Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Engineering Formula Sheet: Formulas Variables Formulas Variables
Uploaded by
aaaachewOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Formula Sheet: Formulas Variables Formulas Variables
Uploaded by
aaaachewCopyright:
Available Formats
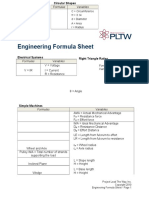
Engineering Formula Sheet
Circular Shapes Formulas Variables
C = d
A = r2
C = Circumference = 3.14 d = Diameter A = Area r = Radius
Electrical Systems Formulas V = IR
Variables V = Voltage I = Current R = Resistance
Right Triangle Ratios Formulas
opposite Sin = hypotenuse adjacent Cos = hypotenuse opposite Tan = adjacent
Variables
= Angle
Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2010 Engineering Formula Sheet - Page 1
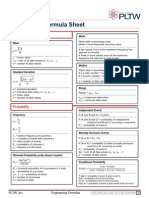
Simple Machines Formulas
AMA =
FR FE
IMA =
DE DR
LE LR
rW rA
Variables AMA = Actual Mechanical Advantage FR = Resistance force FE = Effort force IMA = Ideal Mechanical Advantage DR = Resistance Distance DE = Effort Distance LE = Length from fulcrum to effort LR = Length from fulcrum to resistance rw = Wheel radius ra = Axle radius
LeverIMA =
Wheel and Axle IMA =
Pulley IMA = Total number of strands supporting the load L Inclined Plane or Wedge MA = H L Wedge IMA = T C ScrewIMA = Pitch 1 Pitch = TPI Properties of Materials Formulas F = AO = LO
FL O A OE E= (F F ) L E = 2 1 O ( 2 1 ) AO =
L = Slope length H = Height L = Slope length T = Thickness C = Circumference Pitch = Screw pitch TPI = Threads per inch Variables = Stress F = Axial force Ao = Cross-sectional area = Strain = Deformation Lo = Original length E = Modulus of Elasticity
Fluids Formulas F P= A V1 V2 = T1 T2 P1 ( V1) = P2 ( V2 )
Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2010 Engineering Formula Sheet - Page 2
Variables P = Pressure F = Force A = Area V = Volume
Gear Ratios Formulas
GR = GR = in out Nout Nin
Nout dout = = in = out Nin din out in
Variables GR = Gear ratio in = Driver gear, rpm out = Driven gear, rpm Nin = Number of teeth on driver Nout = Number of teeth on driven din = Diameter of driver dout = Diameter of driven in = Torque of driver, ft-lbs out = Torque of driven, ft-lbs Variables X = Range Vi = Initial velocity g = Acceleration due to gravity = Initial trajectory angle from the horizontal Vix = Initial horizontal velocity Viy = Initial vertical velocity
Kinematics Formulas V 2 *Sin( 2 ) X= i -g Vi = gx Sin( 2 )
Vix = Vi cos
Viy = Vi sin
Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2010 Engineering Formula Sheet - Page 3
Statics Formulas
M=F d
FX = 0 = X right)+ X left) ( ( FY = 0 = Y ( up ) + Y ( down )
Variables M = Moment about a point F = Force d = Perpendicular distance = Sum of X = Force in x-direction Y = Force in y-direction CCW = Counter-clockwise moment CW = Clockwise moment J = Number of joints M = Number of members R = Number of reaction forces IXX = Moment of inertia about x-x axis b = Base dimension h = Height
M = 0 = CCW + CW
2J = M + R
Rectangular Sections bh3 I XX = 12 Work and Power Formulas
W = F D
Variables W = Work F = Force D = Distance P = Power W = Work t = Time V = Volts I = Current P = Rate of heat transfer Q = Energy transfer t = Difference in time k = Thermal conductivity A = Area of thermal conductivity L = Thickness T = Difference in temperature U = Thermal transmittance (U-factor) R = Resistance to heat flow (R-value)
P=
W t
P = V I
P=
Q t
T L Q = UAT 1 U= R P = kA
Project Lead The Way, Inc. Copyright 2010 Engineering Formula Sheet - Page 4
You might also like
- Engineering Formula SheetDocument3 pagesEngineering Formula SheetAlex WhiteheadNo ratings yet
- Engineering Formula Sheet: Formulas VariablesDocument4 pagesEngineering Formula Sheet: Formulas VariablesTomNo ratings yet
