Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deepwater Oil & Gas Facilities
Uploaded by
Zack LeeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deepwater Oil & Gas Facilities
Uploaded by
Zack LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering
Deepwater Oil & Gas Facilities
6th China-US OGIF, New Orleans, USA June 28 29, 2005 200562829
Bill Soester V.P. Engineering J. Ray McDermott
Engineering
Definitions of Deepwater
Relative, change as technologies progress 10 Years ago
Deepwater: >300 meters
Today
Deepwater: > 500 meters Ultra-deepwater: > 1,500 meters
Water Depth Records ( 2004)
Production dry tree: 1,710 m, Devils Tower Spar, GOM Production wet tree: 1,920 m, NaKika Semi, GOM Drilling: 3,051 Meters, Toledo #1, GOM
Engineering
Engineering
Deepwater Development Solutions
Advances in Deep Water Production Capability
2800 2600 2400 2200 Water Depth in Meter 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0
2004
1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010
Engineering
Deepwater Development Solutions
Relative Total Cost
TLP
Spar and Semi
C. Tower
1300 ft
2000 ft
4000 ft
6000 ft
8000 ft
Water Depth
Engineering
Deepwater Development Solutions
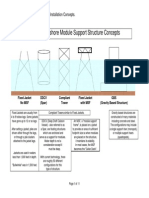
Solutions for Different Water Depths
3500 3000 Water Depth (meter) 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0
Conv. Fixed Jacket
Compliant Tower
TLP
Semi-sub
Spar
FPSO
Engineering
Deepwater Production Facilities for Dry Trees
Compliant Tower
Tension Leg Platform (TLP)
Spar
Engineering
Deepwater Production Facilities for Wet Trees
Floating Production, Storage and Offloading (FPSO)
Semi-submersible (Semi)
Engineering
Inputs to the FPSO vs. non-FPSO Decision
Access to Pipeline Grid or shore Oil Export Site Political or Economical factors Life of Field Dry Tree vs. Wet Tree Reservoir Development Plan Tolerance to Production Down Time
Engineering
Factors in Choosing between Non-FPSO Solutions (Spars, Towers, TLPs, Semis)
Water Depth Environment Conditions Initial vs. future Topside Weight No. of Risers Drilling Program Access to Wells: Wet vs. Dry Installation Capabilities Initial vs. Total Life Cycle Cost
Engineering
Hybrid Solution Obtaining the Benefits of both Types of Facilities
TLP or Spar
Drilling Dry Trees Easy Intervention and
FPSO
Processing Storage Offloading
Engineering
Compliant Tower
Design:
Tower Slender jacket Compliant designed to avoid resonance with large waves
Application most cost effective in
300 to 670 m.
Advantages:
Dry tree Robust relative to payload changes Less steel tonnages required (in the above depth range) Simpler, conventional fabrication Installation flexibility
Disadvantages :
Limited water depth range
Engineering
Compliant Tower Tallest Man Made Structure Compliant Tower Tallest Man Made Structure
Engineering
Semi-submersible
Design vertical columns supporting
topsides and supported on large pontoons, anchored to the seafloor with spread mooring lines.
Applicable W.D. 80 m to 2,500 m Advantages:
Large number of flexible risers possible Quayside Topsides-hull integration
Disadvantages:
Wet tree only high maintenance cost Fatigue motion not friendly to risers Sensitive to deck payload
Engineering
Tension Leg Platform (TLP)
Design Similar to a semi-
submersible but anchored to the seafloor with vertical tendons. from 600 m to 1,200 m
Application - more cost effective Advantages:
Dry tree Friendly to SCR Quayside topsides-hull integration Low maintenance cost Sensitive to deck payload change Active hull system Not friendly to offset drilling Tendon fatigue
Disadvantages:
Engineering
Spar
Design Large vertical column
supporting topsides and connected below to the ballast tank with a truss section. A spread mooring system is used for station-keeping.
Application 550 m to 3,000 m Advantages:
Superior stability Dry trees Friendly to SCR Accommodates payload changes Friendly to offset drilling Passive hull system Low maintenance cost Topside lift at installation site Large derrick barge required for topsides installation
Disadvantages:
Engineering
Deepwater Technology Suppliers
Compliant Tower J. Ray McDermott Wood Group TLP J. Ray McDermott (JV with Keppel) MODEC SBM
Aker-Kvaerner
Spar J. Ray McDermott Technip FPSO Various Semi-submersible Various
Engineering
The Industrys Deepwater Experience
Compliant Tower 3 each Spar 13 TLP 21 Semi (production type) 43 FPSO 119
Engineering
The Future
Improved design tools providing lower weight and less expensive hulls Improved hull shapes greater motion stability and payload capacity Improved deepwater riser technology Synthetic mooring lines for ultra deep water
Engineering
Conclusion
China is proceeding with deepwater exploration Deepwater solutions are available for Chinas O&G development plans, from 300 meters to 3000 meters Cooperation between China and the deepwater technology contractors makes good business sense
Thank You
You might also like
- Design Considerations Multipurpose Jackup Spudcans - Gusto MSCDocument31 pagesDesign Considerations Multipurpose Jackup Spudcans - Gusto MSCOffshore JackupNo ratings yet
- Design of Offshore Structures PDFDocument18 pagesDesign of Offshore Structures PDFKenzari FouadNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Lecture 3 (Dead and Wind Loads)Document10 pagesModule 1 - Lecture 3 (Dead and Wind Loads)SuryaNo ratings yet
- CD CM Overrides For Report Conductor Shielding FactorDocument2 pagesCD CM Overrides For Report Conductor Shielding FactorRamesh SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Calculation and Analysis of Sea-Fastening Support and Welding Strength of Topside ModuleDocument8 pagesCalculation and Analysis of Sea-Fastening Support and Welding Strength of Topside Modulepartha.fernandoNo ratings yet
- Reliability of Jack-Up Platforms Against OverturningDocument27 pagesReliability of Jack-Up Platforms Against OverturningAbdulrahman100% (1)
- Frequency Selection For Transfer Function (PTTEP)Document32 pagesFrequency Selection For Transfer Function (PTTEP)Pop JiNo ratings yet
- Bas Joustra - Master Thesis ReportDocument199 pagesBas Joustra - Master Thesis ReportSean ChoiNo ratings yet
- Inplace Analysis Lifting Analysis Transportation Analysis Seafastening Analysis Fatigue Analysis Miscellaneous Design ChecksDocument10 pagesInplace Analysis Lifting Analysis Transportation Analysis Seafastening Analysis Fatigue Analysis Miscellaneous Design ChecksKenaia Adeleye0% (1)
- Vessel With Stern On Quay - A Simplified Method For Mooring Design - TheNavalArchDocument11 pagesVessel With Stern On Quay - A Simplified Method For Mooring Design - TheNavalArchFederico Babich0% (1)
- Module 1a - IntroductionDocument71 pagesModule 1a - Introductionyash.nth19No ratings yet
- API WSD Punch CodeCheckDocument7 pagesAPI WSD Punch CodeCheckKhải TrươngNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of Oil Platform in CaDocument80 pagesConceptual Design of Oil Platform in Cahoangduy7696No ratings yet
- Case Studies For Evaluating Hydrodynamic Motion Responses Using MOSESDocument26 pagesCase Studies For Evaluating Hydrodynamic Motion Responses Using MOSESATLURI SATYA SRINIVAS oe13m002No ratings yet
- Master Thesis Per VatsvagDocument141 pagesMaster Thesis Per VatsvagMoe LattNo ratings yet
- PLEM Pile Drivability PDFDocument49 pagesPLEM Pile Drivability PDFTharach JanesuapasaereeNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Methods PDFDocument91 pagesFatigue Methods PDFGodwin100% (1)
