Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mental Retardation
Uploaded by
nmyza89Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mental Retardation
Uploaded by
nmyza89Copyright:
Available Formats
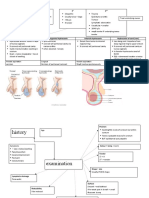
Mental Retardation Significantly subaverage general intellectual functioning resulting in or associated with, concurrent impairment in adaptive behavior &
; manifested during developmental period, b4 18 y/o Significantly subaverage = defined as : IQ approximately 70 OR IQ below 70 OR 2 standard deviation below mean for particular test Genereal intellectual functioning = determined by standardized tests in intelligence DSM A Significantly subaverage intellectual functioning : an IQ of approximately 70 individually administered IQ test (for infants, a clinical judgement of significantly subaverage intellectual functioning) B Concurrent deficit or impairment in present adaptive functioning in 2 of following : Communication Home living Social/interpersonal skills Use of community resources Self direction Functional academic skills Work Leisure Health Safety C Onset b4 18 y/o Code based on degree of severity reflecting level of intellectual impairment Mild MR IQ level 50-55 to approximately 70 Moderate MR IQ level 35-40 to 50-55 Sevre MR IQ level 20-25 to 35-40 Profound MR IQ level below 20 or 25 MR, severity Strong presumption of MR but person unspecified intelligence untested by standard test
nha 0813 : source Kaplan synopsis of psychiatric
Degree o MR profound
Sevre
Mental retardation
Preschool age (0-5 y/o) Maturation & dvlpmnt Gross retardation Minimal capacity for functioning in sensorimotor areas Needs nursing care Constant aid & supervision required Poor motor dvlpmnt Speech minimal Generally unable to profit from training in self help Lilltle or no communication skills
School age (6-20 y/o) Training & education Some motor dvlpmt present May respond to minimal or limited training in self help Can talk or learn to communicate Can be trained in elemental health habits Profits from systematic habit training Unable to profit from vocational training Can profit from training in social & occupational skills Unlikely to progress beyond 2nd grade level in academic subjects May learn to travel alone in familiar places Can learn academic skills up to 6th grade lvl by late teen Can b guided toward social confirmity
Adult ( 20 y/o) Social & vocational adequacy Some motor & speech dvlpmnt May achieve very limited slf-care Needs nursing care May contribute partially to self maintenance under complete supervision Can dvlp selfprotection skills to minimal useful level in controlled environment May achieve selfmaintenance in unskilled or semiskilled work Under sheltered cond Needs supervision & guidance when under mild spocial or economic stress Can usually achieve social & vocational skills adequate to minimal self-support But may nid guidance & assistance when under unusual social or economic stress
moderate
Can talk or learn to communicate Pooor social awarens Fair motor dvlpmnt Profits from training in self-help Can be managed with moderate supervision Can dvlp social & communication skills Minimal retardation in sensorimotor areas Often x distinguished from norm until later age
Mild
Acquired & develpmntal Factors
Etiology
Genetic etiological factor
Genetic MR Syndromes & Behaviour Phenotypes Behaviour phenotypes : a syndrome of observable behavior that occur wif a greater probability than expected among those individuals wif specific genetic abnorm Down Phenyketonuria Lesch-Nyhan syn Syndrome Fragile X Retts d/o Adrenoleukodystrophy synd Prader-Willi Neurofibromatosis Maple syrup urine dz syn Cri-Du-Chat Tuberous sclerosis Enzyme def d/o : syn -galactosemia -glycogen storage dz
Environmental & sociocultural factors Significant deprivation of nutrition & nurturance Poor medical care & poor maternal nutrition Teenage pregnancy Poor postnatal care, malnutrition Family instability Multiple, inadequate caretakers
nha 0813 : source Kaplan synopsis of psychiatric
Prenatal period Uncontrolled DM Anemia Emphysema HPT Long term use of alcohol Narcotic substance Maternal infxn during pregnancy Rubella Cytomegalic Inclusion dz Syphilis Toxoplasmosis Herpes simplex AIDS Prenatal drug exposure Opiods withdrawal sx : Irritability, hypertonis, tremor, vomiting, abnorm sleep pattern CX of pregnancy Toxemia of pregnancy Uncontrolled DM Maternal malnutrition Vaginal h/rage PP Premature separation of placenta Cord prolapse Perinatal period Premature infants Low birthweight infants Infants that experiences : Intracranial h/rage Cerebral ischaemia Socioeconomic deprivation Acquired childhood d/o infxn Encephalitis Meningitis Head trauma d/t : seizures MVA Child abuse Others Cardiac arrest during anaesthesia Asphyxia a/w near drowning Long term exposure to lead intracranial tumour Maternal chronic illnes
