solutions) to counteract dehydration and shock > Monitor strictly vital signs, intake and output and blood sugar levels > Administer medications as ordered Insulin therapy (regular acting insulin/rapid acting insulin peak action of 2 4 hours) Antibiotics to prevent infection
Types of Insulin
Color & consistency
Peak 2-4 6-12 12-24
Rapid Intermediate Long acting
Clear Cloudy Cloudy
Diagnostic Procedures for DM FBS is increased (3 consecutive times with signs
or polyuria, polydypsia, polyphagia and glucosuria confirmatory for DM)
Random Blood Sugar is increased Oral glucose tolerance test is increased most sensitive test
Alpha Glycosylated Hemoglobin is increased
III. CONVALESCENT/RECOVERY PHASE3-12
months.
CHRONIC RF irreversible loss of kidney function....
Pathognomonic sign: (+) rebound tenderness Pain at Rt. iliac region-- MCBURNEYS point site of surgical incision Late sign due pain tachycardia Rovsings sign elicited by palpating the left lower quadrant; this paradoxically causes pain to be felt in the right lower quadrant. Treatment: - appendectomy 24 45 Dont give analgesic pre-diagnosis will mask pain Presence of pain means appendix has not ruptured. Avoid heat application will rupture appendix. Complications: Peritonitis & Septicemia
Predisposing factors: 1. DM 2. HPN 3. Recurrent UTI/ nephritis/ pyelonephritis 4. Exposure to renal toxins Stages of CRF 1. Diminished Reserve Volume asymptomatic Normal BUN & Crea, GFR < 10 30% 2. Renal Insufficiency 3. End Stage Renal disease
ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
sudden immobility of kidneys to excrete nitrogenous waste products & maintain F&E balance due to a decrease in GFR. (N 125 ml/min)
Predisposing factors: Pre renal cause - decrease blood flow Intra-renal cause involves renal pathology = kidney problem Post renal cause involves mechanical obstruction
Stages: Initiation period begins with the initial insult and ends when oliguria develops
I. OLIGURIC STAGE (1-2 weeks) - involves
passage of urine < 400ml/day.
II. DIURETIC PHASE 2-3 weeks Increased
amount of urine
You might also like
- Pancreatitis Definition of TermsDocument6 pagesPancreatitis Definition of TermsDonna Marie Arguelles AmpaNo ratings yet
- No Gallbladder Diet Cookbook: Discover Flavorful and Nourishing Recipes to Revitalize Your Metabolism After Gallbladder Surgery [III EDITION]From EverandNo Gallbladder Diet Cookbook: Discover Flavorful and Nourishing Recipes to Revitalize Your Metabolism After Gallbladder Surgery [III EDITION]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (24)
- NCMB 316 Cu11 Liver, Pancreas, & GallbladderDocument74 pagesNCMB 316 Cu11 Liver, Pancreas, & GallbladderJanine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The StomachDocument26 pagesDisorders of The StomachAnnie Rose Dorothy MamingNo ratings yet
- Definition and Etiology: PancreatitisDocument24 pagesDefinition and Etiology: PancreatitisAliyah Tofani PawelloiNo ratings yet
- PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE 2018 EdittedDocument43 pagesPEPTIC ULCER DISEASE 2018 EdittedJumbe MohamedNo ratings yet
- Week3 PancreasDocument74 pagesWeek3 PancreasriverabeanicoNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Dr. Isbandiyah, SPPD FK UmmDocument25 pagesGastrointestinal Bleeding: Dr. Isbandiyah, SPPD FK Ummikaummu amaliahNo ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument2 pagesPeptic UlcerRAJUNo ratings yet
- Chole CystitisDocument61 pagesChole CystitisPlain GerlNo ratings yet
- Gi NclexDocument14 pagesGi NclexYoke W Khoo100% (3)
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: by Aniedu, UgochukwuDocument32 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease: by Aniedu, UgochukwuManish Sapkota100% (1)
- Acute PancreatitisDocument40 pagesAcute Pancreatitisjpacheco39100% (4)
- Presentation 1Document50 pagesPresentation 1Isaac MwangiNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument49 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseJC LumayaNo ratings yet
- Biliary DisoderDocument50 pagesBiliary DisoderZanida ZainonNo ratings yet
- Gerd Gerd Gerd: Dr. Rocky Danilo Willis, M.D., AMTDocument31 pagesGerd Gerd Gerd: Dr. Rocky Danilo Willis, M.D., AMTRocky Willis100% (1)
- Acute PancreatitisDocument35 pagesAcute Pancreatitisbeejoy ranaNo ratings yet
- GI Stressors II StudentDocument67 pagesGI Stressors II StudentBiji Thomas GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Nursing CareDocument5 pagesPeptic Ulcer Nursing CareFuad TalNo ratings yet
