Professional Documents
Culture Documents
I.S Objective Questions Mid2
Uploaded by
MukeshCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
I.S Objective Questions Mid2
Uploaded by
MukeshCopyright:
Available Formats
JNTU ONLINE EXAMINATIONS [Mid 2 - Information Security]
1. Which of the following documents provides the description of a packet authentication extension to IPv4 and IPv6 a. RFC 2401 b. RFC 2402 c. RFC 2406 d. RFC 2408 2. Which of the following documents provides the description of a packet encryption extension to IPv4 and IPv6 a. RFC 2401 b. RFC 2402 c. RFC 2406 d. RFC 2408 3. IPv6 header has a fixed size of a. 40 octets b. 80 octets c. 20 octets d. 160 octets 4. Which among the following Routing Protocols is used by IP Security a. OSPF b. OPSF c. UDP d. TCP 5. The attack in which intruders create packets with false IP addresses and exploit applications that use authentication based on IP address is called a. Packet sniffing b. IP Spoofing c. Eaves dropping d. Modification 6. A process by which packets from one network are broken into smaller pieces to be transmitted on another network is know as a. segmentation b. bifurcation c. fragmentation d. segregation 7. IPv4 header has a minimum size of a. 180 bits b. 160 bits c. 256 bits d. 512 bits 8. The version field in the IPv4 header has a size of a. 6 bits b. 4 bits c. 8 bits d. 16 bits 9. The number of fields in the IPv4 and IPv6 headers respectively are a. 12 & 8 b. 8 &12 c. 6 & 10 d. 10 &16 10. Which among the following functional areas is not encompassed by IP-level Security a. Integrity b. Authenticity c. Confidentiality d. Key Management 11. Which of the following documents provides an overview of security architecture a. RFC 2401 b. RFC 2402 c. RFC 2406 d. RFC 2408 12. Which of the following documents provides Specification of key management capabilities.
a. RFC 2401 b. RFC 2402 c. RFC 2406 d. RFC 2408 13. Which of the following algorithms are used by IPSec to provide per-packet authentication and data integrity a. HMAC MD5 b. 3DES c. AES d. Digital signatures, based on RSA and DSA 14. Which among the following is carried in AH and ESP headers to enable the receiving system to select the Security associations under which a received packet will be processed a. Security Parameters index b. Security Protocol identifier c. IP destination address d. Network address 15. Masquerade is an attack on a. Data retrieval b. Authentication c. Non-repudiation d. Data access 16. IPSec is provided at the layer a. Below transport Layer b. Below network layer c. At the application layer d. At the physical layer 17. Which among the following indicates whether the Security association is an AH or ESP security association a. Security Parameters index b. Security Protocol identifier c. IP destination address d. Network address 18. Which among the following mechanisms assures the receiver that the received packet was transmitted by authorized person a. Confidentiality b. Non-repudiation c. Authentication d. key management 19. Which among the following mechanisms assures the receiver that the messages are received as sent, with no duplication, insertion, modification, reordering or replays. a. Confidentiality b. Non-repudiation c. Authentication d. Integrity 20. Which among the following mechanisms prevents either sender or receiver from denying a transmitted message a. Confidentiality b. Non-repudiation c. Authentication d. Integrity 21. For transport mode AH using IPv4, where is AH inserted a. After original IPheader & before IP payload b. Before original IP header & before IP payload
Information Security Page 2 of 20 - -2_...
c. Before original IP header & After IP payload d. After original IP header & after IP payload 22. For Tunnel Mode AH, where is Authentication Header inserted a. After original IP header & before IP payload b. After original IP header & before new outer IP header c. Before new outer IP header & before original IP header
d. Between original IP header & new outer IP header 23. AH in transport mode authenticates which of the following a. IP header only b. IP payload only c. IP payload and selected portions of IP Header d. none of IP header and IP payload 24. AH in tunnel mode authenticates which of the following a. inner IP header b. inner IP payload c. inner IP payload + IP Header d. inner IP payload + inner IP Header+ selected portions of outer Ip header +outer IPv6 extension headers 25. Which of the following fields is not present in the Authentication Header a. sequence number b. payload length c. security parameters index d. padding 26. The size of Security parameters index field in Authentication Header is a. 8 bits b. 16 bits c. 32 bits d. 64 bits 27. The sequence number field in the IPSec Authentication Header is designed to thwart which of the following attacks a. Eaves dropping b. Replay c. Interruption d. Modification 28. A 32-bit value used to generate the sequence number field in AH headers is a. Sequence counter overflow b. Sequence number counter c. Anti replay window d. AH information 29. Anti-replay mechanism uses the window size of a. w-1 b. w+1 c. 2w d. w 30. Tunnel mode provides authentication to a. UDP b. TCP c. ICMP d. Entire original IP packet 31. ESP in tunnel mode encrypts which of the following a. Inner IP header b. Inner IP payload c. Inner IP packet d. Inner IP packet+ selected portions of outer IP header +outer IPv6 extension headers 32. Which of the following approaches of authentication covers more fields a. Single ESP SA b. Single ESP SA with ESP authentication option c. Two bundled transport SAs,inner being ESP SA & outer being an AH SA d. Two bundled transport SAs,inner being ESP SA & outer being an ESP SA 33. Which among the following approaches applies authentication before encryption between two hosts using SA bundle consisting of a. Inner AH Transport SA & an outer ESP Tunnel SA b. Inner ESP Transport SA & an outer ESP Tunnel SA c. Inner ESP Tunnel SA & an outer ESP Transport SA d. Inner AH Transport SA & an outer AH Tunnel SA. 34. In transport mode using IPv4, where is the ESP header inserted a. Immediately before the transport layer header b. Between transport layer header and IP payload c. After transport layer header & before ESP trailer d. Before original IP header
