Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project Planning and Execution
Uploaded by
WILL PETERS100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
2K views5 pagesIntroduction to Project Management. For more info www.anstad.com
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIntroduction to Project Management. For more info www.anstad.com
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
2K views5 pagesProject Planning and Execution
Uploaded by
WILL PETERSIntroduction to Project Management. For more info www.anstad.com
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Project Planning and Execution
The process of defining, planning, doing and evaluating the work is the hallmark of
a well-run project.
– I understand the benefits of Project Management
– I can describe and define the requirements and scope of a project
– I can develop a project plan
– I can Identify and manage risk on a project
– I manage project resources as changes occur on projects
– I describe best practices to follow at the end of a project
Definition of a Project
– I recognize a project, as distinguished from a business process.
○ Differs from standard business or people management
Project Characteristics Process Characteristics
One Time Event A repeated event
Moderate to long duration Usually shorter duration
Temporary cross-functional work teams Permanent work teams, usually in the
same dept.
Team members change for different Team members remain constant
projects
– Some challenges of project management as opposed to business processes
○ Problems difficult to anticipate, as specific projects are unique
○ Keeping team members motivated, as projects take longer than
established business processes to complete
○ It may be difficult for project managers to coordinate between project
teams and exercise authority over project team members due to the
temporary and cross-functional composition of project teams.
Common Problems in Projects (Effective project management can help to avoid
these problems)
– I describe common problems that occur in projects.
○ Customers’ expectations on quality and functionality are not met
○ Deadlines are not met
○ Project team members feel overworked
○ Communication on the project status is insufficient
Goal of Project Management
– State the goal of effective project management.
○ Scope of project is clearly defined
○ Customer and team member expectations regarding scope, quality and
schedule are understood and accepted.
○ Everyone affected by the project has the desired level of involvement
and information about the project
○ Project-related issues are handled with minimal harm to the project
○ The final project deliverable is of acceptable quality and is delivered as
per schedule
○ Results are evaluated. The relevant information from the evaluation
exercise is documented and analyzed for the benefit of future projects.
Project Stakeholders (It is important to collaborate with project stakeholders as soon
as inititiated)
– Describe common project stakeholders
○ Stakeholders are people who have an interest in the results and
activities of a project.
Project Stakeholder Role
Project Sponsor – Proposes the idea for the project.
– “Sells” the idea to senior
management.
– Supports the project.
Project Leader – Drives results of the project.
– Coordinates activities of the
project team.
– Communicates status and issues.
Functional/Resource Managers – Provides resources to complete
project.
– Responsible for implementing and
sustaining final outcome of the
project.
Team Members – Provides input to the project
– Complete the work on the project
Customers – Define the requirements for the
project.
– Provide feedback on project
deliverables.
– Accept the final deliverable.
Generic Project Execution Process
– Describe a typical process for managing projects.
1. Project Definition: Foundation for the project is established
a. Key players (stakeholders) are identified
b. Vision of project is decided
c. Requirements for the final deliverable are established
d. Scope of the project is defined
e. Issues the project will address and not address are defined
f. All stakeholders accept
2. Planning Stage: Provides the specifics about how the project will be
executed
a. Project plan created
b. Accepted by stakeholders
c. Scheduled and lays out when important tasks will be completed
d. Critical to establishing a framework that is acceptable to all
stakeholders
3. Development and Implementation Stage: Actual work is done
a. Controlling and Handling changes in the project
b. Managing issues that pose a risk to the project outcome
c. Communicating project status
d. Ensuring desirable progress is made toward the final deliverable
4. Review Stage: Results are evaluated and customer satisfaction is
measured.
a. Provides valuable input to future projects
Assessing requirements and defining scope
– The team needs to understand the specifics about the customer and the
situation before designing a solution.
Understanding the Customer
– The process for determining the characteristics of the customer’s
environment
○ The customer is the stakeholder who accepts the final deliverable of
the project.
○ Define customer requirements
○ Analyze the characteristics of the customer environment
○ What is the problem or issue being addressed? Why is it a problem?
○ What is the current situation? How do things work now?
○ What is the ideal situation? How would things work in the perfect
world?
○ How many people will be using the solution implemented by the
project?
