Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Question Papers
Uploaded by
khanheenakhanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Question Papers
Uploaded by
khanheenakhanCopyright:
Available Formats
OPERATIONS RESEARCH JNTU previous years question papers
Time: 3 hours Max. Marks.80 Answer any Five questions All questions carry equal marks 1. Solve the following problem by Big M method Maximize Z = x1 + 2x2 +3x3 x4 Subject to x1 + 2x2 +3x3 = 15 2x1 + x2 +5x3 = 20 x1 + 2x2 +x3 + x4 = 10 x1, x2, x3, x4 = 0 [16]
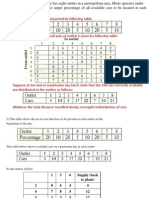
2. Consider the following transportation problem To From 1 2 3 Supply 1 5 1 7 10 2 6 4 6 80 3 3 2 5 15 Demand 75 20 50 If the penalty cost for every unsatisfied demand unit is Rs 5, 3 and 2 for destinations 1, 2 and 3 respectively, find the optimal solution. [16]
3. An air line that operates 7 days a week has time-table as shown below. Crew must have a minimum layover of 5 hours between flights. Obtain the pairing of flights that minimizes layover time away from home. For each pair also mention the town where the crew should be based.[16] Delhi - Jaipur Jaipur - Delhi Flight No Dept. Arrival Flight No Dept. Arrival 1 7.00 a.m 8.00 a.m. 101 8.00 a.m. 9.15 a.m. 2 8.00 a.m 9.00 a.m. 102 8.30 a.m 9.45 a.m. 3 1.30 p.m 2.30 p.m. 103 12 Noon 1.15 p.m. 4 6.30 p.m 7.30 p.m. 104 5.30 p.m 6.45 p.m.
4.a. A bank has two counters for withdrawals. Counter I handles withdrawals of value less than Rs 1000 and counter II Rs 1000 and above. Analysis of service time shows exponential distribution with mean service time of 6 minutes per customer. Arrival of customers follow Poisson distribution with mean 8 per hour for counter I and 5 per hour for counter II. (i) What are the average waiting times per customer of each counter? (ii) If each counter could handle all withdrawals irrespective of their value, how would the average waiting time change? b. At what average rate must a clerk at a super market work in order to ensure a probability of 0.9 that the customer will not have to wait longer than 12 minutes? It is assumed that there is only one counter, to which customers arrive in a Poisson fashion at an average rate of 15 per hour. The
length of service by the clerk has an exponential distribution. [8+8]
5. The annual demand for a product is Rs 500 units. The cost of storage per year is 10% of the unit cost. The ordering cost is Rs 180 per each order. The unit cost depends upon the amount ordered. The range of amount ordered and unit cost price is as follows Range of amount ordered Unit Cost in Rs 0 = q < 500 25 500 = q < 1500 24 1500 = q < 3000 23 3000 = q < 8 22 Find the optimal order quantity and the inventory cost.
6. A and B play a game in which each has three coins, a 5 paise, a 10 paise and a 20 paise. Each selects a coin without the knowledge of the others choice. If the sum of the coins thus selected by them is an odd amount, A wins Bs coin. If the sum is even B wins A coin. Find the best strategy for each player and the value of the game. [16]
7. A group of process plants in an oil refinery are fitted with valves. Over a period of time the failure pattern of these 400 valves has been observed and it is as follows Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Number of valves failing 8 20 48 104 120 56 32 12 It costs Rs 100/- to replace each valve individually. If all the valves are replaced at a time it costs Rs 50/- per valve. The maintenance department is considering the following two replacement policies: i. Replace all valves simultaneously at fixed intervals, in addition to replacing valves as and when they fail ii. Replace valves as and when they fail. Suggest the optimal replacement policy. [16]
8.a. Explain Bellmans Principle of optimality. b. Discuss the advantages and limitations of Simulation.