35. ESP in transport mode encrypts and optionally authenticates which of the following a. IP header b. IP payload c. Both IP header and payload d. None of IP header and payload 36. In tunnel mode ESP, where is the ESP header placed a. After original IP header b. prefixed to the packet c. suffixed to the packet d. before new IP header 37. The extension header that follows the main IP header for encryption is known as the a. Encapsulating Security Payload header b. authentication header c. encryption header d. auxiliary header 38. The size of Sequence number field in Encapsulating Security Payload format is a. 8 bits b. 16 bits c. 32 bits d. 64 bits. 39. The size of Security parameters index field in ESP format is a. 8 bits b. 16 bits c. 32 bits d. 64 bits. 40. Which of the following terms refers to applying more than one security protocol to the same IP packet, without invoking tunneling a. Transport Adjacency b. Iterated tunneling c. Multiple protocols d. Transport coherence 41. Which of the following defines payloads for exchanging key generation and authentication data. a. UDP b. HTTP c. ISAKMP d. TCP 42. The size of the Initiator cookie in ISAKMP header is a. 8 bits b. 16 bits c. 32 bits d. 64 bits 43. Which among the following messages informs the other side that this is the first Security Association being established with the remote system a. Initial-contact b. Responder-lifetime c. Replay-contact d. Anti-replay contact 44. Which among the following ISAKMP Exchanges allows key exchange and authentication material to be transmitted together a. Base exchange b. Identity protection Exchange c. Authentication Exchange d. Aggressive exchange 45. Which among the following payloads indicates the protocol for the SA for which services and mechanisms are being negotiated a. Transform payload b. Proposal payload c. Key exchange payload d. Identification payload 46. Which among the following payloads defines a security transform to be used to secure the communications channel for the designated protocol a. Transform payload
b. Proposal payload c. Key exchange payload d. Identification payload 47. Which among the following payloads transfers a public-key certificate a. Transform payload b. Proposal payload c. Certificate payload d. Identification payload 48. Which among the following payloads contains either error or status information associated with the SA. a. Transform payload b. Proposal payload c. Notification payload d. Identification payload 49. What type of protocol is Oakley a. Routing protocol b. Transport Protocol c. Key exchange protocol d. Communication Protocol 50. Oakley is based on which of the following algorithms a. RSA b. Diffie-Hellman c. 3DES d. RC5 51. Which of the following mechanisms is employed by Oakley algorithm to thwart clogging attacks a. Popups b. Cookies c. Goggles d. Nonces 52. Which of the following is used by Oakley algorithm to ensure against replay attacks a. Popups b. Cookies c. Goggles d. Nonces 53. A Nonce is a a. Fixed Random number b. Locally generated pseudorandom number c. Globally generated pseudorandom number d. Globally generated random number 54. Which among the following messages is used for positive confirmation of the responders election of whether or not the responder will perform anti-replay detection a. Initial-contact b. Responder-lifetime c. Replay-status d. Anti-replay contact 55. Which of the following malicious programs are independent a. Logic bombs b. Trapdoors c. Worms d. Trojan horses 56. Which of the following is a secret entry point into a program that allows someone that is aware of it to gain access without going through the usual security access procedures a. Trap doors b. Logic bomb c. Trojan Horses d. Bacteria 57. Which of the following is a useful program or command procedure containing hidden code that, when invoked, performs some unwanted or harmful function a. Trap door b. Logic bomb c. Trojan Horses
d. Bacteria 58. Which of the following is not a network vehicle for spreading worms a. Electronic mail facility b. Remote execution capability c. Routing facility d. Remote login capability 59. Which of the following programs do not explicitly damage any files but reproduce exponentially a. Worms b. Trojan horses c. Bacteria d. Trap door 60. Who among the following is an individual who is not authorized to use the computer and who penetrates a systems access controls to exploit a legitimate users account. a. Masquerader b. Misfeasor c. Clandestine user d. Casual user 61. Who among the following is an individual who accesses data, programs, or resources for which such access is not authorized a. Masquerader b. Misfeasor c. Clandestine user d. Casual user 62. Who among the following is an individual who seizes supervisory control of the system and uses this control to evade auditing and access controls. a. Masquerader b. Misfeasor c. Clandestine user d. Casual user 63. Which of the following is a code embedded in some legitimate program that is set to "explode" when certain conditions are met a. Trap door b. Logic bomb c. Bacteria d. Worms 64. Which of the following programs uses network connection to spread from system to system a. Trap door b. Logic bomb c. Trojan Horses d. Worm 65. The size of the salt value used in modifying the DES algorithm in UNIX systems is a. 8 bit b. 12 bit c. 16 bit d. 32 bit 66. The size of the key input to Crypt (3) in UNIX systems is a. 32 bit b. 64 bit c. 56 bit d. 128 bit 67. Which among the following is a group of internet computers that are set up, without the owner's knowledge ,to forward transmission to other computers on the internet a. Zombie army b. Rojan c. RIC d. RATs 68. Which is a program that lets anyone hold line keyboard conversation wth people or computer around the world a. RATs