- Common Laboratory ProceduresDocument4 pagesCommon Laboratory ProceduresrahafNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument24 pagesGastrointestinal BleedingGunawan Cahyo SNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal and HepatobiliaryDocument54 pagesGastrointestinal and Hepatobiliaryjeshema100% (2)
- Dyspepsia & GERDDocument65 pagesDyspepsia & GERDFatmala Haningtyas100% (1)
- Acute Pancreatitis - Bahasa Indonesia & InggrisDocument84 pagesAcute Pancreatitis - Bahasa Indonesia & InggrisLuthfi HamdaNo ratings yet
- Epigastric Pain (Up Date) Masroel GontarDocument52 pagesEpigastric Pain (Up Date) Masroel GontarTaufik Akbar Faried Lubis50% (2)
- Gastro NotesDocument24 pagesGastro NotesMicah EllaNo ratings yet
- Acid Peptic DiseaseDocument19 pagesAcid Peptic DiseaseKasuganti koteshwar rao100% (2)
- Acute Chronic PancreatitisDocument78 pagesAcute Chronic PancreatitisSirfaymons Sirfaymons Sirfaymons100% (1)
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: Mashehabat@just - Edu.joDocument46 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease: Mashehabat@just - Edu.joSaddamix AL Omari100% (1)
- Terapi Peptic UlcerDocument19 pagesTerapi Peptic UlcerDita HarefaNo ratings yet
- MR - 20 Okt TB Putus ObatDocument60 pagesMR - 20 Okt TB Putus ObatAnna LiveNo ratings yet
- Caccam, Christine Amor PDocument11 pagesCaccam, Christine Amor PChris Tine CaccamNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Benign ProstaticDocument9 pagesAppendicitis Benign ProstaticSamantha QuintoNo ratings yet
- Organophosphate PoisoningDocument40 pagesOrganophosphate PoisoningMadhu Sudhan PandeyaNo ratings yet
- Student Copy of Gastrointestinal Problems SP 2010 IggyDocument80 pagesStudent Copy of Gastrointestinal Problems SP 2010 IggyJade CentinoNo ratings yet
- Case 1: Cystic FibrosisDocument5 pagesCase 1: Cystic Fibrosiskep1313No ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Gerd 1Document62 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease Gerd 1Kimverly Paredes GallanoNo ratings yet
- Gi SMB - Clin MedDocument5 pagesGi SMB - Clin MedSohil PatelNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Pregnancy-2013Document154 pagesAbnormal Pregnancy-2013Libanos FekaduNo ratings yet
- RTD Ard DR ErwinDocument99 pagesRTD Ard DR ErwinMuhammad Taufiq Rustam AjiNo ratings yet
- Peptis Ulcer-Bs TâmDocument27 pagesPeptis Ulcer-Bs TâmÁnh PhạmNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease FDocument51 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease FSharmila Laxman Dake100% (2)
- Acute PancreatitisDocument46 pagesAcute PancreatitisNurul Azizah MNo ratings yet
- GI Review: Zollinger-Ellison SyndromeDocument14 pagesGI Review: Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome22twink100% (1)
- Chapter 34 Lower GIDocument8 pagesChapter 34 Lower GIRebeccaNo ratings yet
- Nichols GI 09Document59 pagesNichols GI 09marviecute22No ratings yet
- Current Treatment of Dyspepsia: DR Wita Kartika Nurani SP - PDDocument15 pagesCurrent Treatment of Dyspepsia: DR Wita Kartika Nurani SP - PDAditya Rangga FandiartaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Morning Session: Dr. Sadia AfrinDocument37 pagesWelcome To The Morning Session: Dr. Sadia AfrinGENERAL sharpNo ratings yet
- Acute Pancreatitis, HemakshiDocument25 pagesAcute Pancreatitis, HemakshiUmair FirdousNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of FecalDocument6 pagesAbnormalities of FecalKish Gabriel GanadoNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Dr. Ali A. Ramadhan M.B.CH.B., Fibms, Fkbms (G & H)Document27 pagesDiarrhea: Dr. Ali A. Ramadhan M.B.CH.B., Fibms, Fkbms (G & H)Ahmed NazarNo ratings yet
- ConstipationDocument38 pagesConstipationAZNo ratings yet
- GI, GU, Hepatobiliary, Endo HandoutsDocument18 pagesGI, GU, Hepatobiliary, Endo HandoutsCharlie MoquiteNo ratings yet
- Radionuclide DiagnosisDocument25 pagesRadionuclide DiagnosisDaniel AshooriNo ratings yet
- Fnp3-Module 7 Case StudyDocument20 pagesFnp3-Module 7 Case Studyapi-569838480No ratings yet
- Gi NelecDocument52 pagesGi NelecJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Gastro NephroDocument93 pagesGastro Nephrohasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Widiger 1991Document7 pagesWidiger 1991Ekatterina DavilaNo ratings yet
- Exciplex® 308 NM Phototherapy: Autoimmune Disease?Document28 pagesExciplex® 308 NM Phototherapy: Autoimmune Disease?Band CafeNo ratings yet
- Anti-Protozoal Agents: Medicinal Chemistry-IIIDocument21 pagesAnti-Protozoal Agents: Medicinal Chemistry-IIIHimanshu Barman100% (1)
