Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio 111 Final Exam Fall05
Uploaded by
Zeshan AslamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio 111 Final Exam Fall05
Uploaded by
Zeshan AslamCopyright:
Available Formats
Fall 2005 1. DNA molecules have: a. b. c. d. e. 2. a double helix structure. specific pairing of 4 different nitrogen bases.
alternating sugar and phosphate units. All of the above. None of the above.
The structures in DNA that apparently serve the function of "genes" or as the source of coded information is/are the: a. b. c. d. phosphoric acid configuration. nitrogen bases and their sequence. structure of deoxyribose. ribose sequence.
3.
Production of new DNA occurs in: a. b. several locations in the cell the nucleus c. d. in the cytoplasm in the ribosomes
4.
Newly synthesized molecules of
contain one old strand and one new strand.
5.
a. t-RNA b. r-RNA c. m-RNA d. DNA e. protein Which of the following is found in RNA, but not in DNA? a. b. c. adenine guanine uracil d. e. cytosine thymine
6.
Which of the following would be found in DNA, but not in RNA? a. b. c. phosphate group ribose deoxyribose d. e. nitrogen bases all of these are present in both DNA and RNA
7.
The double helix concept is that a molecule of DNA consists of: a. two chains in which each base (A,G,C,T) in one chain is paired with its opposite or
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 b. c. d. 8. complement (T,C,G,A) in the other chain. two chains in which each base in one chain is paired with the same one in the other chain. two chains, each of which is the mirror image of the other. a chain of nucleotides paired with and twisted with a chain of amino acids.
In the comparison of a DNA molecule to a twisted ladder, the uprights (sides) of the ladder would be: a. b. c. d. e. deoxyribose linked to phosphates. nitrogenous bases linked together. deoxyribose linked to sulfates. nitrogenous bases linked to phosphates. hydrogen bonds between the bases.
9.
In the comparison of a DNA molecule to a twisted ladder, the rungs (steps) of the ladder would be: a. b. c. d. deoxyribose linked to phosphates. nitrogenous bases linked together. deoxyribose linked to ribose. nitrogenous bases linked to phosphates.
10.
Nucleotides are composed of: a. b. c. d. phosphates. sugars. nitrogenous bases. all of the above.
11.
In DNA, the amount of cytosine is always equal to the amount of: a. adenine. c. guanine. b. uracil. d. thymine. mRNA molecules carry __________ from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. a. b. c. ribosomal subunits amino acids protein assembly instructions d. e. introns all of the above
12.
13.
The correct sequence of events for protein synthesis is: a. b. c. d. DNA - tRNA - ribosome - mRNA - amino acid. mRNA - DNA - tRNA - ribosome - amino acid. DNA - mRNA - ribosome - tRNA - amino acid. tRNA - DNA ribosome - mRNA - amino acid.
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 14. How many nucleotide bases are needed to specify one amino acid? a. b. 15. 4 3 c. d. 2 1
Which of the following carries amino acids to ribosomes? a. b. c. DNA mRNA rRNA d. e. tRNA none of the above
16.
Messenger RNA contains ______ strand(s). a. one b. two c. three A codon: a. b. c. d. e. d. e. four five
17.
contains instructions for placement of one amino acid. contains instructions for the assembly of an entire protein. is a gene. is a sequence of 4 bases on mRNA. none of the above
18.
Ribosomes are composed of: a. b. c. small proteins proteins and tRNAs proteins and rRNAs d. e. lipids and mRNA rRNAs and tRNAs
19.
If a segment of DNA had the sequence G-A-C-C-G-A-A-A-G, the messenger RNA complementary to it would have the sequence: a. b. c. G-A-C-C-G-A-A-A-G. C-T-G-G-C-T-T-T-C. C-U-G-G-C-U-U-U-C. d. e. A-G-T-T-A-G-G-G-A. A-G-U-U-A-G-G-G-A.
20.
The base sequence CUA on mRNA is recognized by which sequence of nucleotides on tRNA? a. b. c. GAU CAU GAT d. e. GTT CTA
21.