○ Are there any other characteristics of end-users that are important?
Gathering the requirements (the specifications for a project)
– The process for gathering customer requirements for a project
○ Features and functions of the final deliverable
○ Timeframe
○ For efficiency, a brainstorming meeting or focus group would be an
appropriate method for gathering requirements.
Project Essential Helpful Optional
Requirements
Defining Scope
– How to define the scope of a project
○ States the issues to be addressed by the project
○ Described what is included and excluded
Customer and environment characteristics in the description to
help clarify why features have been included (or excluded) from
the scope.
Requirements and relevant input from all groups that
participated in the gathering of requirements.
Reality check of the final scope to ensure that it is manageable
Developing a Plan
– The project plan can be developed once the scope of the project is defined
and accepted by the stakeholders.
– Outlines what is to be done and how it will be done
Components of a Plan
– The typical components of a project plan
○ Describes all relevant aspects of a project
○ Must be clear and complete
○ The plan will serve as a guide
Description of the problem or customer situation
The names and roles of the project stakeholders
List of project team members and their roles
The requirements for the project
The tasks and milestones to be accomplished
Project schedule
Defining Tasks
– The rationale for defining tasks within a project
– In order to plan the work for an entire project, the work needs to be
separated into manageable components called tasks.
○ Knowledge of work processes and skills required to complete them is
essential to developing a task list.
○ Each task should be such that one or two people can complete in a
short period of time
○ Being aware of the skills and abilities of the project team members
helps define tasks of a manageable size.
○ Guidance and feedback to the team on tasks is an integral part of
project execution
Developing a Schedule
– Technique for developing a project schedule
1. Organize project tasks and milestones in chronological order
2. Assign people to tasks
3. Specify the time required to complete each task and subtask
4. Review the schedule and make adjustments as necessary
5. Lay out tasks in a calendar format
Task Assigned Resources Time Required
Problem Suggestions
You might also like
- PM CommunicationManagement14 PDFDocument32 pagesPM CommunicationManagement14 PDFsamii7362No ratings yet
- Project OrganizationDocument24 pagesProject Organizationshawar69No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Project ExecutionDocument16 pagesChapter 4 Project ExecutionczuberekNo ratings yet
- Effective Project Communication and Successful Consortia EngagementsDocument10 pagesEffective Project Communication and Successful Consortia EngagementsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Communication Plan TemplateDocument18 pagesCommunication Plan TemplateWael Khalil Pmp100% (1)
- C M P (P N) : Ommunication Anagement LAN Roject AMEDocument8 pagesC M P (P N) : Ommunication Anagement LAN Roject AMEArun BungseeNo ratings yet
- Project Management MethodologyDocument7 pagesProject Management MethodologykumarNo ratings yet
- Interface Management PDFDocument2 pagesInterface Management PDFEdwin HarrisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11-ProjectControlDocument42 pagesChapter 11-ProjectControlJeng AndradeNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoring PlanDocument2 pagesProject Monitoring PlanharithaNo ratings yet
- EPMO Project Management ProcedureDocument11 pagesEPMO Project Management ProcedureefyandzjyNo ratings yet
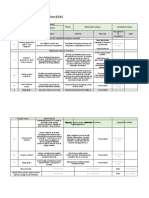
- Playbook Mobilisation Phase ChecklistDocument2 pagesPlaybook Mobilisation Phase Checkliststimayo010809No ratings yet
- Management of Project Communication Pub3711Document13 pagesManagement of Project Communication Pub3711Tsholofelo Majipos StlhanohNo ratings yet
- Template Project Manager ProposalDocument8 pagesTemplate Project Manager ProposalOSCAR ARRIAGANo ratings yet
- Contract ManagementDocument3 pagesContract ManagementAB AgostoNo ratings yet
- Bid DocumentDocument113 pagesBid DocumentDinesh TimalsinaNo ratings yet
- Project Planning Procedure Review 121814Document11 pagesProject Planning Procedure Review 121814Muse Taqim100% (1)
