Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study
Uploaded by
Mitch ArevaloOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study
Uploaded by
Mitch ArevaloCopyright:
Available Formats
Michelle P.
Arevalo NR-23
Mr. Tiamson
CASE STUDY
An 8 year old boy was seen in the Ma. F.Guerrero school complaining abdominal pain accompanied by shortness of breath (SOB). Vital Signs was taken and recorded as follow: Pulse Rate: 136 bpm Respiratory Rate: 35 cpm Temperature: 35.8 degrees Celsius The patient appears weak, pale, and under nourish. He was also manifested slight Tremor and Diaphoresis. A complete assessment and management where rendered, the boy was kept rested and comfortable. The school clinic physician ordered Paracetamol acetaminophen to be given orally at a round a clock basis.
QUESTIONS:
1. Make an assessment pattern concerning the boy pain experience. 2. Make an outline of the entire nursing health problem manifested by the boy in a prioritize approach. 3. List down all appropriate nursing diagnosis based on prioritized nursing health problem. 4. Make at least two pediatric care plan for the priority health problems for the boy. 5. Make a comprehensive drug study concerning with the clients condition.
1. ASSESSEMENT PATTERN ABDOMINAL PAIN PLACE the pain felt by the student is in the abdomen. EFFECTS the student felt shortness of breath and he appears weak and pale. INTENSIFIERS the pain become worse because the student felt shortening of breath and slight tremor and diaphoresis. NULLIFIERS paracetamol may lessen the pain and it may decrease the body temperature of the student.
2. OUTLINE OF NURSING HEALTH PROBLEM I. Abdominal pain accompanied by shortness of breath II. The student appears weak, pale, and under nourish. III. The student was also manifested slight tremor is an intentional rhythmic and muscle movement and diaphoresis an excessive sweating.
3. NURSING DIAGNOSIS PAIN MANAGEMENT Perform a comprehensive assessment of pain to include location and characteristics of pain in order to plan effective treatment. Reduce or eliminate factors that precipitate or increase the students experience abdominal pain. Provide the students optimal pain relief with prescribed by the school nurse. Evaluate the effectiveness of the pain control measures used through ongoing assessment of the students pain experience.
4. PEDIATRIC CARE PLAN 1. ASSESSEMENT SUBJECTIVE DATA The student verbalized masakit po tiyan ko!
OBJECTIVE DATA: Pulse Rate: 136 bpm Respiratory Rate: 35 cpm Temperature: 35.8 degrees Celsius
DIAGNOSIS acute pain related to under nourishment. PLANNING- reduce or eliminate factors that precipitate or increase the students experience abdominal pain. INTERVENTION- provides the students paracetamol to lessen the students body temperature and reduce abdominal pain. EVALUATION after 4 hours of nursing intervention the student abdominal pain decreases and the body temperature lowered from 38.5 degree Celsius to 38 degree Celsius.
2. ASESSMENT the student felt shortness of breath and he appears weak, pale, and under nourish. DIAGNOSIS acute pain related to abdominal pain as manifested by slight tremors and diaphoresis. PLANNING assist the student in comfortable position to lessen the abdominal pain. INTERVENTION accepts students description of pain. RATIONALE: pain is subjective experience and cannot be felt by others. EVALUATION after 4 hours of nursing intervention the student will feel more comfortable.
5. COMPREHENSIVE DRUG STUDY
GENERIC NAME: Acetaminophen BRAND NAME: Tylenol
DOSAGE: The oral dose for a child is based on the child's age, and the range is 40-650 mg every 4 hours. >1 month to 12 years: 10 to 15 mg/kg/dose every 4 to 6 hours as needed (Maximum: 5 doses in 24 hours)
MECHANISM OF ACTION: Acetaminophen belongs to a class of drugs called analgesics (pain relievers) and antipyretics (fever reducers). The exact mechanism of action of acetaminophen is not known. Acetaminophen relieves pain by elevating the pain threshold, that is, by requiring a greater amount of pain to develop before a person feels it. It reduces fever through its action on the heat-regulating center of the brain. Specifically, it tells the center to lower the body's temperature when the temperature is elevated. ADVERSE REACTION: When used appropriately, side effects with acetaminophen are rare. The most serious side effect is liver damage due to large doses, chronic use or concomitant use with alcohol or other drugs that also damage the liver. Chronic alcohol use may also increase the risk of stomach bleeding. Early signs of toxicity: Anorexia, nausea, diaphoresis (excessive sweating), generalized weakness within the first 12-24 hours. Late signs of toxicity: Vomiting, right upper quadrant tenderness elevated liver function tests within 48-72 hours after ingestion. Antidote: Acetylcysteine. FREQUENCY: Repeat every 4-6 hours as needed. Don't give more than 5 times a day. CONTRA INDICATION: Acetaminophen is metabolized (eliminated by conversion to other chemicals) by the liver. Therefore drugs that increase the action of liver enzymes that metabolize reduce the levels of acetaminophen and may decrease the action of acetaminophen. Doses of acetaminophen greater than the recommended doses are toxic to the liver and may result in severe liver damage. The potential for acetaminophen to harm the liver is increased when it is combined with alcohol or drugs that also harm the liver.