2 OPERATIONS RESEARCH JNTU previous years question papers Time: 3 hours Max. Marks.80 Answer any Five questions
All questions carry equal marks 1. Solve the following problem by Big M method Maximize Z = x1 + 2x2 +3x3 x4 Subject to x1 + 2x2 +3x3 = 15 2x1 + x2 +5x3 = 20 x1 + 2x2 +x3 + x4 = 10 x1, x2, x3, x4 = 0. [16]
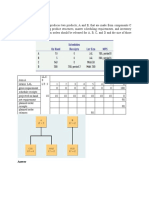
2. A product is produced by four factories A,B,C and D. The unit production costs in them are Rs 2, Rs 3, Re 1 and Rs 5 respectively. Their production capacities are, factory A 50 units, B 70 units, C 30 units and D 50 units. These factories supply the product to four stores, demands of which are 25, 35,105 and 20 units respectively. Unit transport cost in rupees from each factory to each store is given in the table below Stores 1234 A 2 4 6 11 B 10 8 7 5 C 13 3 9 12 Factories D4683 Determine the extent of deliveries from each of the factories to each of the stores so that the total production and transportation cost is minimum. [16]
3.a. Solve the following traveling salesman problem Cities 1 2 3 4 5 1 -- 16 18 13 20 2 21 -- 16 27 14 3 12 14 -- 15 21 4 11 18 19 -- 21 5 16 14 17 12 -b. Four operators O1, O2, O3 and O4 are available to a manager who has to get 4 jobs J1, J2, J3, and J4 done by assigning one job to each operator. The time needed by different operators for different jobs is given in the matrix below. How should the manager assign jobs so that the total time needed for all four jobs is minimum? [16] J1 J2 J3 J4 O1 12 10 10 8 O2 14 12 15 11 O3 6 10 16 4 O4 8 10 9 7
4. A company is planning to replace an equipment whose purchase cost is Rs 1, 00,000. The operating and maintenance cost of the equipment during its first year of operation is Rs 10000 and it increases by Rs 2000 every year thereafter. The resale value of the equipment at the end of the
first year of its operation is Rs 65000 and it decreases by Rs 10,000 every year there after. When should the equipment be replaced if: i. time value of money is ignored ii. if discount rate is 12%.
5.a. Explain principle of dominance with an example. b. Solve the following game graphically. [8+8] Player B I II III IV V Player A I 4 2 5 -6 6 II 7 -9 7 4 8
6a. Explain the characteristics of a queuing system. b. A repairman is to be hired to repair machines which breakdown at an average rate of 3 per hour. The breakdowns follow poisson distribution. Non-productive time of a machine is considered to cost Rs 10 per hour. Two repairmen have been interviewed one is slow but cheap, while the other is fast but expensive. The slow repairman charges Rs 5 per hour and repairs machines at the rate of 4 per hour. The fast repairman charges Rs 7 per hour and he repairs machines at an average rate of 6 per hour. Which repairman should be hired? [8+8]
7. An electronic equipment contains 500 resistors. When any resistor fails, it is replaced. The cost of replacing a resistor individually is Rs 20. If all the resistors are replaced at the same time, the cost per resistor is Rs 5 . The percentage surviving S(i) at the end of month i is given in the table Month i 0 1 2 3 4 5 S ( i) 100 90 75 55 30 0 What is the optimum replacement plan? [16]
8.a. Explain the characteristics and applications of dynamic programming. b. Write short notes on simulation languages
View the Next OPERATIONS RESEARCH Question Paper
3 OPERATIONS RESEARCH JNTU previous years question papers
Time: 3 hours Max. Marks.80
Answer any Five questions All questions carry equal marks 1. Obtain the dual of the following primal problem and solve it. Minimize z = x1 3 x2 2 x3 Subject to 3x1 x2 + 2x3 = 7 2x1 4x2 = 12 - 4 x1 +3x2 + 8x3 = 10 x1, x2 = 0 , x3 is unrestricted [16]
2. Solve the following transportation problem. The elements in the matrix are the cost of transportation in Rupees per unit transported. [16] Warehouses Factories A B C D E Availability W 4 3 1 2 6 40 X 5 2 3 4 5 30 Y 3 5 6 3 2 20 Z 2 4 4 5 3 10 Requirement 30 30 15 20 5
3. A Company has four territories open and four salesmen available for assignment. The territories are not equally rich in their sales potential; it is estimated that a typical salesman operating in each territory would bring in the following annual sales: Territory I II III IV Annual Sales ( Rs) 60,000 50,000 40,000 30,000 The four salesmen are also considered to differ in ability; it is estimated that working under the same conditions, their yearly sales would be proportionately as follows: [16] Salesman A B C D Proportion 7 5 5 4 Assign the salesmen to the territory if the criterion is maximum expected sales.