- Engineering Formula SheetDocument10 pagesEngineering Formula SheetAdarsh Kumar AngNo ratings yet
- IED-Review Engineering Formula SheetDocument10 pagesIED-Review Engineering Formula Sheetedhy_03100% (1)
- POE Formula Sheet Rev 3 - 24 - 12 PDFDocument6 pagesPOE Formula Sheet Rev 3 - 24 - 12 PDFstuart ashrafNo ratings yet
- POE Formula Sheet Rev 3-24-12Document6 pagesPOE Formula Sheet Rev 3-24-12poignantNo ratings yet
- Category: Physics FormulasDocument24 pagesCategory: Physics FormulasKalpana ShankarNo ratings yet
- Formulas To RememberDocument6 pagesFormulas To Rememberuygurzeren100% (3)
- Formulas To RememberDocument6 pagesFormulas To Remembermr.xinbombayNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument4 pagesPhysicsbells tharayilNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) Ronewing949No ratings yet
- Physics Class 9 FormulasDocument13 pagesPhysics Class 9 FormulasJatin Gupta73% (63)
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) RAitazaz AhsanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Formula Sheet 2014Document10 pagesEngineering Formula Sheet 2014api-96433983No ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetMax MartinNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas & SI UnitDocument14 pagesPhysics Formulas & SI Unitönemsiz biriNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design: Horizontal Alignment: CE331 Transportation EngineeringDocument44 pagesGeometric Design: Horizontal Alignment: CE331 Transportation EngineeringHaile G/MariamNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Anchor Length CalculationsDocument3 pagesPipeline Anchor Length CalculationsAmr BadranNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Anchor Length Calculation PDFDocument3 pagesPipeline Anchor Length Calculation PDFAlvin SmithNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Anchor Length CalculationsDocument3 pagesPipeline Anchor Length Calculationslsatchithananthan100% (3)
- Physics Class 9 FormulasDocument13 pagesPhysics Class 9 FormulasEKLABAY SONINo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and Concepts V3 PDFDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and Concepts V3 PDFHector Ledesma IIINo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocument2 pagesO Level Physics Formula SheetYee Kai TanNo ratings yet
- MechatronikDocument1 pageMechatronikRonny LantzschNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulae: R R R RDocument4 pagesPhysics Formulae: R R R Rkjaf364No ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics FormulasDocument1 pageIGCSE Physics FormulasPawan Kolhe80% (30)
- Physics FormulasDocument7 pagesPhysics FormulasaarzujoshipuraNo ratings yet
- Physics Ultimate Every Single Formula-MoatazDocument1 pagePhysics Ultimate Every Single Formula-Moataz22shimmer22No ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet-By Er Rammohan MudgalDocument8 pagesPhysics Formula Sheet-By Er Rammohan MudgalRammohan Mudgal0% (1)
- Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFormula SheetjustpankitNo ratings yet
- Mech 2Document71 pagesMech 2Gino Mandado0% (1)
- Formula Sheet - Applied Mechanics & DesignDocument11 pagesFormula Sheet - Applied Mechanics & DesignAnkur Jay38% (8)
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsAllan Paul Lorenzo Abando76% (17)
- Force and Motion 2Document13 pagesForce and Motion 2sojib yeasinNo ratings yet
- Curve SimpleDocument10 pagesCurve SimpleBrian Rey L. AbingNo ratings yet
- Force Weight On Earth Density: Work Done PowerDocument1 pageForce Weight On Earth Density: Work Done Powerjordi1710No ratings yet
- Aisc 13.0 Properties RodrigoDocument25 pagesAisc 13.0 Properties RodrigoJosé Carlos TorrezNo ratings yet
