Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ISP Reading Text
Uploaded by
Nazuan MatsinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ISP Reading Text
Uploaded by
Nazuan MatsinCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction The topic of ISP (Protocol) contains features, overviews, setup and procedural information for Internet Services.
The guide is written for general users who will be using Internet Services for scanning, printing and faxing documents and for system administrators who will be setting up Internet Services on the network. Objectives Internet Services also functions as a procedure guide for general users and system administrators. How to perform many of the tasks available with Internet Services that would normally be performed using other network applications or performed at the Document Centre control panel, is included. For example, configure the printing, faxing, and scanning. Scope Based on story line about ISP (Protocol). Based on story line about ISP (Provider). Based on story line about what, how, and the use of ISP (Protocol). The use of Printing, Scanning, and Faxing in ISP (Protocol).
ISP (Protocol) VS ISP (Provider) ISP (Protocol) The Internet Protocol (IP) is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams (packets) across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite. Responsible for routing packets across network boundaries, it is the primary protocol that establishes the Internet. IP is the primary protocol in the Internet Layer of the Internet Protocol Suite and has the task of delivering datagrams from the source host to the destination host solely based on their addresses. For this purpose, IP defines addressing methods and structures for datagram encapsulation. ISP (Provider) An ISP is a company that supplies Internet connectivity to home and business customers. ISPs support one or more forms of Internet access, ranging from traditional modem dial-up to DSL and cable modem broadband service to dedicated T1/T3 lines.
Describe Start from the cloud is an ISP (Provider). When it comes to the router and below, it will become an ISP (Protocol). ISP (Provider) came from a main company, such as Telekom Malaysia (TM), Singtel, AT&T, and much more. ISP (Protocol) is a network diagram or network management in a organization or office. It help people to communicate to each other or doing job. For example, printing, faxing, scanning, sending a file or anything. For example, the switch that have a 4 computers, 1 printer and 2 servers. That is an IT Department. They can control every each of the path in the whole network. Because only they have a server (FTP Server and Web Server). They can manage the web hosting and also they can manage every each of the queue printing, scanning and faxing.
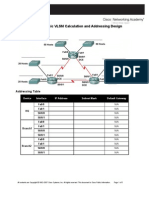
IP Calculation Old Method 20 PCs 2^n 2^5 = 32 (extra 12 PCs or host for future use) Network 192.168.1.0 Broadcast 192.168.1.31 IP Range 192.168.1.1 - 192.168.1.30 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.224 VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask) New Method http://www.vlsm-calc.net/ *Waste of 2 pcs or hosts.
VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Mask) New Method http://www.vlsm-calc.net/
*By using VLSM, you can save 2 extra host. If you have 10 departments, you can safe 20 hosts (2 X 10). CIDR and VLSM Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) is a method for allocating IP addresses and routing Internet Protocol packets. The Internet Engineering Task Force introduced CIDR in 1993 to replace the previous addressing architecture of classful network design in the Internet. Their goal was to slow the growth of routing tables on routers across the Internet, and to help slow the rapid exhaustion of IPv4 addresses. They created VLSM to save the wasted IP Address in IPV4. Access the file through the Internet. Using a browser application, such as Mozilla Firefox or Microsoft Internet Explorer, you can access any Document Centre on a network using the TCP/IP protocol. By entering the Document Centres IP address as the URL in the browser, you have access to the Document Centre for scanning, printing, faxing, performing device management and many other functions you would normally have to execute at the Document Centre control panel.
Why do we need Internet Service? Internet Services gives users access to the Document Centre 220/230/332/340 printing, faxing and scanning control panel features over the internet. Additionally, many system administration tasks can be performed without the use of native network utilities, allowing faster and easier set up of the Document Centre. The features that are described in this section correspond to the tabs that are available within the Internet Services interface. The following features are available with Internet Services: Maintenance Assistance Service Properties Queue Status
maspqs = pronoun mespsques
Services There are three primary areas within Services that are available for general users encompassing Job Submission and Stored Templates selections: Scanning offers the functionality of scanning a paper document into electronic format. Scan options, such as scanning to a specified repository or manipulating templates, allow customisation of scan jobs. Printing offers the high-speed, high-quality, laser printer functionality of the Document Centre. Print ready files can be submitted for printing from the Internet Services user interface. Faxing optionally offers the functionality of a fax machine. If faxing is configured and available on the Document Centre, files can be submitted for faxing from a workstation.
