Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question Bank Chemistry (B.Tech.) : Solid State
Uploaded by
nraiinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Bank Chemistry (B.Tech.) : Solid State
Uploaded by
nraiinCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Bank Chemistry (B.Tech.
)
Solid State
Q1. Copper has an FCC structure and an atomic radius of 1.278 Ao. Calculate its density. Given atomic weight of Copper as 63.5 g/mol and NA 6.023 1023 atoms/mol. Q2. Calculate the number of atoms per unit cell of a material having lattice parameter 2.9 A0 and density 7.87 gcm-3atom-1. Atomic weight of the material is 55.85 g/mol and NA 6.023 1023 atoms/mol. Q3. Sodium chloride (NaCl) crystals have FCC structure. The density of NaCl is 2.18 gcm-3atom-1. Calculate the distance between two adjacent atoms. Atomic weight of sodium is 23 gmol-1 and chlorine is 35.5 gmol-1. Q4. Molybdenum has BCC structure and density of 10.2103 Kgm-3atom-1(10.2 g cm-3 atom-1). Calculate its atomic radius. The atomic weight of molybdenum is 95.94 g mol-1. Q5. Molybdenum forms BCC crystal whose density is 10.3 gcm-3atom-1. Calculate (a) edge length of the unit cube (b) distance between the (110) planes and between the (111) planes. Molar mass of Mo = 95.94 gmol-1. Q6. The density of potassium chloride at 10 oC is 1.9893 gcm-3atom-1 and the length of a side of the unit cell is 629.082 pm as determined by X-ray diffraction. Calculate the value of Avogadros constant. Q7. Use the data given below to find the type of cubic lattice to which the crystal belongs. Atoms a pm gcm3atom-1 M gmol-1 Fe 286 7.86 55.8 5 V 301 5.96 50.94 Pd 388 12.16 106.4
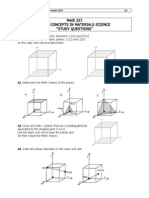
Q8. X-Ray analysis shows that the unit cell length in NaCl is 562.8 pm. Calculate the density you would expect on this basis. Avogadros constant is 6.023 1023 atoms mol-1. It is given that it crystallizes in FCC. Q9. The unit cell of aluminum is a cube with edge length 405 pm. The density of aluminum is 2.70 gcm3atom-1. What is the structure of aluminum crystal? Atomic weight of Aluminum is 26.98 g mol-1. Q10. A substance forms face-centered cubic crystal. Its density is 1.984 gcm3atom-1 and the length of the edge of the unit cell is 630 pm. Calculate the molar mass. Q11. From the fact that the length of the side of the unit cell for lithium is 351 pm. Calculate its atomic radius. Lithium forms BCC crystal. Q12. In a face-centered cubic arrangement of A and B atoms, where A atoms are at the corners of the unit cell and B atoms are at the face-centers, one of the A atoms is missing from one corner in each unit cell. What is the simplest formula of the compound? Q13. In a FCC lattice with all the positions occupied by A atoms, the BCC octahedral hole in it is occupied by an atom B of an appropriate size. For such a crystal, calculate the void space per unit volume of unit cell. Also predict the formula of the compound. Q.14 Write Short Notes on: (a) Weiss and Miller Indices, (b) Laws of crystallography (c) differentiate between amorphous and crystalline solid Q15.Derive general equation for obtaining inetrplanar spacing for a plane in 3 dimension and compute it for simple cubic geometry.
Braggs Equation
Q.16 Silver is known to be crystallized in cubic form. The Bragg angles, using copper Ka, X-ray with = 154.1pm, for the first six diffraction lines are as follows: = 19.080, 22.170, 32.260, 38.740, 40.820, 49.000 (a) What is the type of cubic crystal formed by silver? (b) What is the length of a side of the unit cell? (c) What is the interplanar distance of the plane (111)? (d) What is the density of silver? Given that atomic weight of silver is 108.0 gmol-1. Q.17 The first order reflection from (200) planes of NaCl using X-ray of = 58 pm K line of palladium occurs at an angle of 5.90. Calculate (i) edge length of the unit cell, (ii) volume of the unit cell (iii) molar volume, and (iv) density of sodium chloride.