b. Root kits c. Worms d. IRC 69. A way of protecting password file is through a. Access control b. Assessment control c. Check method d. Nonrepudiation 70. Line tapping can be countered using a. Antivirus software b. Spyware c. Link encryption techniques d. Access control 71. What do you mean by pishing? a. Bogus emails b. Viruses c. RATs d. Worms 72. Which of the following bypasses restrictions on access a. Worm b. Insect c. Trojan horse d. Bacteria 73. the front line of defense against intruders is a. Encryption system b. Password system c. Antivirus system d. Spy ware 74. Typically, salt value in UNIX password scheme is related to which parameter a. Password b. Time c. User Id d. Key generation 75. Which of the following viruses uses compression so that the infected program is exactly the same length as an uninfected version a. Memory-resident virus b. Parasitic virus c. Polymorphic virus d. Stealth Virus 76. Which among the following viruses creates copies during replication that are functionally equivalent but have distinctly different bit patterns. a. Memory-resident virus b. Boot Sector virus c. polymorphic virus d. Stealth Virus 77. Which of the following viruses attaches itself to executable files and replicates, when the infected program is executed a. Memory-resident virus b. Parasitic virus c. Boot sector Virus d. Stealth Virus 78. Which is a virus that mutates with every infection a. Memory-resident virus b. Parasitic virus c. Polymorphic virus d. Stealth Virus 79. Which portion of the virus creates a random encryption key to encrypt the remainder of the virus. a. Mutation engine b. Conversion engine c. Generation engine d. Keying engine 80. In which among the following phases of a virus, is a virus idle and will eventually be activated by
some event a. Dormant phase b. Propagation Phase c. Triggering Phase d. Execution Phase 81. In which among the following phases a virus places an identical copy of itself into other programs or into certain system areas on the disk. a. Dormant phase b. Propagation Phase c. Triggering Phase d. Execution Phase 82. The virus is activated to perform the function for which it was intended in a. Dormant phase b. Propagation Phase c. Triggering Phase d. Execution Phase 83. Which of the following is not a phase of virus a. Triggering phase b. Propagation Phase c. Dedication Phase d. Execution Phase 84. Which of the following viruses lodges in main memory as part of a resident system program. a. Memory-resident virus b. Parasitic virus c. Boot sector Virus d. Stealth Virus 85. Which of the following viruses infects a master boot record a. Memory-resident virus b. Parasitic virus c. Boot sector Virus d. Stealth Virus 86. Which among the following is a form of virus explicitly designed to hide itself from detection by antivirus software a. Memory-resident virus b. Parasitic virus c. Polymorphic virus d. Stealth Virus 87. Which among the following is not an auto executing macro in Microsoft word a. Functional macro b. Command macro c. Automacro d. Autoexecute 88. Activity traps belong to which generation of antivirus software a. First generation b. Second generation c. Third generation d. Fourth generation 89. Which generation of Antivirus software uses heuristic rules to search for probable virus infection a. First generation b. Second generation c. Third generation d. Fourth generation 90. Which generation of Antivirus programs are memory resident programs that identify a virus by its actions rather than its structure in an infected program. a. First generation b. Second generation c. Third generation d. Fourth generation 91. Full-featured protection is provided in which generation of antivirus software a. First generation b. Second generation
c. Third generation d. Fourth generation 92. Which among the following is a platform independent virus a. Macro virus b. Parasitic virus c. Micro virus d. Stealth Virus 93. Which of the following makes it possible to create a macro virus a. Auto executing macro b. Self executing macro c. Auto ejecting macro d. Self ejecting macro 94. Which of the following viruses infects documents and templates, not executable portions of code. a. Macro virus b. Stealth Virus c. Polymorphic virus d. Micro Virus 95. Which generation of Antivirus software requires a virus signature to identify a virus a. First generation b. Second generation c. Third generation d. Fourth generation 96. Which generation of Antivirus products are packages consisting of a variety of antivirus techniques used in conjunction a. First generation b. Second generation c. Third generation d. Fourth generation 97. Which of the systems objective is to provide rapid response time so that viruses can be stamped out almost as soon as they are introduced. a. Digital immune system b. Integrated mail system c. Virus signature scanner d. Mobile program systems 98. In UNIX system, the number of iterations in DES implementation is a. 30 b. 25 c. 35 d. 40 99. Digital immune system was developed by a. Apple b. AT &T c. Microsoft d. IBM 100. Which of the following systems are Integrated Mail systems a. Java b. C++ c. Lotus notes d. Active X 101. The ID in the UNIX operating system is used to a. Retrieve the plain text b. Retrieve the cipher text c. Index into the password file &retrieve the plaintext &cipher text d. Index into the password file &retrieve plaintext salt &encrypted password 102. Which of the following is not an element of a Generic Decryption scanner a. Digital immune module b. CPU emulator c. Virus signature scanner d. Emulation control module 103. Which among the following is a software based virtual computer a. Digital immune module b. CPU emulator c. Virus signature scanner d. Emulation control module