4. For M/M/1 : 8 /FCFS Derive an expression for: (i) Average number of customers in the system (ii) Probability of having n customers in the system (iii) Average queue length (iv) Average waiting time in the system [16]
5. An engineering company is offered two types of material handling equipment A and B. A is priced at Rs 60,000/- including cost of installation, and the costs for operation and maintenance are estimated to be Rs 10,000/- for each of the first five years, increasing by Rs 3,000/- per year in the sixth and subsequent year. Equipment B with a rated capacity same as A, requires an initial investment of Rs 30,000/- and operation and maintenance costs are estimated to be Rs 13,000/per year for the first six years, increasing by Rs 4,000/- per year for each year from 7th year
onwards. If money is worth 10% determine which equipment the company should buy. Neglect the scrap value of the equipment.
6.a. Explain the Principle of dominance to reduce the size of the pay off matrix. b. Solve the following game graphically. [16] Player B B1 B2 A1 1 -3 A2 3 5 Player A A3 -1 6 A4 4 1 A5 2 2 A6 -5 0
7. A manufacturing company purchases 9000 parts of a machine for its annual requirements, ordering one month usage at a time. Each part costs Rs 20. The ordering cost per order is Rs 15 and the carrying charges are 15% of the average inventory per year. You have been assigned to suggest a more economical purchasing policy for the company. What advice would you offer and how much would it save the company per year. [16]
8. Customers arrive at a milk booth for the required service. Assume that inter-arrival and service times are constant and given by 1.8 and 4 time units, respectively. Simulate the system by hand computations for 20 time units. What is the average waiting time per customer? What is the percentage idle time of the facility? Assume that the system starts at t=0.
You might also like
- (2015 Onwards) : M.Sc. Software Systems Degree Examin Tions, April 2018Document6 pages(2015 Onwards) : M.Sc. Software Systems Degree Examin Tions, April 2018Aravind KumarNo ratings yet
- OR Models Exam GuideDocument4 pagesOR Models Exam Guidebogal02No ratings yet
- 07a80809 OperationsresearchDocument11 pages07a80809 OperationsresearchSharanya ThirichinapalliNo ratings yet
- r5311301 Operations ResearchDocument4 pagesr5311301 Operations ResearchSnehaNo ratings yet
- B.E. Production Engineering V Semester PR 331 - Quantitative Techniques in Management exam paperDocument3 pagesB.E. Production Engineering V Semester PR 331 - Quantitative Techniques in Management exam paperShathish GunasekaranNo ratings yet
- Shree Swami Atmanand Saraswati Institute of Technology: Subject: OR (2171901) Class: 7 Sem. (Mech)Document7 pagesShree Swami Atmanand Saraswati Institute of Technology: Subject: OR (2171901) Class: 7 Sem. (Mech)VIPULNo ratings yet
- PM QBDocument7 pagesPM QBmayur_mechNo ratings yet
- B-Tech4191r07i 3Document11 pagesB-Tech4191r07i 3jbj2121No ratings yet
- Question PaperDocument21 pagesQuestion PaperKrishnaa MathiNo ratings yet
- Operational Research Assignment: The Information Is Reproduced in Table 1Document11 pagesOperational Research Assignment: The Information Is Reproduced in Table 1Sakshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Part - A:: COURSE: B. Tech. YEAR: IV Year - Mechanical Engineering SUBJECT NAME: Resource ManagementDocument6 pagesPart - A:: COURSE: B. Tech. YEAR: IV Year - Mechanical Engineering SUBJECT NAME: Resource ManagementNat RatnamNo ratings yet
- Test+Full+O R +++ABC+++Service+SectorDocument4 pagesTest+Full+O R +++ABC+++Service+SectorSameer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Probable QuestionsDocument7 pagesProbable QuestionsBisweswar Dash75% (4)
- Assignment ProblemDocument4 pagesAssignment Problemshreyansh120No ratings yet
- (N D Vohra Unsolved Q-4 Page-594) (Solution: 6 Years)Document15 pages(N D Vohra Unsolved Q-4 Page-594) (Solution: 6 Years)Lokesh GagnaniNo ratings yet
