Professional Documents
Culture Documents
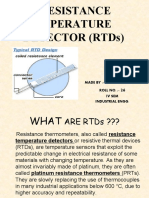
Resistance Thermometers
Uploaded by
AsutoshCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Resistance Thermometers
Uploaded by
AsutoshCopyright:
Available Formats
Resistance thermometers, also called resistance temperature detectors or resistive thermal devices (RTDs), are temperature sensors that
exploit the predictable change in electrical resistance of some materials with changing temperature. As they are almost invariably made of platinum, they are often called platinum resistance thermometers (PRTs). They are slowly replacing the use of thermocouples in many industrial applications below 600 C, due to higher accuracy and repeatability.
While thermocouples use the Seeback effect to generate a voltage, resistance thermometers use electrical resistance and require a power source to operate. The resistance ideally varies linearly with temperature. Resistance thermometers are usually made using platinum, because of its linear resistancetemperature relationship and its chemical inertness. The platinum detecting wire needs to be kept free of contamination to remain stable. A platinum wire or film is supported on a former in such a way that it gets minimal differential expansion or other strains from its former, yet is reasonably resistant to vibration. Commercial platinum grades are produced which exhibit a temperature coefficient of resistance 0.00385/C (0.385%/C) (European Fundamental Interval)[citation needed] The sensor is usually made to have a resistance of 100 at 0 C. This is defined in BS EN 60751:1996 (taken from IEC 60751:1995).
::: CAUSES OF ERROR :::
Measurement of resistance requires a small current to be passed through the device under test. This can cause :::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::; o o o Resistive heating, causing significant loss of accuracy if manufacturers' limits are not respected, or the design does not properly consider the heat path. Mechanical strain on the resistance thermometer can also cause inaccuracy. Lead wire resistance can also be a factor; adopting three- and four-wire, instead of two-wire, connections can eliminate connection lead resistance effects from measurements ; threewire connection is sufficient for most purposes and almost universal industrial practice. Four-wire connections are used for the most precise applications. Thermal EMF errors are produced by the EMF adding to or subtracting from the applied sensing voltage, primarily in DC systems.
Advantages of platinum resistance thermometers ::: High accuracy Low drift
Wide operating range Suitable for precision applications
::: LIMITATIONS :::
RTDs in industrial applications are rarely used above 660 C. At temperatures above 660 C it becomes increasingly difficult to prevent the platinum from becoming contaminated by impurities from the metal sheath of the thermometer. This is why laboratory standard thermometers replace the metal sheath with a glass construction. Compared to thermistors, platinum RTDs are less sensitive to small temperature changes and have a slower response time. However, thermistors have a smaller temperature range and stability.
::: RTD VS THERMOCOUPLE :::
What are the temperature requirements? If process temperatures are between -200 to 500 C (-328 to 932 F), an industrial RTD is the preferred option. Thermocouples have a range of -180 to 2,320 C (-292 to 4,208 F),[8] so for temperatures above 500 C (932 F) they are the only contact temperature measurement device. What are the time-response requirements? If the process requires a very fast response to temperature changesfractions of a second as opposed to seconds (e.g. 2.5 to 10 s)then a thermocouple is the best choice. Time response is measured by immersing the sensor in water moving at 1 m/s (3 ft/s) with a 63.2% step change. What are the size requirements? A standard RTD sheath is 3.175 to 6.35 mm (0.1250 to 0.250 in) in diameter; sheath diameters for thermocouples can be less than 1.6 mm (0.063 in). What are the accuracy and stability requirements? If a tolerance of 2 C is acceptable and the highest level of repeatability is not required, a thermocouple will serve. RTDs are capable of higher accuracy and can maintain stability for many years, while thermocouples can drift within the first few hours of use.
::: STANDARD RESISTANCE THERMOMETER DATA :::
Resistance thermometer elements can be supplied which function up to 1000 C. The relation between temperature and resistance is given by the Callendar-Van Dusen equation,
Here, R(T) is the resistance at temperature T, R(0) is the resistance at 0 C, and the constants (for an alpha=0.00385 platinum RTD) are
Since the B and C coefficients are relatively small, the resistance changes almost linearly with the temperature.