104. A module that scans the target code looking for known virus signatures is a. Digital immune module b. CPU emulator c. Virus signature scanner d. Emulation control module 105. A module that controls the execution of the target code is a. Digital immune module b. CPU emulator c. Virus signature scanner d. Emulation control module 106. Which among the following is not a purpose of salt a. Preventing the visibility of passwords in the password file. b. Effectively increasing the password length. c. Prevent the hardware implementation of DES d. To effectively increase the time of processing. 107. IDS may be configured to report attack occurrences. You just received a notification that an attack occurred, but after checking, you find that it really wasn't an attack at all. What is the term for this type of alarm? a. True positive b. False positive c. True negative d. False negative 108. Which of the following apply to network-based IDS? a. Provides reliable, real-time intrusion data b. Remains active and transparent on the network c. Uses many network or host resources d. Becomes active when identifying intrusions 109. Which of the following intrusion detection systems functions in current or real time to monitor network traffic? a. Network based b. Host based c. Gateway based d. Router based 110. Which of the following describes how a network-based IDS acquires data? a. Passive b. Active c. Very quiet d. Very noisy 111. What does active detection refer to when using an intrusion detection system (IDS)? a. An IDS that is constantly running 24 hours a day b. An IDS that responds to the suspicious activity by logging off a user c. An IDS that simply detects the potential security breach d. An IDS that shuts down the Internet after a suspected attack 112. Which among the following is not a password selection strategy a. User education b. Computer-generated passwords c. Stego password checking d. Proactive password checking 113. In which among the following strategies a system periodically runs its own password cracker to find guessable passwords. a. Proactive password checking b. Reactive password checking c. Active password checking d. Underactive password checking 114. In which of the following schemes the system checks to see if a password selected by a user is allowable and, if not rejects it. a. Proactive password checker b. Reactive password checker c. Active password checker d. Under active password checker 115. Threshold detection comes under which of the following
a. Statistical anomaly detection system b. Rule-based detection system c. Time stamp method d. Detection specific password scheme 116. Which of the following is most useful when detecting network intrusions? a. Audit policies b. Audit trails c. Access control policies d. Audit practices 117. SOCKS service is located on a. TCP port 1080 b. TCP port 1088 c. TCP port 1081 d. TCP port 1082 118. Version 5 of SOCKS is defined in a. RFC 1892 b. RFC 1928 c. RFC 1298 d. RFC 1289 119. Which among the following is typically set up as a list of rules based on matches to fields in the IP or TCP header a. Packet filters b. Application level gateways c. Circuit level gateways d. Session gateway 120. Discarding all packets containing the route information that the packet should take as it crosses the internet router is which attack a. Source routing attack b. IP address spoofing c. Tiny fragment attack d. IP sniffing 121. SOCKS server runs on which of the following platform based firewalls a. UNIX b. Windows c. DOS d. JAVA 122. Which among the following is not a firewall a. packet filters b. application level gateways c. circuit level gateways d. session gateway 123. Which among the following are default policies of a packet filtering router a. discard, forward b. discard, retrieve c. delete, forward d. delete, retrieve 124. Discarding packets with an inside source address if the packet arrived on an external interface is a counter measure to which of the following attacks a. IP address spoofing b. Source routing attack c. Tiny fragment attack d. IP sniffing 125. Which of the following is also called a proxy server a. packet filter b. application level gateway c. circuit level gateways d. session gateway 126. which among the following is a system identified by the firewall administration as a critical strong point in the networks security a. Base host b. Bastion host c. Borland host
d. Prime host 127. A hardened firewall host on an Intranet is a. A software which runs in any of the computers in the intranet b. A software which runs on a special reserved computer on the intranet c. A stripped down computer connected to the intranet d. A mainframe connected to the intranet to ensure security 128. Firewall as part of a router program a. Filters only packets coming from internet b. Filters only packets going to internet c. Filters packets traveling from and to the intranet from the internet d. Ensures rapid traffic of packets for speedy e-Commerce 129. Which among the following determines the types of Internet services that can be accessed inbound or outbound a. user control b. direction control c. service control d. behavior control 130. In a screened host firewall, single-homed bastion configuration, the firewall consists of a. base station & packet filtering router b. packet filtering router & a bastion host c. base station & bastion host d. packet filtering router & packet screening host 131. In which of the following configurations, when the packet filtering router is completely compromised, traffic could flow directly through the router between the internet and other hosts on the private network a. screened subnet firewall b. screened host mono-homed c. screened host firewall, dual homed bastion d. screened host firewall, single-homed bastion 132. Main function of proxy application gateway firewall is a. To allow corporate users to use efficiently all internet services b. To allow intranet users to securely use specified internet services c. To allow corporate users to use all internet services d. To prevent corporate users from using internet services 133. Which among the following is not a limitation of firewalls a. Protection against attacks that bypass the firewall b. Protection against internal threats c. Protection against transfer of virus infected files d. Protection from IP spoofing & routing attacks 134. In which of the following configurations, two packet filtering routers are used a. screened subnet firewall b. screened host mono-homed c. screened host firewall, dual homed bastion d. screened host firewall, single-homed bastion 135. Which among the following configuration offers greater security a. screened subnet firewall b. screened host mono-homed c. screened host firewall, dual homed bastion d. screened host firewall, single-homed bastion 136. Which among the following offers more security a. packet- filtering router b. application level gateway c. screened host firewall, single homed bastion d. packet scanner 137. In a screened host firewall, single-homed bastion, the bastion host performs which of the following functions a. integration b. non repudiation c. segregation d. authentication 138. One of the problems with using SET protocol is a. The merchants risk is high as he accepts encrypted credit card b. The credit card company should check digital signature c. The bank has to keep a database of the public keys of all customers d. The bank has to keep a database of digital signatures of all customers
