Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1308213
Uploaded by
shnmtxtOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1308213
Uploaded by
shnmtxtCopyright:
Available Formats
T h e Te c h n o l o g y C o m p a n y
PLCD Displacement Sensor for Industrial Applications
Essential Fields of Application
s Special Vehicles: e.g. excavators, forklifts s Hydraulic, Pneumatic, Electric Drives: e.g. position of piston in cylinders, positioning of valves s Machines, Plants, and Installation s Level Metering, Flow Metering s Automation: e.g. servomechanism, linear and rotary actuators s Conveyor Technology and Storage Technique s Building and Safety Engineering
Construction and Principle of Function
PLCD-Displacement Sensors (Permanentmagnetic Linear Contactless Displacement Sensors) basically consist of a special soft magnetic core surrounded by a coil, wound arround its entire length. On each end of the core there is a second short coil. A permanent magnet guided close to the sensor causes localized magnetic saturation and thereby a virtual division of the core. The position of the saturated area along the sensor axis can be determinated by the coil system. The sensor is supplied by an external electronic module or by an integrated circuit which also produce the output signal. The output signal is linearly dependent on the position of the magnet. The signal can be conditioned by a standard electronic module, which gives either a current output (4 ... 20 mA) or a voltage output (0 ... 5 V or 0 ... 10 V). Customer specific interfaces are possible.
Magnet
Electronic Module
Construction and principle of function of PLCD
Measuring of Circular Motion
Even in the case of bent arrangements of the sensor the principle of function of the displacement sensor is true. Therefore the PLCD is also suited to measure non-linear motions, e.g. rotary actuators.
Example of PLCD layout for angle measurement
Detailled informations, product samples, drawings and specifications are available on request.
T h e Te c h n o l o g y C o m p a n y
Magnetic Drive
The most significant property of Displacement Sensors PLCD is their operation without any mechanical connection between driving magnet and sensor element.This property enables the driving of the sensor through walls made of nonmagnetic materials. The applications, for which the advantages of this quality are very significant, is the indication of the position of a piston in hydraulik or pneumatic systems. The permanent magnet is simply fixed on the piston and drives the PLCD sensor through the cylinder from e.g. aluminum or brass. The driving distance between magnet and sensor (air gap) is determined mainly by the dimensions and the strength of the magnet. For the above mentioned drive through partitions it is important that only moderate magnet allows rather large air gaps (e.g. approx. 15 mm with a 1 cm3 magnet). For the PLCD sensor the driving magnetic field is only the indicator for the position of the driving magnet. The absolute magnetic field strength, in the first order, does not affect the measurement signal, provided that it is large enough to saturate the sensor core. This fact is very important for the mounting tolerances and the influence of air gap variations on the measurement signal. As long as the air gap distance remains inside a certain range of operation arround the optimum distance the influence on the sensor characteristic is neglectable. The optimum driving distance and the extensoin of the range of operation depend on the dimensions and the configuration of the permanent magnet used. Too close air gaps with rather large magnets result in a non-linear characteristic. If the air gap is too large, the usable measurement range will be markedly reduced. The driving magnets selected are basically governed by the application and economic requirements. Magnetic shielding parts protect the sensor system against the interference of magnetic fields, if necessary.
Characteristics
s Continuous, contactless, linear displacement measurement s No mechanical connection between driving magnet and sensor s Magnetic operation adaptable to individual applications s Control through partitions of non-ferromagnetic materials s Large mounting tolerances
a)
b)
c)
d)
Basical magnetic drive configurations
Detailled informations, product samples, drawings and specifications are available on request.
T h e Te c h n o l o g y C o m p a n y
Engineering Competencies
The majority of our products is developed in close co-operation with our customers. Tyco Electronics offers a comprehensive service and customized package. This covers the entire range from the specific design of complex sensor housings through the development of signal prozessing, the dimensioning of magnetic systems, the simulation, the qualification and the prototyping up to the serial production of customized solutions. On request, we will be able to integrate our prototypes for functional test purposes directly into the customer application. If necessary, an integrable standard signal prozessing (ASIC) is available. The performance of the ASIC includes the appropriate alternating current supply, the self control of the ASIC by internal process signal supervision as well as the linear output signal 0 V to 5 V.
