Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PMP Notes
Uploaded by
remy_georgeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PMP Notes
Uploaded by
remy_georgeCopyright:
Available Formats
PMP NOTES
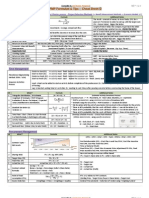
PV = BCWS EV = BCWP AC = ACWP
SIGMA 1 2 3 6
= = = =
68.26 95.46 99.73 99.99
CV = EV AC SV = EV PV CPI = EV / AC SPI = EV / PV EAC = Or Or Or Or BAC CPI (ACWP
EXP. VALUE = Probability x Consequence % $
PERT = BCWP ) BAC
O + 4ML + P 6 P-O 6
STD. DEV. OF TASK = TASK VAR. = CP STD. DEV. =
AC+ ETC AC + BAC EV AC + (BAC EV) CPI
(P O) 6 ________________
ETC = EAC AC VAC = BAC-EAC CV% = CV / EV x 100 SV% = SV / PV x 100 % COMPLETE = EV / BAC x 100 % SPENT = AC / BAC x 100
COMM = (N - N) / 2 Or (N) x (N 1)
FREE FLOAT = ES of Successor minus EF of Predecessor
PV
FV (1+r) PV (1+r)
MEAN ----- Average MEDIUM ---- No. in the middle or avg. of 2 nos. In the middle MODE ------ The most found number RANGE ------ Largest meas. Minus smallest Meas. IRR = ( NCF + NFC + NCF (1+r) (1+r) (1+R)
FV =
NPV = ( PV + PV + PV + PV ) (1+r) (1+r) (1+r) (1+r)
By PMPExamPrep 3/11/2005
PMP NOTES
PMP NOTES DEMING : Plan-Do-Check-Act 85% of Quality problems caused by Mgmt. 15% of Quality problems controllable by workers COMMON CAUSE OF VARIATIONS: (i.e. beyond control of workers on the floor) Poor Raw Materials Poor Design Unsuitable working conditions Equipment not meeting design tolerances SPECIAL ASSIGNABLE CAUSES: (Workers can control variability) Lack of knowledge Worker mistakes CROSBY: Do Things right the first time Quality means conformance to requirements Quality comes from prevention Quality means that the performance std. Is 0 defects Quality is measured by the cost of nonconformance
JURAN: (Jurans Trilogy) Quality Improvement Quality Planning = FITNESS FOR USE Quality Control
TAGUCHI: Quality should be designed into the product, not inspected Quality is best achieved by minimizing the deviation from the target The cost of quality shoul be measured as a function of deviation from the std. And the losses should be measured systemwide Prevention = build quality into product Life Cycle Cost include: Scrap Rework Inspection Returns Warranty (service calls or product replacement
By PMPExamPrep 3/11/2005
PMP NOTES
PMP NOTES COST OF PREVENTION Design review Training Quality planning Surveys Process studies Preventive activities COST OF APPRAISAL Inspection Lab Tests Vendor control In-process testing Internal/external design reviews
COST OF INTERNAL FAILURE (before leaving the control of the organization) Scrap Rework Repair Downtime Defect evaluation Evaluation of scrap Corrective action
COST OF EXTERNAL FAILURE (Determine by Cst. Perception that product does not meet his requirements) Returns and allowances Evaluation of customer complaints Inspection at customers site Customer visits to resolve quality complaints Corrective action
By PMPExamPrep 3/11/2005
PMP NOTES
MATERIALS USED
PMBOK
PROJECT MANAGEMENT A systems approach to Planning, Scheduling and Controlling, 7th Edition By Dr. Harold Kerzner, PhD Read the following chapters, which are well represented in the test. Chapter 1 OVERVIEW particularly sections 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7 and 1.10. Chapter 3 --- ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURES whole chapter. Chapter 5 MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS whole chapter. Chapter 7 CONFLICTS whole chapter. Chapter 23 QUALITY MANAGEMENT whole chapter. Chapter 24 CONTRACTS AND PROCUREMENT whole chapter.
