Professional Documents
Culture Documents
05 Criterio5 Environmental
Uploaded by
d-calvoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
05 Criterio5 Environmental
Uploaded by
d-calvoCopyright:
Available Formats
CRITERION 5.
CURRICULUM Program Curriculum
Complete Table 5-1 that describes the plan of study for students in this program including information on course offerings in the form of a recommended schedule by year and term along with average section enrollments for all courses in the program over the two years immediately preceding the visit. State whether you are on quarters or semesters and complete a separate table for each option in the program. Describe how the curriculum aligns with the program educational objectives. Describe how the curriculum and its associated prerequisite structure support the attainment of the student outcomes. 1. Attach a flowchart or worksheet that illustrates the prerequisite structure of the programs required courses. For each curricular area specifically addressed by either the general criteria or the program criteria as shown in Table 5-1, describe how your program meets the specific requirements for this program area in terms of hours and depth of study. Describe the major design experience that prepares students for engineering practice. Describe how this experience is based upon the knowledge and skills acquired in earlier coursework and incorporates appropriate engineering standards and multiple design constraints. If your program allows cooperative education to satisfy curricular requirements specifically addressed by either the general or program criteria, describe the academic component of this experience and how it is evaluated by the faculty. 2. Describe the materials (course syllabi, textbooks, sample student work, etc.), that will be available for review during the visit to demonstrate achievement related to this criterion. (See the 2011-2012 APPM Section II.G.6.b.(2) regarding display materials.)
A.1. Plan of Study
Table 5.1. displays the course recommended schedule for the Environmental Engineering program. The curriculum is based on semesters and there is one program option. Table 5.1. Curriculum
Curricular Area (Credit Hours)
MATE1203 QUIM1103 QUIM110 1 MBIO1100 MBIO1101 ICYA1113 --MATE1214 FISI1018 2 FISI1019 ICYA1110 --LENG1501 MATE1105, FISI1028 FISI1029 3 ICYA1101A ICYA2301 ICYA2101
Differential Calculus Chemistry Chemistry Laboratory Cell Biology Theory Cell Biology Laboratory Introduction Environmental Engineering CBU A Elective Integral Calculus Differential Equations Physics I Experimental Physics I Environmental Chemistry CBU A Elective Spanish Linear Algebra Physics Ii Experimental Physics Ii Introduction Environmental Problematic Geosciences Environm. Thermochem
R R R R R R SE R R R R SE R R R R R R R
3 3 0 3 0
2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 3 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 3 3 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring
3 3 1 3
3 3 1 3 3 3
161 185 37
for the Last Two Terms the Course was Offered1Average Section Enrollment
31 84 21 85 41 52 68 96 22 89 22 68 95 23
Check if Contains Significant Design ()Engineering Topics
Required Elective or a Selected Elective
Last Two Terms the Course was Offered
Math & Basic Sciences
General Education
Semester
Course
Other
Code
MATE1207 BIOL1322 --4 ISIS1204 ICYA2401 DERE1300 IIND2106, ICYA2001 --5 ICYA2406 ICYA2407 --IIND2401 ICYA3408 6 ICYA2402 --ICYA3501 ICYA3702 ICYA3079 ICYA3605 ICYA3401 7 ICYA3406 ----ICYA3107 ICYA3103 8 ICYA3601 ---------
Vector Calculus Ecology CBU B Elective Object Orient. Programm. Fluid Mechanics Constitution And Democ Probability And Stat. I Modeling And Num. Anal Engineering Elective Potabilization Environ. Microbiology CBU B Elective Investment Analysis Wastewater Treatment Hydraulics Unrestricted Elective Air Quality And Meteorol Solid Waste Management Final Design Project GIS And Environm. Planning Hydrology Environmental Modeling Environm. Engr. Elective CBU B Elective Graduate Project Seminar Final Project Env. Impact Asses. And Aud, Environm. Engr. Elective Environm. Engr. Elective Unrestricted Elective CBU A Elective Total
R R SE R R R R R SE R R SE R R R SE R R R R R R SE SE R R R SE SE SE SE
3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 () 3 3 3 3 3 0 3 3 3 3 3 3 35 69 33 0
2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring
68 91
20 110 105
106
37 42
48 34 97
47 41 46
69 30
2010-Fall 2011-Spring 2010-Fall 2011-Spring
27 26
The curriculum includes CBU courses (Basic Universidad de Los Andes cycle) that are mandatory for all students in all majors. CBU courses expose students to general knowledge, covering topics in Arts and Humanities, Social Sciences, and Science and Technology. Every semester the University updates the list of available CBU courses, which are divided into two
groups: CBU A and CBU B. Students are required to take 3 CBU A courses (9 credits total) and 3 CBU B courses (9 units).
