Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test 12H Review Answers
Uploaded by
tedien252Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test 12H Review Answers
Uploaded by
tedien252Copyright:
Available Formats
Name: ___________Answer Key _________ Honors Physics
Date: ____________________________ Test #12 Review
Waves
1. 2. Read Chapters 12, 13, & 14. Terms to know: mechanical wave, transverse wave, longitudinal wave, surface wave, electromagnetic wave, pulse, medium, cycle, crest, trough, equilibrium position, traveling wave, period, frequency, wavelength, amplitude, phase, principle of superposition, constructive interference, destructive interference, node, antinode, standing wave, resonance, normal, angle of incidence, angle of reflection, law of reflection, refraction, diffraction, pitch, volume (loudness), Doppler shift. What is the difference between a transverse and a longitudinal wave? Draw a picture of each. Give an example of each.
Transverse disturbance perpendicular to wave motion
3. 4.
What is the difference between a traveling wave and a standing wave? What are the conditions necessary to produce a standing wave?
Traveling wave moves along the medium Standing wave appears to stand still need a wave to reflect off of a fixed point
Longitudinal disturbance parallel to wave motion
5.
What is the difference between a mechanical wave and an electromagnetic wave? Give an example of each.
Mechanical wave disturbance that travels through a medium Electromagnetic oscillations of electric charges no medium necessar
6. 7. 8. 9.
Sketch two pulses that will interfere constructively. Sketch two pulses that will interfere destructively. How can you change the speed of a wave in a rope? How can you change the frequency? How can you change the amplitude? How can you change the wavelength? When a wave crosses a boundary from one medium to another (say, from air to water or from a thick spring to a light spring) what characteristic of the wave remains the same?
The frequency stays the same. Its the wavelength, speed and amplitude that change
Sketch a picture of each of the following wave phenomena: reflection, diffraction, interference.
10. As a car honking its horn approaches you standing on a street corner, what do you notice about the frequency, amplitude and wavelength of the sound of the horn? What do you notice about these things as the car passes you and travels away? What is the name for this phenomenon?
Doppler effect Toward you higher frequency, smaller wavelength, no change in amplitude Away from you lower frequency, larger wavelength, no change in amplitude
11. Sketch one cycle of a standing wave and label the nodes and antinodes. Sketch one-half cycle. Sketch 1 cycles. 12. As the pitch of a sound increases, what happens to its frequency? As the loudness of a sound increases, what happens to its amplitude? Increasing pitch means an increase in frequency Increasing sound means an increase in amplitude
276
Directions: Read each question carefully and record your answers in the space provided. Be sure to show all work! Answers should be in significant figures. You will be graded on proper use of the GUESS method. If the GUESS method is not appropriate, show all work to receive partial credit. These will be the same directions on the test. Practice the GUESS method now.
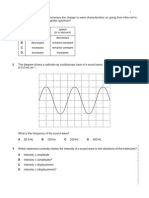
Use the wave to answer questions 1 - 6. 1. What is the wavelength of the wave? 8 m 2. What is the amplitude of the wave? 4 m 3. Over time, particle A will move in which direction? Up until the crest and then down If a student observes 60.0 waves passing in 12 seconds: 4. What is the frequency of the wave? 5. What is the period? 6. What is the velocity of the wave?
f= # waves 60.0waves = = 5.0Hz time 12s 1 1 T= = = 0.20 s f 5.0Hz
v = f = (5.0Hz )(8m) = 40 m s
Use the waves below to answer questions 7 12. Two waves, A and B, are shown below. They are traveling in the same medium at the same time. Both have the same wavelength but different amplitudes. 7. In the space below, show the resultant wave if A and B interfere.
8. What is the wavelength of wave A? 8m 9. What is the amplitude of wave B? 2m 10. What is the wavelength of the combined wave? 8m 11. What is the amplitude of the combined wave? 2m 12. What type of interference is this? Destructive
277
13. What is the wavelength of the following waves?
Wave A
Wave B Wave A = 4.0m Wave B = 16.0 m
14. A student observes 50. waves passing in 10. seconds. a. What is the frequency of the wave?
f= # waves 50.waves = = 5.0Hz time 10.s T= 1 1 = = 0.20 s f 5.0Hz
b. What is the period of the wave? c. If the wavelength is 1.5 meters, what is the velocity of the wave?