Make copies of the following pages and put them in your critical info binder: Page 8 Fig 1-1 Page 19 Fig 2-6 Page 42 Fig 4-1 Page 52 Fig 5-1 Page 66 Fig 6-1 Page 84 Fig 7-1 Page 96 Fig 8-1 Page 108 Fig 9-1 Page 118 Fig 10-1 Page 128 Fig 11-1 Page 148 Fig 12-1
QUANTITAVE METHODS FOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT By Dr. Frank T. Anbari This book (more like a booklet) contains strictly formulae applicable to Project Management.
PMP EXAM PREP FOURTH EDITION By Rita Mulcahy, PMP Excellent source for preparation, it explains concepts in a simplified manner and it forces you to WORK by doing various exercises and completing the test after each chapter.
By PMPExamPrep 3/11/2005
You might also like
- PMP Formulae & Tips Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesPMP Formulae & Tips Cheat Sheetbhaveshkumar78100% (8)
- PMP Study MaterialsDocument90 pagesPMP Study Materialsamira_salama100% (4)
- PMBOK Study Notes PDFDocument83 pagesPMBOK Study Notes PDFshetupuc92% (26)
- PMP Memory SheetsDocument6 pagesPMP Memory Sheets1hass197% (29)
- PMP PDFDocument398 pagesPMP PDFdreamer1982100% (7)
- 568cc1de9a9ce 1305054 SampleDocument22 pages568cc1de9a9ce 1305054 SampleSiddharth ShahNo ratings yet
- PMP IN 45 DAYSDocument10 pagesPMP IN 45 DAYSgolfmaniac48% (21)
- PMP in Mindmaps, 2018, Ahmed Alsenosy' BookDocument10 pagesPMP in Mindmaps, 2018, Ahmed Alsenosy' BookIbrahimSamir100% (9)
- How I Passed My PMPDocument3 pagesHow I Passed My PMPRujuta Kulkarni100% (2)
- 60 Days - PMP Study PlanDocument3 pages60 Days - PMP Study PlanShahram Karimi100% (7)
- PMP Notes FinalDocument24 pagesPMP Notes Finalumerillias89% (9)
- PMP Formulas Cheat Sheet GuideDocument3 pagesPMP Formulas Cheat Sheet GuideSudhir AcharyaNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas Cheat SheetAn Nguyen100% (12)
- Edward PMP Study NotesDocument76 pagesEdward PMP Study NotesWaqas Ahmed94% (16)
- PMP Rapid ReviewDocument270 pagesPMP Rapid Reviewtrau-nuoc100% (33)
- Project Management Process, Tools & Techniques in 40 CharactersDocument3 pagesProject Management Process, Tools & Techniques in 40 CharactersRobincrusoe88% (26)
- The PMP Exam How To Pass On Your First TDocument3 pagesThe PMP Exam How To Pass On Your First TEnglish Learner50% (4)
- ITTO Trick Sheet for PMBOK Guide 6th EditionDocument26 pagesITTO Trick Sheet for PMBOK Guide 6th EditionAbdulla Jawad Alshemary84% (25)
- PMP Prep Book PDF Sample PDFDocument26 pagesPMP Prep Book PDF Sample PDFislamabadbahria91% (11)
- PMP Study Notes: Chapter 1 - Introduction (Project Management Framework)Document53 pagesPMP Study Notes: Chapter 1 - Introduction (Project Management Framework)girishkris92% (25)
- PMI PMP Course Workshop Master Presentation 6th EditionDocument13 pagesPMI PMP Course Workshop Master Presentation 6th Editionmvp2k6100% (1)
- Slides and Practice Exams PMP Exam Power PrepDocument978 pagesSlides and Practice Exams PMP Exam Power PrepHasz Vilicus Operis100% (9)
- 2021 PMP Mock Practice Tests (Gumroad)Document284 pages2021 PMP Mock Practice Tests (Gumroad)Aïda Hajri100% (13)
- PMP Question AnswersDocument12 pagesPMP Question AnswersRashid Mahamood100% (1)
- PMP Exam Cram Test BankDocument260 pagesPMP Exam Cram Test BankEduardo Duarte93% (29)
- Pmbok Guide 6thDocument30 pagesPmbok Guide 6thDewi Indah88% (8)
- PMBOK Processes 6thDocument1 pagePMBOK Processes 6thnguyenkhachiepvn60% (5)
- 2022 Top Tips To Solve Situational Questions in PMP ExamDocument10 pages2022 Top Tips To Solve Situational Questions in PMP ExamKuljinder Virdi100% (1)
- PMP Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPMP Cheat SheetLukinho De SouzaNo ratings yet
- PMP Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pagePMP Cheat Sheet PDFthouartu77% (35)
- A Roadmap to Cracking the Pmp® Exam: A Pmp Exam Preparation Study GuideFrom EverandA Roadmap to Cracking the Pmp® Exam: A Pmp Exam Preparation Study GuideNo ratings yet
- PfMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPfMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- PMP® Simplified Knowledge Areas: Artifacts and activities of the knowledge areasFrom EverandPMP® Simplified Knowledge Areas: Artifacts and activities of the knowledge areasNo ratings yet