A.2. Relationship between curriculum and PEO
Table 5.2 displays the alignment between the Environmental Engineering program courses and the PEO Table 5.2 Alignment between curriculum and PEO
Our graduates will be able to Our graduates lead, plan, will have design, build, and Our graduates communication Our graduates manage will be able to and teamwork will be role infrastructure pursue graduate skills that will models for the projects for the studies, and allow them to society, engaged control and appreciate the succeed as in addressing its mitigation of the value of life-long members of needs environmental learning multidisciplinary pollution (water, teams soil, air) due to human activities
Semester
Code
Course
MATE1203 QUIM1103 QUIM110 1 MBIO1100 MBIO1101 ICYA1113 --MATE1214 FISI1018 2 FISI1019 ICYA1110 --LENG1501 MATE1105, FISI1028 FISI1029 3 ICYA1101A ICYA2301 ICYA2101 MATE1207 BIOL1322 4 --ISIS1204 ICYA2401
Differential Calculus Chemistry Chemistry Laboratory Cell Biology Theory Cell Biology Laboratory Introduction Environmental Engineering CBU A Elective Integral Calculus Differential Equations Physics I Experimental Physics I Environmental Chemistry CBU A Elective Spanish Linear Algebra Physics II Experimental Physics Ii Introduction Environmental Problematic Geosciences Environm. Thermochem Vector Calculus Ecology CBU B Elective Object Orient. Programm. Fluid Mechanics
DERE1300 IIND2106, ICYA2001 5 --ICYA2406 ICYA2407 --IIND2401 ICYA3408 6 ICYA2402 --ICYA3501 ICYA3702 ICYA3079 ICYA3605 ICYA3401 7 ICYA3406 ----ICYA3107 ICYA3103 ICYA3601 8 ---------
Constitution And Democ Probability And Stat. I Modeling And Num. Anal Engineering Elective Drinking water treatment Environ. Microbiology CBU B Elective Investment Analysis Wastewater Treatment Hydraulics Unrestricted Elective Air Quality And Meteorol Solid Waste Management Final Design Project GIS And Environm. Planning Hydrology Environmental Modeling Environm. Engr. Elective CBU B Elective Graduate Project Seminar Final Project Env. Impact Asses. And Aud, Environm. Engr. Elective Environm. Engr. Elective Unrestricted Elective CBU A Elective
From Table 5.2 it is possible to conclude that the PEO are aligned with the courses of the program.