If the DNA triplets were ATG-CGT, the mRNA codons would be:
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 a. b. c. 22. AUG-CGU. ATG-CGT. UAC-GCA. d. e. UAG-CGU. none of the above
If the DNA triplets were ATG-CGT, the tRNA anticodons would be: a. AUG-CGU. d. UAG-CGU. b. ATG-CGT. e. none of the above c. UAC-GCA. Which of the following is found in DNA, but not in RNA? a. b. c. adenine guanine uracil 24. d. e. cytosine thymine
23.
DNA is double-stranded and contains the base uracil, while RNA is single stranded and contains the base thymine. a. true b. false
Matching 25-28. Answers may be used more than once. Indicate if the descriptions below refer to: a. b. c. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. transcription. translation. replication.
Assembly of specific amino acids into a protein. Production of mRNA. Assembly of nucleotides to form 2 identical molecules of DNA. Occurs on ribosome. A gene mutation is defined as a change in: a. b. c. d. e. the structure of the ribosome. the nucleotide sequence of RNA. the nucleotide sequence of DNA. the amino acid sequence of a protein. the way a gene is expressed.
30.
A gene mutation:
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 a. destroys the DNA molecule. b. has no effect on the gene base sequence. c. is always beneficial. d. can be passed on to offspring. e. all of the above are correct The diagram below represents a(an) _______________ mutation. AACGCAGTGAACCCAGTG a. b. c. d. 32. point insertion deletion There is no mutation here.
31.
In a mutation: a. b. c. d. the new codon may specify a different amino acid, but may not change the function of the new protein produced. the new codon may specify the same amino acid as the old codon. the new codon and resulting amino acid may produce a non-functional protein. All of the above may be true.
Matching 33-37. Match each molecule to its description. Answers may be used more than once. a. b. c. d. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. DNA. mRNA. tRNA. ribosomes.
Chromosomes Carries specific amino acids in the cytoplasm Carried protein synthesis instructions out of the nucleus Site of protein synthesis Serves as a blueprint for mRNA
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 38. Recombinant DNA is formed when: a. b. c. d. DNA undergoes a mutation. DNA unzips and then new complementary bases recombine with each half producing two identical DNA strands. DNA from one organism are combined with the DNA from another organism. t-RNA is combined with DNA.
MATCHING 39-40. Select from the following answers. a. b. 39. 40. Intron Exon c. d. Restriction enzyme Plasmid
Segments of the genetic code which are used in building a protein Segments of the genetic code which are not used in building a protein
Matching 41-45. Select from the following answers. Answers may be used only once. a. b. c. d. e. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) gene therapy DNA fingerprinting transgenic organism clone
Product of asexual reproduction. Use of bioengineered cells or viruses to treat human genetic disorders. Crop plants that have a bacterial gene inserted into them. Use of STRs to associate a blood stain with a specific person. Technique for producing a large quantity of DNA from a small sample. Plasmids are: a. b. c. d. used to cut DNA into fragments. normally found in humans. used to copy DNA. circular DNA molecules found in bacteria.
47.
Enzymes used to cut genes in recombinant DNA research are:
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 a. b. c. d. e. 48. ligases. restriction enzymes. transcriptases. DNA polymerases. replicases.
Which of the following enzymes joins the paired sticky ends of DNA fragments? a. b. c. d. e. reverse transcriptase restriction enzymes DNA ligase DNA polymerase helicase
49.
Which among these techniques is used in DNA fingerprinting? a. b. c. d. e. amplification of DNA use of STR primers. gel electrophoresis comparison of different DNA samples all of the above are used in DNA fingerprinting
50.
What type of mutation is represented? CCATAGACT CCACATAGACT a. b. Point Insertion c. d. Deletion There is no mutation.
51.
A hypothesis is: a. b. c. d. e. a test devised to gain information. an initial observation of some event. a possible explanation for something observed. drawing a conclusion. designing an experiment.
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 52. A control is used in an experiment: a. b. c. d. e. 53. to make the experiment more complex. to repeat the experiment and gather more data for statistical purposes. to reduce the experiment error. to insure that at least one group will turn out as expected. to allow for a standard of comparison for the experimental group.