v = f = (5.0Hz)(1.5m) = 7.5 m s
15. What is the frequency of a 3.0 meter wave traveling at 100. m/s? v 100 m s f = = = 33.3Hz 3.0m 16. If the frequency of a wave doubles, while the speed remains constant, what happens to the wavelength? It is cut in half. 17. What is the frequency of a light whose wavelength is: a. 6.7 x 10-7 m? f = b. 5.9 x 10-7 v 3 108 m s = 4.5 1014 Hz 6.7 107 m
3 108 m s m? f = = = 5.1 1014 Hz 7 5.9 10 m
18. What is the wavelength of a light wave whose frequency is 3 x 1014 Hz. v 3 108 m s = 1.0 106 m = = 14 f 3 10 m 19. A sound wave has a frequency of 292 Hz and a wavelength of 0.589 m. What is the speed of the wave?
v = f = 292 Hz (0.589m) = 172 m s
How long will it take for the wave to travel 25 m?
t=
d 25m = = 0.14s v 172 m s 1 1 = = 0.0034s f 292 Hz
278
What is the period of the wave? T =
20. Which phenomenon does not occur when a sound wave reaches the boundary between air and a steel block? (A) reflection (B) polarization (C) absorption (D) refraction
21. As a periodic wave travels from one medium to another, which pair of the waves characteristics cannot change? (A) period and amplitude (B) period and frequency (C) amplitude and wavelength (D) frequency and velocity
22. The distance from the Moon to Earth is 3.9 x 108 meters. What is the time required for a light ray to travel from the Moon to Earth? (A) 0.65 s (B) 3.9 s (C) 1.3 s (D) 2.6 s
23. The diagram below shows a transverse wave moving to the right along a rope.
As the wave passes point X, the motion of x will be (A) left, then right (B) up, then down (C) in a circle (D) down, then up
24. Two waves have the same frequency. Which wave characteristic must also be identical for both waves? (A) intensity (B) phase (C) amplitude (D) period
25. How many nodes are represented in the standing wave diagram below?
(A) 6
(B) 4
(C) 3
(D) 1
26. The frequency of a light wave is 5.0 x 1014 hertz. What is the period of the wave? (A) 6.0 x 107 s (B) 5.0 x 10-14 s (C) 2.0 x 10-15 s (D) 1.7 x 106 s
27. An astronomer on Earth studying light coming from a star notes that the observed light frequencies are lower than the actual emitted frequencies. The astronomer concludes that the distance between the star and Earth is (A) increasing (B) not changing (C) decreasing
279
28. The diagram below shows two pulses, each of length , traveling toward each other at equal speed in a rope.
Which diagram best represents the shape of the rope when both pulses are in region AB?
29. What is the wavelength of a 30. hertz period wave moving at 60. meters per second? (A) 1,800 m (B) 2.0 m (C) 20. m (D) 0.50 m
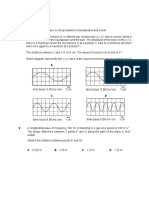
30. The driver of a car sounds the horn while traveling toward a stationary person. Compared to the sound of the horn heard by the driver, the sound heard by the stationary person has (A) higher pitch and longer wavelength (B) lower pitch and shorter wavelength (C) lower pitch and longer wavelength (D) higher pitch and shorter wavelength 31. When an opera singer hits a high-pitch note, a glass on the opposite side of the opera hall shatters. Which statement best explains this phenomenon? (A) The singer and the glass are separated by an integral number of wavelengths. (B) The frequency of the note and natural vibration frequency of the glass are equal. (C) The vibrations of the note are polarized by the shape of the opera hall. (D) The amplitude of the note increases before it reaches the glass. 32. The periodic wave in the diagram below has a frequency of 40. hertz.
What is the speed of the wave? (A) 13 m/s (B) 120 m/s (C) 60. m/s (D) 27 m/s
33. What is the angle between the direction of propagation of a transverse wave and the direction in which the amplitude of the wave is measured? (A) 900 (B) 1800 (C) 450 (D) 00
280
34. In the diagram below, the distance between points A and B on a wave is 0.10 meter.
This wave must have (A) a wavelength of 0.10 m (B) a wavelength of 0.20 m 35. Light is to brightness as sound is to (A) period (B) loudness (C) speed (D) color (C) an amplitude of 0.20 m (D) an amplitude of 0.10 m
36. What is the period of a periodic wave that has a frequency of 60. hertz? (A) 1.7 x 10-2 s (B) 3.3 x 102 s (C) 2.0 x 104 s (D) 3.0 x 10-3 s
37. A monochromatic beam of light has a frequency of 6.5 x 1014 hertz. What color is this light? (A) orange (B) yellow (C) blue (D) violet
