Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab+3+ +Physical+and+Chemical+Properties
Uploaded by
linzelOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab+3+ +Physical+and+Chemical+Properties
Uploaded by
linzelCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 3 - Physical and Chemical Properties of Elements
Timeline: 2 classes
Introduction :
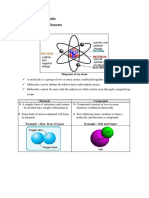
By this time you are expected to be able to draw the Bohr-Rutherford diagram upto
calcium and use the diagram to predict the number and arrangement of outermost
electrons. Similarly, you should also be able to use your diagram to predict the electron
configuration [using the 2,8,8 or s,p,d,f method].
By examining the electron configuration we can gain insight into some periodic properties
of the table of the periodic table. Physical properties tend to fall into three categories:
properties of metals, properties of semi-metals [metalloids] and properties of the
non-metals.
Task 1 - Physical properties and changes
Your first task is composed of a number of sections. The first builds on previous
knowledge. You should have a general idea of some physical properties. However, I
want you to go beyond what you know and find other physical properties you are not -o r
less- familiar with. Do some quick research and find other, easily measurable properties
you can investigate in class. Secondly, using any available equipment [with the teachers
permission] collect data as to which elements and compounds have the physical
properties you know or have learned. Create a data table in your wiki pages to record
and organize your results.
Summary: Time budget
background research on physical properties [h omewor k/ver y smal l cl ass ti me]
gather qualitative physical evidence on the substances provided [i n cl ass]
record and organize your data [i n cl ass an d h omewor k]
conclude with general classification of substances into categories
[metal, non-metal, metalloid, ionic, covalent]
I KNOW!, but research the ionic and covalent anyway!
Task 2 - C hemical properties and changes
Similarly, you have some previous knowledge of chemical properties. Once again, I want
you to go beyond this knowledge and investigate other chemical properties. Many of
these we will not be able to directly investigate to collect evidence. There are some very
basic but informative properties we CAN investigate. Lastly, I want you to research a nd
find the splint tests that allow us to differentiate between H 2 , O 2 and CO 2 gases. When
you do a few of these tests you should collect the gas and test for the different gases.
use pH paper to test the water pH after the reaction. [You can do this for the acids
if you think you'll see a change]
use a thermometer to test for temperature changes
For the following table, describe the level of reaction on a scale of 1 to 5 .
One can describe very little reaction, five very reactive.
the HCl(aq) is 2M and 6M. You will learn what the M refers to soon enough.
In many of the combinations below it will not be possible to collect the gas easily o r
safely therfore we will predict the gas produced using the following common types of
reactions.
Use these common reaction types to predict the gas produced [if any]
metals and acid react to form a salt [an ionic compound] and hydrogen
gas.
metal acid salt hydrogen gas
Mg (s) + HCl (aq) ↔ MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
some metals and water [i f th e metal i s r eacti ve en ou gh ] react to form hydroxide and
hydrogen gas
metal water hydroxide hydrogen gas
Li(s) + H2 O (l) ↔ LiOH(aq) + H2 (g)
carbonate salts and acid react to form an ionic salt, water and carbon
dioxide gas
carbonate salt acid salt water carbon
dioxide
Na 2 CO 3 (s) + HCl (aq) ↔ NaCl (aq) + H2 O (l) + CO 2 (g)
Attempt to classify the elements in terms of their reactivity
Results:
Table 1 - Qualitative evidence for chemical changes/reactions.
Element cold hot dilute [HC l](aq) **gas C onduct Temp. pH
water water HC l produced electricity change Test
(aq)
