Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Safety in Welding
Uploaded by
NAGABHUSHAN CPOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Safety in Welding
Uploaded by
NAGABHUSHAN CPCopyright:
Available Formats
INFORMATION SHEET Topics 1. Electric Shock 2. UV- and Heat radiation 3.
Eye Hazards Information Points Electric Shock from damaged power cables, metals etc.
Most arc welding and cutting processes, torch welding, cutting and brazing, or soldering, produce quantities of ultraviolet radiation. UV radiation can burn the skin, and damage the lens of the eye. Flash burns to the eyes are extremely painful, and, can cause permanent damage.
Welders, workers, and visitors, near areas where arc welding is being performed, must be protected from the hazards of ultraviolet rays. This can be done in two ways: by wearing the appropriate PPE, and by placing non-combustible or flameproof screens, curtains, or other effective barriers around the welding operation. Welding hoods and special welding goggles with UV filters are designed to protect your eyes and face from UV exposure. Appropriate gloves and aprons must be used to protect exposed skin.
4. Burns and fires, fire prevention, fire fighting
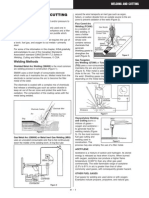
MAIN CAUSES OF FIRES IN WELDING AND CUTTINGFLYING SPARKS Sparks can travel up to 35 feet (10 meters) on a horizontal direction from the work area. Note: Sparks and molten metal can travel greater distances when falling. Sparks can pass through or become lodged in cracks, clothing, pipe holes, and other small openings in floors or partitions. TYPICAL COMBUSTIBLE MATERIALS AND CONDITIONS Parts of buildings such as floors, partitions, and roofs. Contents of buildings such as wood, paper, clothing, plastics, chemicals, and flammable liquids and gases. Outdoor combustible materials include dry leaves, grass, and brush. Welding and cutting have caused explosions when performed in spaces containing Flammable gases, vapors, liquids, or dusts. HOW TO PREVENT FIRES Remove or make safe all combustible materials for a radius of 35 feet (10 meters) around the work area. Protect combustible walls, ceilings, floors, etc., from sparks and heat with fire-resistant covers. Do not dispose of hot slag in containers holding combustible material. Be sure all electrical equipment and wiring are installed properly and have recommended circuit protection. Be sure the work cable is connected to the work as close to the welding area as practical. Work cables connected to the building framework or other locations some distance from the welding area increase the possibility of the welding current passing through lifting chains, crane cables, or other alternate circuits. This can create fire and shock hazards or overheat lifting chains or cables until they fail. In confined spaces, welding can be deadly. Without enough ventilation, toxic fumes and gases can be much stronger. Shielding gases, like argon, can displace the oxygen and kill you. METALS. These are some of the toxic metals: Stainless steel contains nickel and chromium, which can cause asthma. Nickel and chromium 6 can cause cancer. Chromium can cause sinus problems and holes between the nostrils. Carbon steel contains more manganese than some other metals do. Manganese can cause Parkinsons disease, which cripples the nerves and muscles. Zinc in galvanized metal or in paint can cause metal fume fever. It feels like the flu and goes away in a few hours or days after exposure ends.
5. Welding fumes 6. Respiratory hazards
7. Personal protective equipment and clothing
PPEs for Eyes, Head, Breathing, Protecting the body, Hands & Arms, Feet & Legs Cloth: Folding of shirt sleeves & pants shall be avoided during welding Noise Level allowed per day for a human Duration Per Day(Hr.) Sound Level, dB 8 90 Reduction of excessive noise is the first step to hearing protection. Hearing protection starts in the farm shop by keeping the exhaust and muffler system of the tractor in good repair. Machine parts that are not well-lubricated or adjusted also cause loud noises. Need to follow the specific Rules & Regulations formed in each company depending on the kind of Work environment.