A scientific theory: a. b. c. d. e. is an accepted explanation for a natural phenomena. is an educated guess. is less reliable than a hypothesis. will never be changed. none of the above.
54.
Which of the following is/are characteristic of living organisms? a. b. c. d. e. Complex and organized structure Responsiveness to stimuli Maintenance of homeostasis b and c only are correct a, b, and c are correct
55.
To which kingdom would a multicellular, eukaryotic, photosynthetic organism belong? a. b. c. Protista Fungi Plantae d. e. Animalia None of the above
56.
Which organism listed is prokaryotic? a. b. c. Elodea Bacteria Whitefish d. e. Allium (onion) Fungus
57.
As food moves down the food chain, what happens to the amount of useable energy? a. b. It increases. It decreases. c. d. It is the same at each level. Energy cannot move.
58.
To which Kingdom would a multicellular, heterotrophic organism belong?
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 a. b. c. 59. Protista Bacteria Plantae d. e. Animalia None of the above
The Domain __________ is characterized by organisms composed of one or more highly complex cells. a. b. c. Bacteria Archaea Eukarya
60.
What determines the atomic number of an atom? a. b. c. d. e. Number of electrons in the outermost energy level Total number of energy shells Arrangement of neutrons in the atomic nucleus Number of protons in the atomic nucleus. The total number of electrons and neutrons.
61.
If you examined the atoms found in living things, which of the following groups of elements would you find to be the most common? a. b. c. C, O, P, S C, O, N, Na C, H, Ca, Cl d. e. K, S, O, P C, H, O, N
62. 63.
In an atom the number of electrons is the same as the number of protons. a. true b. false Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15. How many electrons are located in its outer shell? a. 2 d. 5 b. 3 e. 8 c. 4 The number of __________ plus the number of __________ is equal to the atomic weight (mass) of an atom. a. b. c. electrons, protons electrons, neutrons protons, neutrons d. e. protons, electrons none of the above
64.
65.
How does one explain the formation of ions? a. Sharing of electrons d. Sharing of protons
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 b. c. 66. Gain or loss of electrons Gain or loss of protons e. Gain or loss of neutrons
10
Substances which dissolve in water are: a. b. hydrophilic. hydrophobic.
67.
If a substance measures 7 on the pH scale, that substance: a. b. c. d. e. has equal concentrations of H+ and OH- ions. is acidic. has a greater concentration of OH- than H+ ions. lacks OH- ions. is basic.
68.
Large biological molecules are synthesized by removing: a. b. c. d. e. carbon. covalent bonds. water. oxygen. nitrogen.
69. Which of the following best summarized the relationship between dehydration reactions and hydrolysis? a. b. c. d. e. 70. Dehydration reactions assemble polymers and hydrolysis breaks them down. Hydrolysis occurs during the day and dehydration happens at night. Dehydration reactions can occur only after hydrolysis. Hydrolysis creates monomers and dehydration reactions destroy them. Dehydration reactions occur only in animals; hydrolysis reactions occur only in plants.
Which of the following is a lipid? a. b. c. steroids oils triglycerides d. e. waxes all of the above
71.
The subunit (monomer) of a protein is a (an): a. b. c. amino acid. monosaccharide. glycerol. d. e. nucleotide. fatty acid.
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 72. The difference between one amino acid and another is found in the: a. b. c. 73. carboxyl group. amino group. R group. d. e. peptide bond. angle of the oxygen link.
11
Which of the following is true about the plasma membrane? a. b. c. d. e. It separates the cell contents from its environment. It allows some substances to move across it freely. It is a lipid bilayer with proteins scattered throughout. It contains pumps for moving molecules against their concentration gradient. All of the above.
74.
To say a membrane is "semipermeable" means: a. b. c. d. e. no molecules can pass through. all molecules can pass through it freely. only certain molecules can pass through, while others cannot. sometimes water can pass through, and sometimes it cannot. the permeability depends on the concentration gradient.
75.
Temperature and the size of the molecule will influence the rate of simple diffusion. a. True b. False
76.