Lithiu m dem o‡ dem o ‡
n/a n/a
Sodiu m dem o ‡ dem o ‡
n/a n/a
Potassiu m dem o ‡ dem o ‡
n/a n/a
Magnesiu m *ch eck
Calciu m
Alu minu m
Copper
Zinc
Iron
Lead
Carbon
Su lpher
Calciu m *ch eck
carbonate
**th e gas pr odu ced can be tested u si n g a spl i n t test. ‡du e to th e r eacti vi ty ...i ts dan ger ou s.
CO2 gas wi l l exti n gu i sh a bu r n i n g spl i n t
H 2 gas wi l l ' pop' wh en l i t by a bu r n i n g spl i n t
O2 gas wi l l r ei gn i te a gl owi n g, exti n gu i sh ed spl i n t.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- SNC1D - Classification of MatterDocument1 pageSNC1D - Classification of MatterlinzelNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- SNC1D - Lab - Chemical ChangesDocument2 pagesSNC1D - Lab - Chemical ChangeslinzelNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Unconventional Oil: Scraping The Bottom of The BarrelDocument52 pagesUnconventional Oil: Scraping The Bottom of The BarrelRyan Van LenningNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Snc1d Quiz OneDocument1 pageSnc1d Quiz OnelinzelNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The PH ScaleDocument2 pagesThe PH ScalelinzelNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grant Proposal of Experimental DesignDocument1 pageGrant Proposal of Experimental DesignlinzelNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Intro To LightDocument8 pagesIntro To LightlinzelNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Activity+2+ +spectrosDocument4 pagesActivity+2+ +spectroslinzelNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- AstroDocument19 pagesAstrolinzelNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Science 1112 CurrDocument178 pagesScience 1112 Curraptureinc100% (1)
- The Formation and Aging of StarsDocument1 pageThe Formation and Aging of StarslinzelNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- WMAP UniverseDocument37 pagesWMAP UniverselinzelNo ratings yet
- Collecting Evidence From SpaceDocument2 pagesCollecting Evidence From SpacelinzelNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Gas ChemistryDocument12 pagesGas ChemistrylinzelNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- IPCC 4th Report Technical SummaryDocument74 pagesIPCC 4th Report Technical Summarylinzel100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Lewis For 3UDocument5 pagesLewis For 3Ulinzel100% (1)
- Lewis and VSEPRDocument18 pagesLewis and VSEPRlinzel100% (14)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Cori CycleDocument14 pagesThe Cori Cyclelinzel100% (7)
- Preparing For The Next Pandemic - Foreign Affiars July 05Document8 pagesPreparing For The Next Pandemic - Foreign Affiars July 05linzelNo ratings yet
- Periodic Ionization and ElectronegativityDocument2 pagesPeriodic Ionization and Electronegativitylinzel100% (5)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Climate Change Holdren LectureDocument82 pagesClimate Change Holdren LecturelinzelNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Summary Related With The Climate ChangeDocument18 pagesSummary Related With The Climate ChangeAratz HernandezNo ratings yet
- Bird Flue Biology - Effect Measure Blog ArticlesDocument15 pagesBird Flue Biology - Effect Measure Blog ArticleslinzelNo ratings yet
- Bird Flue Biology - Effect Measure Blog ArticlesDocument15 pagesBird Flue Biology - Effect Measure Blog ArticleslinzelNo ratings yet
- Nishant Gupta, D-122, Prashant Vihar, Rohini, Delhi-85 Contact: 9953168795, 9268789880Document37 pagesNishant Gupta, D-122, Prashant Vihar, Rohini, Delhi-85 Contact: 9953168795, 9268789880Neeraj SinghNo ratings yet
- 08 Worked Examples PDFDocument30 pages08 Worked Examples PDFlheanne manzulNo ratings yet
- CBRC Gen - EdDocument57 pagesCBRC Gen - EdJAN MARK CHANNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- CLMD4A ScieG7Document40 pagesCLMD4A ScieG7Ronan Thaddeus Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Bonding (p1)Document22 pagesBonding (p1)HashimNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals Revision NotesDocument22 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals Revision Notesrohan thakurNo ratings yet
- CBSE Science Notes - Class 10Document91 pagesCBSE Science Notes - Class 10dinesh_kp764783% (6)
- HydrogenDocument12 pagesHydrogenGayatri Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Workbook by Saya Minn ThantDocument104 pagesChemistry Workbook by Saya Minn ThantMinn ThantNo ratings yet
- 05 - SPSF1 08 B6Document19 pages05 - SPSF1 08 B6Zulkifli Yusof100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non - MetalsDocument15 pagesChapter 3 Metals and Non - MetalsPrabhakar DasNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument25 pagesMatterMarvin De JonggoyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument12 pagesChemical Formulae and EquationKiTTyNo ratings yet
- Practice Set in Inorganic ChemistryDocument3 pagesPractice Set in Inorganic ChemistryKalachuchiNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Properties of Period 3 OxidesDocument6 pagesProperties of Period 3 OxidesCHEE HONG CHANNo ratings yet
- Combined Science Pack 2016 PDFDocument82 pagesCombined Science Pack 2016 PDFShreya LankeswaranNo ratings yet
- ALLEN BioChem Test Series PapersDocument252 pagesALLEN BioChem Test Series PapersViraj Jain100% (1)
- Geochemistry IntroductionDocument25 pagesGeochemistry Introductionkristiano97100% (1)
- Chemistry End of Chapter QuestionsDocument3 pagesChemistry End of Chapter QuestionsHershil SawlaniNo ratings yet
- The Atoms Family Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesThe Atoms Family Cheat Sheet: by VianyellutlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Metals and Non-Metals MCQsDocument13 pagesChapter-3 Metals and Non-Metals MCQsfagstdjdNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Science - Materials - Metals and Non-MetalsDocument6 pagesClass 8 - Science - Materials - Metals and Non-MetalsAyaan KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 Chemistry NotesDocument9 pagesCh-3 Chemistry Noteskartikaryan9250No ratings yet
- Eoy Final Exam Study GuideDocument14 pagesEoy Final Exam Study Guideapi-324757649No ratings yet
- Class X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesDocument14 pagesClass X - Science (Chemistry) Metals and Non-Metals: Chapter NotesSuraj Luwangcha100% (1)
- Chemis - Writing Chemical EquationDocument11 pagesChemis - Writing Chemical EquationZahra PriyonoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Is Matter Around Us Pure: What Is A Mixture?Document19 pagesChapter-2 Is Matter Around Us Pure: What Is A Mixture?Prabha SinghNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Chapter 6 Periodic TableDocument6 pagesForm 1 Chapter 6 Periodic Tableelizabeth ellsaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MCQ2Document28 pagesChemistry MCQ2SABARI SRINIVAS ANo ratings yet
- 8F Quick Check QuizDocument2 pages8F Quick Check QuizClaire LNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet