Professional Documents
Culture Documents
All Reading Questions
Uploaded by
Katherine SauerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
All Reading Questions
Uploaded by
Katherine SauerCopyright:
Available Formats
Quantitative Methods for Economics Dr.
Katie Sauer
Questions for Section 2.2 Reading (math text) 1. What is the difference between a static and dynamic model?
2. What is the difference between a physical and an abstract model?
3. What is the difference between a deterministic and a stochastic model?
4. What are the 4 basic steps to mathematical modeling?
Questions for Section 2.3 Reading (math text) 1. A general demand function is written as Q = f(P, Y, Ps, Pc, Ta, A). We often simplify it to Q=f(P). What assumptions are we making when we do this?
2. When we write demand as Q=f(P), which variable is the dependent variable and which is the independent variable?
3. Most of the time in economics, we plot quantity on the horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis. Explain what this has to do with the inverse demand function.
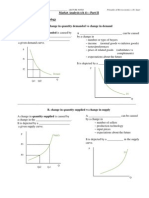
4. For a linear demand function, the Law of Demand implies that what will be true about the slope?
5. For a linear supply function, the Law of Supply implies that what will be true about the slope?
6. For the demand function of P = 200 2Q, if quantity demanded increases by 1 unit, by how many units did price change?
7. For the supply function of P = 20 + 0.33Q, if quantity supplied increases by 1 unit, by how many units did price change?
Questions for Section 3.1 Reading (math text) 1. What are two methods for solving two equations and two unknowns?
2. How would you know if a system of equations has no solution?
3. How would you know if a system of equations has infinitely many solutions?
______________________________________________________________________ Questions for Section 3.2 Reading (math text) 1. Write the demand equation for good x if good x and good y are substitutes.
2. Write the demand equation for good x if good x and good y are complements.
3. How does a per unit tax affect Supply, Demand, and market equilibrium?
4. How does a per unit subsidy affect Supply, Demand, and market equilibrium?
5. What is the formula for calculating the fraction of the tax/subsidy that a consumer pays/receives?
6. What is the formula for calculating the fraction of the tax/subsidy the producer pays/receives?
7. What do we mean when we say a firm is breaking even?
_______________________________________________________________________ Questions for Section 3.3 Reading (math text) 1. Explain what consumer surplus is.
2. Graphically and algebraically, how can we measure consumer surplus?
3. Explain what producer surplus is.
4. Graphically and algebraically, how can we measure producer surplus?
5. Explain what total surplus is.
6. Graphically and algebraically, how can we measure total surplus?
_____________________________________________________________________ Questions for Section 3.4 Reading (math text) 1. Under what conditions does equilibrium national income occur?
2. What is the equation for aggregate expenditure?
3. What are the steps for algebraically finding the equilibrium level of national income?
4. How would you graphically solve for the equilibrium level of national income?
Questions for Section 4.1 (math text) 1. If an equation is of the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, then what is the solution?
2. What is the constraint on a in a quadratic equation?
3. How many solutions will a quadratic equation always have?
4. Explain what an imaginary number is.
5. If you wanted to translate the quadratic equation vertically up by 5 units, how would you manipulate the original equation? Vertically down by 7 units?
6. If you wanted to translate the quadratic equation horizontally to the right by 4 units, how would you manipulate the original equation? Horizontally left by 2 units?
7. What are the 2 general properties of cubic functions?
Questions for Section 4.2 Reading (math text) 1. If you want to multiply numbers with the same base, how do you treat the exponents?
2. If want to divide numbers with the same base, how do you treat the exponents?
3. If you want to raise an exponential to a power, what do you do?
_____________________________________________________________________ Questions for Section 4.3 Reading (math text) 1. Explain how to convert an exponent into a log.
2. How do you solve an equation using the log rules?
____________________________________________________________________ Questions for Section 4.4 Reading (math text) 1. Sketch the graph of the rectangular hyperbola, y = 1/x.
2. When a hyperbola has the form: y = a/ (bx + c), how is the graph of y=1/x changed?
Questions for Section 6.1 (math text) Write down all the different notations that indicate the derivative of y = f(x).
Write down the power rule for differentiation.
Write down the three working rules for differentiating sums and differences.
How do you take a second derivative? Third derivative?
How do you determine if a function is increasing or decreasing?