You might also like
- Comparison of Thermocouples, RTDS, and ThermistorsDocument2 pagesComparison of Thermocouples, RTDS, and ThermistorsAlwyzz Happie RaamzzNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT: To Study and Verify Characteristic OF Resistor Temp. DetectorDocument30 pagesSUBJECT: To Study and Verify Characteristic OF Resistor Temp. DetectorvishalsanziraNo ratings yet
- Rashidakbarpresentation 12974074922752 Phpapp01Document16 pagesRashidakbarpresentation 12974074922752 Phpapp01Eng-anwer kadhimNo ratings yet
- R Vs T Relationship of Various Metals: SensorsDocument6 pagesR Vs T Relationship of Various Metals: SensorsAnbu AyyappanNo ratings yet
- RTD pt100Document6 pagesRTD pt100jyotiblossomsNo ratings yet
- Resistance Temperature Detectors: Element Material Temperature Range Benefits (%/ C)Document4 pagesResistance Temperature Detectors: Element Material Temperature Range Benefits (%/ C)Harish SundarNo ratings yet
- RTD-Resistance Temperature DetectorDocument10 pagesRTD-Resistance Temperature DetectorabhisheksingheeNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation SensorsDocument145 pagesInstrumentation SensorsGulfam ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Sae Technical Paper Series: C. Scott Nelson, David Chen, Joseph Ralph and Eric D'HerdeDocument11 pagesSae Technical Paper Series: C. Scott Nelson, David Chen, Joseph Ralph and Eric D'HerderuchikasaxenaNo ratings yet
- Resistance Thermometer: Resistance Thermometers, Also Called Resistance Temperature Detectors ('RTD'S), AreDocument10 pagesResistance Thermometer: Resistance Thermometers, Also Called Resistance Temperature Detectors ('RTD'S), AreMac Jayson DiazNo ratings yet
- Rtds - or Resistance Temperature Detectors - Are Temperature Sensors That Contain A Resistor ThatDocument6 pagesRtds - or Resistance Temperature Detectors - Are Temperature Sensors That Contain A Resistor Thatmuhammad aliNo ratings yet
- Resistive Temperature Measuring DevicesDocument7 pagesResistive Temperature Measuring DevicesBatuhan KalyoncuNo ratings yet
- RTD Elements and RTD Probes - Resistance Temperature Detection Sensors (RTDS) PDFDocument4 pagesRTD Elements and RTD Probes - Resistance Temperature Detection Sensors (RTDS) PDFTsenatNo ratings yet
- Resistance ThermometrDocument9 pagesResistance Thermometrgopir28No ratings yet
- RTDDocument4 pagesRTDCss GaneshNo ratings yet
- ThermometersDocument2 pagesThermometersAbbasNo ratings yet
- RTD TutorialsDocument11 pagesRTD TutorialsjaigodaraNo ratings yet
- WP 003 Endress TemperatureDocument17 pagesWP 003 Endress Temperaturevenkatesh425No ratings yet
- 1.2.5 Precision Temperature Sensing Resistor PRC100: Length: 13.5mm (Excl. Leads) Diameter: 5mm RS Stock NumberDocument12 pages1.2.5 Precision Temperature Sensing Resistor PRC100: Length: 13.5mm (Excl. Leads) Diameter: 5mm RS Stock NumberEng Bashar MufidNo ratings yet
- RTD, Thermocouple, Thermistors, Manometer, Bourdon TubeDocument36 pagesRTD, Thermocouple, Thermistors, Manometer, Bourdon TubeDINESH KUMAR DRAVIDAMANI100% (1)
- Industrial Transducer: Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDS) & Types By: Ravi DhanejaDocument10 pagesIndustrial Transducer: Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDS) & Types By: Ravi Dhanejaurvish_soniNo ratings yet
- RTD BasicsDocument5 pagesRTD BasicsMourougapragash SubramanianNo ratings yet
- RTD TCDocument10 pagesRTD TCtkaneeshNo ratings yet
- Difference Between RTD, Thermocouple and ThermistorDocument3 pagesDifference Between RTD, Thermocouple and ThermistorVenkata Suresh MandavaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of ThermocoupleDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of ThermocouplekusumgdasNo ratings yet
- Lec One Sensors-1Document26 pagesLec One Sensors-1Basma EltanekhyNo ratings yet
- ThermistorsDocument4 pagesThermistorss_geethanathan9290No ratings yet
- THERMOMETRYDocument8 pagesTHERMOMETRYvivekmariner2812No ratings yet
- Construction: Two-Wire ConfigurationDocument4 pagesConstruction: Two-Wire Configurationdark*nightNo ratings yet
- RTD Standards: AccuracyDocument11 pagesRTD Standards: AccuracyAhmad Adel El TantawyNo ratings yet