If red blood cells are taken from the body and placed in a hypertonic solution, what would happen to the cells? a. b. c. d. e. The cells swell and burst because water moves into the cells. The cells shrivel up because water leaves the cells. The cells remain unchanged due to equal solute concentration inside and outside the cells. The cells remain unchanged due to equal water concentrations inside and outside the cells. Unable to be determined.
77.
Osmosis refers to: a. b. c. d. e. random movement of sugar molecules until equilibrium is reached. the movement of water against it concentration gradient. hydrogen bonding between water molecules. the diffusion of water through a membrane. all of the above are true.
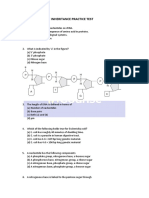
Refer to Figure 1 of the cell for 78-83.
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 78. Structure 4 is the: a. b. c. 79. chloroplast. nucleus. vacuole. d. e. Golgi complex. endoplasmic reticulum.
12
Structure 2 is the: a. b. c. chloroplast. nucleus. mitochondrion. d. e. Golgi complex. ribosome.
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405
13
Figure 1. The Cell
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 80. The function of structure 2 is: a. b. c. d. e. 81. production of protein. packaging substances produced by cell. to control all cellular functions. provide energy by means of cellular respiration. storage of starch.
14
Structure 5 is the: a. b. c. nucleus. nucleolus. Golgi complex. d. e. lysosome. mitochondrion.
82.
Structure 3 is the: a. b. c. nucleus. endoplasmic reticulum. ribosome. d. e. mitochondria. Golgi complex.
83.
Structure 7 (the dot-like-structure) is the: a. b. c. plasmid. mitochondria. ribosome. d. e. Golgi complex. chloroplast.
84.
_______________ contain digestive enzymes and function as the intracellular digestive units for the cell. a. b. c. Golgi complex Ribosomes Mitochondria d. e. Lysosomes Endoplasmic reticula
85.
_______________ are the primary cellular sites for the production of proteins. a. b. c. Golgi complex Ribosomes Mitochondria d. e. Lysosomes Smooth endoplasmic reticula
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 86. Energy: a. b. c. d. e. 87. is created but never destroyed. is constantly lost to the environment as heat. cannot be converted from one form to another. is present in sunlight but not in chemical bonds. is anything that has a mass and takes up space.
15
An enzyme may be inactivated by: a. b. c. d. e. removing its product as fast as it appears. blocking its active site. halving its concentration. doubling its concentration. all of the above
88.
The chemical reaction below is that of a lit bunsen burner. CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O + energy (light-heat) This reaction is: a. exergonic (exothermic). b. endergonic (endothermic).
89.
In the process of photosynthesis, light energy from the sun is converted into: a. b. c. chemical energy. heat energy. electrical energy. d. e. radiant energy. solar energy.
90.
Which of the following life forms cannot photosynthesize? a. b. c. d. plants algae animals all of the above can photosynthesize
91.
Which of the following is used by plants in photosynthesis? a. b. c. d. e. sugar oxygen carbon dioxide amino acids glycerol and fatty acids
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 Why do we perceive chlorophyll as being green? a. b. c. d. e. 93. Blue and yellow wavelenghts combine, producing the high energy green wavelength. Because it absorbs green light. Because it absorbs red light. Because it reflects blue light. Because it reflects green light.
16
92.
The main product of photosynthesis is: a. CO2. b. C6H12O6. c. d. H2O. RuBP.
94.
Most of the photosynthesis in plants occurs in the: a. b. c. d. leaf. stem/trunk. roots. flowers.
95.
Which of the following releases the most energy in the form of ATP? a. b. c. d. e. anaerobic respiration aerobic respiration alcoholic fermentation lactate fermentation all produce the same amount of ATP
Matching 96 - 99. Identify the correct phase of respiration. Answers may be used more than once. a. b. c. 96. 97. 98. 99. Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron Transport System
In which phase is water is formed? Which of these requires oxygen from the air? Which of these produces the most ATP? Which of these occurs in the cytoplasm?
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 100. A mouse is placed in a sealed container. What would happen to the gases in the container? a. b. c. d. 101. Both oxygen and carbon dioxide would decrease. Both oxygen and carbon dioxide would increase. Oxygen would increase and carbon dioxide would decrease. Oxygen would decrease and carbon dioxide would increase.
