Professional Documents
Culture Documents
T103-Section11 4sp03
Uploaded by
chandankumar784Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
T103-Section11 4sp03
Uploaded by
chandankumar784Copyright:
Available Formats
11.
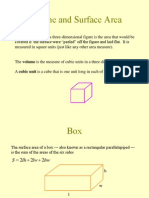
4 Surface Areas There are many real-life problems that involve finding areas buying carpet, laying a hard-wood floor, painting or wallpapering a room, to name a few. A lot of area problems involve finding surface areas of three-dimensional figures such as cylinders, prisms, cones, spheres and pyramids. To find these surface areas, we work with areas of two-dimensional pieces of the 3-d figures. We will use what are called 8/>=: 2-d patterns that can be used to construct 3-d figures. SURFACE AREA OF A RIGHT PRISM A cereal box is a right prism. In fact, it is a right _____________________ prism. Consider the problem of figuring out how much cardboard is needed to construct it. One way to solve the problem is to cut the box in such a way as to be able to lie it down flat. This results in a net. We can then see that it is made up of what kinds of figures?__________________ How many?___________________ Are any of them the same size?_______________ Let's look at a cereal box and its net. The surface area of a cube can be calculated this way also. It has how many sides?_____________ Are they all the same size?________________ What would be the surface area of a cube having an edge of 5 in? ___________________ What about a cube having an edge of size /?___________
5 in e
5 in 5 in e
In general, to calculate the surface area of a cube with edge / units, S.A. _____________________ In general, finding the surface area of right prisms involves finding the lateral surface area and the sum of the areas of the bases. Adding these together results in the surface area. Look at figure 11-57 on page 787. The figure shows a right pentagonal prism with its net. Notice there are 5 rectangles (lateral sides) and two pentagonal bases.
SURFACE AREA OF A CYLINDER An oatmeal box is a right circular cylinder. If you cut out the top and bottom, cut vertically through the remaining open cylinder, you have a net of the cylinder. What shapes do you have? So to find the surface area of a cylinder requires finding the areas of these three figures. Let's consider a cylinder having radius measure < units and height 2 units. What is the formula for its surface area?
Length of the Rectangular Piece: Top r h Bottom r ___________________
In general, the formula for finding the surface area of any right circular cylinder is: S.A. Let's use our calculators to find the area of the oatmeal box. Its radius measures 1 "$ in and its height "' measures 7 " in. %
SURFACE AREA OF A PYRAMID The surface area of a pyramid is the sum of the areas of its lateral faces and the area of its base. A right regular pyramid has lateral faces that are congruent triangles and a base that is a regular polygon. For example, here is a right square pyramid:
Note: Each triangle has altitude 6, called the =6+8> 2/312>. This altitude is different from the altitude of the pyramid. The sides of the base are all the same since it is a regular polygon. The area of each of the triangles is " ,6. If the base is a regular polygon with 8 sides, the the lateral surface area # would be 8 " ,6. So the total surface area of a right regular pyramid is: S.A. B 8 " ,6 where B is # # the area of the base. Example: Find the surface area of the following right square pyramid:
SURFACE AREA OF A CONE Again the surface area of this figure involves adding the areas of its base and its lateral surface. The base is, of course, a circle, so the area of its base is 1r# , where r is the measure of the radius. The area of the lateral surface is 1<6, where 6 is the =6+8> 2/312> of the cone.
Again, note that the =6+8> 2/312> 6 is different from the height of the cone. Example: Find the surface area of this right circular cone:
SURFACE AREA OF A SPHERE The surface area of a sphere is four times the area of a 1</+> -3<-6/ of the sphere. A great circle is any circle whose center and radius are the same as that of the sphere itself. So, the surface area of sphere with radius < is: S.A. 41<#
Calculate the surface area of a sphere of radius 12 in.
Find the surface area of each of these figures:
Right Triangular Prism
Right Regular Pentagonal Pyramid
18 cm 5 cm 4 cm h 7 cm Altitude of the triangular base, h, equals 2.8 cm
5m 8m slant height = 12m
1.
2.
3.
4.