139. The bank has to have the public keys of all customers in SET protocol as it has to a. Check the digital signature of customers b. Communicate with merchants c. Communicate with merchants credit card Company d. Certify their keys 140. Which among the following SET transactions indicates that a responder rejects a message because it fails format or content verification tests a. batch administration b. certificate inquiry and status c. credit d. error message 141. Which of the following SET transactions allows a merchant to communicate information to the payment gateway regarding merchant batches a. batch registration b. batch administration c. batch processing d. batch authorization 142. Which of the following SET transactions allows a merchant to correct a previously request credit a. payment capture b. capture reversal c. credit reversal d. purchase request 143. The Secure Electronic Transaction protocol is used for a. credit card payment b. cheque payment c. electronic cash payments d. payment of small amounts for internet services 144. In SET protocol a customer encrypts credit card number using a. his private key b. bank's public key c. bank's private key d. merchant's public key 145. In SET protocol a customer sends a purchase order a. encrypted with his public key b. in plain text form c. encrypted using Bank's public key d. using digital Signature system 146. Which among the following SET transactions allows the merchant to request payment from the payment gateway a. payment capture b. capture reversal c. credit reversal d. purchase request 147. Which among the following SET transactions allows a merchant to correct a previously request credit a. payment capture b. capture reversal c. credit reversal d. purchase request 148. Alert that indicates an inappropriate message was received as defined in the SSL specification is a. bad _record _mac b. unexpected _message c. illegal _ parameter d. unsupported message 149. Select which reasons secure electronic transaction ( SET) is preferred to SSL a. the vendor can verify the address of the purchaser b. the person making the payment is the legitimate card holder c. the purchaser may verify that the vendor is authorized to engage in payment card transaction d. guarantees delivery of goods or services 150. Which among the SSL specific protocols that use SSL record protocol is the simplest
a. change cipher spec protocol b. TCP c. IP d. Handshake protocol 151. Which of the following is not a SSL handshake protocol message type a. b. Server _hello c. d. client _hello 152. SSL is implemented over which layer a. TCP b. IP c. HTTP d. FTP 153. The handshake protocol, the change cipher spec protocol and the alert protocol are defined as part of which of the following protocols a. HTTP b. IP c. TCP d. SSL 154. SSL sessions are created by which of the following a. Cipher spec protocol b. TCP c. IP d. Handshake protocol 155. A session state from SSL specification is not defined by which of the following parameters a. Server write MAC secret b. Session identifier c. Master secret d. Peer certificate 156. A connection state from SSL specification is not defined by which of the following parameters a. Client write MAC secret b. Server write key c. Client write key d. Session identifier 157. Which is not a SSL record protocol operation a. Adding MAC b. Compression c. Encryption d. Expansion 158. Which among the following certificate type are not identified by TLS a. rsa _sign b. dss _sign c. rsa _fixed _dh d. rsa _ephemeral _dh 159. Ephemeral Diffie-Hellman involves signing the Diffie-Hellman parameter with a. RSA b. DES c. IDEA d. triple DES 160. The maximum length of padding that can be added prior to encryption of user data that results in a total that is a multiple of cipher's block length is a. 32 bytes b. 64 bytes c. 128 bytes d. 255 bytes 161. Which alert indicates that this handshake is being canceled for some reason unrelated to a protocol failure as defined in TLS a. decrypt _error b. user _canceled c. no _renegotiation d. record _overflow 162. Which of the following alert codes is not defined in TLS
a. no _certificate b. unknown _ca c. access _denied d. decode _error 163. In the TLS certificate verify message, the MD5 and SHA-1 hashes are calculated over a. master secret b. pads c. session key d. handshake _messages 164. The current draft version of TLS is very similar to a. SSL b. SSLv2 c. SSLv3 d. SNMP 165. TLS includes all of the key exchange techniques of SSLv3 , with the exception of a. RSA b. Fixed Diffie-Hellman c. Anonymous Diffie-Hellman d. Fortezza 166. TLS includes all of the symmetric encryption algorithms found in SSLv3, with the exception of a. DES b. Triple DES c. IDEA d. Fortezza 167. What is PRF a. pseudo redundant fault b. pseudo random fault c. pseudo random function d. perfect random function 168. Killing of user threads is a a. Integrity threat b. Confidentialitythreat c. Authentication threat d. Denial of service 169. Information about which client talks to server is a threat to a. Integrity b. Confidentiality c. Authentication d. Privacy 170. Encryption web proxies is a countermeasure to threats on a. Integrity b. Confidentiality c. Authentication d. Privacy 171. Which threat is difficult to prevent a. Integrity threat b. confidentialitythreat c. Authentication threat d. denial of service 172. Modification of user data is a threat to a. Integrity b. Confidentiality c. Authentication d. Privacy 173. Trojan horse browser is a threat to a. Integrity b. Confidentiality c. Authentication d. Privacy 174. Information about network configuration is a threat to a. Integrity b. Confidentiality c. Authentication d. privacy 175. Isolating machine by DNS attacks is