8. Noise hazards
9. Specific rules & regulations
You might also like
- Weld Safe For StudentsDocument4 pagesWeld Safe For StudentsCharlyn PandaNo ratings yet
- 9-Welding and CuttingDocument19 pages9-Welding and CuttingAhmed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Safety Precaution in Welding: Ashok Kumar Engineer Sales-Chennai D&H Secheron Electrodes PVT - LTDDocument36 pagesSafety Precaution in Welding: Ashok Kumar Engineer Sales-Chennai D&H Secheron Electrodes PVT - LTDPrakash RajNo ratings yet
- Installation and Maintenance of ServicesDocument68 pagesInstallation and Maintenance of Servicesgodson.jacksonNo ratings yet
- Smaw 12 Module 1Document7 pagesSmaw 12 Module 1Francis Rico Mutia RufonNo ratings yet
- Welding Safety: Amit Gola Assistant Director (Safety)Document21 pagesWelding Safety: Amit Gola Assistant Director (Safety)Vishwash GoyalNo ratings yet
- MIG-200L ManualDocument30 pagesMIG-200L ManualV-Man systemNo ratings yet
- Linkedin: Main Content Starts BelowDocument14 pagesLinkedin: Main Content Starts BelowShakeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Welding Safety: Cummins Southern Plains, LTDDocument32 pagesWelding Safety: Cummins Southern Plains, LTDSaras AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Work Instruction For Welder: Pre-Operation Check For SafetyDocument4 pagesWork Instruction For Welder: Pre-Operation Check For SafetyNnandkishoreNo ratings yet
- Day 5 Apply-Safety-PracticesDocument16 pagesDay 5 Apply-Safety-Practicestrustfaith49No ratings yet
- 1 Electric Gas Welding SafetyDocument34 pages1 Electric Gas Welding SafetyPrincess Mae DesaculaNo ratings yet
- Common 1 General Safety Precaution in WeldingDocument49 pagesCommon 1 General Safety Precaution in WeldingEgghead YTCNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Safety at Work JahangirDocument59 pages1.6 Safety at Work JahangirSaid AbkharNo ratings yet
- Safety Precautions in Welding Operation1Document11 pagesSafety Precautions in Welding Operation1sivaNo ratings yet
- Plasma YH-400 English ManualDocument29 pagesPlasma YH-400 English ManualOLVERACNCMAQUINAS EMPRESANo ratings yet
- Written Report: Electrical Safety Hazards Negative Effects of Inhaling Fumes From Soldering Iron ComponentsDocument8 pagesWritten Report: Electrical Safety Hazards Negative Effects of Inhaling Fumes From Soldering Iron ComponentsAliceNo ratings yet
- MIG Welding Training NotesDocument11 pagesMIG Welding Training NotesJrich19No ratings yet
- JSA Detailed InfoDocument15 pagesJSA Detailed InfoGuptaNo ratings yet
- HSE 9531 TECSM10 Safety in Arc WeldingDocument25 pagesHSE 9531 TECSM10 Safety in Arc WeldingKashish ShahNo ratings yet
- Department of EducationDocument7 pagesDepartment of EducationJay BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Welding Hazards AFSCME Fact SheetDocument11 pagesWelding Hazards AFSCME Fact SheetMuhammad Attaulla KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Eye ProtectionDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Eye ProtectionBuddz WiserNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Safety and Health Hazards (2003)Document18 pagesIntroduction To Safety and Health Hazards (2003)Buddz WiserNo ratings yet
- Thermal Metal SprayingDocument4 pagesThermal Metal SprayingArlen NurlanNo ratings yet
- 17 WeldingDocument18 pages17 WeldingMohan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Q3 Ulas Tle10 Smaw Week1Document13 pagesQ3 Ulas Tle10 Smaw Week1FERNANDO COMEDOY JRNo ratings yet
- Summer Training ReportDocument44 pagesSummer Training ReportPrince KumarNo ratings yet