You might also like
- Organic I Reactions (COMPLETE) PDFDocument10 pagesOrganic I Reactions (COMPLETE) PDFcztinu88% (50)
- Wcpss - Grade 6 Unit 1 Area and Surface Area 1Document8 pagesWcpss - Grade 6 Unit 1 Area and Surface Area 1api-261280308No ratings yet
- Text 11.4 Area of ParallelogramDocument4 pagesText 11.4 Area of ParallelogramJenalyn MerazNo ratings yet
- Información de Transmisión CVT ToyotaDocument151 pagesInformación de Transmisión CVT ToyotaMauricio Exequiel Chavez93% (15)
- 11 Risks and Rates of Return KEYDocument12 pages11 Risks and Rates of Return KEYkNo ratings yet
- Eps Manual NissanDocument8 pagesEps Manual Nissanjoiler pajueloNo ratings yet
- Jss1 3rd Term MathsDocument39 pagesJss1 3rd Term MathsGloria Ngeri Dan-Orawari78% (18)
- Testing of Semifinished Products of Thermoplastics Bases - Indications Directive DVS 2201-1Document4 pagesTesting of Semifinished Products of Thermoplastics Bases - Indications Directive DVS 2201-1OscarNo ratings yet
- Matrix Structural Analysis of BeamsDocument28 pagesMatrix Structural Analysis of BeamsKristine May Maturan0% (1)
- Surface Area of Pyramids Cylinders and Cones Notes and ExamplesDocument17 pagesSurface Area of Pyramids Cylinders and Cones Notes and Examplesapi-308587685No ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration MATH 005 (TIP Reviewer)Document14 pagesSolid Mensuration MATH 005 (TIP Reviewer)James Lindo80% (5)
- Conical FrustumDocument11 pagesConical FrustumRajaKuppanNo ratings yet
- GBE Version 3: API: New API SpecificationDocument44 pagesGBE Version 3: API: New API SpecificationAdi BauNo ratings yet
- Area Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaDocument12 pagesArea Formulas: Gemonrty FormulaPankaj Jirafe100% (1)
- Chap3 VolumeDocument46 pagesChap3 Volumesquishyapply100% (1)
- Grade 9 Math-CompleteDocument26 pagesGrade 9 Math-CompleteLucille Gacutan Aramburo0% (1)
- Unit 8 Syllabus: Surface Area & VolumeDocument18 pagesUnit 8 Syllabus: Surface Area & VolumeGoldycrystal100% (1)
- BHEL Turbine ManualDocument58 pagesBHEL Turbine Manualnivasssv75% (4)
- Math 6 Surface AreaDocument31 pagesMath 6 Surface AreaGuiteb ESNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 3d Geometry TestDocument4 pagesUnit 9 3d Geometry Testapi-233623316No ratings yet
- Surface AreaDocument4 pagesSurface Areaapi-245820546No ratings yet
- Ramon Teves Pastor Memorial - Dumaguete Science High School: Prepared By: Miss Kassandra VenzueloDocument10 pagesRamon Teves Pastor Memorial - Dumaguete Science High School: Prepared By: Miss Kassandra Venzuelomarjun catanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 7: School Year 2022-2023Document48 pagesMathematics 7: School Year 2022-2023ハンナジュリーNo ratings yet
- Cube Definition: Surface Area Formula For The CubeDocument3 pagesCube Definition: Surface Area Formula For The CubeJohn Joshua ReyesNo ratings yet
- CuboprojectDocument23 pagesCuboprojectapi-277698547No ratings yet
- Mathematics 6: Quarter 3 - Week 7Document9 pagesMathematics 6: Quarter 3 - Week 7Nicole AlanaNo ratings yet
- Volume and Surface AreaDocument12 pagesVolume and Surface AreaDeepali GargNo ratings yet
- CuboprojectDocument23 pagesCuboprojectapi-310388070No ratings yet
- TSA Andvolume of SolidsDocument14 pagesTSA Andvolume of SolidsJairNo ratings yet
- CubopaperDocument16 pagesCubopaperapi-281827073No ratings yet
- 6.3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and ConesDocument24 pages6.3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and ConesBahati ValerianNo ratings yet