A.3. Relationship between curriculum and SO
Table 5.3 displays the alignment between the Environmental Engineering program courses and the SO. Table 5.3 Alignment between curriculum and SO
Semester
1
Code
MATE1203 QUIM1103 QUIM110 MBIO1100 MBIO1101 ICYA1113
Course
Differential Calculus Chemistry Chemistry Laboratory Cell Biology Theory Cell Biology Laboratory Introduction Environmental Engineering
--MATE1214 FISI1018 2 FISI1019 ICYA1110 --LENG1501 MATE1105, FISI1028 FISI1029 3 ICYA1101A ICYA2301 ICYA2101 MATE1207 BIOL1322 4 --ISIS1204 ICYA2401 DERE1300 IIND2106, ICYA2001 5 --ICYA2406 ICYA2407 --IIND2401 ICYA3408 6 ICYA2402 --ICYA3501 ICYA3702 ICYA3079 ICYA3605 ICYA3401 7 ICYA3406 ----ICYA3107 ICYA3103 ICYA3601 8 ---------
CBU A Elective Integral Calculus Differential Equations Physics I Experimental Physics I Environmental Chemistry CBU A Elective Spanish Linear Algebra Physics II Experimental Physics II Introduction Environmental Problematic Geosciences Environm. Thermochem Vector Calculus Ecology CBU B Elective Object Orient. Programm. Fluid Mechanics Constitution And Democ Probability And Stat. I Modeling And Num. Anal Engineering Elective Drinking water treatment Environ. Microbiology CBU B Elective Investment Analysis Wastewater Treatment Hydraulics Unrestricted Elective Air Quality And Meteorol Solid Waste Management Final Design Project GIS And Environm. Planning Hydrology Environmental Modeling Environm. Engr. Elective CBU B Elective Graduate Project Seminar Final Project Env. Impact Asses. And Aud, Environm. Engr. Elective Environm. Engr. Elective Unrestricted Elective CBU A Elective
From Table 5.3 it is possible to conclude that the SO are aligned with the courses of the program. However, it is worth mentioning that only the courses taught by the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering use tools to directly assess the attainment of the SO. We recognize that assumptions were made for other courses in terms of their alignment with the SO, based on our knowledge of the topics covered by these courses. Additionally, the curriculum has been developed in the light of the Universitys mission (see Criterion 2). This promotes that the curriculum supports the attainment of the SO because, as stated in the mission, the University fosters a flexible and interdisciplinary environment, which is essential for integrating arts, sciences, technology, and humanities, and for stimulating comprehensive education. This is the reason why all the curriculums of the University, include elective courses from disciplines different from engineering, providing the students a broad education. The curriculum is structured in a system of pre-requisites (see section A.4.), that is design so students gradually integrate knowledge from different disciplines, which will ultimately allow them to attain the SO.
A.4. Prerequisite Structure of the Program
Figure 5.1. shows a flow chart illustrating the prerequisite structure of the program
Figure 5.1 Prerequisite structure of the program Additionally to the prerequisite structure shown in Figure 5.1 (i.e., arrows indicate both prerequisites and corequisites), to be able to register level 3 courses (i.e., level 3 courses are those with the numerical portion of the code starting with 3, AAAA3XXX) students must have approved all level 1 courses (i.e., level 1 courses are those with the numerical portion of the code starting with 1, AAAA1XXX).
A.5. Compliance of the requirements for the program area
Table 5.4 displays the fulfillment of the requirements in terms of credit hours by the Environmental Engineering program. Table 5-4 Fulfillment of the requirements by the Environmental Engineering program
Curricular Area Total Credits Percentage of the credits required for graduation (%) General Criteria Requirement (%)
Math. & Basic Sciences Engineering Topics General Education Other Total
35 69 33 0 137
25.5 50.5 24.0 0 100
25 37.5 -------
In the description below, it is shown that the program fulfills not only the General Criteria requirements (Table 5.4), but also the Program Criteria requirements for Environmental Engineering, in terms of the topics for which graduates are prepared. Math. and Basic Sciences Curricular Area The program covers mathematics, including calculus, linear algebra, differential equations, and probability and statistics. These topics are covered in the following courses: MATE1203: Differential Calculus 3 credit hours MATE1204: Integral Calculus and Differential Equations 3 credit hours MATE1105: Linear Algebra 3 credit hours MATE1207: Vector Calculus 3 credit hours IIND2106: Probability and Statistics I 3 credit hours