17
The waste products of aerobic respiration that are used for photosynthesis are: a. b. c. d. carbon dioxide and oxygen. water and carbon dioxide. water and oxygen. water, carbon dioxide, and oxygen.
102.
Oxygen is necessary for aerobic respiration because oxygen combines with: a. b. c. d. e. carbon dioxide and water to form glucose. carbon to form carbon dioxide. electrons and hydrogen ions to form water. nitrogen to form proteins. electrons to form carbon dioxide.
103. When the genetic material is in the uncoiled condition it is not visible with a light microscope. In this form it is usually referred to as: a. centromere. b. chromatin. c. spindle fibers. 104. d. chromosome. e. sex cell.
The two halves of a duplicated chromosome are called: a. b. c. spindle fibers. centrioles. centromeres. d. microtubules. e. chromatids.
105.
In a cell undergoing mitosis, you observe that the chromosomes are lined up in the center of the cell. Which phase of mitosis are you observing? a. b. c. prophase metaphase interphase d. e. anaphase telophase
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 106. Which of the following occurs only in plant cell mitosis? a. b. c. d. e. 107. The cell pinches itself into two daughter cells. The chromosomes separate. The chromosomes become visible with a light microscope. Only half of the daughter cells have chromosomes. A cell plate forms.
18
How many chromosomes would be present in the sex cells of an organism with 20 chromosomes in its body cells? a. b. c. 2 5 10 d. e. 15 20
108.
What is the importance of crossing over? a. b. c. d. e. It provides extra genetic material for the daughter cells. It increases the likelihood that daughter cells contain different genetic information. It produces proteins that are associated with the DNA in the chromosomes. It increases the chromosome condensation. It separates the pairs of homologous chromosomes.
109.
An individual possessing two different alleles (such as Dd) is said to be: a. b. homozygous. recessive. c. d. linked. heterozygous.
110.
A tall pea plant (TT) and a tall pea plant (Tt) have the same: a. b. alleles. genotype. c. d. phenotype. none of these.
111.
In squash white fruit color is dominant over yellow. If a heterozygous white fruited plant is crossed with a yellow fruited plant, what type and proportion of offspring will be expected? a. b. c. all white white, yellow 3 white, 1 yellow d. e. all yellow more than one of the above
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 112. When two blue-flowered plants are crossed, 25% of their offspring are white. What are the genotypes of the blue plants? a. b. 113. BB Bb c. d. bb bbb
19
A recessive allele is one: a. b. c. d. e. that is not expressed as strongly as a dominant allele. whose effect is masked by a dominant one. that produces no effect when present in the homozygous condition that appears only in a heterozygote. that is always lethal in the homozygous condition
114.
If an organism has the genotype Aa BB, how many different types of sex cells can be produced? a. b. c. 1 2 3 d. e. 4 5
115. In fruit flies, gray body is dominant to black body and straight wing is dominant to curled wing. If a homozygous black-bodied, straight-winged fly is mated with a homozygous gray-bodied, curledwinged fly, how many different phenotypes will be produced in the F1 generation? a. b. c. 116. 1 2 4 d. e. 16 more than 100
If the pattern of inheritance is autosomal recessive, a male showing the trait would have the following genotype: a. b. c. AA Aa aa d. e. XaY XAY
117.
In a certain species of birds, homozygotes are either black or white. The heterozygous condition produces blue birds. If two blue birds are mated the offspring will be: a. b. c. all blue 1 black: 1 blue 1 black: 2 blue: 1 white d. e. 3 blue: 1 white 3 black: 1 white
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405
20
118. Assume red is dominant to white, and tall is dominant to short. If a plant that is homozygous for red flowers and heterozygous for tallness is crossed with a plant that is white and short, what will the phenotypic ratio of their offspring be? a. b. c. d. 119. 1 tall red and 1 short red 9 tall red to 3 short red to 3 tall white to 1 short white 3 tall red to 1 short red to 1 tall white 1 short white to 2 short red to 1 tall white
In snapdragons, red x white pink. What is expected for the cross pink x red? a. b. c. red and pink All pink red and white d. e. All red red and pink
120.