- Directions: Match Column A With Column B. Write The Letter of The Correct Answer A BDocument3 pagesDirections: Match Column A With Column B. Write The Letter of The Correct Answer A BSharra LopezNo ratings yet
- Solid Geometry ExplainedDocument9 pagesSolid Geometry Explainedfachira_humairaNo ratings yet
- 10-4 Perimeters and Areas of Similar FiguresDocument7 pages10-4 Perimeters and Areas of Similar Figuresnickypoo1995100% (1)
- ShapesDocument11 pagesShapesanissafeniNo ratings yet
- 3 Math6Q3Week1Document25 pages3 Math6Q3Week1Dhan MangmangonNo ratings yet
- 1 The CubeDocument19 pages1 The Cubesmartyshah14No ratings yet
- Grade 6 GeometryDocument6 pagesGrade 6 GeometryNguyen Thi Thien MinhNo ratings yet
- EulerDocument21 pagesEulerCheria AliNo ratings yet
- Surface Area and VolumeDocument27 pagesSurface Area and VolumeRiNo ratings yet
- Solving Cone Problems and Finding Volumes, Areas, Radii & HeightsDocument4 pagesSolving Cone Problems and Finding Volumes, Areas, Radii & HeightsabiNo ratings yet
- Cube in A CubeDocument14 pagesCube in A Cubeapi-310388070No ratings yet
- How to Find the Area of a Parallelogram by SubtractionDocument10 pagesHow to Find the Area of a Parallelogram by SubtractionJenonymouslyNo ratings yet
- CuboDocument17 pagesCuboapi-397358195No ratings yet
- SDOC-F4D56E129586EC6F5932A51480140E2B-04-07-SIDocument65 pagesSDOC-F4D56E129586EC6F5932A51480140E2B-04-07-SIbuknoydaculesNo ratings yet
- CuboDocument17 pagesCuboapi-282458946No ratings yet
- Quarter 3 - Week 2 and 3 LasDocument2 pagesQuarter 3 - Week 2 and 3 LasZyra Catherine MoralesNo ratings yet
- SurfaceAreaandVolume TEXTDocument26 pagesSurfaceAreaandVolume TEXTprabsahiNo ratings yet
- POLYGONSDocument45 pagesPOLYGONSBlessa Mae100% (1)
- Quadrilaterals Digital TextDocument14 pagesQuadrilaterals Digital TextAmruthaNo ratings yet
- 7.5.1 - Surface Area of A Prism and CylinderDocument5 pages7.5.1 - Surface Area of A Prism and CylinderGaran WisemanNo ratings yet
- Feb7 Friday Math Group ChallengeDocument7 pagesFeb7 Friday Math Group Challengeapi-238894479No ratings yet
- Surface Area and Volumes: Done By: M.Vaishnavi Grade: 9PDocument17 pagesSurface Area and Volumes: Done By: M.Vaishnavi Grade: 9Pmahindra100% (1)
- Final Exam in Math 106 Plane and Solid GeometryDocument4 pagesFinal Exam in Math 106 Plane and Solid Geometryjennifer reyes100% (1)
- PGL-Lesson 69-70Document11 pagesPGL-Lesson 69-70Jomabelle UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Summative Geometry Problems and CalculationsDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Summative Geometry Problems and CalculationsBen SimonNo ratings yet
- CubeprojectDocument12 pagesCubeprojectapi-352849690No ratings yet
- Cone, Cylinder, and Sphere: Created By: Nurina Ayuningtyas Wahyu Fajar S. Yan Aditya P Yola Yaneta HDocument31 pagesCone, Cylinder, and Sphere: Created By: Nurina Ayuningtyas Wahyu Fajar S. Yan Aditya P Yola Yaneta HJR DevienteNo ratings yet
- Lesson On Solid MensurationDocument18 pagesLesson On Solid MensurationKelly Lulu100% (1)
- Class 7 Mathematics Prerequisite KnowledgeDocument9 pagesClass 7 Mathematics Prerequisite KnowledgeMuhammad TufailNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Note for Grade 10Document8 pagesMathematics Note for Grade 10darseziyad34No ratings yet
- MensurationDocument8 pagesMensurationSABINA SALMANo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Lesson 3 TrianglesDocument9 pagesUNIT 1 Lesson 3 TrianglesAaron BrennNo ratings yet
- 10 4 Areas of Regular Polygons and Composite FiguresDocument26 pages10 4 Areas of Regular Polygons and Composite FiguresДиана Данова100% (1)
- MATH - 1 - SA - CircleDocument3 pagesMATH - 1 - SA - CirclePradesh ShyamNo ratings yet
- Estimating The Volumes of Solid Figures With Curved SurfacesDocument8 pagesEstimating The Volumes of Solid Figures With Curved Surfacesuberuber12No ratings yet
- Installation Guide Moses DecoderDocument1 pageInstallation Guide Moses Decoderchandankumar784No ratings yet
- Aromatic Conversion ChartDocument1 pageAromatic Conversion Chartchandankumar784No ratings yet
- Maths Project 2011 Class X On Volume and Surface Area of Cubes and CuboidsDocument14 pagesMaths Project 2011 Class X On Volume and Surface Area of Cubes and Cuboidschandankumar7840% (3)
- GTSDocument7 pagesGTSrobindetolensNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Business Statistics: ProbabilityDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Business Statistics: ProbabilityNghĩa PhùngNo ratings yet
- 1900.65A Monitor DatasheetDocument26 pages1900.65A Monitor DatasheetAncuța DanielNo ratings yet
- Lesson 17: Lightning Accidents: Grade 9-Science-Sussex College - WennappuwaDocument5 pagesLesson 17: Lightning Accidents: Grade 9-Science-Sussex College - WennappuwaSwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- Homework1 PDFDocument3 pagesHomework1 PDFYuanhao LiuNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument45 pagesSeminar Reportmanaskollam0% (1)
- State Standards: Common CoreDocument24 pagesState Standards: Common CoreEddy R. VélezNo ratings yet
- General Physics1 Q2 W8 Module8 ThermodynamicsDocument23 pagesGeneral Physics1 Q2 W8 Module8 ThermodynamicsRegine Ann ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Fulltext PDFDocument454 pagesFulltext PDFVirmantas JuoceviciusNo ratings yet
- Planetary AlignmentDocument7 pagesPlanetary AlignmentEbn MisrNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Analysis of Chlorpheniramine Maleate Marketed in NigeriaDocument7 pagesQuality Control Analysis of Chlorpheniramine Maleate Marketed in Nigeriaحمزة الفنينيNo ratings yet
- Wound ScaleDocument4 pagesWound ScaleHumam SyriaNo ratings yet
- TM View Software User - S ManualDocument190 pagesTM View Software User - S ManualLuis SánchezNo ratings yet
- AC axial compact fan technical specificationsDocument5 pagesAC axial compact fan technical specificationsdhanasekhar27No ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 CirclesDocument2 pagesProblem Set 1 Circlesapi-339611548100% (1)
- Modular Forms Exam - Homework RewriteDocument2 pagesModular Forms Exam - Homework RewritejhqwhgadsNo ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument69 pagesMachine DesignSushant TiwariNo ratings yet
- JasminDocument125 pagesJasminudoraboxNo ratings yet
- Types of VerbDocument4 pagesTypes of VerbFaisal MalikNo ratings yet
- 3 - Molecules and Compounds: Practice TestDocument2 pages3 - Molecules and Compounds: Practice Testfamily_jvcNo ratings yet
- IMME19 Schedule PDFDocument39 pagesIMME19 Schedule PDFVikram JainNo ratings yet
- Essay For Villa Savoye AbstractDocument1 pageEssay For Villa Savoye AbstractFrancis PohNo ratings yet
- Waterproof BoxDocument129 pagesWaterproof BoxVenkata Narayana BoddapatiNo ratings yet
- Dental Material Final ReportDocument7 pagesDental Material Final ReportAbdullah Muhammed khaleel HassanNo ratings yet