The program covers physical (calculus-based), chemical, biological, and earth sciences (i.e., geosciences). These topics are covered in the following courses: QUIM1103: Chemistry 3 credit hours QUIM1104: Chemistry laboratory 0 credit hours FISI1018: Physics I 3 credit hours FISI1019: Experimental Physics I 1 credit hour FISI1028: Physics II 3 credit hours FISI1029: Experimental physics II 1 credit hour ICYA2301: Geosciences 3 credit hours MBIO1100: Cell Biology Theory 3 credit hours MBIO1101: Cell Biology laboratory 0 credit hours BIOL1322: Ecology 3 credit hours
Engineering Topics Curricular Area The program covers several engineering topics, which fulfill both the General Criteria and Program Criteria for Environmental Engineering. The engineering courses, which add up to 69 credit hours, are: ICYA 1101A: Introduction to Environmental Problems 3 credit hours ICYA 1113: Introduction to Environmental Engineering 3 credit hours ICYA 1110: Environmental Chemistry 3 credit hours ISIS 1204: Object Oriented Programming 3 credit hours
ICYA 2001: Numerical simulation and analysis - 3 credit hours General engineering elective 3 credit hours ICYA 2101: Environmental Thermochemistry 3 credit hours ICYA 2401: Fluids Mechanics 3 credit hours ICYA 2402: Hydraulics 3 credit hours ICYA 2406: Water Potabilization 3 credit hours ICYA 2407: Environmental Microbiology 3 credit hours ICYA 3079: Final design project in Environmental Engineering 3 credit hours ICYA 3401: Hydrology 3 credit hours ICYA 3406: Environmental Modeling 3 credit hours ICYA 3408: Wastewater Treatment 3 credit hours ICYA 3501: Air Quality and Meteorology 3 credit hours ICYA 3601: Environmental Impact Assessment and Auditing 3 credit hours ICYA 3605: GIS and Environmental Planning 3 credit hours ICYA 3702: Solid Waste Management 3 credit hours ICYA 3103: Graduation project in Environmental Engineering 3 credit hours 3 Environmental engineering elective courses 9 credit hours
In the previous lists of courses, the following Environmental Engineering Program Criteria are covered: Fluid Mechanics: ICYA 2401 Fluid Mechanics Introductory level knowledge of environmental issues associated with: o Water: ICYA 2402: Hydraulics 3 credit hours ICYA 2406: Water Potabilization 3 credit hours ICYA 3401: Hydrology 3 credit hours ICYA 3408: Wastewater Treatment 3 credit hours o Air: ICYA 3501: Air Quality and Meteorology 3 credit hours o Land: ICYA 3702: Solid Waste Management 3 credit hours o Associated Health Impacts ICYA 3601: Environmental Impact Assessment and Auditing 3 credit hours In the following courses, laboratory experiments are conducted and data is critically analyzed and interpreted (three major environmental engineering focus areas: air, water, land): o o o o ICYA 1110: Environmental Chemistry 3 credit hours ICYA 2101: Environmental Thermochemistry 3 credit hours ICYA 2401: Fluid Mechanics 3 credit hours ICYA 2406: Potabilization 3 credit hours
o o o o
ICYA 2407: Environmental Microbiology 3 credit hours ICYA 3406: Environmental Modeling 3 credit hours ICYA 3605: GIS and Environmental Planning 3 credit hours ICYA 3702: Solid Waste Management 3 credit hours
In the following courses, students apply advance principles and practice relevant to the program objectives: o o o o o o o o o ICYA 3401: Hydrology 3 credit hours ICYA 3406: Environmental Modeling 3 credit hours ICYA 3408: Wastewater Treatment 3 credit hours ICYA 3501: Air Quality and Meteorology 3 credit hours ICYA 3601: Environmental Impact Assessment and Auditing 3 credit hours ICYA 3605: GIS and Environmental Planning 3 credit hours ICYA 3702: Solid Waste Management 3 credit hours ICYA 3079: Final design project 3 credit hours ICYA 3103: Graduation project in Environmental Engineering 3 credit hours
In the following courses, understand concepts of professional practice and the roles and responsibilities of public institutions and private organizations pertaining to environmental engineering: o ICYA 3501: Air Quality and Meteorology 3 credit hours o ICYA 3601: Environmental Impact Assessment and Auditing 3 credit hours o ICYA 3605: GIS and Environmental Planning 3 credit hours o ICYA 3702: Solid Waste Management 3 credit hours o ICYA 3079: Final design project in Environmental Eng. 3 credit hours
General Education Curricular Area The program covers a general education component that complements the technical component of the curriculum. The courses included in this curricular area are: o o o o o DERE 1300: Constitution and Democracy 3 credit hours LENG 1501: Spanish: Think, Read, and Write Spanish 3 credit hours IIND 2401: Investment Analysis 3 credit hours 6 CBU: University Basic Cycle 18 credit hours 2 Free elective courses 6 credit hours
This curricular area is aligned with the Universitys mission (see Criteria 2). As stated in section A.3., the University fosters a flexible and interdisciplinary environment, which is essential for integrating arts, sciences, technology, and humanities, and for stimulating comprehensive
education. As it was explained in Criteria 2, the program PDI is aligned with the University mission and PDI.