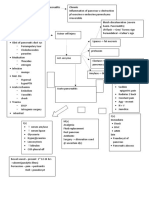
History
PE
Diagnosis From parents or caretaker Include : Mothers pregnancy, labour, delivery Family hx of mental illns Consanguinity of parents Hereditary d/o Assess overall level of fx & intellectuality o parents Size of head Microcephaly Hydrocephalus Down syn face Hypertelorism Flat nasal bridge Prominent etebrow Corneal opacities Retinal Protruding tongue Facial expression Dermatoglyphics Diagnostic tool Abnorm in : chromosome d/o person who is prenatally infected w rubella
Neuro exam (sensory impairment)
Hearing diff Visual disturbance
Disturbance o motor areas
Imaging
Blindns Disturbance of spatial concepts Design cognition Concpts of body image Abnor in muscle tone (spasticity or hypotonia) Reflexes (hyperreflexia) Involuntary mvmnt (choreoathetosis) Loss of coordination Skull X-ray,Ct scan, MRI, EEG
Course & prognosis Mostly intellectual impairment does not improve BUT level of adaptation DEPENDS on supportive environment Mild & moderate MR = hv most flexibility in adapting to various environmental cond IF hv MENTAL d/o + MR = standard tx for mental d/o r REQUIRED
nha 0813 : source Kaplan synopsis of psychiatric
Chromosome studies
Urine & blood analysis
Electroencephalopathy Neuroimaging Hearing & speech evaluation Psychological assessment
Lab exam Karyotype in genetic lab indicated when : Suspected chromosomal d/o Cause of MR is unknown Amniocentesis Chronic villi sampling Using enzyme or organix or AA : Lesch-Nyhan syn Galactosemia PKU Hurlers syn Test metabolic fx in : Unexplained growth abnorm Seizure d/o Ataxia Bone or skin abnorm Eye abnorm When seizue d/o is suspected As above Should b done routinely Infants : Gesell & Bayley scale Cantell Infant Intelligence scale Children Standard Binet Intelligence scale 3rd edition o Wenchsler Intelligence scale for chidren
DDX Cerebral palsy Convulsice d/o Chronic brain syn Isolated handicaps : Fail to read (alexia) Fail to write (agraphia) Fail to communicate (aphasia) Delay or failure in dvlpmnt in specific are : reading or math but norm dvlpmnt in other areas BUT MR general delay in most areas May co-exist Hv IQ <70 Hv distortion of timing, rate & sequence of many basic psychological fx necessary for social dvlpmnt Hence > problem in socializing Children < 18y/o who met criteria for dementia & hv IQ < 70 = dementia AND MR Px that hv IQ <70 aftr age 18 y/o & new onset of cognitive d/o = DEMENTIA
Children w learning d/o Pervasive dvlpmntal d/o
Hellers dz Dementia
10 Prevention general public knowledge & awarens Continuing effeort of health professional to ensure & upgrade prevention public health policies Legislation tp provide maternal & child health care Family & genetic ounselling\proper prenatal & postnatal 20 & 30 prevention medical care Education for child Behavioural, cognitive & psychodynamic theraphy Family education Social intervention
nha 0813 : source Kaplan synopsis of psychiatric
You might also like
- Anxiety Disorder: Yerkes-Dodson Law:an Empirical Relationship Between Arousal andDocument4 pagesAnxiety Disorder: Yerkes-Dodson Law:an Empirical Relationship Between Arousal andnmyza89No ratings yet
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument3 pagesMental Status Examinationnmyza89No ratings yet
- Major Depressive Episodes Manic Episode Mixed Episode Hypomanic EpisodeDocument7 pagesMajor Depressive Episodes Manic Episode Mixed Episode Hypomanic Episodenmyza89No ratings yet
- Mood StabilizerDocument2 pagesMood Stabilizernmyza89No ratings yet
- Defense MechanismsDocument5 pagesDefense Mechanismsnmyza89No ratings yet
- DSM OcdDocument2 pagesDSM Ocdnmyza89No ratings yet
- Evaluation o Suicide RiskDocument2 pagesEvaluation o Suicide Risknmyza89No ratings yet
- Classification of AnaemiaDocument1 pageClassification of Anaemianmyza89No ratings yet
- PsychiatricDocument1 pagePsychiatricnmyza89No ratings yet
- INFO Student-Driven AssessmentDocument1 pageINFO Student-Driven Assessmentnmyza89No ratings yet
- REVISED Year 4 PPDSupervisor ReportDocument1 pageREVISED Year 4 PPDSupervisor Reportnmyza89No ratings yet
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument7 pagesValvular Heart Diseasenmyza89No ratings yet