- Sensor Compare ChartDocument3 pagesSensor Compare ChartPopescu QescuNo ratings yet
- Unit 3onthermistorsDocument8 pagesUnit 3onthermistorssvnet vizagNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Lab.: RTD Thermistors Thermocoupl eDocument31 pagesInstrumentation Lab.: RTD Thermistors Thermocoupl eGAURAV SINGHNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Resistive Temperature DetectorDocument8 pages2.3 Resistive Temperature DetectorsatsakthiNo ratings yet
- Ther Mist orDocument14 pagesTher Mist orDheeraj YadavNo ratings yet
- Temperature MeasurementDocument35 pagesTemperature MeasurementAlaa Shahwan88% (8)
- 2 Car Sensors V1-TemperatureDocument35 pages2 Car Sensors V1-TemperatureWNo ratings yet
- Choosing The Right Temperature SensorDocument1 pageChoosing The Right Temperature SensorJinu MathewNo ratings yet
- Resistance Thermometer: By: Shashank Pathak EN - 4 YearDocument16 pagesResistance Thermometer: By: Shashank Pathak EN - 4 YearShashank PathakNo ratings yet
- Resistance ThermometryDocument52 pagesResistance ThermometryRAJANo ratings yet
- ThermistorsDocument6 pagesThermistorsمحمد نصیریNo ratings yet
- RTD Questions and AnswersDocument19 pagesRTD Questions and AnswersJêmš NavikNo ratings yet
- RTD - Theory Temperature PDFDocument6 pagesRTD - Theory Temperature PDFpandit1010No ratings yet
- Thermistor Working Principle Instrumentation ToolsDocument8 pagesThermistor Working Principle Instrumentation ToolsAbarajithan RajendranNo ratings yet
- RTD Temperature Measurement 917ADocument16 pagesRTD Temperature Measurement 917Amitha07No ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To Improving Temperature Measurement Accuracy White Paper Moore IndustriesDocument5 pagesA Practical Guide To Improving Temperature Measurement Accuracy White Paper Moore IndustriesNXSkeeperNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 TransducerDocument12 pagesAssignment 3 TransducerFirzan HaraziNo ratings yet
- Resistance Thermometer and ThermistersDocument21 pagesResistance Thermometer and ThermistersRavi HemanthNo ratings yet
- SensorsDocument55 pagesSensorsellyNo ratings yet
- Ther Mist orDocument1 pageTher Mist orAnonymous mqIqN5zNo ratings yet
- Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) - Principle of Operation, Materials, Configuration and BenefitsDocument5 pagesResistance Temperature Detector (RTD) - Principle of Operation, Materials, Configuration and BenefitsSaad NasirNo ratings yet
- RTD Gen Specs RefDocument4 pagesRTD Gen Specs RefRamesh SubramanianNo ratings yet
- 6Document52 pages6Virendra Kumar PareekNo ratings yet
- RTD Theory: So What Exactly Is An RTD?Document6 pagesRTD Theory: So What Exactly Is An RTD?ouhamidNo ratings yet
- Measurement of TemperatureDocument24 pagesMeasurement of Temperaturehadeed shaikhNo ratings yet
- Industrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionFrom EverandIndustrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Advanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionFrom EverandAdvanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Thermal Insulation Handbook for the Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical IndustriesFrom EverandThermal Insulation Handbook for the Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical IndustriesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- M&a Trend Report 2014 - DeloitteDocument40 pagesM&a Trend Report 2014 - DeloitteAsutoshNo ratings yet
- Monetizing Mobile - Mckinsey PDFDocument9 pagesMonetizing Mobile - Mckinsey PDFAsutoshNo ratings yet
- Bruce Lee - Original Manuscript - Jeet Kune Do PDFDocument18 pagesBruce Lee - Original Manuscript - Jeet Kune Do PDFSteven AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Temperature: Steinhart-Hart EquationDocument5 pagesMeasurement of Temperature: Steinhart-Hart EquationAsutoshNo ratings yet
- Works and Fuzzy Logic PDFDocument550 pagesWorks and Fuzzy Logic PDFmicuadriandanut100% (2)
- BHELDocument7 pagesBHELwenger713No ratings yet
- Mathematics Through Paper Folding (Gnv64)Document64 pagesMathematics Through Paper Folding (Gnv64)Asutosh100% (6)