A.6. Major Design Experience
Towards the end of the Environmental Engineering program, students are exposed to several courses where design is a major component. However, the main design experience corresponds to a mandatory project-based-learning (PBL) course. This course, called Final Design Project in Environmental Engineering, was conceived to expose students to environmental engineering design-related problems within a realistic and complex context. In this design experience, students work in teams of 5 to 6 six members. Each group selects one out of the 25 municipalities of the Bogot-Sabana region. For the municipality selected, each group investigates and analyzes the current socio-economic situation, as well as the land use regulations and development plans. The collected information is used to identify a problem that could be solved with an environmental engineering project. The main objective of the course is that the groups design this solution. Each group has complete freedom to select the environmental engineering solution to be designed, depending on the interests of its groups members, and framed on the needs and constraints of the municipality. In summary, the following are stages for the design project: Selection of the municipality, Investigation and analysis of the socio-economic situation, land use regulations, environmental policy, and development plans of the municipality. Identification of a real-world environmental problem of the municipality. Identification of the environmental engineering project that could contribute to the solution of the problem, and preliminary evaluation of the viability of the project. Presentation of a formal proposal of the corresponding project (context, description of the project, proposed methodology, project planning, list of variables, list of available resources, etc.). Design of the project. During this stage, students can approach faculty from the Department, School, and/or University, to solve questions and receive advice. Presentation of the project. The groups have to present the project to an audience that includes professors from the Environmental Engineering program, who will ask questions to the students and grade the project. At the end of this design experience is expected that students: Recognize the socio-economic reality of the region, the main development needs and the current local legislation and development plans of a specific community. Recognize the different roles of the professional practice of an environmental engineer. Develop the capability of identifying technical complex problems and the ability of proposing a valid solution that is restrained by a particular socio-economic context.
Recognize the typical restraints that can be found while conducting an environmental engineering design project, as well as the different stages involved in such a process. Develop and/or improve their skills to identify, plan and conduct all the stages of a design project: from the initial stage of identification of the problem to the final technical solution. Develop and/or improve their skills to manage open and complex problems characterized by multiple restraints. Develop and/or improve their teamwork, leadership, creativity, and decisionmaking skills, as well as their oral and written communications skills.
A.7. Cooperative Education
As explained in section E. of Criterion 1, the students are allowed to homologate internship work for academic. However, internships are optional, and not a mandatory requirement for graduation from the program.
A.8. Materials available for reviewing
For the core courses of the Environmental Engineering program, the following material will be available for review during the visit: Course syllabi. Textbooks. Examples of assignments and exams. Examples of student work, ranging from excellent through poor.
Course Syllabi
In Appendix A, include a syllabus for each course used to satisfy the mathematics, science, and discipline specific requirements required by Criterion 5 or any applicable program criteria. For required courses with multiple sections that do not use a common syllabus, please include a syllabus for each of the different sections.