a. Integrity threat b. Confidentiality threat c. Authentication threat d. Denial of service 176. Data forgery is a threat to a. Integrity b. Confidentiality c. Authentication d. Non repudiation 177. Cryptographic checksums is a countermeasure to threats on a. Integrity b. Confidentiality c. Authentication d. Privacy 178. In relation to SNMP which of the following is defined by identification and correction of a defective element, and return to normal service a. Fault management b. Performance management c. Layer management d. Network management 179. In relation to SNMP which of the following is defined by the monitoring of network parameters to enable early indication of deterioration in operation to be detected, and corrective action to be taken a. Fault management b. Performance management c. Layer management d. Network management 180. In relation to SNMP which of the following is defined by the ongoing adjustment to host and device configurations in a network without taking element out of service a. Fault management b. Performance management c. Layer management d. Network management 181. Which is a string of numbers, with each number representing a level in a hierarchial tree a. MIB b. Trap c. OID d. SMI 182. In relation to SNMP which of the following is defined by any network element that may be written to or read from, by a network manager a. managed object b. network object c. routed object d. managed subject 183. Expand MIB a. Management information base b. management information block c. master information base d. master information block 184. Which is a one-way communication from an agent to manager a. Traps b. Inform c. MIB d. ODI 185. Expand SNMP a. signal network management protocol b. serial network management protocol c. simple network management protocol d. switching network management protocol 186. Which protocol is used to administer and manage networked devices a. TCP b. IP c. HTTP
d. SNMP 187. Which of the following defines the modern language of an SNMP MIB document a. SMIv2 b. SSL c. SET d. SNMPv3 188. Which is a software process that responds to queries using the SNMP to provide status and statistics about a network node a. Agent b. MIB c. Manger d. Server 189. Which one of the following looks at system logs for evidence of malicious or suspicious application activity in real time a. host monitor b. network monitor c. reference monitor d. security kernel database 190. Which of the following devices is used to monitor network traffic, including DoS attacks in real time? a. A host-based Intrusion Detection System b. A network-based Intrusion Detection System c. A router-based Intrusion Detection System d. A server-based Intrusion Detection System 191. Where are the important security events, such as detected security violations and authorised changes to the security kernel database stored a. reference file b. security kernel database c. audit file d. object 192. Which are the two security levels assigned to subjects at logon on the basis of criteria such as the terminal from which the computer is being accessed and the user involved, as identified by password/ID a. Low, high b. level 1, level 2 c. public, sensitive d. public, private 193. Which of the following rightly defines "secure even against an opponent with unlimited time and unlimited computing resources" a. strictly secure b. unconditionally secure c. widely secure d. wide sense secure 194. Which is the most suitable point to detect the attack and respond to the attack. a. Security kernel database b. Reference monitor c. Audit file d. Object 195. Which of the following security devices acts more like a detective rather than a preventative measure? a. IDS b. DMZ c. NAT d. Proxy 196. ' No read up' is referred to as a. Simple security property b. *- property c. #-property d. Strict security property 197. 'No write down' is referred to as
a. Simple security property b. *- property c. #-property d. Strict security property 198. Which is a controlling element in the hardware and OS of a computer that regulates the access of subjects to objects on the basis of security parameters of the subject and object a. Security kernel database b. Reference monitor c. Audit file d. Object 199. The reference monitor has access to a file, known as a. Reference file b. Security kernel database c. Audit file d. Object 200. Which property of reference monitor, is 'the reference monitor and database are protected from unauthorized modification' a. complete mediation b. isolation c. verifiability d. transparency 201. What does the acronym IDS stand for? a. Intrusion Detection System b. Internet Detection Standard c. Internet Detection System d. Intrusion Detection Standard 202. In which model, holding an unforgeable reference to an object provides access to the object; access is conveyed to another party by transmitting such a capability over a secure channel a. In a capability-based model b. Access Control List-based model c. RCL-based model d. DSS 203. In which model, a subject's access to an object depends on whether its identity is on a list associated with the object; access is conveyed by editing the list. a. In a capability-based model b. Access Control List-based model c. RCL-based model d. DSS 204. Which of the following is a secret undocumented entry point in to a program, used to grant access with out normal methods of access authentication a. Trap door b. Trojan Horse c. Virus d. Worm 205. Using Username & password a user is provided access at which level of security? a. Operation system level security b. Database level security c. Application software level security d. User level security 206. The row wise decomposition of access matrix gives a. subject b. object c. access control list d. capability tickets 207. The column wise decomposition of access matrix gives a. Access list b. Control list c. Access control list d. Permission list 208. The entries in the access matrix represents a. Process b. segment