Q.18 When a certain crystal was studied by the Bragg technique using X-ray of wavelength 229 pm, an X-ray reflection was observed at an angle 23020. (a) What is the corresponding interplaner spacing? (b) When another X-ray source was used, a reflection was observed at 15026. What was the wavelength of these X-rays? Q.19 Molybdenum forms BCC crystal whose density is 10.3 gcm-3atom-1. Calculate: (a) edge length of the unit cube, (b) distance between the (110) planes and between the (111) planes. Molar mass of Mo = 95.94 gmol-1. Q.20 Gold has a cubic face centered lattice with an edge length of the unit cube of 407 pm. Calculate the diffraction pattern when copper X-ray of wave length 154 pm are used. Q.21 When an X-ray powder pattern of crystalline Copper is obtained using X-ray from Copper target (the wave length of the K-line is 154.05 pm), reflections are found at 21.650, 25.210, 37.060, 44.960, 47.580 and other angles. (a) What is the type of cubic crystal formed by Copper? (b) What is the length of a side of the unit cell? (c) Find out the volue of Avogadros constant if density of Copper is 8.812 gcm-3atom-1? (d) Calculate the radius of Copper atom? Q.22 The X-ray powder pattern for Molybdenum has reflections at = 20.250, 29.300, 36.820, 43.810, 50.690, 58.800, 66.300 and other larger angles when K X-ray from Cu are used (= 154pm). (a) What is the type of cubic crystal formed by Mo? (b) What is the length of a side of the unit cell? (c) What is the density of the molybdenum? Q.23 A powder diffraction pattern for a given substance was obtained using X-ray from a Cu target where = 154 pm. The distance of capillary to the film was 5.0 cm. Diffracted lines were obtained, two of which were at a distances 1.2 and 3.4 cm from the undeflected beam. Calculate the spacing for the planes that give rise to these lines. Q.24 Magnesium oxide (M= 40.0gmol-1) is cubic and has a density of 3.620 gmol-1atom-1. An X-ray diffraction diagram of MgO powder has lines at values of Sin = 0.399, 0.461, 0.652, 0.764, 0.798 and 0.922. Index the pattern and determine the type of cubic structure. Calculate the wavelength of X-ray used. Assume that the number of MgO units per unit cell is smallest constituent with the structure type.
Q.25 Write short notes on (a) Graphite and fullerene (b) Intercalation products of graphite of first , second and third order (c) Braggs equation (d) electrical conduction of I and II group metal complexes. Q.26 Derive the Braggs equation in terms of Miller indices and their importance in calculating geometry.
Environmental Chemistry
Q27.The bond energy of O2 is 498.7 KJ/mol. Calculate the maximum wavelength (nm) of a photon that can cause the dissociation of an O2 molecules. Q.28 The highly reactive OH radical is believed to be involved in some atmospheric processes. The bond energy for the oxygen to hydrogen bond in OH as 460 KJ/mol. What is the longest wavelength in nm of radiation that can bring about the reaction? Q.29The green color observed in aurora borealis is produced by the emission of a photon by an electronically excited oxygen atom at 550 nm. Calculate the energy difference between the two levels involved in the emission process. Q.30The average bond energy of the C-Cl and C-F bonds are 340 KJ/mol and 485 KJ/mol respectively. Based on this information, explain why the C-Cl bond in CFC is preferentially broken by solar radiation at 250 nm. Q.31Like CFCs certain bromine containing compounds such as CF3Br can also participate in the destruction of ozone by a similar mechanism starting with the Br atom: CF3Br CF3. + Br. Given that the average C-Br bond energy is 276 KJ/mol, estimate the longest wavelength required to break this bond. Will this compound be decomposed in the troposphere only or in both the troposphere and stratosphere? Q.32What is the Green House effect? What is the criterion for classifying a gas as a Green House gas? Q.32 Deforestation contributes to the Green House effect in two ways? What are they? Q.33 Is ozone a Green Hose gas? If so, sketch three ways an ozone molecule can vibrate? Q.34Why are CFCs more effective Green House gases than methane and carbon dioxide? Q.35 The annual production of zinc sulfide (ZnS) is 4.0104 tonns. Estimate the number of tons of SO2 produced by roasting it to extract zinc metal.
