Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Engineering Lab
Uploaded by
Zul ZiellerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering Lab
Uploaded by
Zul ZiellerCopyright:
Available Formats
1.Refrigerator - All refrigerator system have four basic part,the condenser,the compresser,throttling or expension valve and evaporater. 1.
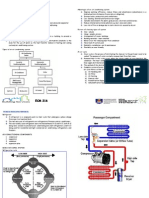
1 There are three types of condensers: air cooled, water cooled and evaporative. - Air cooled condensers: Air cooled condensers are used in small units like household refrigerators, deep freezers, water coolers, window air-conditioners, split airconditioners, small packaged air-conditioners etc. These are used in plants where the cooling load is small and the total quantity of the refrigerant in the refrigeration cycle is small. Air cooled condensers are also called coil condensers as they are usually made of copper or aluminum coil. Air cooled condensers occupy a comparatively larger space than water cooled condensers. - Water cooled condensers: Water cooled condensers are used for large refrigerating plants, big packaged air-conditioners, central air-conditioning plants, etc. These are used in plants where cooling loads are excessively high and a large quantity of refrigerant flows through the condenser. - Evaporative condensers: Evaporative condensers are usually used in ice plants. They are a combination of water cooled and air cooled condensers. In these condensers the hot refrigerant flows through the coils. Water is sprayed over these coils. At the same time the fan draws air from the bottom side of the condenser and discharges it from the top side of the condenser. The spray water that comes in contact with the condenser coil gets evaporated in the air and it absorbs the heat from the condenser, cools the refrigerant and condenses it. 1.2 A refrigerant is a substance used in a heat cycle usually including, for enhanced efficiency, a reversible phase change from a gas to a liquid. Traditionally, fluorocarbons, especially chlorofluorocarbons were used as refrigerants, but they are being phased out because of their ozone depletion effects. Other common refrigerants used in various applications are ammonia, sulfur dioxide, and non-halogenated hydrocarbons such as methane .
2. Air Conditioning
1.1 Air conditioning is the removal of heat from indoor air for thermal comfort.In another sense, the term can refer to any form of cooling, heating, ventilation, or disinfection that modifies the condition of air.[1] An air conditioner (often referred to as AC or air con.) is an appliance, system, or machine designed to stabilise the air temperature and humidity within an area (used for cooling as well as heating depending on the air properties at a given time), typically using a refrigeration cycle but sometimes using evaporation, commonly for comfort cooling in buildings and motor vehicles. 1.2 Air-conditioning units the heat is taken from the low temperature reservoir and thrown to the high temperature reservoir; hence this process requires external power which is given to the compressor. The compressor sucks low pressure and low temperature refrigerant from the evaporator and compresses it to high pressure and high temperature gaseous state. The larger the size of the refrigeration plant, the larger the compressor will be and the more power will be required.
You might also like
- CondensorDocument20 pagesCondensorLaka 98No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Group 4Document3 pagesAir Conditioning Group 4Kline MicahNo ratings yet
- Types of Compressor 1. Reciprocating CompressorsDocument9 pagesTypes of Compressor 1. Reciprocating CompressorsAnthropophobe NyctophileNo ratings yet
- Air - ConditioningDocument4 pagesAir - ConditioningDinesh ChahalNo ratings yet
- RAC Blue Print ObjectivesDocument10 pagesRAC Blue Print Objectivesdawit solomonNo ratings yet
- AirconDocument142 pagesAirconJervin Ocampo0% (2)
- Split SystemDocument16 pagesSplit Systemjhaamit4No ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning UnitsDocument10 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning Unitssnowgalvez44No ratings yet
- ChillerDocument10 pagesChillerkhansartaj19995No ratings yet
- The Four Types of Refrigeration Systems You Need To KnowDocument2 pagesThe Four Types of Refrigeration Systems You Need To KnowtakayNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument5 pagesAir ConditioningDC1234No ratings yet
- Type of EvaporatorsDocument6 pagesType of EvaporatorsEVANGELISTA REYMUND V.No ratings yet
- Hvac EquipmentsDocument16 pagesHvac EquipmentsRahul Prajapati100% (1)