38. A periodic wave travels through a rope, as shown in the diagram below.
As the wave travels, what is transferred between points A and B? (A) neither mass nor energy (B) energy, only (C) both mass and energy (D) mass, only
39. The distance between successive antinodes in the standing wave pattern shown below is equal to
(A) 2 wavelength
(B) 1/2 wavelength
(C) 1/3 wavelength
(D) 1 wavelength
Answers:
14. a. b. c. 15. 16. 17. a. b. 18. 19. a. b. 20. B 21. B 22. C 23. D 24. D 25. B 26. C 27. A 28. C 29. B 30. D 31. B 32. C 33. A 34. B 35. B 36. A 37. C 38. B 39. B
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13.
8m 4m up 5 Hz 0.20 s 40 m/s see sheet 8m 2m 8m 2m Destructive A = 4 m, B = 16 m .. 5.0 Hz 0.20 s 7.5 m/s 33.3 Hz cut in .. 4.5 x 1014 Hz 5.1 x 1014 Hz 1.0 x 10-6 m .. 172 m/s 0.14 s
281
282
You might also like
- Perfect Score Chapter 1 WavesDocument29 pagesPerfect Score Chapter 1 Wavesigori76No ratings yet
- Resonance: Sound Waves - 251Document27 pagesResonance: Sound Waves - 251Ankit JhaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9Document7 pagesTutorial 9angel lopezNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Integrated Science 2nd Edition Hewitt Test Bank DownloadDocument27 pagesConceptual Integrated Science 2nd Edition Hewitt Test Bank DownloadSteve Duncan100% (27)
- 1 0wave1 11 2activityDocument10 pages1 0wave1 11 2activityNisa Hj MohamadNo ratings yet
- F5-1-Wave Calculation Answer 2 PDFDocument4 pagesF5-1-Wave Calculation Answer 2 PDFKhairul WarsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Praactice QuizDocument3 pagesChapter 14 Praactice QuizNano MohammadNo ratings yet
- Phys 125 Pex 5Document9 pagesPhys 125 Pex 5Richard OuNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument39 pagesPhysicsRosdy DyingdemonNo ratings yet
- 9702 p1 Waves AllDocument17 pages9702 p1 Waves AllNushanKhan100% (1)
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch14 Test BankDocument29 pagesWolfson Eup3 Ch14 Test Bankifghelpdesk100% (1)
- Physics Module Form 5 GCKL 2010Document29 pagesPhysics Module Form 5 GCKL 2010Jo Ey Goh75% (4)
- Honors Physics Spring Semester Exam - June 2021 - Period 3Document7 pagesHonors Physics Spring Semester Exam - June 2021 - Period 3Olivia CaffreyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physical Science 14Th Edition Shipman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Physical Science 14Th Edition Shipman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFlinda.bertozzi514100% (13)
- Lesson 6.2 Physics F5Document10 pagesLesson 6.2 Physics F5Siti Arbaiyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties CrevDocument7 pagesWave Properties CrevFatah BanyunukiNo ratings yet
- General Revision-With More FiguresDocument4 pagesGeneral Revision-With More Figuresapi-202182511No ratings yet
- Wave On A StringDocument25 pagesWave On A StringgokulNo ratings yet
- Waves & OscillationsDocument10 pagesWaves & OscillationsDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Question Bank 3rd TermDocument18 pagesGrade 10 Question Bank 3rd Termsaadkhalid964No ratings yet
- Exam9 1363073656Document7 pagesExam9 1363073656Evan MosseriNo ratings yet
- 9 Science TP 12 1Document5 pages9 Science TP 12 1SaurabhNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument7 pagesWavesChongNo ratings yet
- Igcse 31 PropertiesofwavesDocument23 pagesIgcse 31 PropertiesofwavesHany ElGezawy100% (1)
- Dps WavesDocument3 pagesDps WavessanjibnandaNo ratings yet
- Waves and Light Unit Exam Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesWaves and Light Unit Exam Practice QuestionsobaidaaljoboryNo ratings yet
- Examview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Document9 pagesExamview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Tajay Billings100% (1)