If a pea plant shows a recessive phenotype: a. b. c. d. e. it can be either TT or Tt. it can be either Tt or tt. it can be only TT. it can be only tt. it can be TT, Tt, or tt.
121.
Color-blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A color-blind woman will pass the gene for colorblindness to: a. b. her sons only. her daughters only. d. e. all her children. none of her children.
122. Mary has blood type AB. Scott has blood type O. Which of the following blood types is NOT possible for their children? a. b. 123. A B c. d. AB all of these are possible
Color blindness is more common in men than in women because: a. b. c. d. e. men have only one X chromosome. the gene is located on the Y chromosome. crossing over only occurs in women. women cannot inherit the gene from their fathers. men have more copies of the gene than women.
BIO 111, FINAL EXAM,BIO 111 / Disk 405 124. The failure of chromosomes to segregate properly during meiosis is called: a. b. c. 125. nondisjunction. translocation. replication. d. e. inversion. independent assortment.
21
The pattern of inheritance seen below would be described as: a. b. autosomal dominant. autosomal recessive. c. d. sex linked recessive. none of the above.
Have A Good Break!
KFEDSM404
You might also like
- Biology 111 EXAM 2 Study GuideDocument15 pagesBiology 111 EXAM 2 Study GuidecuckoofourkokoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis ACEDocument14 pagesProtein Synthesis ACEZhiTing96No ratings yet
- Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids Questions with AnswersDocument7 pagesNucleotides & Nucleic Acids Questions with AnswersZainab JasimNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance Practice TestDocument13 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance Practice TestPartha Shee100% (1)
- Microbiology Final Exam Questions AnswersDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Final Exam Questions AnswersShafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Full Book Short QuestionsDocument31 pagesChemistry Full Book Short QuestionsOwais MaqboolNo ratings yet
- Ezyme 2Document3 pagesEzyme 2Nini Besi100% (1)
- This Set of Molecular Biology Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument392 pagesThis Set of Molecular Biology Multiple Choice QuestionsRohit ChavariyaNo ratings yet
- MCQs BioDocument4 pagesMCQs BioDrbee10No ratings yet
- Embedded Systems in Industrial Application PDFDocument46 pagesEmbedded Systems in Industrial Application PDFnavabnavab786No ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument30 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyAlthea Mandal100% (1)
- Biology McqsDocument58 pagesBiology Mcqskamilbisma100% (2)
- Assessment of Proximate Composition and Phytochemical Properties of Bitter Leaf (Vernonia Amygdalina) and Water Leaf (Talinum Triangular)Document9 pagesAssessment of Proximate Composition and Phytochemical Properties of Bitter Leaf (Vernonia Amygdalina) and Water Leaf (Talinum Triangular)UIJRT United International Journal for Research & TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Quiz - Enzymes and Vitamins - Answer KeyDocument8 pagesBiochemistry Quiz - Enzymes and Vitamins - Answer KeyKennethNo ratings yet
- NMAT Question BankDocument36 pagesNMAT Question BankAbdur Rahmaan HudliNo ratings yet
- Dna Review Packet UpdatedDocument4 pagesDna Review Packet Updatedapi-259727482No ratings yet
- Class-XI Ch-10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument12 pagesClass-XI Ch-10 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionPoonam MeenaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Genetics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument25 pagesIntroduction to Genetics Multiple Choice QuestionsTracy CuiNo ratings yet
- Structure of Nuclear Genetic Material - Dna, Rna and Gene: CourseDocument65 pagesStructure of Nuclear Genetic Material - Dna, Rna and Gene: Coursebharath margamNo ratings yet
- Practice ExamDocument9 pagesPractice ExamVanandi100% (1)