- Infectious Diseases of The HorseDocument337 pagesInfectious Diseases of The HorseBuţurcă Ioan50% (2)
- Siadh Patient Case - Final1Document43 pagesSiadh Patient Case - Final1api-589685298No ratings yet
- Complication of MI (Myocardial Infarction)Document2 pagesComplication of MI (Myocardial Infarction)Zahid QamarNo ratings yet
- Achalasia: History & ExamDocument28 pagesAchalasia: History & ExamMicija CucuNo ratings yet
- Felocell Felv Helps Prevent Disease Cause by Feline Leukemia Virus (Felv)Document1 pageFelocell Felv Helps Prevent Disease Cause by Feline Leukemia Virus (Felv)Reginaldo ParcianelloNo ratings yet
- 2021 Article ClinicalCharacteristicsAndDayDocument14 pages2021 Article ClinicalCharacteristicsAndDayCarolina MartinsNo ratings yet
- Rsik of ICH in Anticoagulation Primary Brain Tumor PatientDocument7 pagesRsik of ICH in Anticoagulation Primary Brain Tumor PatientFithry RahmaNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle Diseases Affecting The Nursing Faculty at Tarlac State University During Covid 19 PandemicDocument19 pagesLifestyle Diseases Affecting The Nursing Faculty at Tarlac State University During Covid 19 PandemicDeinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- C2b - Hydatidiform Mole (H-Mole Pregnancy) ContentDocument4 pagesC2b - Hydatidiform Mole (H-Mole Pregnancy) ContentGLADYS MAY GUDELOS MEJIASNo ratings yet
- Open Book Exam - Renal Dz. 2019Document2 pagesOpen Book Exam - Renal Dz. 2019Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Current Diagnosis and Treatment Cardiology 5Th Edition Michael H Crawford Full ChapterDocument67 pagesCurrent Diagnosis and Treatment Cardiology 5Th Edition Michael H Crawford Full Chapterkaty.manley552100% (4)
- Pathological FractureDocument92 pagesPathological FractureSeptyAuliaNo ratings yet
- Syndrome D'apnées Du Sommeil Chez Le Sujet Âgé: B. Desrues RennesDocument36 pagesSyndrome D'apnées Du Sommeil Chez Le Sujet Âgé: B. Desrues RennesminattaNo ratings yet
- Neurocognitive Disorders: Ares Mari R. PadrejuanDocument33 pagesNeurocognitive Disorders: Ares Mari R. PadrejuanAres Mari PadrejuanNo ratings yet
- Grays Anatomy For Students 5th Edition 2023Document16 pagesGrays Anatomy For Students 5th Edition 2023AnandSreeNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Disease Case Study Learning ActivityDocument8 pagesMetabolic Disease Case Study Learning ActivityKhali Sciola0% (1)
- Tumor TulangDocument23 pagesTumor TulangPrina Margaret Perangin-anginNo ratings yet
- Nplex Micro ChartDocument12 pagesNplex Micro Chartapi-26938624100% (2)
- Neonatal Cholestasis: Priyanka VishwakarmaDocument38 pagesNeonatal Cholestasis: Priyanka VishwakarmaAlex100% (1)
- Case Study Outline - Christina OngDocument6 pagesCase Study Outline - Christina Ongapi-396204505No ratings yet
- Vulvitis in Childhood: Information For Parents and CarersDocument8 pagesVulvitis in Childhood: Information For Parents and CarersSammar ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Trial of ScarDocument18 pagesTrial of ScarJones KondoweNo ratings yet
- Prostate 4.2.0.0.rel CapcpDocument26 pagesProstate 4.2.0.0.rel CapcpkarimahihdaNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument43 pagesAtelectasismulan557100% (1)
- Blood Tests & Normal RangeDocument40 pagesBlood Tests & Normal RangeSuria KumarNo ratings yet
- Hot Tub Folliculitis: Symptoms and CausesDocument5 pagesHot Tub Folliculitis: Symptoms and CausesDennis NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Pre EclamsiaDocument66 pagesCase Presentation: Pre EclamsiaEugene Evan Endaya UyNo ratings yet
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (32)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (254)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- Critical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsFrom EverandCritical Thinking: How to Effectively Reason, Understand Irrationality, and Make Better DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (39)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (60)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingFrom EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1138)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)


![No Gallbladder Diet Cookbook: Discover Flavorful and Nourishing Recipes to Revitalize Your Metabolism After Gallbladder Surgery [III EDITION]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/591540228/149x198/6ba6cc3b38/1713999276?v=1)