- Sample Project Charter PDFDocument9 pagesSample Project Charter PDFAli HajirassoulihaNo ratings yet
- 10 - PM - Communication ManagementDocument16 pages10 - PM - Communication ManagementEmran HossainNo ratings yet
- PGPM 31Document11 pagesPGPM 31vasan_establishmentsNo ratings yet
- QM 105 Construction Execution PlanDocument1 pageQM 105 Construction Execution PlanAlejandro PáramoNo ratings yet
- Managing Project Resources 1227191402446602 9Document38 pagesManaging Project Resources 1227191402446602 9Rishab AttriNo ratings yet
- C M P (P N) : OST Anagement LAN Roject AMEDocument7 pagesC M P (P N) : OST Anagement LAN Roject AMERoqaia AlwanNo ratings yet
- 1.1.3 Project Execution PlanDocument7 pages1.1.3 Project Execution PlanlisahunNo ratings yet
- Work Performance Report in Project ManagementDocument3 pagesWork Performance Report in Project Managementmm.No ratings yet
- General Principles of Project ManagementDocument6 pagesGeneral Principles of Project ManagementCopet FxNo ratings yet
- Sample PIDDocument32 pagesSample PIDtnnorukah100% (1)
- " Project Charter ": Reading AssignmentDocument26 pages" Project Charter ": Reading AssignmentJankey NdagileNo ratings yet
- PROJECT STANDARD and SPECIFICATIONS Project Coordination Procedure Rev01 WebDocument6 pagesPROJECT STANDARD and SPECIFICATIONS Project Coordination Procedure Rev01 WebPham Manh Hieu67% (3)
- 1 Project Scheduling PDFDocument14 pages1 Project Scheduling PDFJeric CaberNo ratings yet
- Project Execution and ControlDocument0 pagesProject Execution and ControlMahnooranjumNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Project Organization: "Organize - To Form Into An Association For A Common Purpose or Arrange Systematically"Document30 pagesCh4 Project Organization: "Organize - To Form Into An Association For A Common Purpose or Arrange Systematically"Sri RamNo ratings yet
- Project Closing - Post Implementation SurveyDocument7 pagesProject Closing - Post Implementation SurveyMegat Zainurul Anuar bin Megat Johari100% (1)
- What Is Project Execution?Document5 pagesWhat Is Project Execution?Russell EndoyNo ratings yet
- Project Management Proj - LifecycleDocument5 pagesProject Management Proj - LifecycleSohini DasNo ratings yet
- Project InitiationDocument18 pagesProject Initiationapi-19916368No ratings yet
- Project Standards and Specifications Schedule Control Procedure Rev01 WebDocument3 pagesProject Standards and Specifications Schedule Control Procedure Rev01 WebhiyeonNo ratings yet
- Ssg-Ng01012401-Gen-Aa-5760-00001 - R04 - Project Execution PlanDocument114 pagesSsg-Ng01012401-Gen-Aa-5760-00001 - R04 - Project Execution PlanStroom Limited100% (7)
- Project CharterDocument2 pagesProject Charteralina_avri5545No ratings yet
- Chapter One: Background To The Project Management Tools and TechniquesDocument34 pagesChapter One: Background To The Project Management Tools and TechniquesNalyanyaNo ratings yet
- Procurement Methods CHPBDocument6 pagesProcurement Methods CHPBNilan GamageNo ratings yet
- Project Communications ManagementDocument8 pagesProject Communications ManagementilleziaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Project ManagementDocument24 pagesBasic Concepts of Project ManagementFred Wekesa Wafula100% (6)
- Project Management KPIDocument4 pagesProject Management KPIBrittoNo ratings yet
- Project Cycle Model IPPMC and DEPSADocument12 pagesProject Cycle Model IPPMC and DEPSAyetmNo ratings yet
- Schedule Change ManagementDocument10 pagesSchedule Change ManagementFreydell A BarretoNo ratings yet
- S-990-5131-311 - 0 Project Control ProcedureDocument15 pagesS-990-5131-311 - 0 Project Control ProcedureMahadevan Mahalingam100% (1)
- Statement of Project ObjectivesDocument24 pagesStatement of Project ObjectivestalashNo ratings yet
- Cost Management PlanDocument7 pagesCost Management PlanmaxvolumeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Project Procurement ManagementDocument40 pagesChapter 12 Project Procurement ManagementMohamed El ArabiNo ratings yet
- Project Integration ManagementDocument37 pagesProject Integration Managementsagarthegame100% (1)
- VII 2 GEN - Project Execution Plan Guideline - 01Document21 pagesVII 2 GEN - Project Execution Plan Guideline - 01lampardbkNo ratings yet
- WBS StructureDocument17 pagesWBS StructureWickedadonis0% (1)
- Project Execution PlanDocument62 pagesProject Execution PlanAhmed KassemNo ratings yet