How do you determine if the slope is increasing or decreasing?
Questions for Section 6.3 (math text) What does optimization mean?
At a turning point, the slope of a function must equal what value?
If the slope of a function equals zero, does that mean it is a turning point?
Write down the steps for the max/min method.
Questions for Section 6.5 (math text) Explain curvature and its application in economics.
On a first-quadrant graph, illustrate concave up/down and convex/concave to the origin.
What is an inflection point and how do you locate one?
Write down the relationships between average cost and marginal cost.
Questions for Section 6.6 (math text) Write down the exponential and natural log rules for differentiation.
Write down the chain rule for differentiation.
Write down the product and quotient rules for differentiation.
Questions for Section 6.7 (math text) Write down the formula for point elasticity using derivatives.
What is the general form for functions with constant elasticity?
Questions for Ch 7 (math text) What is a partial derivative? How do you take one? What is its notation?
What is a straight second-order partial derivative and what is a mixed second-order partial derivative? Write some examples of the notation for each.
Write the general form of the Cobb-Douglas production function.
Work through tables 7.4 and 7.5. These will be very handy references for you in future classes. In looking at a Cobb-Douglas production function, how can you determine what type of returns to scale it exhibits?
Explain the long and short run laws of production.
Write the general formulas for finding price elasticity of demand, income elasticity of demand and cross-price elasticity of demand.
Write the general formulas for finding the partial elasticities of labor and capital. How are these elasticites interpreted?
Write out the steps for optimizing functions with two variables.
What do we mean by constrained optimization?
Write out the general form for the Lagrangian.
Questions for Ch 8 (math text) What is integration?
Write down the notation for taking an integral of a function.
Write the power rule for integration.
Write down the exception to the power rule.
Write down the rule for integrating a constant.
Write down the working rules for integration.
Write down the rule for integrating a function with base e.
Write down the rules for taking a definite integral.
Write down the general expression for finding consumer surplus using integration.
Write down the general expression for finding producer surplus using integration.
Write down the general expression for finding the area between two curves.
Descriptive Statistics (ch 2 stats) Complete the following table by filling in the appropriate formulas. Add any notes that might help you use the formulas.
Raw Data Population Mean
Grouped Data
Sample Mean
Mid-Interval Value
Median
Mode
1st Quartile
2nd Quartile
3rd Quartile
Range
.. . .
Raw Data Variance
Grouped Data
Standard Deviation
InterQuartile Range Quartile Deviation
Write the formula for the Coefficient of Variation. What does it tell you?
Write the formula for Pearsons Coefficient of skewness. What does it tell you?
Explain how to construct a box plot.
Explain the grouping assumption.
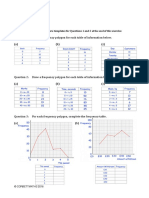
What is a frequency distribution? How do you construct one?
What is a cumulative frequency graph (Ogive)? How do you construction one?
What is a weighted average?
Sampling Distributions for Means and Proportions (ch 6 stats) What is the difference between a statistic and a parameter?
What is a point estimator?
What does the notation
refer to?
What does the notation
refer to?
What does standard error of the mean refer to?
What is sampling error?
What does the Central Limit Theorem say?
What is a proportion?
How do you calculate the mean for a sample proportion?
How do you calculate the standard error for a sample proportion?
How do you do a sampling distribution of proportions?
How do you calculate the mean and standard error for sample proportions when the population proportion is unknown?
Explain the desirable properties of estimators.
Confidence Intervals for Means and Proportions (ch 7 stats) Write the formula for a (1-)(100%) confidence interval for :
In general terms, what *is* a confidence interval?
How do you find a confidence interval for n > 30 when is unknown?
Review the very useful chart on page 292.
What is a one-sided confidence interval?
How do you construct a one-sided confidence interval?
How do you construct a confidence interval for proportions?
Review the very useful chart on page 298.
What are the effects of , the level of confidence and n on the precision of the confidence interval?
How do you calculate the sample needed to yield a confidence interval of a given level of precision?
Write the expression for the distribution for the difference of 2 means.
Write the expression for the confidence interval for the difference of 2 means.
Write the expression for the distribution for the difference to 2 proportions.
Write the expression for the confidence interval for the difference of 2 proportions.
Review the very useful chart on page 308.
How do you interpret a confidence interval?