- ExamView - Waves and Sound - Practice TestDocument9 pagesExamView - Waves and Sound - Practice TestMohan RajNo ratings yet
- Focus 01 AtomsDocument29 pagesFocus 01 AtomsLuiz Felipe SantoroNo ratings yet
- Nature of WaveDocument6 pagesNature of WaveMohammad Tanweer AkhtarNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument69 pagesPhysicsMohamedNo ratings yet
- Waves, Light Waves, Sound Waves and Ultrasound (The Physics Of)Document15 pagesWaves, Light Waves, Sound Waves and Ultrasound (The Physics Of)ShatiJanzour TicketingNo ratings yet
- Waves Revision MC TestDocument36 pagesWaves Revision MC Testlove_241No ratings yet
- Understanding Waves: - Physics Module Form 5 Chapter 1: Waves GCKL 2011Document29 pagesUnderstanding Waves: - Physics Module Form 5 Chapter 1: Waves GCKL 2011rush7240No ratings yet
- 00 01 MC Paper 1 MC IGCSE Physics Light and Waves QPDocument8 pages00 01 MC Paper 1 MC IGCSE Physics Light and Waves QPStephen MceleaveyNo ratings yet
- Waves and Sound Notes and QuestionsDocument28 pagesWaves and Sound Notes and QuestionsFelixNo ratings yet
- A Wave Is A Phenomenon In: Which Energy Is Transferred ThroughDocument53 pagesA Wave Is A Phenomenon In: Which Energy Is Transferred ThroughAlan MeysamianNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.2Document10 pagesLesson 6.2Tok PutihNo ratings yet
- ASSSESMENT g7Document4 pagesASSSESMENT g7Marie PhillineNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan SoalDocument34 pagesKumpulan SoalDaraFelisiaArdhityasariNo ratings yet
- Waves AssignmentDocument18 pagesWaves AssignmentMohan PonduriNo ratings yet
- Waves: Name - TeacherDocument47 pagesWaves: Name - TeachersaadNo ratings yet
- Waves and SHM Practice Test PDFDocument7 pagesWaves and SHM Practice Test PDFAyushi MNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Waves AnswersDocument66 pages3.3 Waves Answersmarkmattesz06No ratings yet
- Module Test 2 Waves Around YouDocument33 pagesModule Test 2 Waves Around YouRaymond ManalastasNo ratings yet
- Waves, Light Waves, Sound Waves and Ultrasound (The Physics Of)Document15 pagesWaves, Light Waves, Sound Waves and Ultrasound (The Physics Of)Jc C. GomezNo ratings yet
- Physics Q &A ReviewerDocument5 pagesPhysics Q &A ReviewerZoey DutcheeNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pressure:-From Boyel's Law P V ConstantDocument6 pagesEffect of Pressure:-From Boyel's Law P V Constantamit34521No ratings yet
- Final PhysicsREVISEDDocument6 pagesFinal PhysicsREVISEDalecksander2005No ratings yet
- 10 h2 Waves Motion Tutorial QuestionsDocument10 pages10 h2 Waves Motion Tutorial QuestionsSudibyo GunawanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Vibration and WavesDocument3 pagesWorksheet Vibration and WavesHindNo ratings yet
- Waves Problems Worksheet IIDocument2 pagesWaves Problems Worksheet IIAnkit MalikNo ratings yet
- Physics G8 2021-22 3RD Term Revision SheetDocument14 pagesPhysics G8 2021-22 3RD Term Revision SheetAya ChoucairNo ratings yet
- Properties of WavesDocument4 pagesProperties of WavesrohmawatiNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound and Elastic Waves: Frequently Asked QuestionsFrom EverandUltrasound and Elastic Waves: Frequently Asked QuestionsNo ratings yet
- De Thi Hoc Ky I Lop 12 HBTDocument6 pagesDe Thi Hoc Ky I Lop 12 HBTtedien252No ratings yet
- KSCL10A Lan 2cvpDocument7 pagesKSCL10A Lan 2cvptedien252No ratings yet
- Khao Sat 10lexoay20122013Document4 pagesKhao Sat 10lexoay20122013tedien252No ratings yet
- (DapAn) MotSoBTHoaHocSuDungBienLuan 2012 (Lemongrass.31.08)Document20 pages(DapAn) MotSoBTHoaHocSuDungBienLuan 2012 (Lemongrass.31.08)thaihungnguyen2011No ratings yet
- Chuyen de - Dai So To HopDocument13 pagesChuyen de - Dai So To Hoptedien252No ratings yet
- De Dap An Thi Hk1 09-10 PGD Ly9Document2 pagesDe Dap An Thi Hk1 09-10 PGD Ly9tedien252No ratings yet