- ABS Jacket Analysis ProcedureDocument8 pagesABS Jacket Analysis ProcedureJolly Jack100% (1)
- Fatigue AnalysisDocument2 pagesFatigue AnalysisZulham MochtarNo ratings yet
- IGSDC-2014 FoundationsforOffshoreDocument34 pagesIGSDC-2014 FoundationsforOffshoreanilsmg09100% (1)
- 00007-310-SJ-RP-0030 Structural Computer Model Production JacketDocument63 pages00007-310-SJ-RP-0030 Structural Computer Model Production JacketneelcorNo ratings yet
- 14 - Flexible Pipe InstallationDocument28 pages14 - Flexible Pipe InstallationRaphael Owusu kyerematengNo ratings yet
- ABS Fatigue Life Assessment 2014Document1 pageABS Fatigue Life Assessment 2014Fandy SipataNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - InPEX Masela FLNG Korea-Batam (Calm)Document5 pagesMathcad - InPEX Masela FLNG Korea-Batam (Calm)fahmyits100% (1)
- Steel Catenary RisersDocument29 pagesSteel Catenary RisersZadeh NormanNo ratings yet
- Great Waters - Business Track Record 2012-16Document16 pagesGreat Waters - Business Track Record 2012-16KK NairNo ratings yet
- Offshore Jacket Inplace Analysis For Beginners With Sacs 1614129844Document63 pagesOffshore Jacket Inplace Analysis For Beginners With Sacs 1614129844Sholeh Khuddin A MadridistaNo ratings yet
- Conductor Analysis SpreadsheetDocument5 pagesConductor Analysis SpreadsheetzapspazNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments of FAST For Modelling Offshore Wind TurbinesDocument11 pagesRecent Developments of FAST For Modelling Offshore Wind TurbinesJACKNo ratings yet
- Check List For Jacket/Topsides Transportation AnalysisDocument2 pagesCheck List For Jacket/Topsides Transportation AnalysisRamesh SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Design of Offshore PlatformsDocument37 pagesDesign of Offshore PlatformsAbdullah OthmanNo ratings yet
- Skidding For Jacket PlatformDocument10 pagesSkidding For Jacket PlatformAndra PadaNo ratings yet
- Offshore Platforms Design OverviewDocument12 pagesOffshore Platforms Design OverviewΈνκινουαν Κόγκ ΑδάμουNo ratings yet
- PLAXIS 3D2017 Tutorial Lesson 03 Loading of Suction PileDocument10 pagesPLAXIS 3D2017 Tutorial Lesson 03 Loading of Suction PileRayodcNo ratings yet
- Buoyed Up: Proven in The Past, Prepared For The FutureDocument10 pagesBuoyed Up: Proven in The Past, Prepared For The FutureantidemosNo ratings yet
- Esdep Offshore Structures General IntroductionDocument187 pagesEsdep Offshore Structures General Introductiondfal13No ratings yet
- Ageing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityFrom EverandAgeing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityNo ratings yet
- Design Shear WallDocument26 pagesDesign Shear WallCaoTrungThành100% (2)
- Cms 830 03 GL 70021 Jacket Foundation DesignDocument23 pagesCms 830 03 GL 70021 Jacket Foundation DesignRajesh DodejaNo ratings yet
- Anchor Penetration: Pumping Out WaterDocument12 pagesAnchor Penetration: Pumping Out Watergamidi67No ratings yet
- Fpso Design and Conversion Practice: OGP Conference London, March 17, 2003Document30 pagesFpso Design and Conversion Practice: OGP Conference London, March 17, 2003Aleksandr FilonenkoNo ratings yet
- Wave Impact Reduction of Planing BoatsDocument14 pagesWave Impact Reduction of Planing BoatshaujesNo ratings yet
- GoM Offshore Structures Design CriteriaDocument32 pagesGoM Offshore Structures Design CriteriaDonald.KNo ratings yet
- 04) ZEEPod & Other Project ExperienceDocument72 pages04) ZEEPod & Other Project Experiencebapaobao100% (1)
- Seismic Design For Concrete Cast in PlaceDocument41 pagesSeismic Design For Concrete Cast in PlacejazmontzNo ratings yet