- Test Funda Nmat Mock 1Document79 pagesTest Funda Nmat Mock 1Samantha SaoitNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument53 pagesDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDeborah Chloe EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Markovnikov's Rule ExplainedDocument3 pagesMarkovnikov's Rule Explaineddescata100% (1)
- Question Bank Midterm 1Document48 pagesQuestion Bank Midterm 1joselin MontenegroNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells WorksheetsDocument17 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells WorksheetsZaigham ZiaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 12 Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 12 Nucleic AcidsJulia IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document17 pagesChapter 3Anna CortiNo ratings yet
- Gene definition and allele differencesDocument3 pagesGene definition and allele differencesibdpNo ratings yet
- All in Trans Molecular BiologyDocument12 pagesAll in Trans Molecular BiologyCASTILLO, ANGELA ALEXA A.No ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Preclass QuizDocument3 pagesMolecular Biology Preclass QuizElizabeth DouglasNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment #2 (Chapters 2, 3-4.1)Document5 pagesHomework Assignment #2 (Chapters 2, 3-4.1)joseNo ratings yet
- Microbial Taxonomy and DiversityDocument7 pagesMicrobial Taxonomy and DiversitySabbir ShuvoNo ratings yet
- BS ChemistryDocument73 pagesBS Chemistryawais gujjarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Question Bank V 1.0e: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument39 pagesBiochemistry Question Bank V 1.0e: Multiple Choice QuestionsArulkumar ManiNo ratings yet
- Xhweet Kashu . : Biology Complete Important Mcqs For Medical Entry Test PreparationDocument47 pagesXhweet Kashu . : Biology Complete Important Mcqs For Medical Entry Test PreparationawaisjinnahNo ratings yet
- Answers Are Here:: Pwxwtkrlxvzh6Wlwagrsc/Edit?Usp SharingDocument10 pagesAnswers Are Here:: Pwxwtkrlxvzh6Wlwagrsc/Edit?Usp SharingCharlotte KimNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument7 pagesBiochemistryAbdelwahab AliNo ratings yet
- Informational Passages RC - ElementsDocument2 pagesInformational Passages RC - ElementsandreidmannnNo ratings yet
- Dbms Questions AddonDocument7 pagesDbms Questions Addonaadi1988No ratings yet
- AP Bio Unit 7 Study Guide Chapter 43Document7 pagesAP Bio Unit 7 Study Guide Chapter 43Huma KhanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 SPINELDocument5 pagesModule 1 SPINELDharmendra Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- CHEM1 Chapter 2 - MeasurementDocument147 pagesCHEM1 Chapter 2 - MeasurementRomalyn GalinganNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Test 3Document11 pagesCell Biology Test 3Carol HathawayNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Nucleic Acids - Lecture - BIOCHEMISTRYDocument13 pagesQuiz On Nucleic Acids - Lecture - BIOCHEMISTRYAlliah Turingan100% (1)
- Biology Test PrepDocument26 pagesBiology Test PrepHeather HollandNo ratings yet
- (Assignment For 1 ST Year) Communicative English Skill IIDocument4 pages(Assignment For 1 ST Year) Communicative English Skill IIasheNo ratings yet
- 18.1.8 DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pages18.1.8 DNA Replication WorksheetJose Barrera GaleraNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Chapter 1 Assignment Class 9 CBSEDocument2 pagesBIOLOGY Chapter 1 Assignment Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora873875% (8)
- Technical Preboard Exam 2Document6 pagesTechnical Preboard Exam 2Allan BitonNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing MCQDocument71 pagesData Warehousing MCQYash SulkahaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules MCQ-1Document4 pagesBiomolecules MCQ-1BikashNo ratings yet
- SAMBA (J&K) (NAAC Accredited B) Recognized by J&K Govt. and Affiliated to the University of JammuDocument11 pagesSAMBA (J&K) (NAAC Accredited B) Recognized by J&K Govt. and Affiliated to the University of JammuajaysmbNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Slides Lab 8Document17 pagesUrinary System Slides Lab 8Asad Javed Mehmood100% (1)
