Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk For Aspiration
Uploaded by
cotyboyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk For Aspiration
Uploaded by
cotyboyCopyright:
Available Formats
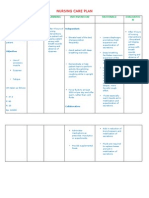
ASSESSMENT S> the patients wife verbalized, Simula nang na admit siya, nilagyan na siya ng endotracheal tube.
Para raw makahinga siya ng mabuti at hindi mahirapan. O> Patient cant ambulate nor sit. After client do active range of motion, RR=34, PR=97 bpm and BP=140/100. T=37.7C
NURSING DIAGNOSIS Risk for aspiration r/t presence of endotracheal tube and reduced level of consciousnes s.
SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE Both acute and chronic conditions can place patients at risk for aspiration. Acute conditions, such as postanesthesia effects from surgery or diagnostic tests, occur predominantly in the acute care setting. Chronic conditions, including altered consciousness from head injury, spinal cord injury, neuromuscular weakness, hemiplegia and
PLANNING After 8 hours of nursing intervention, the patients risk of aspiration will decrease as a result of ongoing assessment and early intervention.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS Independent Monitor level of consciousness
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
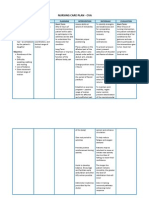
Auscultate breath sounds for development of crackles and/or rhonchi.
After 8 hours of nursing intervention, A decreased level the patients risk of of consciousness is aspiration was a prime risk factor decreased as a result for aspiration. of ongoing assessment and early intervention. Aspiration of small amounts can occur without coughing or sudden onset of respiratory distress, especially in patients with decreased levels of consciousness. To prevent aspiration of secretions and maintain open airway.
Position patient who have a decreased level of consciousness on their sides. Keep suction machine available for use.
dysphagia from stroke, use of tube feedings for nutrition, endotracheal intubation, or mechanical ventilation may be encountered in the home, rehabilitative, or hospital settings. Elderly and cognitively impaired patients are at high risk. Aspiration is a common cause of death in comatose patients. Reference: http://www1.us .elsevierhealth. com/MERLIN/ Gulanick/Cons
Explain to the relative the need for proper positioning. Collaborative Collaborate with the respiratory therapist to determine the effectiveness of the cuff of the ET tube. Dependent Perform suctioning as ordered by the physician.
To clear secretions and provide patent airway. Reference: http://www1.us.els evierhealth.com/M ERLIN/Gulanick/ Constructor/index. cfm?plan=04
tructor/index.cf m?plan=04
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Skin BreakdownDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For Skin BreakdownShelli Miller Pryor82% (11)
- Nursing care plan for risk of aspirationDocument6 pagesNursing care plan for risk of aspirationWendy Escalante100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPaudreyNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Related To BronchospasmReylan Garcia100% (4)
- Spinal Cord Injury NCPDocument2 pagesSpinal Cord Injury NCPShengxy Ferrer100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan2 CVADocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan2 CVAhermesdave1No ratings yet
- NCP For AnaphylacticDocument3 pagesNCP For AnaphylacticRommar Romero67% (3)
- NCP Risk of AspirationDocument2 pagesNCP Risk of AspirationNura Zein100% (1)
- NCP - Self-Care DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP - Self-Care DeficitEricka B. Banaszczuk100% (15)
- Deficient diversion nursingDocument2 pagesDeficient diversion nursingKimsha Concepcion100% (2)
- Oxygenation - NCPDocument5 pagesOxygenation - NCPCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Aspiration NCPGrace Beltran67% (3)
- NCP-RISK For ASPIRATIONDocument3 pagesNCP-RISK For ASPIRATIONChristine S. Samaniego100% (1)
- Risk For Aspiration Related To Impaired Swallowing Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument3 pagesRisk For Aspiration Related To Impaired Swallowing Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentChenee MabulayNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeeNo ratings yet
- NCP - CapDocument4 pagesNCP - CapSherryNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Nursing Care Plans: Assessment, Interventions & OutcomesDocument1 pagePneumonia Nursing Care Plans: Assessment, Interventions & Outcomesjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- Risk For Impaired SwallowingDocument3 pagesRisk For Impaired SwallowingCalimlim Kim100% (1)
- Risk For AspirationDocument2 pagesRisk For AspirationGly Mtg100% (6)
- Viii. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument1 pageViii. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationJohn Linero100% (2)
- NCP - Risk For InjuryDocument3 pagesNCP - Risk For InjuryMatty JolbitadoNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2Neil Abraham Mendoza Lalap100% (2)
- NCP CR Impaired Spontaneous VentilationDocument8 pagesNCP CR Impaired Spontaneous VentilationJosett Romano75% (4)
- NCP Near DrowningDocument1 pageNCP Near Drowningchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan (CVA)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan (CVA)Mel Rodolfo50% (2)
- NCP - Impaired Verbal Communication Related To Neuromascular Impairment As Manifested by AphaisaDocument2 pagesNCP - Impaired Verbal Communication Related To Neuromascular Impairment As Manifested by AphaisaKristina Angela CarbonNo ratings yet
- Self Care DeficitDocument4 pagesSelf Care DeficitEllaine RamirezNo ratings yet
- Improving Physical Mobility Through Nursing InterventionsDocument2 pagesImproving Physical Mobility Through Nursing InterventionsPrincess Averin Navarro50% (2)
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocument2 pagesImpaired Verbal CommunicationEjay Barayuga100% (2)
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument1 pageNCP Impaired Physical MobilityKarl EnriquezNo ratings yet
- NCP Violence - OtherDocument2 pagesNCP Violence - OtherRosean Venus SilangNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for Post-Op PatientDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Post-Op Patientromelyn100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Breathing Pattern Hepatic MassRheegell Ellar-Fuertes100% (3)
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Physical MobilityJohn Michael FernandezNo ratings yet
- Impaired mobility assessmentDocument2 pagesImpaired mobility assessmentVhin Lim100% (2)
- NCP-Impaired Physical Mobility - E+ ImbalanceDocument3 pagesNCP-Impaired Physical Mobility - E+ ImbalanceRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesNcp-Ineffective Airway Clearancelouanne0550% (2)
- #1 Risk For Aspirations DCDocument2 pages#1 Risk For Aspirations DCtanyav26No ratings yet
- Risk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionDocument6 pagesRisk For Aspiration: Risk For Aspiration: at Risk For Entry of Gastrointestinal Secretions, Oropharyngeal SecretionAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Risk For AspirationDocument11 pagesRisk For AspirationSanket TelangNo ratings yet
- FDARDocument1 pageFDARjesabel_caraigNo ratings yet
- Answer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheDocument14 pagesAnswer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheMikeeNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Physical Mobility-2Document4 pagesNCP Impaired Physical Mobility-2ejoanbNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired PhysicalDocument1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN Problem Body Weakness Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physicalmitchie riveraNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument2 pagesNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Goals Interventions EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Goals Interventions EvaluationAav Canlas100% (1)
- NEJM VICM Viewers ChoiceDocument19 pagesNEJM VICM Viewers ChoiceAnonymous cQWavnNo ratings yet
- Ex TurbaciónDocument4 pagesEx TurbaciónAlberto EscotoNo ratings yet
- Pembagian Baca B. InggrisDocument7 pagesPembagian Baca B. InggrisPutriNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Nursing Care-1Document9 pagesPostoperative Nursing Care-1MegaaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0733862722000384 MainDocument13 pages1 s2.0 S0733862722000384 Maincoca12451No ratings yet
- RAPID SEQUENCE INTUBATION TECHNIQUEDocument55 pagesRAPID SEQUENCE INTUBATION TECHNIQUElorkan19100% (1)
- Maxillofacial Trauma: Dr. Azher A. Auda Bds CabsDocument17 pagesMaxillofacial Trauma: Dr. Azher A. Auda Bds CabsHaider F YehyaNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Nursing Care: Essential Steps in PACU RecoveryDocument10 pagesPostoperative Nursing Care: Essential Steps in PACU RecoveryFholsen FrohansenNo ratings yet
- Concious Sedation PedoDocument29 pagesConcious Sedation PedodrkameshNo ratings yet
- Online LectureDocument9 pagesOnline LectureJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus PatoDocument2 pagesDiabetes Mellitus PatocotyboyNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone OmepraDocument3 pagesDexamethasone OmepracotyboyNo ratings yet
- Felodipine CefuroximeDocument3 pagesFelodipine CefuroximecotyboyNo ratings yet
- Meningioma Patho DataDocument6 pagesMeningioma Patho DatacotyboyNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide, Allopurinol, KetosterilDocument9 pagesHydrochlorothiazide, Allopurinol, KetosterilcotyboyNo ratings yet
- Hydrochlorothiazide, Allopurinol, KetosterilDocument3 pagesHydrochlorothiazide, Allopurinol, KetosterilcotyboyNo ratings yet
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDocument9 pagesFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetic ThyDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Diabetic ThycotyboyNo ratings yet
- How Leptospirosis Is Treated With AntibioticsDocument2 pagesHow Leptospirosis Is Treated With AntibioticscotyboyNo ratings yet