- How to Pass the PMP Exam on Your Second AttemptFrom EverandHow to Pass the PMP Exam on Your Second AttemptRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- PMP® Full Exam: 2: 200 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP® Full Exam: 2: 200 Questions and AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Earned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamFrom EverandEarned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The PMP® Exam - Master and Leverage the ITTOsFrom EverandThe PMP® Exam - Master and Leverage the ITTOsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- PfMP® Full Exam: 2:170 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPfMP® Full Exam: 2:170 Questions and AnswersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PMP® Full Exam: 1: 200 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPMP® Full Exam: 1: 200 Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- The Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationFrom EverandThe Complete Project Management Exam Checklist: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional Certification: 500 Practical Questions & Answers for Exam Preparation and Professional CertificationNo ratings yet
- PMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamFrom EverandPMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Q & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionFrom EverandQ & As for the PMBOK® Guide Sixth EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- PgMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandPgMP® Full Exam: 1: 170 Questions and AnswersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Earned Value Management: 60 Minutes Compact Knowledge: The Best Methods and Tools to Keep Your Project Under ControlFrom EverandEarned Value Management: 60 Minutes Compact Knowledge: The Best Methods and Tools to Keep Your Project Under ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Project Management Professional® (PMP): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandProject Management Professional® (PMP): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Dice Tech Salary Survey 2014Document11 pagesDice Tech Salary Survey 2014scribuoyNo ratings yet
- BPHDocument10 pagesBPHmukesh697No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting Lecture EssentialsDocument105 pagesFinancial Accounting Lecture Essentialsmukesh697No ratings yet
- Service TaxDocument39 pagesService TaxSatyendra13kumarNo ratings yet
- IT Project Management Procedures ReviewDocument14 pagesIT Project Management Procedures Reviewmukesh697No ratings yet
- Oracle Accounting EntriesDocument17 pagesOracle Accounting Entriesmohanivar77No ratings yet
- Icebreakers PDFDocument20 pagesIcebreakers PDFGyula BallaNo ratings yet
- Oracleebsr12financialsconfigurationssummary 13030815Document27 pagesOracleebsr12financialsconfigurationssummary 13030815mukesh697No ratings yet
- Adjustingtheaccount 1#$Document49 pagesAdjustingtheaccount 1#$mukesh697100% (1)
- PramirolDocument5 pagesPramirolmukesh697No ratings yet
- R12 FinancialsDocument60 pagesR12 Financialsmukesh697No ratings yet
- Oracle PayablesDocument12 pagesOracle Payablesmukesh697No ratings yet
- Da Vinci and The 40 AnswersDocument311 pagesDa Vinci and The 40 Answersvbocan100% (4)
- Overview of Oracle Project BillingDocument125 pagesOverview of Oracle Project Billingmukesh697100% (2)
- Oracle AppsDocument20 pagesOracle AppssarrojNo ratings yet
- Read Only SchemaDocument3 pagesRead Only Schemamukesh697No ratings yet
- Oracle Match Invoice To Po4Document29 pagesOracle Match Invoice To Po4mukesh697No ratings yet
- Oracle AR AP & GL SetupsDocument4 pagesOracle AR AP & GL Setupsmukesh697No ratings yet
- IM010 UM Inter Company 1Document11 pagesIM010 UM Inter Company 1mukesh697No ratings yet
- Accelerator Implementation GuideDocument14 pagesAccelerator Implementation GuidevishaldattachowdaryNo ratings yet
- Oracle Apps Integration White PaperDocument11 pagesOracle Apps Integration White PaperbubkaNo ratings yet