- Instructions ReportDocument7 pagesInstructions Reportapi-610023363No ratings yet
- Fire Hazards and Life SafetyDocument35 pagesFire Hazards and Life SafetyEdwin AlejoNo ratings yet
- Group 7Document10 pagesGroup 7Dharyl Libarra BardelasNo ratings yet
- SMAWDocument7 pagesSMAWShinNo ratings yet
- Xti-160 Xti-161 DV: Operator ManualDocument16 pagesXti-160 Xti-161 DV: Operator ManualVicente SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Welding & Cutting 1Document14 pagesWelding & Cutting 1Engr. Saruar J. ShourovNo ratings yet
- Growth Series Manual PDFDocument304 pagesGrowth Series Manual PDFMarco CarrierNo ratings yet
- Idustrial Hazards Due To Fire Acciddents, Mechanical and Electrical EquipmentsDocument29 pagesIdustrial Hazards Due To Fire Acciddents, Mechanical and Electrical EquipmentsLisa ValdezNo ratings yet
- Circuit Protection DevicesDocument28 pagesCircuit Protection DevicesRomantic ChickenNo ratings yet
- 5 WeldingDocument18 pages5 WeldingAchref MastouriNo ratings yet
- Welding and CuttingDocument12 pagesWelding and CuttingHarlal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- General Welding Safety PrecautionsDocument11 pagesGeneral Welding Safety PrecautionsDikaAfriandiNo ratings yet
- What Is Polyvinyl ChlorideDocument21 pagesWhat Is Polyvinyl ChlorideAnonymous vcadX45TD7No ratings yet
- Smaw Facilitator GuideDocument62 pagesSmaw Facilitator Guidekhairy2013No ratings yet
- CobramaticDocument40 pagesCobramaticHiram MartinezNo ratings yet
- WELDINGDocument12 pagesWELDINGAsnel TiffaNo ratings yet
- Welding Safety Lectures: Know Your Worksite and SafetyDocument8 pagesWelding Safety Lectures: Know Your Worksite and SafetyNick PieperNo ratings yet
- Safe Welding Practices: Smaw Quarter 1 Week 5 Module 5Document22 pagesSafe Welding Practices: Smaw Quarter 1 Week 5 Module 5Jessel Mejia Onza100% (1)
- Cutting / Welding & Hot Work: Master Builders of IowaDocument38 pagesCutting / Welding & Hot Work: Master Builders of IowaDee DeeNo ratings yet
- Practical Work Book For Health Safety and EnvironmentDocument69 pagesPractical Work Book For Health Safety and EnvironmentAreejNo ratings yet
- WeldingDocument2 pagesWeldingGhodke ParmeshwarNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument3 pagesPosterRahul NambiarNo ratings yet
- Welding Safety PPT 2Document65 pagesWelding Safety PPT 2cfcshakerNo ratings yet
- Safe Soldering Work PracticesDocument2 pagesSafe Soldering Work PracticesKatherine ZumaragaNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding: Name:Elton Adams Teacher: Sir Azam Class: 11tvetDocument13 pagesArc Welding: Name:Elton Adams Teacher: Sir Azam Class: 11tvetelton adamsNo ratings yet
- M.Tech. AMC Lab ManualDocument26 pagesM.Tech. AMC Lab ManualupenderNo ratings yet
- GMAW Facilitator GuideDocument42 pagesGMAW Facilitator GuideEng trk100% (1)
- SIF MTS300/400 Welder ManualDocument20 pagesSIF MTS300/400 Welder Manualsteven5140No ratings yet
- Dust Collection Systems and Solutions for Every Budget: Complete Guide to Protecting Your Lungs and Eyes from Wood, Metal, and Resin Dust in the WorkshopFrom EverandDust Collection Systems and Solutions for Every Budget: Complete Guide to Protecting Your Lungs and Eyes from Wood, Metal, and Resin Dust in the WorkshopNo ratings yet
- Family Handyman Do-It-Yourself Basics Volume 2From EverandFamily Handyman Do-It-Yourself Basics Volume 2Family HandymanRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Thermal Insulation Handbook for the Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical IndustriesFrom EverandThermal Insulation Handbook for the Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical IndustriesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Motor Body Rework SWIPDocument45 pagesMotor Body Rework SWIPNAGABHUSHAN CPNo ratings yet
