Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract
Uploaded by
Chetan SharmaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract
Uploaded by
Chetan SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract
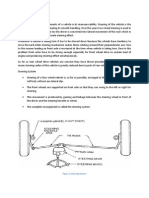
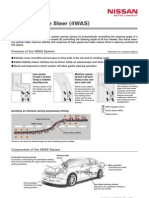
FOUR WHEEL STEERING SYSTEM Four-Wheel Steering Rear Wheels Control. For parking and low-speed maneuvers, the rear wheel steer in the opposite direction of the front wheels, allowing much sharper turns. At higher speeds, the rest wheel steer in the same direction as the front wheels. The result is more stability and less body lean during fast lane changes and turns because the front wheels dont have to drag nonsteering rear wheels onto the path. KEY WORDS:Four-Wheel Steering, 4WS, Rear Wheels Control 1. INTRODUCTION Four-wheel steering, 4WS, also called rear-wheel steering or all-wheel steering, provides a means to actively steer the rear wheels during turning maneuvers. It should not be confused with four-wheel drive in which all four wheels of a vehicle are powered. It improves handling and helps the vehicle make tighter turns. Production-built cars tend to under steer or, in few instances, over steer. If a car could automatically compensate for an under steer /over steer problem, the driver would enjoy nearly neutral steering under varying conditions. 4WS is a serious effort on the part of automotive design engineers to provide near-neutral steering. The front wheels do most of the steering. Rear wheel turning is generally limited to half during an opposite direction turn. When both the front and rear wheels steer toward the same direction, they are said to be in-phase and this produces a kind of sideways movement of the car at low speeds. When the front and rear wheels are steered in opposite direction, this is called anti-phase, counter-phase or opposite-phase and it produces a sharper, tighter turn.
2. SYSTEM 4WS Contemporary rear axles allows for coincidental steering through the influence of variation of elastic kinematic steering; rear wheels rotate, due to an influence of variation of vertical load of wheels (tilting), in the same directions front wheels. Nevertheless, such a turn of rear wheels is very small and drivers will-independent. A disadvantage of this so-called passive steering system is that it operates even when driving in straight direction when single wheel of an axle hits surface irregularity (deterioration of directional stability).New generation of active steering systems distinguishes a need of steering of rear wheels for the reason of directional stability from a need of steering of rear wheels for the reason of cornering at slow speed. Therefore, the active system means that rear wheels are possible to be turned either coincidently or non-coincidently. The increase of the maneuverability when parking the vehicle is achieved by means of disconcordant steering, meanwhile the increase of the driving stability at higher speeds is achieved through concordant steering
Advantages of 4WS:1. The vehicles cornering behavior becomes more stable and controllable at high speeds as well as on wet or slippery road surfaces. 2. The vehicles response to steering input becomes quicker and more precise throughout the vehicles entire speed range. 3. The vehicles straight-line stability at high speeds is improved. Negative effects of road irregularities and crosswinds on the vehicles stability are minimized. 4. Stability in lane changing at high speeds is improved. The vehicle is less likely to go into a spin even in situations in which the driver must make a sudden and relatively large change of direction. 5. By steering the rear wheels in the direction opposite the front wheels at low speeds, the vehicles turning circle is greatly reduced. Therefore, vehicle maneuvering on narrow roads and during parking becomes easier. The diagram showing 4WS steering system under small radius of curvature:-
You might also like
- Four Wheel Steering SystemDocument8 pagesFour Wheel Steering SystemPawan mehtaNo ratings yet
- Four-Wheel Steering ReportDocument6 pagesFour-Wheel Steering ReportMàñjü SPNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering ReportDocument8 pagesFour Wheel Steering Reportvijayan m g100% (12)
- SynopsisDocument2 pagesSynopsisPrateek RajNo ratings yet
- 4-Wheel Steering MechanismDocument15 pages4-Wheel Steering MechanismMohseen KarcheNo ratings yet
- 4 Wheel Steering SystemsDocument5 pages4 Wheel Steering SystemsVishal VsNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering ReportDocument8 pagesFour Wheel Steering ReportPradyumna Keshari NahakNo ratings yet
- Four-Wheel Steering ReportDocument21 pagesFour-Wheel Steering ReportMuralee Dharan PillaiNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Four Wheel Steering MechanismDocument50 pagesFabrication of Four Wheel Steering MechanismMechWindNaniNo ratings yet
- Four-Wheel Steering SystemDocument14 pagesFour-Wheel Steering SystemmadhurautoNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Four Wheel Steering SystemDocument14 pagesFabrication of Four Wheel Steering SystemRenju PaulNo ratings yet
- B.V'S Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of TechnologyDocument25 pagesB.V'S Jawaharlal Nehru Institute of TechnologyShaikh NihalNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering System Full Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesFour Wheel Steering System Full Seminar ReportYashwanth Raj50% (6)