Examples of Housings of PLCD
Typical Specification of the PLCD
Measurement Range Linear: 15 mm to 400 mm Measurement Range Angle: 20 to 270 Gap Magnet Sensor: 120 mm Driving Magnetic Field: 2030 mT Operating Temperatur Range: up to 180 C Protection Class: IP 67 (higher on request) Typical Linearity: <2 % Typical Resolution: 0.1 % of measurement range Hysteresis: < 0,2 % of measurement range Threshold Frequencies: 0 Hz / <100 Hz Available Signal Processing (ASIC): Operating Voltage: VP = 5 V 10 % Current Consumtion: < 20 mA Output Signal Ua : 0.5 V ... 4.5 V Second Output Signal Uak : 4.5 V ... 0.5 V
Tyco Electronics AMP GmbH certified according ISO 9001, QS 9000/ VDA 6.1, ISO 14000 certification is in preparation.
2001 Tyco Electronics AMP GmbH Industrial Siemensstr. 13, D-67346 Speyer http://www.tycoelectronics.com 13082134MST04-01 For further informations please contact your local Tyco Electronics Office or your Product Information Center AMP and TYCO are registered trademarks
You might also like
- Scania DC09, DC13, DC16 Industrial Engines - Electrical System - CompressedDocument40 pagesScania DC09, DC13, DC16 Industrial Engines - Electrical System - CompressedMaurice ConnorNo ratings yet
- Fault Detection in TM LineDocument25 pagesFault Detection in TM Linenaveen gNo ratings yet
- Installation of Vibration Sensors: A GuideDocument8 pagesInstallation of Vibration Sensors: A GuidenmguravNo ratings yet
- Electronic Principles IV, 7-8. Military Curriculum Materials For Vocational and Technical Education.Document571 pagesElectronic Principles IV, 7-8. Military Curriculum Materials For Vocational and Technical Education.SolNo ratings yet
- P&ID ManualDocument35 pagesP&ID Manualdharan kumarNo ratings yet
- Putzmeister Pump TrucksDocument17 pagesPutzmeister Pump Truckslwin_oo243575% (4)
- Analysis of Excessive Hydrogen Generation in TransformersDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Excessive Hydrogen Generation in TransformersandikaubhNo ratings yet
- Electronic Sensors in Off-Road VehiclesDocument8 pagesElectronic Sensors in Off-Road VehiclesKrunal Gandhi100% (1)
- Manual LDM5 U enDocument3 pagesManual LDM5 U enLuizAugustoMedeirosNo ratings yet
- Benzophenone/THF StillDocument3 pagesBenzophenone/THF Stillbloggsjoe1970No ratings yet
- Class XII Computer Project - Hotel ManagementDocument29 pagesClass XII Computer Project - Hotel ManagementLakshmi Puthiyedath71% (7)
- Edge Baffle AsslyDocument4 pagesEdge Baffle AsslyVikram TambeNo ratings yet
- Hall-Effect Sensors: Theory and ApplicationFrom EverandHall-Effect Sensors: Theory and ApplicationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Dynamics and Bifurcations-HaleDocument577 pagesDynamics and Bifurcations-Halealaa alqurasheyNo ratings yet
- AathichudiDocument16 pagesAathichudiமுரளி கிருஷ்ணன் alias முகி100% (9)
- 25-Sub-Question Objective Test on Textile Fibres and Manufacturing ProcessesDocument7 pages25-Sub-Question Objective Test on Textile Fibres and Manufacturing ProcessesJoshi Parth100% (1)
- Effect of Restraint, Volume Change, and Reinforcement On Cracking of Mass ConcreteDocument26 pagesEffect of Restraint, Volume Change, and Reinforcement On Cracking of Mass ConcreteDIDIER ANGEL LOPEZ RINCONNo ratings yet
- Syngas Synthesis & Its UseDocument18 pagesSyngas Synthesis & Its UseAekkasit SenaartNo ratings yet
- Digital Substation AlstomDocument36 pagesDigital Substation Alstomdipteshypatel100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Flowmeter User Manual: SHM "Gives You Trust"Document22 pagesElectromagnetic Flowmeter User Manual: SHM "Gives You Trust"Rudi SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Sensor Brochure UKDocument16 pagesCylinder Sensor Brochure UKifm electronicNo ratings yet
- G Series GP GH Analog DPulseDocument18 pagesG Series GP GH Analog DPulseVayu Laxman BNo ratings yet
- Ams Position Sensor OverviewDocument31 pagesAms Position Sensor OverviewLestherBorgeNo ratings yet