Q.36Calcium Oxide or quicklime (CaO) is used in steel making cement manufacturing, and pollution control. It is prepared by the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate: CaCO3 (s) CaO in the US is 1.71010 Kg. Q.37 Water and sulfur dioxide are both polar molecules and their geometry is similar Why is SO2 not considered a major Green House gas? Q.38 Name the gas that is largely responsible for the acid rain phenomenon? Q.39 List three detrimental effects of acid rain. Q.40 Briefly discuss two industrial processes that lead to acid rain. Q.41 An electric power station annually burns 3.1107 Kg of coal containing 2.4% S by mass. Calculate the volume of SO2 emitted at STP. Q.42 The concentration of SO2 in the troposphere over a certain region is 0.16 ppm by volume. The gas dissolves in rain water as follows: SO2(g) + H2O(l) H+(aq) + HSO3-(aq) Given that the equilibrium constant for the preceding reaction is 1.3 10-2, calculate the pH of the rain water. Assume that the reaction does not affect the partial pressure of SO2. Q.43Carbon monoxide has a much higher affinity for Hb than oxygen does (a) Write the equilibrium constant expression (Kc) for the following process: CO(g) + HbO2(aq) O2(g) + HbCO (aq) Where HbO2 and HbCO are oxygenated hemoglobin and Carboxyhemoglobine, respectively. (b) The composition of a breath of air inhaled by a person smoking a cigarette is 1.9106 mol/L CO and 8.610-3 mol/L O2. Calculate the ratio of [HbCO] to [HbO2], given that Kc is 212 at 37oC. Q.44Briefly describe the harmful effects of the following substances: O3, SOx, NOx, CH3COOONO2 (PAN). Q.44 Write Short notes on: (a) Green house effect (b) Acid Rain and Smog (c) Ozone Layer depletion (d) Oxides of Nitrogen, Sulphur and Carbon Q. 45 What is Air pollution? Explain the methods for its control. Q.46 Describe the phenomenon of acid rain and its harmful effects. Q.47 Describe smog and fog. CaO (s) + CO2 (g) Calculate the yearly release of CO2 (in Kg) to the atmosphere if the annual production of
UNIT-IV Fuels and Combustion, Lubricants
Q.48 1 0.58 g of a sample of coal was used in a bomb calorimeter for the determination of calorific value. Calorific value of coal was found to be 8,600 cal/g. The ash formed in the bomb calorimeter was extracted with acid and the acid extract was heated with Ba(NO3)2 solution and a precipitate of BaSO4 was obtained. The precipitate was filtered, dried and weighed. The weight of precipitate was found to be 0.05g. Calculate the % of sulphur in the coal sample. Q.49 A gaseous fuel has the following composition by volume. Methane 5%, Hydrogen 20%, Carbon monoxide 25%, Carbon dioxide 6%, and rest nitrogen. If 20% excess of air is used for combustion, then calculate volume of air per m3 of fuel and composition of dry fuel gases. Q.50 A sample of coal was analyzed as follows: exactly 2.500 g was weighed into silica crucible. After heating for one hour at 110 0C, the residue weighed 2.415g. The crucible next was covered with a vented lid and strongly heated for exactly seven minutes at 95020 0C the residue weighed 1.528 g. The crucible was then heated without the cover, until a constant weight was obtained. The last residue was found to weight 0.245g. Calculate the percentage result of above analysis. Q.51 3.12 g of coal was Kjeldahlized and NH3 gas thus evolved was absorbed in 50 mL of 0.1N sulphuric acid. After absorption, the excess (residual) acid required 12.5 mL of 0.1N sodium hydroxide for exact neutralization. Determine the % of nitrogen in the sample of coal. Q.52 0.72g of fuel containing 80% carbon, when burnt in a bomb calorimeter increased the temperature of water from 27.30C to 29.10C. If the calorimeter contains 250 g of water and its water equivalent is 150g, calculate the HCV of fuel in KJ/Kg. Q.53 Calculate the gross and net calorific value of coal having the following composition Carbon = 85%, Hydrogen = 8%, Sulphur = 1%, Nitrogen = 2%, Ash = 4%. Latent heat of steam = 587 cal/g. Q.54 A sample of coal contains Carbon = 93%, Hydrogen = 6% and Ash = 1%. The following data were obtained when the above coal was tested in bomb calorimeter: (i) weight of coal burnt = 0.92 g (ii) weight of water taken = 550 g (iii) water equivalent of bomb calorimeter = 2,200g (iv) rise in temperature = 2.42 0C (v) fuse wire correction =