- Madanapalle Institute of Technology & ScienceDocument40 pagesMadanapalle Institute of Technology & ScienceRavikanth NssNo ratings yet
- Physics: Senior Secondary School: SecondDocument53 pagesPhysics: Senior Secondary School: SecondHASSAN OLUMIDENo ratings yet
- Waves QuestionsDocument14 pagesWaves QuestionsCealaNo ratings yet
- Caie As Level: PHYSICS (9702)Document19 pagesCaie As Level: PHYSICS (9702)Abdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- On Sound: Phys130, A04 Dr. Robert MacdonaldDocument24 pagesOn Sound: Phys130, A04 Dr. Robert MacdonaldAlinaBogoiNo ratings yet
- PHYS 2214 Assignment 4 Fall 2010Document4 pagesPHYS 2214 Assignment 4 Fall 2010Kira GidronNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Acoustics and Noise Control Syllabus: General Principles of Acoustics Module (Compulsory) Learning OutcomesDocument19 pagesDiploma in Acoustics and Noise Control Syllabus: General Principles of Acoustics Module (Compulsory) Learning OutcomesViktor MickovskiNo ratings yet
- Wave QuestionsDocument30 pagesWave QuestionsMeera ChawdaNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Lesson 22 Vibrations and WavesDocument6 pagesPhysics Worksheet Lesson 22 Vibrations and WavesRizky HermawanNo ratings yet
- Eye Sight SLDocument28 pagesEye Sight SLmardel11No ratings yet
- LectureCh15Waves of MotionDocument41 pagesLectureCh15Waves of MotionJimmy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 114Document23 pages114physicsdocsNo ratings yet
- Eksperimen MeldeDocument6 pagesEksperimen MeldeLulu RohmahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 WavesDocument4 pagesChapter 5 WavesPauling Chia0% (1)
- ch16 PDFDocument24 pagesch16 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- Microwave Absorbing MaterialsDocument401 pagesMicrowave Absorbing MaterialsAna Paula OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Lecture 1revisedDocument133 pagesTransmission Line Lecture 1revisedLhorie Ladica Valerio100% (2)
- Manual AT-3200D Kit Entrenamiento de Antenas PDFDocument135 pagesManual AT-3200D Kit Entrenamiento de Antenas PDFAndrea SanchezNo ratings yet
- Phy 102 Lecture 8 - Electrical Energy and Capacitance (B)Document72 pagesPhy 102 Lecture 8 - Electrical Energy and Capacitance (B)chipango lungoweNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Week 5 Topic 3.3 Solutions 1Document20 pagesModule 3 Week 5 Topic 3.3 Solutions 1Syed Arafat KadriNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Levitation Machine Using Arduino: T He Object Oat SDocument8 pagesUltrasonic Levitation Machine Using Arduino: T He Object Oat SJose A Perez Delgado100% (1)
- Chapter 12 Waves 2: NameDocument27 pagesChapter 12 Waves 2: NamesciencedocsmanNo ratings yet
- Chem12 c03 3 3Document5 pagesChem12 c03 3 3Eric McMullenNo ratings yet
- CFD Simulation of A Thermoacoustic EnginDocument4 pagesCFD Simulation of A Thermoacoustic EnginShubhamNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument39 pagesPhysicsRosdy DyingdemonNo ratings yet
- Non-Contact Acoustic Manipulation in Air PDFDocument2 pagesNon-Contact Acoustic Manipulation in Air PDFMikela LjermontovaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2.2 PDFDocument10 pagesQuiz 2.2 PDFsalehalbaba5No ratings yet
- Wright Et Al. 1979 - Morphodynamics of Reflective and Dissipative Beach and Inshore Systems-Southern AustraliaDocument36 pagesWright Et Al. 1979 - Morphodynamics of Reflective and Dissipative Beach and Inshore Systems-Southern AustraliaMahmoud FelflaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4.5 - Standing WavesDocument30 pagesTopic 4.5 - Standing Waves이수연No ratings yet
- Standing Waves Per Unit Volume-Derivation-blackbody RadiationDocument19 pagesStanding Waves Per Unit Volume-Derivation-blackbody RadiationRachit MadanNo ratings yet