Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP & Fdar
Uploaded by
kingawesome21Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP & Fdar
Uploaded by
kingawesome21Copyright:
Available Formats
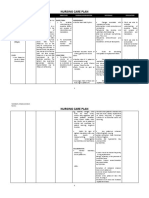
ASSESSMENT SUBJECTIVE:
DIAGNOSIS Deficient fluid volume related to active fluid loss Limangarawnaakongnagtatae due to diarrhea at suka as verbalized by the patient.
OBJECTIVE: y y y y y Dry mucous membranes Cold, clammy skin Restlessness Poor skin turgor Slow capillary refill
PLANNING After 24 hours of nursing interventions, the Patient will maintain fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced by individually adequate urinary output and stable vital signs, moist mucous membranes, good skin turgor, and prompt capillary refill.
V/S taken as follows T: 36.3C P: 88 R: 17 BP: 110/ 80
INTERVENTION Independent y Monitor urinary output. y Weigh daily and compare with 24-hour fluid balance. y Evaluate clients ability to manage own hydration. y Ascertain clients beverage preferences, and set up a 24-hour schedule for fluid intake. y Turn frequently, gently massage skin, and protect bony prominences. y Provide skin and mouth care. y Provide safety precautions.
RATIONALE -Fluid replacement needs are based on correction of current deficits and ongoing losses. -Measurement provides useful data for comparison. -Impaired gag and swallow reflexes and change in level of consciousness are among the factors that affect clients ability to replace fluids orally. -Relieves thirst and discomfort of dry mucous membranes and augments parenteral replacement. -Tissues are susceptible to breakdown because of vasoconstriction and increased fragility. -Skin and mucous membranes are
EVALUATION After 24 hours of nursing interventions, the Patientwas able to maintain fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced by individually adequate urinary output with normal specific gravity, stable vital signs, moist mucous membranes, good skin turgor, and prompt capillary refill.
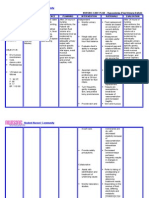
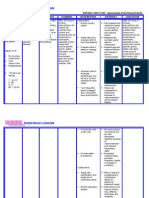
Focus Hypovelimia
data SUBJECTIVE: Limangarawnaakongnagtatae at suka as verbalized by the patient. OBJECTIVE: y y y y y Dry mucous membranes Cold, clammy skin Restlessness Poor skin turgor Slow capillary refill
dry with decreased elasticity because of vasoconstriction and reduced intracellular water. -Decreased cerebral tissue perfusion frequently results in changes in mentation. -be present and action Response require correction. After 24 hours of nursing y Monitor urinary output. interventions, the Patientwas y Weigh daily and compare able to maintain fluid volume at with 24-hour fluid balance. a functional level as evidenced y Evaluate clients ability to by individually adequate manage own hydration. y Ascertain clients beverage urinary output with normal specific gravity, stable vital preferences, and set up a signs, moist mucous 24-hour schedule for fluid membranes, good skin turgor, intake. and prompt capillary refill. y Turn frequently, gently massage skin, and protect bony prominences. y Provide skin and mouth care. y Provide safety precautions.
FDAR-
You might also like
- Acute Gastroentiritis (NCP)Document3 pagesAcute Gastroentiritis (NCP)April ParanganNo ratings yet
- NCP - Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP - Fluid Volume DeficitPatrice LimNo ratings yet
- Patient 3 NSDDocument20 pagesPatient 3 NSDBea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- Fdar UTIDocument2 pagesFdar UTINickaela CalalangNo ratings yet
- CaseanalysisDocument2 pagesCaseanalysisChrislyn Dian Pene100% (1)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPmimingdot33No ratings yet
- NCP For HHSDocument1 pageNCP For HHSLizzuly Galindo100% (1)
- Focus Data Action ResponseDocument3 pagesFocus Data Action ResponseSitty Aizah MangotaraNo ratings yet
- Flank Pain, Anxiety...Document7 pagesFlank Pain, Anxiety...reneighdNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument5 pagesDischarge PlanRaymond BasiloniaNo ratings yet
- Scrub and Circulating Practitioner Simulation Script - Salimbagat, UsmanDocument12 pagesScrub and Circulating Practitioner Simulation Script - Salimbagat, UsmanChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- FdarDocument1 pageFdarEloisa Claire DayananNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPJ. ishtelleNo ratings yet
- NCPsDocument13 pagesNCPsRocel DevillesNo ratings yet
- FDARDocument1 pageFDARCzar BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Bubbleshe Assessment: BREASTS 1. Palpate Both Breasts ForDocument3 pagesBubbleshe Assessment: BREASTS 1. Palpate Both Breasts Forallyssa joyNo ratings yet
- Home Visit Record (HVR) #1Document2 pagesHome Visit Record (HVR) #1kyle0% (1)
- Gordon's HisDocument4 pagesGordon's HisJee ShangNo ratings yet
- Afinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramDocument4 pagesAfinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Crisostomo Soapie ChartingDocument2 pagesCrisostomo Soapie ChartingMica OmotsosircNo ratings yet
- After 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital SignsDocument3 pagesAfter 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital Signsroma_elonaNo ratings yet
- NCP Allergic Reaction To FoodDocument3 pagesNCP Allergic Reaction To FoodCassie ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Fdar ChartingDocument4 pagesFdar ChartingVic Intia PaaNo ratings yet
- NCP DysuriaDocument1 pageNCP DysuriaJerico Geronimo DacutNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward...Document11 pagesPedia Ward...Ella Ramirez MedinaNo ratings yet
- CHN ActivitiesDocument11 pagesCHN ActivitiesEjie Boy IsagaNo ratings yet
- FDAR Chart - CamahalanDocument1 pageFDAR Chart - CamahalanCamahalan, Johnry G.100% (1)
- Pediatric Ward Journal Binwag BSN 2aDocument2 pagesPediatric Ward Journal Binwag BSN 2aVincentus BinNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning FinalDocument5 pagesDischarge Planning FinalRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Final NCPDocument21 pagesFinal NCPkoringring100% (1)
- Ob Ward-NcpDocument3 pagesOb Ward-NcpGiezel PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Document1 pageNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NCP - FeverDocument2 pagesNCP - FeverJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Patient's Name: Mr. X Age: 61 Address: Larap, Jose Panganiban, Camarines Norte Date / Time Focus Data, Action, Response Chest PainDocument4 pagesDay 1 Patient's Name: Mr. X Age: 61 Address: Larap, Jose Panganiban, Camarines Norte Date / Time Focus Data, Action, Response Chest PainJulliza Joy PandiNo ratings yet
- NCP (Age)Document5 pagesNCP (Age)justinmhayNo ratings yet
- Learning Feedback DiaryDocument1 pageLearning Feedback DiaryRendel FernandezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: at The End of 1 DependentDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: at The End of 1 DependentThomas FarrishNo ratings yet
- NCP HypertensionDocument1 pageNCP HypertensionCharisse VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- DPADocument4 pagesDPAZeeham EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Kristyn Joy D. Atangen October 25, 2020 BSN IV/ Section A/ Group D Josephine Minger Fdar PediaDocument1 pageKristyn Joy D. Atangen October 25, 2020 BSN IV/ Section A/ Group D Josephine Minger Fdar PediaTyn TynNo ratings yet
- Home Visit Record (HVR) #2: Kyle! Salamat Kay Ari Ka Naman Di." Goal MetDocument2 pagesHome Visit Record (HVR) #2: Kyle! Salamat Kay Ari Ka Naman Di." Goal MetKYLE CAÑADANo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJennirose JingNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument6 pagesPhysical AssessmentLondera BainNo ratings yet
- NCP DMDocument6 pagesNCP DMstara123No ratings yet
- NCP UtiDocument1 pageNCP UtiElaisa Mae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Tpo Eo Poa LFDDocument4 pagesTpo Eo Poa LFDEzra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Study of Illness ConditionDocument6 pagesStudy of Illness Conditionyong_gret100% (2)
- Fdar Charting: Date, Time, and Shift Focus Progress NotesDocument1 pageFdar Charting: Date, Time, and Shift Focus Progress NotesYuvi Luardo100% (1)
- Discharged PlanDocument6 pagesDischarged Planqueenieann100% (1)
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDocument3 pagesDisturbed Sleep PatternLorette Diane C. Roque100% (2)
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityVhin Lim100% (2)
- NCP For OxygenationDocument6 pagesNCP For OxygenationChriz LechNo ratings yet
- Introduction of FNCP 1Document2 pagesIntroduction of FNCP 1Helen QuibuyenNo ratings yet
- Jil 1Document1 pageJil 1Jillybanie LigsayNo ratings yet
- Deficit)Document2 pagesDeficit)Lee DeeNo ratings yet
- Hypovolemia (Fluid Deficit)Document2 pagesHypovolemia (Fluid Deficit)Lyn Reyes100% (1)
- Deficit)Document2 pagesDeficit)goldenboyjNo ratings yet
- Deficit) 1Document2 pagesDeficit) 1Richard AcibarNo ratings yet
- Hypo Vole MiaDocument2 pagesHypo Vole MiaAladil TapsiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume DeficitDan Gerald Alcido SalungaNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoriesDocument5 pagesNursing TheoriesThuganamix100% (19)
- Instruction: Indicate The Appropriate Numerical Rating Using The Label BelowDocument10 pagesInstruction: Indicate The Appropriate Numerical Rating Using The Label Belowkingawesome21No ratings yet
- Aaa SN PsycDocument2 pagesAaa SN Psyckingawesome21No ratings yet
- Stroke: Brain Attack and Acute Ischemic Cerebrovascular Syndrome (Modeled AfterDocument15 pagesStroke: Brain Attack and Acute Ischemic Cerebrovascular Syndrome (Modeled Afterkingawesome21No ratings yet
- Area Technique Normal Findings Analysis and Interpretation A. SkullDocument7 pagesArea Technique Normal Findings Analysis and Interpretation A. Skullkingawesome21100% (1)