- ST Elevation MI, STEMIDocument3 pagesST Elevation MI, STEMInmyza89No ratings yet
- Sudden Cardiac Death: Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesSudden Cardiac Death: Ischaemic Heart Diseasenmyza89No ratings yet
- ? DX Lie N Presentation: Abdominal Palpation VE Auscultation Fetal Heart Sonography /radiographyDocument2 pages? DX Lie N Presentation: Abdominal Palpation VE Auscultation Fetal Heart Sonography /radiographynmyza89No ratings yet
- Surgery - Tools RevisedDocument7 pagesSurgery - Tools Revisednmyza89No ratings yet
- HydrocoeleDocument2 pagesHydrocoelenmyza89No ratings yet
- Fast DPL CTDocument6 pagesFast DPL CTnmyza89No ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument1 pagePancreatitisnmyza89100% (1)
- Past-Years' Exam Questions Cns Anticonvulsant 3. Local AnaestheticDocument2 pagesPast-Years' Exam Questions Cns Anticonvulsant 3. Local Anaestheticnmyza89No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- So My Cat Has Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesSo My Cat Has Chronic Kidney DiseaseNur Alisya Hasnul HadiNo ratings yet
- Sample Internal Medicine Admission NoteDocument4 pagesSample Internal Medicine Admission NoteMayer Rosenberg100% (8)
- Dengue 2 AlertDocument4 pagesDengue 2 AlertJayant Jain100% (1)
- Topic 5. MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY EDUCATIONDocument7 pagesTopic 5. MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY EDUCATIONSophia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Urdaneta City University Graduate School UrdanetaDocument13 pagesUrdaneta City University Graduate School UrdanetaMa Theresa PunoNo ratings yet
- Infection Control in ORDocument10 pagesInfection Control in ORaaminah tariqNo ratings yet
- 1-Collection, Storage and Transportataion of MicrobiologicalDocument49 pages1-Collection, Storage and Transportataion of MicrobiologicalSummi NizNo ratings yet
- Revisiting Structural Family TherapyDocument2 pagesRevisiting Structural Family TherapyKim ScottNo ratings yet
- Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews: Sadaf Aghevlian, Amanda J. Boyle, Raymond M. ReillyDocument17 pagesAdvanced Drug Delivery Reviews: Sadaf Aghevlian, Amanda J. Boyle, Raymond M. ReillyKamila MartinNo ratings yet
- Clark 2004Document18 pagesClark 2004Joo XanderNo ratings yet
- Sambong UploadDocument6 pagesSambong UploadRaymond Christopher LimNo ratings yet
- Sample Operative ReportDocument3 pagesSample Operative ReportLem AregloNo ratings yet
- Keith Edwards Score For Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. IJP.03Document3 pagesKeith Edwards Score For Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. IJP.03Diego Bedon AscurraNo ratings yet
- University of Northern PhilippinesDocument4 pagesUniversity of Northern PhilippinesCatherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis Media: Jama Patient PageDocument1 pageAcute Otitis Media: Jama Patient PageS. JohnNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument11 pagesAcute PancreatitisJunaid Masoodi100% (4)
- Dengue OutlineDocument6 pagesDengue OutlineLouie George NeriNo ratings yet
- Date/Time Focus Data, Action, ResponseDocument2 pagesDate/Time Focus Data, Action, ResponseRoland Yuste67% (3)
- Carboplatin MonographDocument9 pagesCarboplatin Monographmerkuri100% (1)
- GRP2Document87 pagesGRP2Veronica ChanNo ratings yet
- 2018 Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDocument12 pages2018 Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenYudit Arenita100% (1)
- Barksy - The Paradox of Health PDFDocument5 pagesBarksy - The Paradox of Health PDFdani_g_1987No ratings yet
- Ss Ecg IntroDocument0 pagesSs Ecg Introreusougenio4162No ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Pathology: Abel B. (MD) Pathology Lectures, NMEI, DBUDocument59 pagesCerebrovascular Pathology: Abel B. (MD) Pathology Lectures, NMEI, DBUdenekeNo ratings yet
- Errors 2Document5 pagesErrors 2Anggun rahmi PutriNo ratings yet
- The Human Microbiome and Infectious Diseases: Beyond KochDocument151 pagesThe Human Microbiome and Infectious Diseases: Beyond KochRamesh ShahNo ratings yet
- VTE Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesVTE Risk AssessmentpriyopanjiNo ratings yet
- Shock SepticDocument35 pagesShock SepticAkbar SyarialNo ratings yet
- Pfizer Vaccine Explainer Version 2Document9 pagesPfizer Vaccine Explainer Version 2nqosa neidscqNo ratings yet
- 4D CT With Respiratory GatingDocument2 pages4D CT With Respiratory GatingLaura Karina Sanchez ColinNo ratings yet