- Project Close Out ReportDocument3 pagesProject Close Out ReportChristopher De WetNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument49 pagesProject Management0890No ratings yet
- How To Identify and Manage Project StakeholdersDocument9 pagesHow To Identify and Manage Project StakeholdersTaschyana HurterNo ratings yet
- General Instructions On Procurement and Project ManagementDocument22 pagesGeneral Instructions On Procurement and Project ManagementShardul RawleNo ratings yet
- The Medical Device Development Process at DeviceLabDocument27 pagesThe Medical Device Development Process at DeviceLabDeviceLabNo ratings yet
- Resume Peng WangDocument2 pagesResume Peng Wangpoonam09892No ratings yet
- Project Management NotesDocument19 pagesProject Management NotesSatyendr Suhas KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Unger-Gemuenden Aubry PMO PDFDocument14 pagesUnger-Gemuenden Aubry PMO PDFYamil Sejas SuarezNo ratings yet
- 5 Control ProcurementsDocument22 pages5 Control ProcurementsHenryNo ratings yet
- 2 Benefit and Advantage of AgileDocument19 pages2 Benefit and Advantage of AgileRelaxation TvNo ratings yet
- Microsoft CRM Project PlanDocument4 pagesMicrosoft CRM Project PlanSusan ShackNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information Systems: 9 EditionDocument44 pagesAccounting Information Systems: 9 EditionlazylawstudentNo ratings yet
- A Handbook of Business Transformation Management MethodologyDocument5 pagesA Handbook of Business Transformation Management MethodologyalfiettaNo ratings yet
- 3 Day Course On Project ManagementDocument196 pages3 Day Course On Project ManagementPeyman MznNo ratings yet
- It Project Manager ResumeDocument6 pagesIt Project Manager Resumeafdmgoqxi100% (1)
- What Is The Secure Software Development Life Cycle - SynopsysDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Secure Software Development Life Cycle - Synopsysgong688665No ratings yet
- Prosci ADKAR Model 2017 Training BuffetDocument80 pagesProsci ADKAR Model 2017 Training BuffetJames Tham100% (4)
- Continuous Delivery Github Alain HelailiDocument46 pagesContinuous Delivery Github Alain Helailisplit_2002No ratings yet
- 4.1 OUM Cloud Approach Presentation-ManagerDocument24 pages4.1 OUM Cloud Approach Presentation-ManagerFeras AlswairkyNo ratings yet
- Project Management - CPM-PERTDocument49 pagesProject Management - CPM-PERTAbu BasharNo ratings yet
- Sap Senior Application Consultant Hitachi Zosen Inova AgDocument17 pagesSap Senior Application Consultant Hitachi Zosen Inova AgRamiro SanchezNo ratings yet
- Intercom On Onboarding PDFDocument117 pagesIntercom On Onboarding PDFAbhishek SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Computronics Systems (India) Private LimitedDocument17 pagesComputronics Systems (India) Private Limitedbvkaushik21No ratings yet
- Terms of Reference (Tor)Document12 pagesTerms of Reference (Tor)bagumaNo ratings yet
- APM Project Management Qualification Sample Answer Document 2021 v1Document24 pagesAPM Project Management Qualification Sample Answer Document 2021 v1CarmineBruno100% (1)
- Book6 ProjectQualityManagement TOCDocument20 pagesBook6 ProjectQualityManagement TOCAnmol GargNo ratings yet
- AOA DiagramDocument3 pagesAOA DiagramMarium RazaNo ratings yet
- Ask PMI Anything: How Do I Get Started in A Project Management Career Path?Document2 pagesAsk PMI Anything: How Do I Get Started in A Project Management Career Path?paulaNo ratings yet
- Project Control Using EVMDocument40 pagesProject Control Using EVMAbdul NaseerNo ratings yet
- SBI General Insurance Recruiting For Various VacanciesDocument30 pagesSBI General Insurance Recruiting For Various VacanciesCareerNotifications.comNo ratings yet
- Book Sustainability InterventionsDocument92 pagesBook Sustainability Interventionsayeshaarif3100% (1)
- IS301 P1 Theory June 2021 P1 TheoryDocument20 pagesIS301 P1 Theory June 2021 P1 Theory50902849No ratings yet
- Workbookand Study GuideDocument50 pagesWorkbookand Study GuideAnton_Young_1962No ratings yet
- Managing Time (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandManaging Time (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (47)
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeFrom EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (36)
- 300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionFrom Everand300+ PMP Practice Questions Aligned with PMBOK 7, Agile Methods, and Key Process Groups - 2024: First EditionNo ratings yet