Tests of Hypothesis for Means and Proportions (ch 8 stats) What is a null hypothesis?
What assumption do we make about the null hypothesis?
How would you test a null hypothesis?
What is an alternative hypothesis?
What is a p-value?
What is a significance test?
What are the steps for a classical method hypothesis test?
How can you informally describe the t-statistic? Formally?
What is a Type I error?
What is the maximum probability of making a Type I error?
What is a Type II error?
What is the power of a test?
What is a one-sided test? Two-sided?
What are the steps for hypothesis testing?
How are Confidence Intervals and hypothesis tests related?
How do you conduct a hypothesis test for proportions?
How do you conduct a hypothesis test for the difference between means or proportions?
How do you conduct a pooled estimate of variance?
Inference from Small Samples (ch 9 stats) What is a t-distribution? When is it used?
How do you calculate the number of degrees of freedom?
How do you construct a confidence interval for n < 30 when is known and the population is normal?
How do you construct a confidence interval for n < 30 when is unknown?
What test statistic would you use for a small sample with unknown population standard deviation?
How do you construct a confidence interval and perform a hypothesis test for a difference of means from small, independent samples?
What is the formula for the pooled estimate of variance? When is it used?
What is an F-test? How do you perform one? When do you perform one?
What is a paired sample?
How do you construct a confidence interval and perform a hypothesis test for the difference in means from a paired sample?
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- IA 05 Formal MethodsDocument5 pagesIA 05 Formal MethodsAuthierlys DomingosNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Well FoundationDocument40 pagesAnalysis and Design of Well Foundationdhanabal100% (1)
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Document4 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Worksheet - IntroductionDocument2 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Worksheet - IntroductionKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Model Summary TemplateDocument1 pageModel Summary TemplateKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Reading Outline - IntroductionDocument3 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Reading Outline - IntroductionKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Microeconomic Theory Katherine M. Sauer, Ph.D. ECO 3010 AD 530-R 303-556-3037 Fall 2012 Ksauer5@msudenver - EduDocument5 pagesIntermediate Microeconomic Theory Katherine M. Sauer, Ph.D. ECO 3010 AD 530-R 303-556-3037 Fall 2012 Ksauer5@msudenver - EduKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Lecture - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Document17 pagesPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Lecture - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine Sauer100% (1)
- Financial Wellness Programming: An Administrative PerspectiveDocument16 pagesFinancial Wellness Programming: An Administrative PerspectiveKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Document4 pagesChapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Katherine SauerNo ratings yet
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch04 Consumer ChoiceDocument7 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch04 Consumer ChoiceKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter08 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter08 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch03 PreferencesDocument8 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch03 PreferencesKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter09 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter09 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch02 S D and EquilibriumDocument7 pagesIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch02 S D and EquilibriumKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Reading Notes Economics - Dr. SauerDocument6 pagesReading Notes Economics - Dr. SauerKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Non-Linear Functions 4.1 Quadratic, Cubic and Other Polynomial FunctionsDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Non-Linear Functions 4.1 Quadratic, Cubic and Other Polynomial FunctionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter07 StatsDocument3 pagesReadingNotes Chapter07 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter02 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter02 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter01 StatsDocument5 pagesReadingNotes Chapter01 StatsKatherine Sauer100% (1)