c. Program d. Access rights 209. The rows in the access matrix represent a. Program b. Subject c. Access rights d. Object 210. The columns in the access matrix represent a. object b. process c. subject d. access right 211. The basic element of the data access control is a. port b. computer c. subject d. access
You might also like
- HCIA - Routing & Switching v2.5 MoocDocument4 pagesHCIA - Routing & Switching v2.5 MoocSuzanne Zakaria100% (4)
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityFrom EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks - CCNAv7 Module-1Document42 pagesIntroduction To Networks - CCNAv7 Module-1Mukesh0% (1)
- Cisco Introduction To Cyber Security Chap-1Document9 pagesCisco Introduction To Cyber Security Chap-1Mukesh80% (5)
- Hcia Security Mock PDFDocument5 pagesHcia Security Mock PDFIct lab0% (1)
- HCIP-Security-CISN V3.0 Mock ExamDocument4 pagesHCIP-Security-CISN V3.0 Mock ExamToffe Gokale Michel100% (1)
- Mtcna 2020Document4 pagesMtcna 2020Agus sutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Basic Router and Switch Configuration - CCNAv7 Module 2Document36 pagesBasic Router and Switch Configuration - CCNAv7 Module 2MukeshNo ratings yet
- Trusted Systems, Firewalls, Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument18 pagesTrusted Systems, Firewalls, Intrusion Detection SystemsMukesh100% (34)
- 3038 SUSE Linux Advanced AdministrationDocument3 pages3038 SUSE Linux Advanced AdministrationKevin Nyota0% (1)
- Tomcatx Performance TuningDocument51 pagesTomcatx Performance Tuningharihar12No ratings yet
- 009-3240-008 (39XX 51XX SAOS 6.12 Configuration) RevADocument798 pages009-3240-008 (39XX 51XX SAOS 6.12 Configuration) RevAReno TkNo ratings yet
- Iot MCQDocument10 pagesIot MCQRui ManjrekarNo ratings yet
- Iot MCQDocument18 pagesIot MCQShweta kumbharNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Security+ SY0-301 Practice TestDocument28 pagesCompTIA Security+ SY0-301 Practice TestMichael RoseNo ratings yet
- What Are The Advantages of Address Translation Techniques Included? (Multiple Choice)Document46 pagesWhat Are The Advantages of Address Translation Techniques Included? (Multiple Choice)Rachid AbdelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cyber SecurityDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Cyber Securityrahulbias.dbgNo ratings yet
- SNA Bullet 11 MCQSDocument12 pagesSNA Bullet 11 MCQSMursaleen UmerNo ratings yet
- Draft InternHiringQuestionnaireDocument8 pagesDraft InternHiringQuestionnaireShekhar SumanNo ratings yet
- Internet MCQsDocument8 pagesInternet MCQstamoorqureshi100% (1)
- Multiple Choice 2Document5 pagesMultiple Choice 2fabien.yvanNo ratings yet
- Soal XXXXXXXXDocument24 pagesSoal XXXXXXXXrizkyrahmadani1027No ratings yet
- MCQDocument29 pagesMCQmuralitmps100% (1)
- IoT QuizDocument15 pagesIoT Quizsharad pareekNo ratings yet
- Fraud Chapter 14Document3 pagesFraud Chapter 14Jeffrey O'LearyNo ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking Test 1Document15 pagesEthical Hacking Test 1EUGENE DEXTER NONESNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument7 pagesNetworkingTHIRUNEELAKANDANNo ratings yet
- 210-260 V11.02Document215 pages210-260 V11.02Maybe CcieNo ratings yet
- Ccie Sec Written Jan 20 - Full PoolDocument571 pagesCcie Sec Written Jan 20 - Full PoolSerge BesséNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document6 pagesSheet 2Amir TarekNo ratings yet
- CNP Unit 4 &5 QBDocument2 pagesCNP Unit 4 &5 QBTaru JauhariNo ratings yet
- Pass 4 TestDocument6 pagesPass 4 TestAbdel Rahman Jamil AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- Networking FundamentalDocument5 pagesNetworking FundamentalAto SyamNo ratings yet
- Lat. SoalMTA Netwokring DG Jawaban SoalDocument14 pagesLat. SoalMTA Netwokring DG Jawaban SoalAto Syam100% (1)
- 50 MCQsDocument8 pages50 MCQsJhon SnowNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV MCQDocument5 pagesUnit-IV MCQSaloni WaikarNo ratings yet
- CFA E3 E4 Question BankDocument17 pagesCFA E3 E4 Question BankNARSAIAHNo ratings yet
- Net1130 Final Study Part 1Document62 pagesNet1130 Final Study Part 1robpierce78No ratings yet
- MtcnaDocument22 pagesMtcnaปิยะพงษ์ แดงขําNo ratings yet
- D. Internet Assigned Numbers Authority: 1. o o o oDocument9 pagesD. Internet Assigned Numbers Authority: 1. o o o oAnand KalNo ratings yet
- CCIE SCOR v1.0 - 350-701 - Expert - 05-Oct-21Document165 pagesCCIE SCOR v1.0 - 350-701 - Expert - 05-Oct-21ehaballamNo ratings yet
- Security Mock ExamDocument11 pagesSecurity Mock Examhamza syaho100% (1)
- Question 1Document9 pagesQuestion 1kaushalyaNo ratings yet
- Encore 350-401 DumpsDocument43 pagesEncore 350-401 Dumpsrezu11100% (3)
- L IV 2013 ExamDocument12 pagesL IV 2013 ExamAbebe Gosu100% (4)
- Chap No.1: Introduction To Computer Security and Security TrendsDocument11 pagesChap No.1: Introduction To Computer Security and Security TrendsBen TenNo ratings yet
- Ccna Dumps 75qDocument31 pagesCcna Dumps 75qMaroof Raza100% (1)
- Bài tập CCNADocument17 pagesBài tập CCNAOằn Tà Là Vằn100% (1)
- MCQ TestDocument6 pagesMCQ Test4AL19CS059 BHAGYASREENo ratings yet
- Unit 4 1. Secure Socket Layer ProtocolDocument12 pagesUnit 4 1. Secure Socket Layer ProtocolSohel SutriyaNo ratings yet
- MCQsDocument16 pagesMCQsmanobillimano613No ratings yet
- CEH v5 Exam Study GuideDocument98 pagesCEH v5 Exam Study Guideapi-3699464100% (7)
- Computer Network 50 MCQ Question With Answer PDFDocument8 pagesComputer Network 50 MCQ Question With Answer PDFAnkit Kumar100% (8)
- Tes MikrotikDocument6 pagesTes MikrotikMuhammad YogiNo ratings yet
- Tes MikrotikDocument6 pagesTes MikrotikRian Wakhid100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Grandmaster MeowNo ratings yet
- Final Exam QuestionsDocument10 pagesFinal Exam Questionsmomo082298No ratings yet
- 2.PassLeader 210-260 Exam Dumps (31-60)Document8 pages2.PassLeader 210-260 Exam Dumps (31-60)Shaleh SenNo ratings yet
- NSQ 1Document4 pagesNSQ 1Mithun MangaloreNo ratings yet
- 2Document5 pages2Puji WahyonoNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNP Security 300-210 Exam QuestionsDocument21 pagesCisco CCNP Security 300-210 Exam QuestionsDND AZNo ratings yet