- Building a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialFrom EverandBuilding a Second Brain: A Proven Method to Organize Your Digital Life and Unlock Your Creative PotentialRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (238)
- The PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeFrom EverandThe PARA Method: Simplify, Organize, and Master Your Digital LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsFrom EverandHarvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Agile: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandAgile: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- The Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeFrom EverandThe Manager's Path: A Guide for Tech Leaders Navigating Growth and ChangeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (99)
- High Velocity Innovation: How to Get Your Best Ideas to Market FasterFrom EverandHigh Velocity Innovation: How to Get Your Best Ideas to Market FasterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Quiet Leadership: Six Steps to Transforming Performance at WorkFrom EverandQuiet Leadership: Six Steps to Transforming Performance at WorkRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- Change Management for Beginners: Understanding Change Processes and Actively Shaping ThemFrom EverandChange Management for Beginners: Understanding Change Processes and Actively Shaping ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Myth of Multitasking: How "Doing It All" Gets Nothing DoneFrom EverandThe Myth of Multitasking: How "Doing It All" Gets Nothing DoneRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PMP Exam Prep: Master the Latest Techniques and Trends with this In-depth Project Management Professional Guide: Study Guide | Real-life PMP Questions and Detailed Explanation | 200+ Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP Exam Prep: Master the Latest Techniques and Trends with this In-depth Project Management Professional Guide: Study Guide | Real-life PMP Questions and Detailed Explanation | 200+ Questions and AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Strategist: Be the Leader Your Business NeedsFrom EverandThe Strategist: Be the Leader Your Business NeedsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- PMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamFrom EverandPMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Project Management All-in-One For DummiesFrom EverandProject Management All-in-One For DummiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Project Management: The Ultimate Guide for Managing Projects, Productivity, Profits of Enterprises, Startups and Planning with Lean, Scrum, Agile.From EverandProject Management: The Ultimate Guide for Managing Projects, Productivity, Profits of Enterprises, Startups and Planning with Lean, Scrum, Agile.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Business Analysis for Practitioners: A Practice Guide - SECOND Edition: A Practice GuideFrom EverandBusiness Analysis for Practitioners: A Practice Guide - SECOND Edition: A Practice GuideNo ratings yet
- The Third Wave: An Entrepreneur's Vision of the FutureFrom EverandThe Third Wave: An Entrepreneur's Vision of the FutureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (63)
- Agile Product Management: Product Owner: 27 Tips to Manage Your Product and Work with Scrum TeamsFrom EverandAgile Product Management: Product Owner: 27 Tips to Manage Your Product and Work with Scrum TeamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Crossing the Chasm, 3rd Edition: Marketing and Selling Disruptive Products to Mainstream CustomersFrom EverandCrossing the Chasm, 3rd Edition: Marketing and Selling Disruptive Products to Mainstream CustomersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Creating High Value PMOs: Your Essential GuideFrom EverandCreating High Value PMOs: Your Essential GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Secrets of Home Staging: The Essential Guide to Getting Higher Offers Faster (Home décor ideas, design tips, and advice on staging your home)From EverandSecrets of Home Staging: The Essential Guide to Getting Higher Offers Faster (Home décor ideas, design tips, and advice on staging your home)No ratings yet
- PMP Exam Code Cracked: Success Strategies and Quick Questions to Crush the TestFrom EverandPMP Exam Code Cracked: Success Strategies and Quick Questions to Crush the TestNo ratings yet