- L7-L9 DC ChopperDocument103 pagesL7-L9 DC Choppersrnankit100% (1)
- Simple Curves or Circular Curves 04 11 2015Document124 pagesSimple Curves or Circular Curves 04 11 2015HanafiahHamzahNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksFrom EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianFrom EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Powerful Pulleys - Lesson - TeachEngineeringDocument8 pagesPowerful Pulleys - Lesson - TeachEngineeringOsama AsgharNo ratings yet
- The Plane Which Is UninclinedDocument24 pagesThe Plane Which Is UninclinedAnonymous oQEx3zNo ratings yet
- Pressure LectureDocument75 pagesPressure LecturezhainogNo ratings yet
- Lifting & Rigging ModuleDocument40 pagesLifting & Rigging ModuleEndy DestriawanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Week 5: by Engr. A.R.SalangsangDocument12 pagesModule 1 Week 5: by Engr. A.R.SalangsangAshanty CruzNo ratings yet
- Design Analysis of A Portable Manual Tyre Changer: European Journal of Engineering Research and Science November 2020Document13 pagesDesign Analysis of A Portable Manual Tyre Changer: European Journal of Engineering Research and Science November 2020Sakman SulaemanNo ratings yet
- MECHANICS SyllabusDocument2 pagesMECHANICS SyllabusRaNo ratings yet
- Solved PapersDocument284 pagesSolved PapersAlfiya PathanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Jack or Hydraulic PressDocument8 pagesHydraulic Jack or Hydraulic PressAnand HaseNo ratings yet
- Water SafetyDocument12 pagesWater SafetyBea Lou SabadoNo ratings yet
- Automotive Science and Mathematics: Allan BonnickDocument27 pagesAutomotive Science and Mathematics: Allan BonnickTsegay TeklayNo ratings yet
- Chap 10Document24 pagesChap 10uaragieNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Roda Gigi (Kelompok 2)Document30 pagesAplikasi Roda Gigi (Kelompok 2)Fandrio PermataNo ratings yet
- Class 2 Lever Effort Force CalculationDocument10 pagesClass 2 Lever Effort Force CalculationvenkateswaranNo ratings yet
- Aeronautical ScienceDocument31 pagesAeronautical Sciencejorgerosas454No ratings yet
- Pulley-Test - FINAL 01-19-10Document11 pagesPulley-Test - FINAL 01-19-10Henok AmdiyeNo ratings yet
- SLG 13.3.2 Simple Machines, Mechanical Advantage and EfficiencyDocument6 pagesSLG 13.3.2 Simple Machines, Mechanical Advantage and EfficiencyKifrannwNo ratings yet
- Wheel and Axle and Winch Crab PDFDocument15 pagesWheel and Axle and Winch Crab PDFAnonymous B0cm7LZhNo ratings yet
- Pulley Problems M1Document6 pagesPulley Problems M1Pratik BhosaleNo ratings yet
- ASTB Study Guide and Drill SheetDocument9 pagesASTB Study Guide and Drill SheetAmy Laurin100% (1)
- QB For Mid1 OldDocument7 pagesQB For Mid1 Oldhod mechNo ratings yet
- Em Lab Manual 1Document42 pagesEm Lab Manual 1atikmkaziNo ratings yet
- EGB111 Week 8 Studio SlidesDocument23 pagesEGB111 Week 8 Studio SlidesWinston BoonNo ratings yet
- To Calculate The Efficiency ofDocument10 pagesTo Calculate The Efficiency ofMayank BarserNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts - TOMDocument63 pagesBasic Concepts - TOMIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Winching Operations in Forestry (fctg001) PDFDocument30 pagesWinching Operations in Forestry (fctg001) PDFMichael BatleyNo ratings yet
- Levers:: Pivoted About The FulcrumDocument14 pagesLevers:: Pivoted About The Fulcrumprashant mishraNo ratings yet
- 0 JVQwu YOlv TM6 Iz Ds 2 Q GDocument60 pages0 JVQwu YOlv TM6 Iz Ds 2 Q GdhanukrishnagNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument4 pagesLab ReportHammad HassanNo ratings yet









































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)