- Displacement TransducersDocument20 pagesDisplacement Transducerstibi7hac7No ratings yet
- Displacement Transducers GuideDocument20 pagesDisplacement Transducers GuideRobsonNunesDalColNo ratings yet
- Cat OptoNCDT enDocument36 pagesCat OptoNCDT enNikhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- R Series RP RH AnalogDocument14 pagesR Series RP RH AnaloghaggNo ratings yet
- Brochure Btl's AmetekDocument86 pagesBrochure Btl's AmetekGerardo Cruz EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Universal - Current - Sensors - Report KARTHIKDocument23 pagesUniversal - Current - Sensors - Report KARTHIKKarthik SDNo ratings yet
- ASC DriveBay BrochureDocument2 pagesASC DriveBay Brochureaudy2010No ratings yet
- Micro EpsilonDocument36 pagesMicro EpsilonOrnélio ClossNo ratings yet
- Edge Bafflesautomation: KeywordsDocument4 pagesEdge Bafflesautomation: KeywordsNguyễn Hoàng TuyểnNo ratings yet
- Tyco SensoresDocument10 pagesTyco SensoresFernando Nerys da Silva Nerys NerysNo ratings yet
- R Series RD4 FlexDocument8 pagesR Series RD4 FlexskumarNo ratings yet
- Sensor PDFDocument8 pagesSensor PDFConstanzaNo ratings yet
- Sensor Selecccion Magneto-ResistivosDocument10 pagesSensor Selecccion Magneto-ResistivosMarco Martinez SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Displacement and PositionDocument6 pagesDisplacement and PositioncoolhemakumarNo ratings yet
- Sensors Trainers ST 9000 07.06.2023Document2 pagesSensors Trainers ST 9000 07.06.2023Scienscope SDN BHDNo ratings yet
- Automotive Sensor Technologies Hall Sensors Current SensorsDocument5 pagesAutomotive Sensor Technologies Hall Sensors Current SensorsAhamed Lebbe FaizNo ratings yet
- Sipartps2 Ps2 Fi01 enDocument25 pagesSipartps2 Ps2 Fi01 enpauluspuNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Encoder Sept 2010Document32 pagesMagnetic Encoder Sept 2010zotya54No ratings yet
- Bosch Knock Sensors PiezoDocument2 pagesBosch Knock Sensors Piezoschraeuble100% (1)
- G Series GP GH Analog DPulseDocument17 pagesG Series GP GH Analog DPulsekqarlitosNo ratings yet
- Magnetic EncodersDocument5 pagesMagnetic EncodersGarcia F. Marcio100% (1)
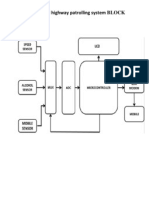
- Unmanned Highway Patrolling System BLOCK: DiagramDocument7 pagesUnmanned Highway Patrolling System BLOCK: DiagramLavanya VijayanNo ratings yet
- A New Generation of Contactless Magnetic Position SensorsDocument7 pagesA New Generation of Contactless Magnetic Position SensorsGautham SidharthNo ratings yet
- MLX91205 DatasheetDocument14 pagesMLX91205 DatasheetRicardo ReisNo ratings yet
- Reed Switch Appln PDFDocument15 pagesReed Switch Appln PDFJeeva BharathiNo ratings yet
- RSF Electronik MS3x Series CatalogDocument20 pagesRSF Electronik MS3x Series CatalogElectromateNo ratings yet
- SWITCH NEW PageDocument6 pagesSWITCH NEW PageSayak BoseNo ratings yet
- GP2Y0D340K: Distance Measuring Sensor Unit Digital Output (400 MM) TypeDocument9 pagesGP2Y0D340K: Distance Measuring Sensor Unit Digital Output (400 MM) TypeAndac KizilirmakNo ratings yet
- Comparision of Torsional Vibration Measurement TechniquesDocument16 pagesComparision of Torsional Vibration Measurement TechniquesRikkinNo ratings yet
- Quadrature Speed and Direction Sensors: SNG-Q SeriesDocument10 pagesQuadrature Speed and Direction Sensors: SNG-Q SeriesShafuan AzizanNo ratings yet
- MCR The Modular Compact Rheometer SeriesDocument20 pagesMCR The Modular Compact Rheometer SeriesKAKAWNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: The Magnetostrictive Position SensorsDocument19 pagesInstruction Manual: The Magnetostrictive Position SensorsJoe Santi LozanoNo ratings yet
- LVDT WhitePaperDocument3 pagesLVDT WhitePaperdetrutamiNo ratings yet
- Proximity Sensor Terminology: Break Function (N.C., Normally Closed) Protection Degree Installation NotesDocument5 pagesProximity Sensor Terminology: Break Function (N.C., Normally Closed) Protection Degree Installation Notespata nahi hai mujeNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic-Flow Meter-Data SheetDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic-Flow Meter-Data SheetAhmed S ElalaftyNo ratings yet