- Four Wheel Steering SystemDocument14 pagesFour Wheel Steering SystemChakri KankipatiNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering System Full Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesFour Wheel Steering System Full Seminar ReportTobin NainanNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering System Full Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesFour Wheel Steering System Full Seminar ReportAman MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Four Wheel Steering System: Suraj Kumar Sumit Kumar Vikash Kumar Vivek Singh YadavDocument20 pagesFabrication of Four Wheel Steering System: Suraj Kumar Sumit Kumar Vikash Kumar Vivek Singh Yadavvishnu9746567525No ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering SystemDocument12 pagesFour Wheel Steering Systemvijayan m gNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Two Modes of Steering FinalDocument38 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Two Modes of Steering FinalS18M168 SUJAN BALAJI SNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel SteeringDocument7 pagesFour Wheel SteeringsamratsamudraguptaNo ratings yet
- 3 Mode SteeringDocument30 pages3 Mode SteeringAnonymous j0aO95fgNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON " 4WS " System: Neeraj Gautam (07ME026)Document27 pagesPresentation ON " 4WS " System: Neeraj Gautam (07ME026)Neeraj GautamNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering SystemDocument9 pagesFour Wheel Steering SystemSai AbhinavNo ratings yet
- Done By: Ahmad Rafiq: Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentDocument6 pagesDone By: Ahmad Rafiq: Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DepartmentahmadNo ratings yet
- Development of Four Wheel Steering System For A Car: K. Lohith, Dr. S. R. Shankapal, M. H. Monish GowdaDocument8 pagesDevelopment of Four Wheel Steering System For A Car: K. Lohith, Dr. S. R. Shankapal, M. H. Monish GowdaGaurav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Steering System FinalDocument25 pagesSteering System Final05 namrata pawarNo ratings yet
- 360 Degree Load CarrierDocument28 pages360 Degree Load CarrierTanviNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel SteeringDocument8 pagesFour Wheel SteeringKesav Rajan0% (1)
- ACEDocument22 pagesACEVijay VinniNo ratings yet
- Screenshot - 2017 03 18 07 22 35Document2 pagesScreenshot - 2017 03 18 07 22 35Srêyas Raj PkNo ratings yet
- Steering Mechanism With Zero Turning RadiusDocument19 pagesSteering Mechanism With Zero Turning RadiusAbhay RanjanNo ratings yet
- 4was enDocument1 page4was endarkman2No ratings yet
- Integral Steering SystemDocument5 pagesIntegral Steering SystemDhanushka MarasingheNo ratings yet
- Suspension and Steering Systems PDFDocument15 pagesSuspension and Steering Systems PDFVijay SotaniNo ratings yet
- Good Morning .?: Presentation On Vehicle Steering Systems by Pari, D.J & K.CDocument29 pagesGood Morning .?: Presentation On Vehicle Steering Systems by Pari, D.J & K.CSrikar ChinmayaNo ratings yet
- SteeringDocument24 pagesSteeringapi-19890903No ratings yet
- SteeringDocument27 pagesSteeringSHARATH.R.SHETTIGARNo ratings yet
- Ninty Degree SteeringDocument48 pagesNinty Degree Steeringparas bhogulkarNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Four Wheel Steering System With Accident Avoidance Brake SystemDocument9 pagesFabrication of Four Wheel Steering System With Accident Avoidance Brake SystemganeshNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering SystemDocument15 pagesFour Wheel Steering Systemjatinshukla4310% (1)
- Fourwheel Steering SystemDocument11 pagesFourwheel Steering SystemelangandhiNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering SystemDocument26 pagesFour Wheel Steering SystemRavindra Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Steering System DocumentDocument20 pagesFour Wheel Steering System DocumentBala comfortNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Four Wheels SteeringDocument74 pagesMechanical Four Wheels Steeringvijayan m g91% (22)
- Independent Suspension SystemDocument38 pagesIndependent Suspension Systemzankar kiran100% (1)
- TO Automotive Steering SystemDocument22 pagesTO Automotive Steering SystemJ Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Front Wheel Stearing Moveable HeadlightsDocument42 pagesFront Wheel Stearing Moveable HeadlightsVinoth RamNo ratings yet
- Project Presentation Four Wheel SterringDocument33 pagesProject Presentation Four Wheel Sterringvijayan m g100% (3)
- Automotive Steering SystemDocument31 pagesAutomotive Steering SystemTanzim Rafat AyonNo ratings yet
- Bma4723 Vehicle Dynamics Chap 7Document63 pagesBma4723 Vehicle Dynamics Chap 7Fu HongNo ratings yet
- Steering SystemDocument12 pagesSteering Systemmayur_lanjewarNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel Drive-SynopsDocument8 pagesFour Wheel Drive-SynopsManoj MalikNo ratings yet
- Four Wheels SteeringDocument19 pagesFour Wheels SteeringBharathNaikPanjaNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel, Three Mode Steering System - 3Document9 pagesFour Wheel, Three Mode Steering System - 3Tejzas Parab100% (1)
- Study of Four Wheel Steering Mechanism: JournalDocument4 pagesStudy of Four Wheel Steering Mechanism: JournalSiva HariNo ratings yet
- 3 Mode Steering System For 4 WheelersDocument56 pages3 Mode Steering System For 4 WheelersGokul ManikantaNo ratings yet
- Four Wheel SteeringDocument5 pagesFour Wheel SteeringMectrosoft Creative technologyNo ratings yet