- HVAC PrinciplesDocument60 pagesHVAC PrinciplesshreyashNo ratings yet
- Week 6maint MGMT BIE2016 MechanicalDocument90 pagesWeek 6maint MGMT BIE2016 MechanicalaimanfznnnNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument26 pagesRefrigerationTeeyansh singh SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Condenser in Re-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesCondenser in Re-WPS OfficeMalecha SebastianNo ratings yet
- What Is RefrigerationDocument10 pagesWhat Is RefrigerationxyonieNo ratings yet
- Window & Packaged Ac Chilled Water Plant: G.Siddharth Moorthe 12RBAR033Document14 pagesWindow & Packaged Ac Chilled Water Plant: G.Siddharth Moorthe 12RBAR033Logesh WaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3Document8 pagesChapter 1-3Paul MendozaNo ratings yet
- BoilerDocument9 pagesBoilerkhansartaj19995No ratings yet
- Types of Air-Conditioning SystemDocument9 pagesTypes of Air-Conditioning SystemkimNo ratings yet
- Hvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerDocument36 pagesHvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerMohd Tarique AnwarNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning: (Intensive Course)Document146 pagesAir Conditioning: (Intensive Course)MohamedSayedNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11-Hvac For Small HouseDocument9 pagesExperiment 11-Hvac For Small Houseengrjayasis20No ratings yet
- How Do Chillers Work by Nathan SchumacherDocument5 pagesHow Do Chillers Work by Nathan SchumacherNathan SchumacherNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 9 Calculate The Specific Heat of Water ObjectiveDocument2 pagesExperiment No 9 Calculate The Specific Heat of Water Objectiveyasir_mushtaq786No ratings yet
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2 Air ConditioningDocument8 pagesECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2 Air ConditioningAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (3)
- Refrigerator and Air-Conditioner Condensers: Condenser CondenserDocument2 pagesRefrigerator and Air-Conditioner Condensers: Condenser CondenserKifayat UllahNo ratings yet
- On Air ConditioningDocument26 pagesOn Air ConditioningTej KalyanNo ratings yet
- Airconditioning ProcessDocument5 pagesAirconditioning ProcessMark Anthony SibayanNo ratings yet
- Building Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1Document32 pagesBuilding Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1TaanayaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsAhmad MujahidNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning - Building ServiceDocument12 pagesAir Conditioning - Building ServiceHarini Andal AgnihotramNo ratings yet
- Introduction - : Refrigeration Is The Process ofDocument11 pagesIntroduction - : Refrigeration Is The Process ofNikita ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Condenser and TypesDocument1 pageCondenser and TypesLAURA JIMENA CAMARGO VEGANo ratings yet
- Split Type AcuDocument40 pagesSplit Type AcuKristine Ann ReclosadoNo ratings yet
- ME LAB ASSESSMENT 2 and 3Document20 pagesME LAB ASSESSMENT 2 and 3Emilio Joaquin FloresNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document27 pagesLecture 3Shubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Types of Condenser Air Cooled CondensersDocument2 pagesTypes of Condenser Air Cooled CondensersAnthropophobe NyctophileNo ratings yet
- Module Iii Refrigeration CycleDocument16 pagesModule Iii Refrigeration CycleDiether RigorNo ratings yet
- Types of HVAC SystemsDocument6 pagesTypes of HVAC Systemsm2110100% (1)
- Components of VCRS NewDocument37 pagesComponents of VCRS Newmesfn derbNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument29 pagesRefrigerationaaisha pariNo ratings yet
- Active Solar Heating and Air Conditioning SystemsDocument14 pagesActive Solar Heating and Air Conditioning Systemss3od.123No ratings yet
- CondenserDocument12 pagesCondenserPrabir Kumar Pati100% (1)
- Refrigeration: "Refrigeration Is The Process of Removing Heat From An Enclosed Space, orDocument16 pagesRefrigeration: "Refrigeration Is The Process of Removing Heat From An Enclosed Space, ordjgondalNo ratings yet
- Building Services: Assignment 2Document40 pagesBuilding Services: Assignment 2Vivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Research 1 - Mechanical System BU2Document17 pagesResearch 1 - Mechanical System BU2Zachary Yassir GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Study On Air-Conditioning and Its ProcessDocument5 pagesStudy On Air-Conditioning and Its Processsdeep1990No ratings yet
- Group 4 IADocument11 pagesGroup 4 IAcervanamonica13No ratings yet