Course sillabi of the courses of the Environmental Engineering program, can be found in Appendix A as requested.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chapter 9 Deflections of Beams: X Axis and The Tangent To The DeflectionDocument5 pagesChapter 9 Deflections of Beams: X Axis and The Tangent To The DeflectionRimon GawandeNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication Module 4Document34 pagesSatellite Communication Module 4JKNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 3210 Fall 2012 PDFDocument4 pagesSyllabus 3210 Fall 2012 PDFRahul KarnaNo ratings yet
- Prob AnswersDocument4 pagesProb AnswersDaniel KirovNo ratings yet
- CA-Clipper For DOS Version 5.3 Programming and Utilities GuideDocument718 pagesCA-Clipper For DOS Version 5.3 Programming and Utilities GuideChris Harker91% (11)
- 201 28-NM1 1Document186 pages201 28-NM1 1rajabalihvacNo ratings yet
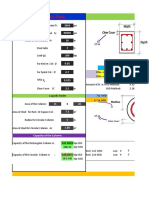
- Column Design With ExcelDocument40 pagesColumn Design With ExcelMatiur Rahman BasumNo ratings yet
- LatheDocument74 pagesLatheChandrakantha K100% (1)
- Dr. Rife and Philip Hoyland's 3.3 MHZ SweepDocument2 pagesDr. Rife and Philip Hoyland's 3.3 MHZ SweepKhalid Ibrahim100% (1)
- FG200308-malfatti Circles PDFDocument11 pagesFG200308-malfatti Circles PDFMario DalcínNo ratings yet
- 1 Priority KeywordDocument8 pages1 Priority KeywordKavithaNo ratings yet
- Eaton Xeffect Industrial Switchgear Range Catalog Ca003002en en UsDocument379 pagesEaton Xeffect Industrial Switchgear Range Catalog Ca003002en en UsMAURIZIO MARININo ratings yet
- Parola A Do ZDocument8 pagesParola A Do ZjovicaradNo ratings yet
- Planets and Solar System The Complete Manual 2016Document132 pagesPlanets and Solar System The Complete Manual 2016Sonechka Sonya100% (3)
- Hana Table PartitioningDocument12 pagesHana Table PartitioningGowri Prasanth Chaduvula0% (1)
- BS DanielDocument6 pagesBS Danielsandy30694No ratings yet
- Magnetism: Teacher Notes and Answers 19 MagnetismDocument3 pagesMagnetism: Teacher Notes and Answers 19 Magnetismmahsan abbas100% (1)
- Tetzaveh Parsha GematriaDocument1 pageTetzaveh Parsha GematriaRabbi Benyomin HoffmanNo ratings yet
- Fortinac: Juniper Ex Switch 802.1X-Mac-Authentication Device IntegrationDocument14 pagesFortinac: Juniper Ex Switch 802.1X-Mac-Authentication Device IntegrationSaid bel haj letaiefNo ratings yet
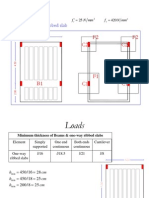
- Slab DesignDocument96 pagesSlab Designdilrangi100% (2)
- 10 - Chapter 4 PDFDocument143 pages10 - Chapter 4 PDFKalyan ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- ManageEngine Application Manager Best PracticesDocument12 pagesManageEngine Application Manager Best PracticesNghiêm Sỹ Tâm PhươngNo ratings yet
- Transportation ProblemDocument3 pagesTransportation ProblemSalilNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0191886910006215 Main PDFDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0191886910006215 Main PDFOscar Iván Negrete RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 08-A2dDocument3 pagesExperiment 08-A2dapi-277396867No ratings yet
- Identification - of - Vulkan Vulastik-L CouplingsDocument2 pagesIdentification - of - Vulkan Vulastik-L CouplingsBill NevisNo ratings yet
- Subjects Revised Curriculum BS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGDocument18 pagesSubjects Revised Curriculum BS ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGData StatsNo ratings yet
- TractionDocument26 pagesTractionYogesh GurjarNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Grade 10 FinalDocument9 pagesModule 5 Grade 10 FinalSandy CarbonillaNo ratings yet
- Math 11-CORE Gen Math-Q2-Week 1Document26 pagesMath 11-CORE Gen Math-Q2-Week 1Christian GebañaNo ratings yet