10.0 cal (vi) acid correction= 50.0 cal. Calculate gross and net calorific value of the coal, assuming the latent heat of condensation of steam as 580 cal/g. Q.55 The following data is obtained in a bomb calorimeter experiment: (i) weight of crucible = 3.649g (ii) weight of crucible and fuel = 4.678g (iii) water equivalent of the calorimeter = 570g (iv) water taken in the calorimeter = 2200g (v) observed rise in temperature is 2.30C (vi) cooling correction = 0.0470C (vii) acid correction is 62.6 cal (viii) fuse wire correction is 3.8 cal (ix) cotton thread correction = 1.6 cal. Calculate the gross calorific value of the fuel sample. If the fuel contains 6.5%H, determine the net calorific value Q.56 Calculate the GCV and NCV in the coal containing C=93%, H=6% and ash=1% Having weight of Coal=0.92 gm., Weight of water=550 gm., Water equivalent=2200 gm., Rise in temperature=2.42C, Fuse wire correction=10 cal, Acid correction=50 cal, Latent heat for steam=580 cal/gm. Q.57 Calculate the HCV and LCV in the fuel sample containing C=75%, H=5.2%, O=12.1%, N=3.2% and ash=4.5%: (i)Calculate the Air required for combustion of 1 Kg. of fuel (ii) Calorific value of C=8080 Kcal/Kg, H=34,500 Kcal/Kg, S=2240 Kcal/Kg. Q.58 Describe non conventional sources of energy, their uses? Q.59. Describe Biomass and Biogas and their merits over the unconventional use of biomass? Q.60 Define the importances of esterification and transesterification in fuel science? Q.61 Define Lubricants and their importances? Q.62 Define the following theory of Lubrication (i) Fluid film (Hydrodynamic) Lubrication (ii) Boundary lubrication (Thin-film lubrication) (iii) Extreme pressure lubrication. Q.63 What are liquid lubrications and their types? Define them with suitable examples. Q.64 What are the solid and semisolid lubricants? Define them with suitable examples. Q.65 Define viscosity index (VI) of lubricants. What are the parameters on which it depends? Describe their method of determination. Q.66 Describe the following characteristics of good lubricants (i) Flash Point (ii) Fire point (iii) Pour Point (iv) Cloud Point (v) Aniline Points Q.67 Tabulate the choice of lubricants based on operating conditions.
(Question Bank): Chemistry Q1. What is Molecular orbital theory? Give the MO diagram of CO, O2, NO-. Q2. What is Metallic bonding? Explain the types of Semiconductors. Q3. Write short notes on: (i) Hydrogen Bonding (ii) VSEPR Theory (iii) Hybridization Q4. What is Phase Rule ? Explain in details Phase, Component and Degree of Freedom. Q5. Explain the Water Phase diagram. How many components and Phases are there in the System containing CaCO3(s), CaO(s) and CO2(g). Q6. What is Polymer. Explain its Classification. Q7. (a) Give the difference between Addition and Condensation Polymerisation. (b) What are thermosetting and thermoplastic Polymers? Q8. Write Short Notes on: (i) PMMA (ii) Polyamides (iii) Polyesters Q9. What are Conducting polymers? Give their important applications. Q10. What are Natural and Synthetic rubbers. Explain the vulcanization process of rubbers. Q11. Write Short notes on: (a) Grren house effect (b) Acid Rain and Smog (c) Ozone Layer depletion (d) Oxides of Nitrogen, Sulphur and Carbon Q12. What is Air pollution? Explain the methods for its control. Q13. What is Fuel? Give its Classification and Characteristics of a good fuel. Q14. Describe the Calorimetric method to find out GCV(HCV) and NCV(LCV) of fuel. Q15. Calculate the GCV and NCV in the coal containing C=93%, H=6% and ash=1% Having weight of Coal=0.92 gm., Weight of water=550 gm.,Water equivalent=2200 gm., Rise in temperature=2.42C, Fuse wire correction=10 cal, Acid correction=50 cal, Latent heat for steam=580 cal/gm. Q16. Calculate the HCV and LCV in the fuel sample containing C=75%, H=5.2%, O=12.1%, N=3.2% and ash=4.5%:
(i)Calculate the Air required for combustion of 1 Kg. of fuel (ii) Calorific value of C=8080 Kcal/Kg, H=34,500 Kcal/Kg, S=2240 Kcal/Kg Q17. Calculate the Lime-Soda Requirement for the following water sample: (i) Volume of water= 50,000 L (ii) MgCO3=144 ppm, CaCO3=25 ppm, MgCl2=95 ppm, CaCl2=111 ppm, Fe2O3=25 ppm, Na2SO4=15 ppm (iii) Purity of Lime is 74% and that of Soda is 92%. Q18. Compare the Lime Soda, Zeolite and Ion Exchange process to soft the water. Q19. Write short notes on: (i) Break point Chlorination (ii) Desalination of Brackish water by Reverse Osmosis (iii)Boiler feed Water Specifications Q20.(a)Write Short notes on: (i) Biogas (ii) Solar Energy (b) Different types of fuels including Petroleum (c) Floating and Fixed Dome type Biogas Generator Q21.(a) What is Lubricant? Give its Classification (b)What is the criteria for the selection of a Lubricant. (c) Explain the mechanism of Lubrication Q22.(a) Explain the Pitting and Galvanic Corrosion. (b) Find out the Emf equation for Electrode and Electrolyte Concentration Cell. Q23. For a first order reaction, the rate constant is found to be 7*10-7 at 7C and 9*10-4 at 57C. Calculate the energy of activation and specific reaction rate at 127C. Q24. The fcc crstal of copper has atomic weight 63.54g/mol and atomic radius 1.278A. Calculate the volume density of copper. Q25. Derive the Expression for the rate constant of second order reaction having same concentration of reactants and its half life periods. Q26. Write Short Notes on: (i)Activation Energy (ii) Difference between Order and Molecularity Q27. The optical rotation of Sucrose in presence of dil.HCl at various intervals is given in the following table: Time(min) Rotation() 0 32.4 10 28.8 20 25.5 40 19.6 90 10.3 100 6.1 -14.1
Q28. For a first order reaction complete 15% in 20 minutes. How long will it take to be 60% complete. Q29. What is corrosion? Give its classification and protective measures to prevent Corrosion. Q30. Write Short Notes on: (i) Braggs equation (ii) Weiss and Miller Indices (iii) Graphite and fullerenes with applications. Q31. What is Nernst Equation? Calculate the equilibrium constants for the reaction: Sn2+ (aq) + Pb(s) == Sn(s) + Pb 2+ (aq) Given that E Sn2+/Sn = -0.14V, E Pb2+/Pb = -0.13V Q32. The Emf of a cell measured by means of a hydrogen electrode against a saturated calomel electrode at 298K is0.4188V. If the pressure of H2(g) is maintaind at 1 atm, Calculate the pH of unknown solution. Given potential of reference calomel electrode is 0.2415V. Q33. From the following data show that the decomposition of H2O2 in aqueous solution is a first order where N is the no. of ml. of KMnO4 required to decompose a definite volume of H2O2 : Time(min) 0 10 20 30 N 25 16 10.5 7.8
Q34. The thermal decomposition of arsine on glass surface: 2AsH3(g)->2As(s)+3S2(g) was investigated kinetically. The researchers found that below 350C the total pressure of the system varied as: Show that the reaction is of first order. Time(hrs) 0 4.33 16.0 25.5 37.66 44.75 Pressure(cmHg) 39.2 40.34 43.65 45.35 48.05 48.85 Q35. The volume density of -iron is7.86gm/cc in a BCC structure. Calculate the value of a and the atomic radius of the iron atom. Q36. An exhausted zeolite softner was regenerated by passing 200L of NaCl solution containging 112.50 gm/l of NaCl. How many litres of hard water sample having hardness of 540 ppm can be softened by using this softner. Q37. The specific rate constant for the decomposition of formic acid is 5.5*10-4sec-1 at 413K. Calculate the specific rate constant at 458K if the energy of activation is 2.37*104 cal/mol. Q38. An element having atomic mass 52 occurs in bcc structure with a cell edge of 288 pm , d=7.2 g/cc. Calculate Avagadros number. Q39. The rate constant for the first order decomposition of ethylene oxide into CH4 and CO may be described by: log10k(s-1)=14.34-1.25*104/T K (i) What is the activation energy for the reaction? (ii) What is the value of k at 670K. Q40. Explain the L-S process to soft the water.