- St. Mary Sabah 2013 M3 (Q) PDFDocument2 pagesSt. Mary Sabah 2013 M3 (Q) PDFSTPMmathsNo ratings yet
- TP & AP-QP ProblemsDocument15 pagesTP & AP-QP ProblemsSidharth DaveNo ratings yet
- 01BF250682E948FB9B248B2273097D9CDocument3 pages01BF250682E948FB9B248B2273097D9CjalanayushNo ratings yet
- MENG448 MDTRM1 Spring 16 SolutionDocument4 pagesMENG448 MDTRM1 Spring 16 SolutionSara AhmedNo ratings yet
- nr321501 Operations ResearchDocument3 pagesnr321501 Operations ResearchSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Transportation & Assignment Model Problems2007-09Document12 pagesTransportation & Assignment Model Problems2007-09Ketaki SomanNo ratings yet
- BREAK-EVEN ANALYSIS AND NEW DESIGN ECONOMICSDocument7 pagesBREAK-EVEN ANALYSIS AND NEW DESIGN ECONOMICSGarima PalNo ratings yet
- Operations Research - 2013Document106 pagesOperations Research - 2013vinit557% (7)
- IPCC Capital Budgeting and FFS ScannerDocument27 pagesIPCC Capital Budgeting and FFS ScannerMadan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Or RevisionDocument6 pagesOr RevisionlulughoshNo ratings yet
- Or AssignmentDocument7 pagesOr AssignmentAditya Sharma0% (1)
- R7410301 Operations ResearchDocument8 pagesR7410301 Operations ResearchsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument4 pagesGujarat Technological Universityjigu369No ratings yet
- Exam 2007 (Memo Incl)Document15 pagesExam 2007 (Memo Incl)Dantè ChiapperiniNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques Construction AssignmentsDocument6 pagesQuantitative Techniques Construction Assignmentsavdesh7777No ratings yet
- Thirdtrimester: X X Z X XDocument3 pagesThirdtrimester: X X Z X XKumar KrNo ratings yet
- UECM2043, UECM2093 Operations Research Tutorial 1Document5 pagesUECM2043, UECM2093 Operations Research Tutorial 1kamun00% (2)
- OSDocument4 pagesOSRaja RamNo ratings yet
- Or Question PaperDocument25 pagesOr Question PaperjaxshahNo ratings yet
- HT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2010-11 Production Planning & Materials ManagementDocument4 pagesHT TP: //qpa Pe R.W But .Ac .In: 2010-11 Production Planning & Materials ManagementAparna DuggiralaNo ratings yet
- Cost Control Techniques PDFDocument3 pagesCost Control Techniques PDFHosamMohamed100% (1)
- Assignment LPP. & Assignment ModelDocument5 pagesAssignment LPP. & Assignment ModelishudeepNo ratings yet
- E Book Mgt705Document20 pagesE Book Mgt705haf472No ratings yet
- Bukit Mertajam 2013 M3 (Q&a)Document5 pagesBukit Mertajam 2013 M3 (Q&a)STPMmathsNo ratings yet
- Question Bank or PutDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank or PutNITESH SONINo ratings yet
- Mathematics ModelDocument31 pagesMathematics ModelBrian BurchNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 BankDocument27 pagesExam 2 BankRishabh SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document5 pagesChapter 05TayyabNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 5 PDFranjeet singhNo ratings yet
- Aqa Acc7 W QP Jun08Document8 pagesAqa Acc7 W QP Jun08Aimal FaezNo ratings yet
- Invest Choice, Profit Function, Linear Programming, Network Diagram, Inventory CostDocument4 pagesInvest Choice, Profit Function, Linear Programming, Network Diagram, Inventory CostZAii ARiessNo ratings yet
- Final Exam April 2011Document5 pagesFinal Exam April 2011dluvjkpopNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting 2013Document3 pagesCost Accounting 2013GuruKPO0% (1)
- Strategic Cost Management Concepts for M.Com StudentsDocument4 pagesStrategic Cost Management Concepts for M.Com StudentsSupritha KNo ratings yet
- 97 ZaDocument7 pages97 ZaMeow Meow HuiNo ratings yet
- T3 Set 7 Q & ADocument10 pagesT3 Set 7 Q & AEnnovy TsuNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument5 pagesQuestion BankAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Sums On Project AnalysisDocument26 pagesSums On Project AnalysisAlbert Thomas80% (5)
- OR 7th Sem NIT Raipur QPaperDocument37 pagesOR 7th Sem NIT Raipur QPaperShashi Bhushan PatelNo ratings yet
