Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air Conditioning Basics
Uploaded by
Laurice Ortiz LuisOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air Conditioning Basics
Uploaded by
Laurice Ortiz LuisCopyright:
Available Formats
BgUtil 2: MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS
Air Conditioning Basics: The Basics of an Air Conditioning System
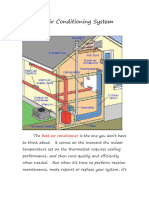
An air conditioner is basically a refrigerator without the insulated box. It uses the evaporation of a refrigerant, like Freon, to provide cooling. The mechanics of the Freon evaporation cycle are the same in a refrigerator as in an air conditioner. An Air conditioning system includes both the cooling and heating of air. It also cleans the air and controls the moisture level. An air conditioner is able to cool a building because it removes heat from the indoor air and transfers it outdoors. A chemical refrigerant in the system absorbs the unwanted heat and pumps it through a system of piping to the outside coil. The fan, located in the outside unit, blows outside air over the hot coil, transferring heat from the refrigerant to the outdoor air. Basic Operations Most air conditioning systems have four common components:
A Compressor An Expansion valve or metering device An Evaporator coil and blower A Chemical Refrigerant
The compressor (which is controlled by the thermostat) is the "heart" of the system. The compressor acts as the pump, causing the refrigerant to flow through the system. Its job is to draw in a low-pressure, low-temperature, refrigerant in a gaseous state and by compressing this gas, raise the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant. This high-pressure, high-temperature gas then flows to the condenser coil. The condenser coil is a series of piping with a fan that draws outside air across the coil. As the refrigerant passes through the condenser coil and the cooler outside air passes across the coil, the air absorbs heat from the refrigerant that causes the refrigerant to condense from a gas to a liquid state. The high-pressure, hightemperature liquid then reaches the expansion valve. The expansion valve is the "brain" of the system. By sensing the temperature of the evaporator, or cooling coil, it allows liquid to pass through a very small orifice, which causes the refrigerant to expand to a low-pressure, low-temperature gas. This "cold" refrigerant flows to the evaporator. The evaporator coil is a series of piping connected to a furnace or air handler that blows indoor air across it, causing the coil to absorb heat from the air. The cooled air is then delivered to the house through ducting. The refrigerant then flows back to the compressor where the cycle starts over again. Most central air conditioning units operate by means of a split system. That is, they consist of a "hot" side, or the condensing unitincluding the condensing coil, the compressor and the fanwhich is situated outside your home, and a "cold" side that is located inside your home. The cold side consists of an expansion valve and a cold 1|AIR CONDITIONING BASICS
BgUtil 2: MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL SYSTEMS
coil, and it is usually part of your furnace or some type of air handler. The furnace blows air through an evaporator coil, which cools the air. Then this cool air is routed throughout your home by means of a series of air ducts. A window unit operates on the same principal, the only difference being that both the hot side and the cold side are located within the same housing unit.
2|AIR CONDITIONING BASICS
You might also like
- Lab Experiment # 06: Objective: Air ConditioningDocument5 pagesLab Experiment # 06: Objective: Air ConditioningSayam AliNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning SystemDocument5 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning SystemLArry Vasquez100% (2)
- An Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantDocument11 pagesAn Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantRitu SinghNo ratings yet
- Portable Air Conditioner Project SynopsisDocument4 pagesPortable Air Conditioner Project SynopsisAmit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Document33 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Christina OhNo ratings yet
- Building Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1Document32 pagesBuilding Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1TaanayaNo ratings yet
- Basic Air Conditioning Guide in 38 CharactersDocument37 pagesBasic Air Conditioning Guide in 38 CharacterscspolaNo ratings yet
- 16 - Air Conditionng Systems - Vaishnavi C. KambleDocument13 pages16 - Air Conditionng Systems - Vaishnavi C. KambleVaishnavi KambleNo ratings yet
- Ac How It WorksDocument4 pagesAc How It Workshassanain_100No ratings yet
- Basics of Air Conditioning PDFDocument3 pagesBasics of Air Conditioning PDFMarcelo RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Architectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Document8 pagesArchitectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Vedita Bhat100% (1)
- HVAC Systems Guide: Types, Components & How AC WorksDocument3 pagesHVAC Systems Guide: Types, Components & How AC WorksDen Mas DeepNo ratings yet
- Principle of VRFDocument5 pagesPrinciple of VRFghazanfarhayat456No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Report.Document15 pagesAir Conditioning Report.Ethan XavierNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning: Qus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniDocument56 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning: Qus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniMalik MussaNo ratings yet
- Mapua Institute of Technolog1Document15 pagesMapua Institute of Technolog1Ian KasaiNo ratings yet
- How AC Works: The 5 Components That Drive CoolingDocument5 pagesHow AC Works: The 5 Components That Drive CoolingSNEHA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning SystemannNo ratings yet
- Central Air Conditioning System-converted_2Document24 pagesCentral Air Conditioning System-converted_2gmusama1No ratings yet
- 1,2 - Unit 1Document137 pages1,2 - Unit 1Saran T SNo ratings yet
- Cooling Mode: Principles of Heat Pump OperationDocument1 pageCooling Mode: Principles of Heat Pump OperationSushant MishraNo ratings yet
- How It Works?Document2 pagesHow It Works?saimunNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - Air ConditionDocument62 pagesUNIT I - Air ConditionNeha JojanNo ratings yet
- HVAC Unit 1&2Document22 pagesHVAC Unit 1&2LOYOLA RS 200No ratings yet
- Mondragon, Allan Cristian M. AT 19 Auto Air-Conditioning Bsat-3A 2 Output No. 3Document2 pagesMondragon, Allan Cristian M. AT 19 Auto Air-Conditioning Bsat-3A 2 Output No. 3Cristian MondragonNo ratings yet
- ChillerDocument3 pagesChillerSajib Chandra RoyNo ratings yet
- Hvac PoDocument2 pagesHvac PoJhon Ciryl M. CalayNo ratings yet
- Centralised20ac20system 190120171416Document23 pagesCentralised20ac20system 190120171416Saba ArifNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument12 pagesAir ConditioningSNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning Systemabenezer1425No ratings yet
- OJT Outputs: Raphael Justine D. Hismana Bsme 5Document27 pagesOJT Outputs: Raphael Justine D. Hismana Bsme 5Khaster NavarraNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument10 pagesAbstractabushasolomon75% (4)
- R&AC Lab ManualDocument29 pagesR&AC Lab ManualPARAMESHNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument7 pagesAir Conditioning SystemT SRNo ratings yet
- Group-07 - Schematic Details of Various AC Systems and the Concept of ZoningDocument37 pagesGroup-07 - Schematic Details of Various AC Systems and the Concept of ZoningVipin VetriNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsAhmad MujahidNo ratings yet
- Bu ResearchDocument10 pagesBu ResearchToteng TanglaoNo ratings yet
- Air Condationing FinalDocument40 pagesAir Condationing FinalPeterson muchiriNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 HVACDocument66 pagesUnit 2 HVACJaya SubhaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument7 pagesAir Conditioning SystemPapri MahataNo ratings yet
- UCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)Document11 pagesUCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)shehan harshithaNo ratings yet
- Split Air Conditioner Learning SimulationDocument19 pagesSplit Air Conditioner Learning SimulationkablasNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveSayam AliNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesLab Experiment # 05: ObjectiveSayam AliNo ratings yet
- Performance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantDocument26 pagesPerformance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration PlantGigi Sales100% (2)
- Chapter 6Document61 pagesChapter 6Dayang Azraa AfeefaaNo ratings yet
- Heat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Document46 pagesHeat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Sagar GoyalNo ratings yet
- Window Air Conditioner GuideDocument24 pagesWindow Air Conditioner GuideNitin GrewalNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Test RigDocument28 pagesRefrigeration Test RigOxmere SalesNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration CycleDocument29 pagesRefrigeration CycleShyam WanaskarNo ratings yet
- Question 2Document2 pagesQuestion 2MUHAMMAD FARIS IQBAL BIN RIDUANNo ratings yet
- Central Air ConditioningDocument14 pagesCentral Air ConditioningHashim MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Airconditioning ProcessDocument5 pagesAirconditioning ProcessMark Anthony SibayanNo ratings yet
- Heat Pump TrainerDocument6 pagesHeat Pump TrainerAfzaal FiazNo ratings yet
- Study of RefrigiratorDocument14 pagesStudy of RefrigiratorRobo RajaNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsDocument25 pagesGroup 2 Basic Refrigerationsystem and ComponentsVipin VetriNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Air ConditioningDocument2 pagesThe Fundamentals of Air Conditioningkrish_cvr2937No ratings yet
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2 Air ConditioningDocument8 pagesECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2 Air ConditioningAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (3)
- Aircon System and Fire Protection SystemDocument31 pagesAircon System and Fire Protection SystemReijen Canary S TierraNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Biography of William Ernest HenleyDocument2 pagesBiography of William Ernest HenleyLaurice Ortiz LuisNo ratings yet
- Biography of William Ernest HenleyDocument2 pagesBiography of William Ernest HenleyLaurice Ortiz LuisNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning BasicsDocument2 pagesAir Conditioning BasicsLaurice Ortiz LuisNo ratings yet
- The Fourmula One For HealthDocument4 pagesThe Fourmula One For HealthLaurice Ortiz LuisNo ratings yet