- Positioning Medical Instrument PositioningDocument1 pagePositioning Medical Instrument PositioningBalluff SensorsNo ratings yet
- Proximity Sensor SME 8Document5 pagesProximity Sensor SME 8Violeta Castillo SolorioNo ratings yet
- SIEMENS CatalougeDocument21 pagesSIEMENS CatalougekaicyemNo ratings yet
- Dse 1610.15 Ahz & Dse 1810.35 SHZDocument2 pagesDse 1610.15 Ahz & Dse 1810.35 SHZTaller ManttoNo ratings yet
- Abb Tzid PositionerDocument18 pagesAbb Tzid PositionerMohamed MeeranNo ratings yet
- Vibration Meter IRD811DDocument3 pagesVibration Meter IRD811DNasir RamzanNo ratings yet
- Gaging Probes Get Results - 2013-06-10 - Quality MagazineDocument5 pagesGaging Probes Get Results - 2013-06-10 - Quality MagazinemehdiNo ratings yet
- Kmi15 4Document16 pagesKmi15 4Munish JainNo ratings yet
- Sensor de Toner Ts0524lbDocument5 pagesSensor de Toner Ts0524lbjaag93No ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Searching Literature On 3D FabricsDocument1 pageSearching Literature On 3D FabricsshnmtxtNo ratings yet
- 2012 Gate PaperDocument11 pages2012 Gate PaperSheena BansalNo ratings yet
- Textile Research JournalDocument11 pagesTextile Research JournalshnmtxtNo ratings yet
- Intel GFX CoinDocument2 pagesIntel GFX CoinshnmtxtNo ratings yet
- Meat Cutters DressDocument5 pagesMeat Cutters DressshnmtxtNo ratings yet
- PCM Phase ChangeDocument15 pagesPCM Phase ChangePaulo BarrosNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness Conversion Chart Tables - Engineers EdgeDocument10 pagesSurface Roughness Conversion Chart Tables - Engineers Edgejames.anitNo ratings yet
- DBMS Queries OverviewDocument98 pagesDBMS Queries OverviewAbhinay YadavNo ratings yet
- Basic use of datum planes in Creo ParametricDocument8 pagesBasic use of datum planes in Creo ParametricKartik BhararaNo ratings yet
- Power Generation Engine Performance DataDocument4 pagesPower Generation Engine Performance Dataacere18100% (1)
- Measure Runoff and Soil Loss at Erosion Plots in TanzaniaDocument19 pagesMeasure Runoff and Soil Loss at Erosion Plots in TanzaniaMohd Sofiyan Bin SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Q1 - Answer KeyDocument2 pagesQ1 - Answer KeyJustine AligangaNo ratings yet
- Wilo Fire Fighting BrochureDocument20 pagesWilo Fire Fighting BrochureAkhmad Darmaji DjamhuriNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument20 pagesJavaSivasakthi MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument32 pagesThesis783255No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition - Bergman, Lavine, Incropera, DeWitt (1) - p0015Document1 pageFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition - Bergman, Lavine, Incropera, DeWitt (1) - p0015CladyNo ratings yet
- METAL CLUSTER COMPLEXESDocument13 pagesMETAL CLUSTER COMPLEXESKeybateNo ratings yet
- Noc18 cs48 Assignment3Document4 pagesNoc18 cs48 Assignment3shweta100% (1)
- SSC Questions On Ratio and Proportion PDFDocument7 pagesSSC Questions On Ratio and Proportion PDFRobert ShortNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet 6AV6545-0DA10-0AX0: General InformationDocument8 pagesData Sheet 6AV6545-0DA10-0AX0: General InformationSean MorrisonNo ratings yet
- Ug1085 Zynq Ultrascale TRMDocument1,158 pagesUg1085 Zynq Ultrascale TRMLeandros TzanakisNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction - Derivatives GreeksDocument50 pages1 - Introduction - Derivatives GreeksThomas GallantNo ratings yet
- Leviton ManualDocument82 pagesLeviton ManualRobby Larson100% (1)
- BA (Hons) Philosophy CurriculumDocument123 pagesBA (Hons) Philosophy CurriculumDARSHAN RAAJANNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Investigation of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument12 pagesMathematical Investigation of Trigonometric FunctionsFirasco100% (13)