- Network Assessment Checklist - NSE4 Exam PDFDocument19 pagesNetwork Assessment Checklist - NSE4 Exam PDFZokou Oscar FabriceNo ratings yet
- CompnetworkDocument64 pagesCompnetworkFikru TesefayeNo ratings yet
- Zonal Telecom Training Centre, KalyaniDocument10 pagesZonal Telecom Training Centre, KalyaniArun Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- Deadlocks in Operating SystemsDocument37 pagesDeadlocks in Operating SystemsMukeshNo ratings yet
- Protocols and Reference Models - CCNAv7-1Document41 pagesProtocols and Reference Models - CCNAv7-1MukeshNo ratings yet
- Cisco Introduction To Cyber Security Chap-4Document9 pagesCisco Introduction To Cyber Security Chap-4MukeshNo ratings yet
- Cisco Introduction To Cyber Security Chap-2Document9 pagesCisco Introduction To Cyber Security Chap-2MukeshNo ratings yet
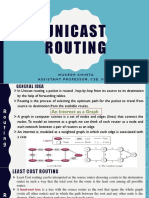
- Unicast Routing - MukeshDocument29 pagesUnicast Routing - MukeshMukeshNo ratings yet
- Assymetric Cryptography, Kerberos, X.509 CertificatesDocument34 pagesAssymetric Cryptography, Kerberos, X.509 CertificatesMukesh80% (5)
- Quality of ServiceDocument40 pagesQuality of ServiceMukeshNo ratings yet
- Next Generation IP - IPv6Document46 pagesNext Generation IP - IPv6Mukesh100% (1)
- Transport Layer - MukeshDocument54 pagesTransport Layer - MukeshMukeshNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Data and ProtocolsDocument59 pagesMultimedia Data and ProtocolsMukesh100% (1)
- Unicast Routing Protocols - RIP, OSPF and BGPDocument48 pagesUnicast Routing Protocols - RIP, OSPF and BGPMukesh100% (1)
- Multicasting and Multicast ProtocolsDocument50 pagesMulticasting and Multicast ProtocolsMukeshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SecurityDocument37 pagesIntroduction To SecurityMukeshNo ratings yet
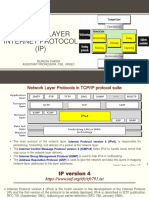
- Network Layer - IP - MukeshDocument19 pagesNetwork Layer - IP - MukeshMukesh100% (2)
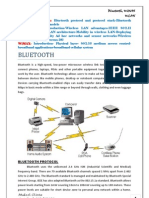
- Bluetooth, IEEE 802.11, WIMAXDocument30 pagesBluetooth, IEEE 802.11, WIMAXMukesh71% (7)
- Classsical Encryption Techniques MukeshDocument13 pagesClasssical Encryption Techniques MukeshMukeshNo ratings yet
- Symmetric Encryption, DES, AES, MAC, Hash Algorithms, HMACDocument76 pagesSymmetric Encryption, DES, AES, MAC, Hash Algorithms, HMACMukesh86% (7)
- OS Process Synchronization, DeadlocksDocument30 pagesOS Process Synchronization, DeadlocksMukesh100% (4)
- Introduction To Networks, Reference ModelsDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Networks, Reference ModelsMukesh100% (2)
- MC (Unit-7) MANET'sDocument23 pagesMC (Unit-7) MANET'sMukesh93% (42)
- JSP NotesDocument35 pagesJSP NotesMukesh71% (14)
- MVC & Struts NotesDocument6 pagesMVC & Struts NotesMukesh100% (1)
- Operating Systems: Files Concept & Implementing File SystemsDocument27 pagesOperating Systems: Files Concept & Implementing File SystemsMukesh88% (48)
- Operating Systems - DeadlocksDocument14 pagesOperating Systems - DeadlocksMukesh100% (3)
- Database Issues in Mobile ComputingDocument20 pagesDatabase Issues in Mobile ComputingMukesh90% (51)
- Servlets NotesDocument18 pagesServlets NotesMukesh100% (8)
- GUI On Raspberry PiDocument27 pagesGUI On Raspberry PisvdpuranikNo ratings yet
- Bis303 Mis q3 DoneDocument4 pagesBis303 Mis q3 DoneHf CreationNo ratings yet
- 10 Things You Can Do To Become A Better PHP DeveloperDocument15 pages10 Things You Can Do To Become A Better PHP DeveloperAlejandro NajarroNo ratings yet
- AnuragAbbu 4.6 Years Weblogic Administrator BangaloreDocument3 pagesAnuragAbbu 4.6 Years Weblogic Administrator Bangalorevali07No ratings yet
- TBEN EtherNet ConfigDocument57 pagesTBEN EtherNet Configruso21_2002No ratings yet
- Power Quality Monitors 1 F80e975ba9Document4 pagesPower Quality Monitors 1 F80e975ba9DOLORES PONCENo ratings yet
- Implementing The Cisco Adaptive Security ApplianceDocument74 pagesImplementing The Cisco Adaptive Security ApplianceAbdelali RhazouaniNo ratings yet
- TK06A GPS Tracker User ManualDocument8 pagesTK06A GPS Tracker User ManualChambilla Lanchipa Alfredo LuisNo ratings yet
- Basic of PCMDocument15 pagesBasic of PCMPablo TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Model Site WBC694 - Chhat Singimari..2G+FDD+L2100..GKDocument18 pagesModel Site WBC694 - Chhat Singimari..2G+FDD+L2100..GKbiswanath.bhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Wi-Fi - Quick Guide What Is Wi-Fi ?Document6 pagesWi-Fi - Quick Guide What Is Wi-Fi ?Anbazhagan SelvanathanNo ratings yet
- HC 12 433 Si4463 Wireless Serial ModuleDocument5 pagesHC 12 433 Si4463 Wireless Serial ModulecjaganNo ratings yet
- Real Time Scenario For Abstract Class and Interface: Industry Oriented Java-1Document18 pagesReal Time Scenario For Abstract Class and Interface: Industry Oriented Java-1dev eloperNo ratings yet
- DRX Cycle For WCDMA PDFDocument3 pagesDRX Cycle For WCDMA PDFDaniele SambenedettoNo ratings yet
- Eaton - FD120 Diesel Engine Fire Pump ControllerDocument2 pagesEaton - FD120 Diesel Engine Fire Pump ControllerAlejandro Chumpitaz MarchanNo ratings yet
- All TCL ScriptsDocument3 pagesAll TCL ScriptsRavinderNo ratings yet
- Configuring The Active Directory InfrastructureDocument76 pagesConfiguring The Active Directory InfrastructurerodrigobenicaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Mind Map For Internet Infrastructure AssetsDocument1 pageDetailed Mind Map For Internet Infrastructure AssetsranamzeeshanNo ratings yet
- Sh1106 Sino WealthDocument49 pagesSh1106 Sino WealthAnonymous Im6zx7xiyNo ratings yet
- Sys Admin Guide Xerox WorkCentre 7775Document185 pagesSys Admin Guide Xerox WorkCentre 7775dankorzon1No ratings yet
- 150ONU 804iDocument2 pages150ONU 804inmc79No ratings yet
- Siemens SIMATIC Step 7 Programmer PDFDocument71 pagesSiemens SIMATIC Step 7 Programmer PDFkamelNo ratings yet
- AO DataSheet SFP ReferenciaDocument2 pagesAO DataSheet SFP ReferenciaAntero CasaniNo ratings yet
- MavisDocument26 pagesMavisTarasNo ratings yet
- R002 - How To Make A Diagnostic and Start On LULC07Document7 pagesR002 - How To Make A Diagnostic and Start On LULC07Alvaro Coy H.No ratings yet
- MXF White PaperDocument18 pagesMXF White Papertwitter3600No ratings yet