- Heat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Document46 pagesHeat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Sagar GoyalNo ratings yet
- Refrigerator Air ConditionerDocument61 pagesRefrigerator Air ConditionerVijay GanapathyNo ratings yet
- M&E Assignment 3Document12 pagesM&E Assignment 3han0701No ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument52 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningYashawantha Gowda100% (1)
- Building Utilities 2 Air ConditioningDocument4 pagesBuilding Utilities 2 Air ConditioningianyanNo ratings yet
- Condensers NotesDocument6 pagesCondensers NotesTalha ArifNo ratings yet
- Blower Filter Dampers Ductwork Ventilation System: Function Ahu RoomDocument2 pagesBlower Filter Dampers Ductwork Ventilation System: Function Ahu RoomSyed Zulfaizzuan AljufriNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Air-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&AFrom EverandAir-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&ARating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Tensile ReportDocument18 pagesTensile ReportHafsa KhanNo ratings yet
- Activities Term 2Document6 pagesActivities Term 2studies for sundarNo ratings yet
- Compressors - Fans & Blowers TrainingDocument107 pagesCompressors - Fans & Blowers TrainingArjun Shantaram ZopeNo ratings yet
- End Plate (Simple Connection)Document10 pagesEnd Plate (Simple Connection)floi dNo ratings yet
- DCS BeamDesign Lect3Document14 pagesDCS BeamDesign Lect3Rahul ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- CDTPDocument1 pageCDTPfauzidarmaNo ratings yet
- Manual de Propietario PDF Valve PumpDocument1 pageManual de Propietario PDF Valve PumpJulio Enrique AravenaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials - Poisson's RatioDocument11 pagesMechanics of Materials - Poisson's RatioDavid Clark100% (5)
- ME 601 - Stress Analysis Assignment 1 - Review of Strength of Materials Due Date: 27/07/2015, at The Beginning of The ClassDocument6 pagesME 601 - Stress Analysis Assignment 1 - Review of Strength of Materials Due Date: 27/07/2015, at The Beginning of The Classfatty acidNo ratings yet
- Demand of Pharmaceutical Facility Functionality - Validation and Qualification of HVAC SystemDocument17 pagesDemand of Pharmaceutical Facility Functionality - Validation and Qualification of HVAC Systemraju1559405No ratings yet
- Secadores Sullair RN y OtrsoDocument268 pagesSecadores Sullair RN y Otrsoramiro alvarezNo ratings yet
- Lec-34,35-36 Effectiveness NTU MethodDocument33 pagesLec-34,35-36 Effectiveness NTU MethodMazhar aliNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument106 pagesRefrigerationRiyadh SalehNo ratings yet
- Cascade Refrigeration System "For Blood Storage"Document4 pagesCascade Refrigeration System "For Blood Storage"International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Gases: Charles' LAWDocument33 pagesBehavior of Gases: Charles' LAWJennifer MagangoNo ratings yet
- Planted ColumnDocument7 pagesPlanted Columnabdul khaderNo ratings yet
- ASTM D7760 - Permeability of TDADocument6 pagesASTM D7760 - Permeability of TDASarangi M PNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ThermodynamicsDocument104 pagesChapter 2 ThermodynamicsSaathiran Marshall100% (1)
- Cehdra 1 Obe Syllabus T2 2019 2020Document6 pagesCehdra 1 Obe Syllabus T2 2019 2020Jemina SamsonNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument37 pagesIntroductionsomsubhraNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Vars Component (Evaporator) Using Ansys SoftwareDocument22 pagesSimulation of Vars Component (Evaporator) Using Ansys SoftwareSanket BhilareNo ratings yet
- Lecture4 PDFDocument21 pagesLecture4 PDFCarlos Aparisi CanteroNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Strength of MaterialsDocument2 pagesProblem Set Strength of MaterialsRoku Dee13% (8)
- BFC21103 Assignment No. 2 PDFDocument10 pagesBFC21103 Assignment No. 2 PDFKavi Maran100% (2)
- Abstract-This Experiment Is To Examine The Time DomainDocument1 pageAbstract-This Experiment Is To Examine The Time DomainSajjad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Internal Energy and Energy Transfers 2Document39 pagesInternal Energy and Energy Transfers 2muhammadshadid4No ratings yet
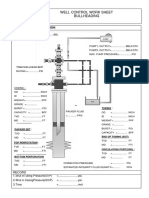
- Worksheet BullheadDocument3 pagesWorksheet BullheadHary WijayaNo ratings yet
- ME 413 - Refrigeration EngineeringDocument2 pagesME 413 - Refrigeration EngineeringOrley G FadriquelNo ratings yet
- ME 331 Thermo II Steam Cycle 2Document81 pagesME 331 Thermo II Steam Cycle 2Mimo Ammar90% (10)
- Shaft Design Question On PulleyDocument22 pagesShaft Design Question On Pulleykyaji rautNo ratings yet