- Solar Water Heater TankDocument24 pagesSolar Water Heater TankNAGABHUSHAN CPNo ratings yet
- Pylon Construction: 3G WeldingDocument24 pagesPylon Construction: 3G WeldingNAGABHUSHAN CPNo ratings yet
- Carta Maestra de Soldadura y CortDocument7 pagesCarta Maestra de Soldadura y CortAlejandro Del Valle TovarNo ratings yet
- 11 Heat and Material BalanceDocument26 pages11 Heat and Material BalanceCristhofer HernandezNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 NewDocument4 pagesHomework 4 NewnooraNo ratings yet
- MasterTop BSFDocument3 pagesMasterTop BSFnawazkhan23No ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: ProductDocument4 pagesSafety Data Sheet: ProductAchraf Ben DhifallahNo ratings yet
- SOP - Bamboo ScaffoldingDocument10 pagesSOP - Bamboo ScaffoldingsAuRaBhNo ratings yet
- Nuri ProposalDocument26 pagesNuri Proposalkassahun meseleNo ratings yet
- Sabic® PP 575P: PP Homopolymer For Injection MouldingDocument1 pageSabic® PP 575P: PP Homopolymer For Injection MouldingPrinchipi YounesNo ratings yet
- Base Oil Production IIDocument15 pagesBase Oil Production IIrvsinghNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics - QBDocument13 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics - QBInduPalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Compiled by Dr. Soundarajan KrishnanDocument17 pagesLecture Notes Compiled by Dr. Soundarajan KrishnanShanthana LoshiniNo ratings yet
- BASF Company ProfileDocument4 pagesBASF Company ProfileAhmed Mostafa AL-AboudyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8Document4 pagesExperiment 8api-252952453100% (3)
- Worldwide Engineering Standards: Aluminized Sheet SteelDocument7 pagesWorldwide Engineering Standards: Aluminized Sheet SteelJose ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Oxidizing Alcohols LabDocument4 pagesOxidizing Alcohols LabAaron LauNo ratings yet
- BS 1881 201 1986 Testing ConcreteDocument28 pagesBS 1881 201 1986 Testing ConcreteShvan Najeeb100% (1)
- Mivan 9Document40 pagesMivan 9vishaliNo ratings yet
- Basalt Catalogue-CDocument4 pagesBasalt Catalogue-Cdanny buiNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of MatterDocument5 pagesKinetic Theory of Matterapi-3839633No ratings yet
- Normal ResistivityDocument1 pageNormal ResistivityShahzad KhanNo ratings yet
- Endalkachew AbrhameDocument93 pagesEndalkachew Abrhamelibanhaji25No ratings yet
- Cupola Malleable Iron: Standard Specification ForDocument4 pagesCupola Malleable Iron: Standard Specification ForHenriqueNo ratings yet
- DuroplastDocument7 pagesDuroplastBharath ChalmalasettyNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 PTDocument136 pagesUnit-5 PTTanay NaikNo ratings yet
- Manual For Water Filter SystemDocument2 pagesManual For Water Filter Systemgjnxjbm8pbNo ratings yet
- Chemistry STPM Experiment 8 Qualitative Analysis (Second Term) (Cation Anion Inorganic)Document3 pagesChemistry STPM Experiment 8 Qualitative Analysis (Second Term) (Cation Anion Inorganic)Ning Jie Lee89% (36)
- BecherDocument7 pagesBechervalholNo ratings yet
- Water and Waste Management SystemDocument7 pagesWater and Waste Management SystemRhoselle Mae GenandaNo ratings yet
- Aluminum 1100 InformationDocument1 pageAluminum 1100 InformationaxatpgmeNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - MCQs Test - 3Document3 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers - MCQs Test - 3Prasant KumarNo ratings yet