- Problems and Solutions on MRO Spare Parts and Storeroom 6th Discipline of World Class Maintenance Management: 1, #5From EverandProblems and Solutions on MRO Spare Parts and Storeroom 6th Discipline of World Class Maintenance Management: 1, #5No ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6No ratings yet
- Cost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsFrom EverandCost & Managerial Accounting II EssentialsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- BSA4A-Midterm Exam - Questions PDFDocument6 pagesBSA4A-Midterm Exam - Questions PDFRochelleDianRaymundoNo ratings yet
- Final PresentationDocument23 pagesFinal PresentationalijinbabaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Price Level Changes: Concept MethodsDocument4 pagesAccounting For Price Level Changes: Concept MethodsLucky'rishika' UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management: University of Eastern Philippines Laoang CampusDocument11 pagesEngineering Management: University of Eastern Philippines Laoang CampusJ. Robert TanNo ratings yet
- Restaurant Management ServicesDocument12 pagesRestaurant Management ServicesHaris AslamNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Managerial Accounting 5th Edition Braun Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Managerial Accounting 5th Edition Braun Solutions Manual PDFlinnet.discreet.h5jn2s100% (9)
- Problems For PresentationDocument15 pagesProblems For PresentationNachiketa0% (1)
- Never Quit Exam TipsDocument20 pagesNever Quit Exam Tipsmonzkymine57% (7)
- Supply Chain Management ChapterDocument110 pagesSupply Chain Management ChapterSudhir Patel100% (4)
- Manufacturing ExcellenceDocument2 pagesManufacturing Excellencenishant100% (1)
- Job Order Costing: Cost Accounting: Foundations and Evolutions, 8eDocument34 pagesJob Order Costing: Cost Accounting: Foundations and Evolutions, 8eFrl RizalNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Tally.ERP 9ecDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Tally.ERP 9ecRakibul HassanNo ratings yet
- Improving Cash Flow Using Credit ManagementDocument25 pagesImproving Cash Flow Using Credit ManagementSharath RajarshiNo ratings yet
- Bet AssignmentDocument16 pagesBet AssignmentshimelisNo ratings yet
- Internal Copy 2Document30 pagesInternal Copy 2Angel Alejo AcobaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Process Costing: Click On LinksDocument15 pagesChapter 4 - Process Costing: Click On LinksNiraj PatilNo ratings yet
- AMA - Marketing Q&A (30 Questions)Document14 pagesAMA - Marketing Q&A (30 Questions)InfoSoft GlobalNo ratings yet
- Payroll CycleDocument31 pagesPayroll Cyclehiwatari_sasukeNo ratings yet
- Excercise 5,6Document4 pagesExcercise 5,6sume shquidecNo ratings yet
- Retail FormulasDocument5 pagesRetail FormulasAnil Kumar KashyapNo ratings yet
- SAP MM Questions and AnswersDocument32 pagesSAP MM Questions and AnswersMohan Ganganala100% (7)
- Question Notes On Production Management (Final)Document63 pagesQuestion Notes On Production Management (Final)Vineet Walia100% (1)
- Audit of Accounting Changes and Correction of ErrorsDocument24 pagesAudit of Accounting Changes and Correction of ErrorsHarvey Dienne Quiambao90% (10)
- A Study On Effectiveness of Supply Chain Management With Special Reference To Bisleri International PVT LTDDocument113 pagesA Study On Effectiveness of Supply Chain Management With Special Reference To Bisleri International PVT LTDGautam Kumar100% (1)
- Accounting For InventoriesDocument32 pagesAccounting For InventoriesShery HashmiNo ratings yet
- SCMDocument177 pagesSCMelwisNo ratings yet
- Sap Mm1 NotesDocument5 pagesSap Mm1 Notesanon_468655827No ratings yet
- Answers 2014 Vol 3 CH 4 PDFDocument8 pagesAnswers 2014 Vol 3 CH 4 PDFLian Blakely CousinNo ratings yet
- BSNL by Mayank and ApoorvaDocument26 pagesBSNL by Mayank and ApoorvaMayank SaxenaNo ratings yet
- British Petroleum cash conversion cycle analysisDocument8 pagesBritish Petroleum cash conversion cycle analysisSVPSNo ratings yet