- 07 Nucleic Acids TestDocument6 pages07 Nucleic Acids TestdishaNo ratings yet
- Viruses: Capsid: The Outer Protein Layer That Surrounds The Genetic Material of A VirusDocument2 pagesViruses: Capsid: The Outer Protein Layer That Surrounds The Genetic Material of A VirusKlutz4LifeNo ratings yet
- The Creators College of Science & Commerce: 1 TermDocument2 pagesThe Creators College of Science & Commerce: 1 TermJhangir Awan33% (3)
- Immunogenetics: How Antibodies and T Cell Receptors Recognize Foreign InvadersDocument46 pagesImmunogenetics: How Antibodies and T Cell Receptors Recognize Foreign Invadersrekha19780% (1)
- MCQ MolecularDocument11 pagesMCQ MolecularMahmOod Gh100% (2)
- 12 Review WSDocument11 pages12 Review WSJASON WILLSNo ratings yet
- MBB 10 2nd Long Exam ReviewerDocument7 pagesMBB 10 2nd Long Exam ReviewerAnonymous YRORccnMNo ratings yet
- Immunocytochemistry PDFDocument17 pagesImmunocytochemistry PDFmortezah0% (1)
- General Pathology First PPT Lecture PDFDocument47 pagesGeneral Pathology First PPT Lecture PDFMaria BelNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram - Group 2Document4 pagesSchematic Diagram - Group 2kierstyn cabalanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 13 SummaryCharlotteNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Dna QuizDocument3 pagesGrade 12 Dna QuizDawnNo ratings yet
- Cell Culture MediaDocument52 pagesCell Culture MediaSivamani SelvarajuNo ratings yet
- EXOSOME PresentationDocument28 pagesEXOSOME PresentationAlina1102No ratings yet
- PEG PreparationDocument22 pagesPEG PreparationAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Phylogenetic Tree and Neuron Injury DiagramDocument5 pagesExam 2 Phylogenetic Tree and Neuron Injury DiagramJohn Louis Reyes AguilaNo ratings yet
- DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 5: FERTILIZATION PROCESSDocument12 pagesDEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 5: FERTILIZATION PROCESSRajat K. SNo ratings yet
- Laminin TherapyDocument5 pagesLaminin TherapyCristian JimenezNo ratings yet
- Arch Facial Plast SurgDocument5 pagesArch Facial Plast SurgEliann GabaldónNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument3 pagesIntroishika mohanNo ratings yet
- PRP in Facial Rejuvenation - Dras. Rawashdeh y TorricoDocument68 pagesPRP in Facial Rejuvenation - Dras. Rawashdeh y TorricoDra. Andrea Jiménez BelloNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology 2019 PDFDocument11 pagesCape Biology 2019 PDFFelecia Hutchins100% (1)
- I Year IPE - Cell Biology: Short Answer QuestionsDocument3 pagesI Year IPE - Cell Biology: Short Answer QuestionsRaj EevNo ratings yet
- Cloning StrategiesDocument41 pagesCloning StrategiesKumar Aavula100% (2)
- BIBLIOGRAFIE Neural Conduction Synaptic TransmisionDocument16 pagesBIBLIOGRAFIE Neural Conduction Synaptic TransmisionMirela GiurgeaNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin and Myoglobin Structure, Function and GeneticsDocument48 pagesHemoglobin and Myoglobin Structure, Function and GeneticsLuis VicenteNo ratings yet
- Cellville City BlueprintDocument3 pagesCellville City BlueprintJ-Rod MichaelNo ratings yet
- Nervous System WebquestDocument6 pagesNervous System Webquestapi-294104473No ratings yet
- Lesson 21 Cellular RespirationDocument41 pagesLesson 21 Cellular RespirationJanine NacunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Active Reading Guide PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 5 Active Reading Guide PDFMcKenzie Swift-Ramirez50% (2)
- SupDocument2 pagesSupjoshNo ratings yet
- Kuis Imun UTSDocument8 pagesKuis Imun UTSichiNo ratings yet
- Cell & Molecular Biology CourseDocument4 pagesCell & Molecular Biology CourseNatasha ChitiNo ratings yet
- Immunology First Exam..Document7 pagesImmunology First Exam..Abdallah Essam Al-Zireeni100% (1)
- Sel Dan JaringanDocument1 pageSel Dan JaringanBakhitah Nurul100% (1)
- ABO Blood Group SystemDocument60 pagesABO Blood Group SystemAlick MwambunguNo ratings yet
- Published PDFDocument347 pagesPublished PDFSharifAr-RaffiNo ratings yet