- Subsea StructureDocument2 pagesSubsea StructureobumuyaemesiNo ratings yet
- Offshore Structures MethodDocument24 pagesOffshore Structures MethodLarasita PulunganNo ratings yet
- 5020-SPE ATW-Dry Tree Vs Wet Tree Considerations For Deepwater Field DevelopmentDocument23 pages5020-SPE ATW-Dry Tree Vs Wet Tree Considerations For Deepwater Field DevelopmentHoang Truong MinhNo ratings yet
- Set-Up Effect of Cohesive Soils in Pile Capacity - SvinkinDocument7 pagesSet-Up Effect of Cohesive Soils in Pile Capacity - SvinkinkyrheeNo ratings yet
- Balmoral Group HandbookDocument172 pagesBalmoral Group HandbookneelcorNo ratings yet
- Waves on Beaches and Resulting Sediment Transport: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar, Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, and the Coastal Engineering Research Center, U. S. Army, at Madison, October 11–13, 1971From EverandWaves on Beaches and Resulting Sediment Transport: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar, Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, and the Coastal Engineering Research Center, U. S. Army, at Madison, October 11–13, 1971R. E. MeyerNo ratings yet
- Lifting Analysis Preview)Document4 pagesLifting Analysis Preview)Faisal AjaNo ratings yet
- Cap08&09 Ensaios OffshoreDocument50 pagesCap08&09 Ensaios OffshoreThalles Giangiarulo de AguiarNo ratings yet
- Offshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsFrom EverandOffshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Cpc-Clpp-L-E-0001 CLPP Iws DatasheetDocument52 pagesCpc-Clpp-L-E-0001 CLPP Iws DatasheetNguyen Ninh BinhNo ratings yet
- (DNV) Det Norske Veritas - 2005 - Material Risk - Ageing Offshore InstallationsDocument66 pages(DNV) Det Norske Veritas - 2005 - Material Risk - Ageing Offshore InstallationsKaroline Neumann100% (1)
- Internship Report-Sandhya DixitDocument58 pagesInternship Report-Sandhya DixitSandhya Dixit100% (1)
- Evolution of Pile Shaft Capacity Over Time in Mari PDFDocument15 pagesEvolution of Pile Shaft Capacity Over Time in Mari PDFRazvan-Ionut SimionNo ratings yet
- Allianz Middle East Ship Mangament LLC: "WWE 210" 210ft Positioning (Crane) Barge 4PMDocument2 pagesAllianz Middle East Ship Mangament LLC: "WWE 210" 210ft Positioning (Crane) Barge 4PMCyril J PadiyathNo ratings yet
- 6.offshore ConceptsDocument0 pages6.offshore Conceptshaidar1992No ratings yet
- Exam Solution 2009-10gDocument9 pagesExam Solution 2009-10gConstAntinosNo ratings yet
- Offshore PlatformsDocument46 pagesOffshore PlatformsmasoudNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Analysis Methods For Reinforced Concrete Buildings With Shear WallsDocument8 pagesNonlinear Analysis Methods For Reinforced Concrete Buildings With Shear Wallsakif-benzer-6764No ratings yet
- AASHTO LRFD Bridge Construction Specifications With 2010 and 2011 Interim Revisions PDFDocument658 pagesAASHTO LRFD Bridge Construction Specifications With 2010 and 2011 Interim Revisions PDFSergio Alejandro AyalaNo ratings yet
- Use of Thermal Analysis Techniques For Evaluation of The Stability and Chemical Properties of Papaya Biodiesel (Carica Papaya L.) at Low TemperaturesDocument6 pagesUse of Thermal Analysis Techniques For Evaluation of The Stability and Chemical Properties of Papaya Biodiesel (Carica Papaya L.) at Low TemperaturesSergio Alejandro AyalaNo ratings yet
- Coupling of Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics and Finite Element Method ForDocument10 pagesCoupling of Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics and Finite Element Method ForSergio Alejandro AyalaNo ratings yet