10
You might also like
- ChE 413 Tutorials Problem Set 7-5-16 Solid State Chemistry and Bonding PDFDocument1 pageChE 413 Tutorials Problem Set 7-5-16 Solid State Chemistry and Bonding PDFNika A. BungabongNo ratings yet
- Seminario 1Document5 pagesSeminario 1Javier FrancoNo ratings yet
- Engr2026 Dec10Document18 pagesEngr2026 Dec10Mohamed AlqaisiNo ratings yet
- MT 1 Study QuestsDocument3 pagesMT 1 Study QuestsCaner AkkuşNo ratings yet
- Solid State 2013Document8 pagesSolid State 2013dasari karthikNo ratings yet
- Assignment IDocument2 pagesAssignment Idominhphung100% (1)
- 295 4 Solid State Practice ProblemsDocument11 pages295 4 Solid State Practice ProblemsArijit SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 4Document2 pages12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 4Mohd UvaisNo ratings yet
- Deber - 3 - Defectos Sobre Redes Cristalinas - Aragon CMB.Document6 pagesDeber - 3 - Defectos Sobre Redes Cristalinas - Aragon CMB.Yajaira AragonNo ratings yet
- The Solid State: Unit-1Document7 pagesThe Solid State: Unit-1Rams ChanderNo ratings yet
- Taller 2 - 2019Document2 pagesTaller 2 - 2019DAHANA CAICEDO PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Solved Problem SheetDocument2 pagesSolved Problem SheetAbdla DoskiNo ratings yet
- Assignemnt 1-Material ScienceDocument1 pageAssignemnt 1-Material ScienceMohit NarayanNo ratings yet
- Chapt 03 Sect 1 To 6Document18 pagesChapt 03 Sect 1 To 6Jesse McClureNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 QuestionsDocument1 pageAssignment 1 QuestionsYassir HindiNo ratings yet
- Materials Important Math Solution Collected From Different BooksDocument2 pagesMaterials Important Math Solution Collected From Different BooksMohiuddin A SiddikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 and 3Document50 pagesChapter 2 and 3Christian Peterson75% (8)
- Assignment 1 - Semester 2, 2017-18Document2 pagesAssignment 1 - Semester 2, 2017-18Student ServicesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1AASHISH CHAULAGAIN0% (1)
- Worksheet - 01 The Solid State: ChemistryDocument2 pagesWorksheet - 01 The Solid State: ChemistryAbhyudith BharadwajNo ratings yet
- IE 114 Material Science and General Chemistry Recitation #3Document2 pagesIE 114 Material Science and General Chemistry Recitation #3azizieh5701No ratings yet
- Fme 251 Tutorial Problems 2Document3 pagesFme 251 Tutorial Problems 2Majak MarialNo ratings yet
- ps3 2022Document2 pagesps3 2022Fake Account 1No ratings yet
- 04 Askeland ChapDocument6 pages04 Askeland ChapEstudiante2346No ratings yet
- 499347059chemistry Question Bank (2013-14)Document94 pages499347059chemistry Question Bank (2013-14)amanverma60% (1)
- Chemistry Question Bank 2013 14Document94 pagesChemistry Question Bank 2013 14Ashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Recitation 2 QuestionsDocument14 pagesRecitation 2 QuestionsfzfwsbyxrhNo ratings yet
- Test Series:1Chemistry MM: 50Document1 pageTest Series:1Chemistry MM: 50Rakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- The Solid StateDocument1 pageThe Solid StateJyoti SirandhanaNo ratings yet
- Chapt 11Document30 pagesChapt 11Ben NweeangNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document98 pagesCH 03Jonathan AlvinNo ratings yet
- Problem #1: Session #15: Homework ProblemsDocument2 pagesProblem #1: Session #15: Homework ProblemsDAVID MAURICIO MUÑOZ D�AZNo ratings yet
- In Situ Synthesis of Super-Long Cu Nanowires Inside Carbon Nanotubes With Coal As Carbon SourceDocument3 pagesIn Situ Synthesis of Super-Long Cu Nanowires Inside Carbon Nanotubes With Coal As Carbon SourceRamon Roman DovalNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 2Document4 pagesProblem Sheet 2Siddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- 3.091 Introduction To Solid State ChemistryDocument11 pages3.091 Introduction To Solid State ChemistryDrew JenkinsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Carbon NanotubesDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Carbon NanotubesSudeb SarkarNo ratings yet
- Homework Chapter 10Document3 pagesHomework Chapter 10Zac75% (4)
- CMF001 Tutorial 4 Physical ChemistryDocument4 pagesCMF001 Tutorial 4 Physical ChemistrycjcmoneyNo ratings yet
- BOARD EXAM QUESTIONS (Che-1 & Che-2)Document33 pagesBOARD EXAM QUESTIONS (Che-1 & Che-2)Swara AquaNo ratings yet
- Solid State Made BY KeshavPandey EngineerDocument6 pagesSolid State Made BY KeshavPandey EngineerVibhansh BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics (PHY 1051) (Regular)Document2 pagesEngineering Physics (PHY 1051) (Regular)aryansorout1612No ratings yet
- HW 5 - Due Thurs 110515 at 845am - Soln KeyDocument11 pagesHW 5 - Due Thurs 110515 at 845am - Soln Keyshayanebra100% (6)
- Arc Discharge ApplicationDocument15 pagesArc Discharge ApplicationHong Chun LeeNo ratings yet
- The Solid State Class 12 MCQs Questions With AnswersDocument19 pagesThe Solid State Class 12 MCQs Questions With AnswersRohit Chavariya100% (1)
- PHM Question ............. 22222Document4 pagesPHM Question ............. 22222Jonathan LukwichiNo ratings yet
- DPP 4 (Solid State) : Ans: (I) 2RDocument1 pageDPP 4 (Solid State) : Ans: (I) 2RajaxNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Important Questions Solid State 01Document7 pages12 Chemistry Important Questions Solid State 01Shahariya ShejeerNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Study Material Chemistry SA-1Document92 pagesClass 12 Study Material Chemistry SA-1VipinVKumarNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions w3Document2 pagesPractice Questions w3Hiểu Lam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Important Quuestions - Physical ChemistryDocument8 pagesImportant Quuestions - Physical ChemistryAvikant PathakNo ratings yet
- Type of Solid Intermolecular Forces Properties Examples: The Key Crystalline SolidsDocument18 pagesType of Solid Intermolecular Forces Properties Examples: The Key Crystalline SolidsSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Resource 20210531095551 Enrichment Work ChemistryDocument4 pagesResource 20210531095551 Enrichment Work ChemistryAditya SallyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Chapter 3 AnswerDocument9 pagesAssignment 1 - Chapter 3 AnswerHarryzam MartelNo ratings yet
- Solid State Physics MCQsDocument7 pagesSolid State Physics MCQsAhsan MoinNo ratings yet
- Imperfections in The Atomic and Ionic ArrangementsDocument66 pagesImperfections in The Atomic and Ionic Arrangementssusanweb100% (1)
- Physics ImportantDocument4 pagesPhysics ImportantSameer SamNo ratings yet
- Endohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideFrom EverandEndohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideNo ratings yet
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesFrom EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceFrom EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- NSO Sample Paper Class 3 PDFDocument12 pagesNSO Sample Paper Class 3 PDFpatnaikanupNo ratings yet
- Amazing Things To Do in OmanDocument8 pagesAmazing Things To Do in OmannraiinNo ratings yet
- NSO Sample Paper Class 2Document11 pagesNSO Sample Paper Class 2nilesh.cNo ratings yet
- SOF Sample Paper Class 3Document8 pagesSOF Sample Paper Class 3govimano100% (1)
- Fly AshDocument30 pagesFly AshnraiinNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste ManagementDocument16 pagesSolid Waste ManagementnraiinNo ratings yet
- Air and Its Major PollutantsDocument2 pagesAir and Its Major PollutantsnraiinNo ratings yet
- Shiv ChalishaDocument4 pagesShiv ChalishanraiinNo ratings yet
- Photochemical Smog and Chemical SmogDocument1 pagePhotochemical Smog and Chemical SmognraiinNo ratings yet
- Transport No. & Kohlrausch LawDocument15 pagesTransport No. & Kohlrausch LawnraiinNo ratings yet
- Shiv ChalishaDocument4 pagesShiv ChalishanraiinNo ratings yet
- Do's and Don'tsDocument2 pagesDo's and Don'tsnraiinNo ratings yet
- Schedule For Special Back Paper Examination September 2011 Phase IIDocument4 pagesSchedule For Special Back Paper Examination September 2011 Phase IInraiinNo ratings yet
- 1Document12 pages1nraiinNo ratings yet
- CHM Flio HAHA FAILDocument26 pagesCHM Flio HAHA FAILLoi Reng TeckNo ratings yet
- Gizmos: Photosynthesis LabDocument5 pagesGizmos: Photosynthesis LabRandom DooodNo ratings yet
- Fire Prevention and Safety Seminar: Bureau of Fire Protection Rosario Fire Station-LuDocument59 pagesFire Prevention and Safety Seminar: Bureau of Fire Protection Rosario Fire Station-LuJohn Ray BernalNo ratings yet
- Gherghel Cristian F 201004 M.a.scDocument170 pagesGherghel Cristian F 201004 M.a.scSaksham PatelNo ratings yet
- Floating Disk Lab 2018Document7 pagesFloating Disk Lab 2018Daniel De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Crandall, B.C. (Ed.) - NanotechnologyDocument216 pagesCrandall, B.C. (Ed.) - Nanotechnologyjacobi84No ratings yet
- Zirconia ProbeDocument3 pagesZirconia ProbeAbhik BasuNo ratings yet
- Potential Hazards in Chemical IndustriesDocument33 pagesPotential Hazards in Chemical IndustriesAMOL RASTOGI 19BCM0012No ratings yet
- Stoichiometry & The Mole Concept - TeachifyMe PDFDocument5 pagesStoichiometry & The Mole Concept - TeachifyMe PDFMuhammad Tauseef100% (2)
- Oxyfuel BurnersDocument31 pagesOxyfuel BurnersMohammed Abdul NaseerNo ratings yet
- Activity Periodic TableDocument2 pagesActivity Periodic TableNitRbeNo ratings yet
- Biomass PhotosynthesisDocument14 pagesBiomass PhotosynthesisAnonymous UKuUBsiNo ratings yet
- Respirometer 2012.DCDocument16 pagesRespirometer 2012.DCdchabiraNo ratings yet
- Difco ManualDocument860 pagesDifco ManualArpit BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Practice - Mass Transfer PDFDocument5 pagesEngineering Practice - Mass Transfer PDFjuanNo ratings yet
- SC F1 C7 Air NotesDocument36 pagesSC F1 C7 Air Notesjasonyeoh333No ratings yet
- Test Bank For The Economic Way of Thinking 13Th Edition by Heyne Boettke Prychitko Isbn 0132991292 978013299129 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For The Economic Way of Thinking 13Th Edition by Heyne Boettke Prychitko Isbn 0132991292 978013299129 Full Chapter PDFaaron.dixon139100% (11)
- Introduction To Explosives and PropellantsDocument68 pagesIntroduction To Explosives and PropellantsManish K. BhartiNo ratings yet
- Combustion Lab Manual Comb SolidDocument6 pagesCombustion Lab Manual Comb SolidDiego FrancoNo ratings yet
- AirSep As-R DatasheetDocument2 pagesAirSep As-R Datasheetdj22500No ratings yet
- All Gas LawDocument5 pagesAll Gas LawdasaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Lab Oxygenation To Suctioning of Tracheostomy QuestionsDocument6 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Lab Oxygenation To Suctioning of Tracheostomy Questionsclaire dimaano (colosus)No ratings yet
- Ib Course Companion Answer KeyDocument100 pagesIb Course Companion Answer KeyCarlos Ch67% (3)
- OWC Part12Document4 pagesOWC Part12Boby FaesalNo ratings yet
- B2 4 Respiration Questions and AnswersDocument28 pagesB2 4 Respiration Questions and AnswersIlincaVasilescu100% (2)
- Introduction To Chemistry 4th Edition Bauer Test BankDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry 4th Edition Bauer Test BankLisa Milne100% (41)
- Glossary - Igcse Chemistry School Book CDDocument9 pagesGlossary - Igcse Chemistry School Book CDPrincess KimNo ratings yet
- Grade V Week 3 555Document64 pagesGrade V Week 3 555Annielyn Corpuz Mercado-PedemonteNo ratings yet
- AMCP 706-177, Properties of ExplosivesDocument404 pagesAMCP 706-177, Properties of Explosiveswerdna67No ratings yet
- Role of Iron Fe in BodyDocument9 pagesRole of Iron Fe in Bodymuntada3000.mkNo ratings yet