- PM Guilds QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Guilds QuestionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter06 StatsDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter06 StatsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- ReadingNotes Chapter08 MathDocument2 pagesReadingNotes Chapter08 MathKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- PM Income Tax History QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Income Tax History QuestionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- This Chapter Is Kind of Intense. I Don't Recommend Trying To Read Through The Whole Thing in One SittingDocument5 pagesThis Chapter Is Kind of Intense. I Don't Recommend Trying To Read Through The Whole Thing in One SittingKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- PM Iceland Krona QuestionsDocument2 pagesPM Iceland Krona QuestionsKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Taxes Individuals Pay: Citizen's Guide To Economics Dr. Katie SauerDocument21 pagesTaxes Individuals Pay: Citizen's Guide To Economics Dr. Katie SauerKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Information SheetDocument1 pageExam 3 Information SheetKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Big Mac IndexDocument2 pagesLecture Notes - Big Mac IndexKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - TaxesDocument3 pagesLecture Notes - TaxesKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Big Mac IndexDocument11 pagesLecture - Big Mac IndexKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Information SheetDocument3 pagesExam 2 Information SheetKatherine SauerNo ratings yet
- Design of AC Chopper Voltage Regulator Based On PIC16F716 MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesDesign of AC Chopper Voltage Regulator Based On PIC16F716 MicrocontrollerabfstbmsodNo ratings yet
- Aerated Concrete Production Using Various Raw MaterialsDocument5 pagesAerated Concrete Production Using Various Raw Materialskinley dorjee100% (1)
- Concrete Lab ManualDocument20 pagesConcrete Lab ManualkelmazodroNo ratings yet
- Email ID: Contact No: +971562398104, +917358302902: Name: R.VishnushankarDocument6 pagesEmail ID: Contact No: +971562398104, +917358302902: Name: R.VishnushankarJêmš NavikNo ratings yet
- SL 4001Document2 pagesSL 4001ardiNo ratings yet
- The Invisible SunDocument7 pagesThe Invisible SunJay Alfred100% (1)
- Feasibility and Optimization of Dissimilar Laser Welding ComponentsDocument366 pagesFeasibility and Optimization of Dissimilar Laser Welding Componentskaliappan45490No ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Item N°: Curve Tolerance According To ISO 9906Document3 pagesData Sheet: Item N°: Curve Tolerance According To ISO 9906Aan AndianaNo ratings yet
- Exp - P7 - UPCTDocument11 pagesExp - P7 - UPCTSiddesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Rules and Fallacies For Categorical SyllogismsDocument5 pagesRules and Fallacies For Categorical SyllogismsFatima Ismael PortacioNo ratings yet
- Frequency Polygons pdf3Document7 pagesFrequency Polygons pdf3Nevine El shendidyNo ratings yet
- Sample File: The Ultimate Adventurers Guide IDocument6 pagesSample File: The Ultimate Adventurers Guide IDingusbubmisNo ratings yet
- Distillation Column DesignDocument42 pagesDistillation Column DesignAakanksha Raul100% (1)
- Kazi Shafikull IslamDocument3 pagesKazi Shafikull IslamKazi Shafikull IslamNo ratings yet
- WallthicknessDocument1 pageWallthicknessGabriela MotaNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Amr P2Document8 pagesAhmed Amr P2Ahmed AmrNo ratings yet
- Spelling Grammar Punctuation: Teacher BookDocument8 pagesSpelling Grammar Punctuation: Teacher BookNeil MenezesNo ratings yet
- Each Life Raft Must Contain A Few ItemsDocument2 pagesEach Life Raft Must Contain A Few ItemsMar SundayNo ratings yet
- Stevenson Chapter 13Document52 pagesStevenson Chapter 13TanimNo ratings yet
- 2014 Abidetal. TheoreticalPerspectiveofCorporateGovernance BulletinofBusinessDocument11 pages2014 Abidetal. TheoreticalPerspectiveofCorporateGovernance BulletinofBusinessOne PlusNo ratings yet
- Three Revolutionary Architects - Boullee, Ledoux, and Lequeu PDFDocument135 pagesThree Revolutionary Architects - Boullee, Ledoux, and Lequeu PDFTran LeNo ratings yet
- TMS320C67x Reference GuideDocument465 pagesTMS320C67x Reference Guideclenx0% (1)
- Soil Liquefaction Analysis of Banasree Residential Area, Dhaka Using NovoliqDocument7 pagesSoil Liquefaction Analysis of Banasree Residential Area, Dhaka Using NovoliqPicasso DebnathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Axial and Torsional ElementsDocument57 pagesChapter 2 Axial and Torsional ElementsAhmad FaidhiNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Shear Modulus SoilDocument14 pagesDynamic Shear Modulus SoilMohamed A. El-BadawiNo ratings yet
- Grimm (2015) WisdomDocument17 pagesGrimm (2015) WisdomBruce WayneNo ratings yet
- The Logic of Repetition: A Guide To Trading, Thinking, and The Cycles of LifeDocument10 pagesThe Logic of Repetition: A Guide To Trading, Thinking, and The Cycles of LifeRaghvendra kNo ratings yet
- Changing Historical Perspectives On The Nazi DictatorshipDocument9 pagesChanging Historical Perspectives On The Nazi Dictatorshipuploadimage666No ratings yet