- Associated Fiber BundleDocument1 pageAssociated Fiber BundleAsutoshNo ratings yet
- BS 5422 2001 Method For Specifying Thermal Insulating Materials For Pipes, Tanks, Vessels, DuctDocument60 pagesBS 5422 2001 Method For Specifying Thermal Insulating Materials For Pipes, Tanks, Vessels, DuctRamiAl-fuqahaNo ratings yet
- YuzurtDocument2 pagesYuzurtFranco Ascari100% (1)
- Components of A Rainwater Harvesting SystemDocument38 pagesComponents of A Rainwater Harvesting SystembudiperNo ratings yet
- Jan Precious Mille BDocument1 pageJan Precious Mille BJebjeb C. BrañaNo ratings yet
- Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR), Synthetic Latex: ApplicationDocument2 pagesNitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR), Synthetic Latex: ApplicationbobNo ratings yet
- The Modern Fire Attack - Phil Jose and Dennis LegearDocument7 pagesThe Modern Fire Attack - Phil Jose and Dennis LegearTomNo ratings yet
- Practical Approach To Electron Beam Dosimetry at Extended SSDDocument10 pagesPractical Approach To Electron Beam Dosimetry at Extended SSDAhmet Kürşat ÖzkanNo ratings yet
- TQM Assignment 3Document8 pagesTQM Assignment 3ehte19797177No ratings yet
- Intelligent: - 60 AMP - 80 AMPDocument8 pagesIntelligent: - 60 AMP - 80 AMPHayson NuñezNo ratings yet
- Types of Shops Shopping: 1. Chemist's 2. Grocer's 3. Butcher's 4. Baker'sDocument1 pageTypes of Shops Shopping: 1. Chemist's 2. Grocer's 3. Butcher's 4. Baker'sMonik IonelaNo ratings yet
- Astm c126 Jtvo9242Document5 pagesAstm c126 Jtvo9242Nayth Andres GalazNo ratings yet
- TinyEYE Online Speech Therapy Media GuideDocument4 pagesTinyEYE Online Speech Therapy Media GuideTinyEYE Therapy ServicesNo ratings yet
- NSF 型錄2Document2 pagesNSF 型錄2Nermeen ElmelegaeNo ratings yet
- Rubber Dam (Tooth Isolation)Document9 pagesRubber Dam (Tooth Isolation)NonoNo ratings yet
- Clay Analysis - 1Document55 pagesClay Analysis - 1JCSNo ratings yet
- PU-133AB - 規格GMXa spc 2022Document5 pagesPU-133AB - 規格GMXa spc 2022Ý TrầnNo ratings yet
- All About Ocean Life-Rachel BladonDocument6 pagesAll About Ocean Life-Rachel BladonRichard TekulaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Feasibility Report: at Plot No. 15/B-3, Jigani Industrial Area Anekal Taluk, Bangalore South District Karnataka byDocument41 pagesPre-Feasibility Report: at Plot No. 15/B-3, Jigani Industrial Area Anekal Taluk, Bangalore South District Karnataka by12mchc07No ratings yet
- Banco de Oro (Bdo) : Corporate ProfileDocument1 pageBanco de Oro (Bdo) : Corporate ProfileGwen CaldonaNo ratings yet
- Organic Facial Remedies Versus Inorganic Facial RemediesDocument13 pagesOrganic Facial Remedies Versus Inorganic Facial Remediesapi-271179911No ratings yet
- HRM Report CIA 3Document5 pagesHRM Report CIA 3SUNIDHI PUNDHIR 20221029No ratings yet
- B1 SpeakingDocument5 pagesB1 SpeakingHoàng Nam Thắng100% (2)
- (Clinical Sociology - Research and Practice) Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Auth.), Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Eds.) - Handbook of Clinical Sociology-Springer US (2001) PDFDocument441 pages(Clinical Sociology - Research and Practice) Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Auth.), Howard M. Rebach, John G. Bruhn (Eds.) - Handbook of Clinical Sociology-Springer US (2001) PDFMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Envirotainer RKN E1 Operations ManualDocument46 pagesEnvirotainer RKN E1 Operations ManualJorge de oliveiraNo ratings yet
- Trophic Levels - 10% RuleDocument5 pagesTrophic Levels - 10% RulerebbiegNo ratings yet
- Hand-Pallet Truck - NewDocument2 pagesHand-Pallet Truck - NewAkhilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Acid Base Problem Set: O O CH CH OH O O-H CH CH ODocument2 pagesChapter 4. Acid Base Problem Set: O O CH CH OH O O-H CH CH Osnap7678650No ratings yet
- FPSB 2 (1) 56-62oDocument7 pagesFPSB 2 (1) 56-62ojaouadi adelNo ratings yet
- ms1471pt5-99 - Vocabulary Smoke ControlDocument8 pagesms1471pt5-99 - Vocabulary Smoke ControlBryan Ng Horng HengNo ratings yet
- Msds M-Toluoyl ChlorideDocument4 pagesMsds M-Toluoyl ChloridecrisNo ratings yet