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES: 1. Right Patient Medication is given to the intended client. 2. Right Medication The medication given was the medication ordered. 3. Right Dosage The dose ordered is appropriate for the client. 4. Right Route Give the medication by the ordered route.
5. Right Time Give the medication at the right frequency and at the time ordered according to agency policy. 6. Right Documentation Record the drug administered 7. Right Client Education Explain information about the medication to the client. 8. Right to Refuse Clients have the right to refuse in medication.
9. Right Assessment Some medication requires specific assessment prior to administration. 10. Right Evaluation Conduct appropriate follow-up.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- USNI Medication TestDocument8 pagesUSNI Medication Testusni100% (31)
- Transdermal Delivery of DrugsDocument17 pagesTransdermal Delivery of DrugsRitha PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Agitasi: 190100032 - Tonggo Mario Saragih - B10Document6 pagesMekanisme Agitasi: 190100032 - Tonggo Mario Saragih - B10atika fahiraNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Evaluation of Furosemide Tablets Marketed in LibyaDocument7 pagesA Comparative Evaluation of Furosemide Tablets Marketed in LibyaMediterr J Pharm Pharm SciNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - Pharmaceuticacl Chemistry I - SUMMER 2020Document3 pagesCourse Outline - Pharmaceuticacl Chemistry I - SUMMER 2020JP Tinaya100% (1)
- June19 PDFDocument4 pagesJune19 PDFAnkur ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- The History of EcstasyDocument24 pagesThe History of Ecstasyshakahs204386% (7)
- Pharmaceutical Calculations VIOLET PACOPDocument41 pagesPharmaceutical Calculations VIOLET PACOPSan DarraNo ratings yet
- Potency Class Topical Corticosteroid FormulationDocument5 pagesPotency Class Topical Corticosteroid FormulationgowindamijayaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For B Pharmacy 2020Document170 pagesSyllabus For B Pharmacy 2020Ravi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of TB - Handout (Final) 4-08Document3 pagesPharmacotherapy of TB - Handout (Final) 4-08Ahmedshaker21No ratings yet
- Course Outcome & Practical Outcome of PH-IIDocument9 pagesCourse Outcome & Practical Outcome of PH-IIpoonamNo ratings yet
- Droperidol (Inapsine)Document1 pageDroperidol (Inapsine)ENo ratings yet
- Clarithromycin: Navigation SearchDocument15 pagesClarithromycin: Navigation SearchMayank ShankhwarNo ratings yet
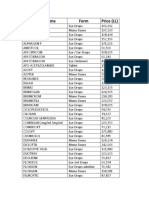
- Brand Name Form Price (LL)Document3 pagesBrand Name Form Price (LL)Ihab HAJ HASSANNo ratings yet
- PharmDocument16 pagesPharmEi SetteNo ratings yet
- Front PageDocument11 pagesFront PageJake PaduaNo ratings yet
- Handbook1 Non Steroidal 1Document60 pagesHandbook1 Non Steroidal 1مها عقديNo ratings yet
- Additional Information Form - HigenDocument6 pagesAdditional Information Form - Higenkhaleel HasanNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Amlodipin UdtDocument7 pagesJurnal Amlodipin UdtdidiisafitriNo ratings yet
- Section ADocument4 pagesSection APAO Janiuay District OfficeNo ratings yet
- Periodic Safety Report PsurDocument12 pagesPeriodic Safety Report PsurKrishna Mohan.p.rNo ratings yet
- USONA INSTITUTE - 2018 - Psilocybin Investigator BrochureDocument59 pagesUSONA INSTITUTE - 2018 - Psilocybin Investigator BrochureSandro RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Louisiana Coronavirus Vaccine LocationsDocument5 pagesLouisiana Coronavirus Vaccine LocationsThe Courier and Daily CometNo ratings yet
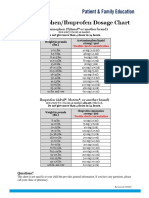
- Acetaminophen Ibuprofen Dosage ChartDocument1 pageAcetaminophen Ibuprofen Dosage ChartByron DubowNo ratings yet
- Final Output PDFDocument43 pagesFinal Output PDFApril Anne CostalesNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Organic Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument19 pagesModule 1 - Organic Pharmaceutical ChemistryMichaela100% (2)
- Polypharmacy in The ElderlyDocument3 pagesPolypharmacy in The ElderlyJC Cris DuroyNo ratings yet
- No Person Can Dispence Medicnine Other Then Reg PharmacistDocument22 pagesNo Person Can Dispence Medicnine Other Then Reg PharmacistSandeep PandeyNo ratings yet
- M Pharm Pharmaceutics Thesis PDFDocument8 pagesM Pharm Pharmaceutics Thesis PDFafknjdsta100% (2)