Queue The Queue feature includes options for both users and system administrators: viewing jobs that are processing promoting, cancelling and releasing jobs from the held queue. Status The Status feature includes options for both users and system administrators: Input tray configuration and availability Output tray configuration and availability Tray ready or faulted
Properties Many system options can be set using Internet Services. The Properties feature includes options for system administrators: Modify the system default template that defines how to file, fax, or distribute a scanned document. Define attributes, such as filing policy and confirmation sheet, for stored templates. Obtain device information, such as device profile, fault history, support contacts and billing meters. Maintenance The Maintenance feature includes options for both users and system administrators: Available fonts. Generate configuration and font reports. Generate a test page. Assistance The Assistance feature includes links to additional web pages for both users and system administrators. The Main Problem Statement In Kliuc IP Conflict Any user that expert in Addressing the IP Address can easily enter the IP Address into any any pc. This can cause an IP conflict. Should be 1 IP Address for 1 pc. But in KLIUC, if you know the IP Address you can enter the IP Address whenever that you want Solution For The Main Problem Statement In Kliuc Router IP Static Configuration Each of the router or switch must fix the IP static to 1 location only. For example, Block Academic star from 10.1.1.1 until 10.1.1.254 and the others cant use the same IP Address that are used by Block Academic.
Show CMD Command Telnet and FTP to the main server of www.kliuc.edu.my Easily hacker or an unauthorized user can hack into the main server.
Summary Introducing Internet Services, contains features and support information available with Internet Services. Setting Up Internet Services, contains general overview and setup information for system, network and browser software. also provides scanning, printing and faxing requirements and general setup for Internet Services. Using Internet Services, contains procedures for performing many user and system administrator tasks with Internet Services.
Journal Reference The Internet Protocol Journal Ole J. Jacobsen, Editor and Publisher Getting Started with Internet Services Multinational Professional Services TCP/IP Tutorial and Technical Overview Lydia Parziale David T. Britt Chuck Davis Jason Forrester Wei Liu Carolyn Matthews Nicolas Rosselot The TCP/IP Protocol Suite Fujitsu Network Communications, Inc.
You might also like
- Operational Plan N Financial PlanDocument10 pagesOperational Plan N Financial PlanNazuan MatsinNo ratings yet
- Subdir HtaccessDocument1 pageSubdir HtaccessNazuan MatsinNo ratings yet
- Routing 1 (A)Document5 pagesRouting 1 (A)Nazuan MatsinNo ratings yet
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Dwnload Full Discovering Computers Essentials 2018 Digital Technology Data and Devices 1st Edition Vermaat Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Discovering Computers Essentials 2018 Digital Technology Data and Devices 1st Edition Vermaat Solutions Manual PDFjapitserre5100% (12)
- Care For Network and Computer HardwareDocument209 pagesCare For Network and Computer HardwareBiniyam Efrem50% (2)
- Service MarketingDocument12 pagesService MarketingHemant JainNo ratings yet
- Zimbabwe's Draft Computer Crime and Cybercrime Bill Laymans Draft July 2013Document28 pagesZimbabwe's Draft Computer Crime and Cybercrime Bill Laymans Draft July 2013Business Daily ZimbabweNo ratings yet
- Web Browser Basics: Internet Explorer and FirefoxDocument30 pagesWeb Browser Basics: Internet Explorer and FirefoxAnime 4youNo ratings yet
- Piecewise Word ProblemsDocument2 pagesPiecewise Word Problemsfrankdan79% (14)
- Army Men - World War - Manual - PCDocument29 pagesArmy Men - World War - Manual - PCAnonymous utXYfMAX100% (1)
- Leica gs15 Gps GSM Profile and Bluetooth Guide PDFDocument23 pagesLeica gs15 Gps GSM Profile and Bluetooth Guide PDFebs payNo ratings yet
- Zuckerberg Responses To Commerce Committee QFRs1Document229 pagesZuckerberg Responses To Commerce Committee QFRs1TechCrunch100% (2)
- It Ethics Chap 3Document8 pagesIt Ethics Chap 3Kathleen Gunio100% (1)
- Training REPORTDocument34 pagesTraining REPORTJagannathWijekoonNo ratings yet
- VoIP Office Presentation-Ilovepdf-Compressed PDFDocument14 pagesVoIP Office Presentation-Ilovepdf-Compressed PDFAnoyNo ratings yet
- Profile of Tele Phone IndustryDocument5 pagesProfile of Tele Phone IndustryRavi JoshiNo ratings yet
- 2011 Country Commercial Guide For BotswanaDocument66 pages2011 Country Commercial Guide For BotswanaKago KhachanaNo ratings yet
- Cisco Employee Scholarship Official Rules 3 2Document5 pagesCisco Employee Scholarship Official Rules 3 2MahmudulHasanNo ratings yet
- Network Journal 1Document138 pagesNetwork Journal 1Pushpendu GhoshNo ratings yet
- Ra 9775Document89 pagesRa 9775sajdy100% (1)
- Multinational E-CommerceDocument60 pagesMultinational E-CommerceLong KimQuyNo ratings yet
- Class 5 Computer PDFDocument2 pagesClass 5 Computer PDFMohamed GerezaNo ratings yet
- COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BROADBAND SERVICES OF TELECOM SECTOR" WPDocument75 pagesCOMPARATIVE STUDY OF BROADBAND SERVICES OF TELECOM SECTOR" WPBhavesh GajeraNo ratings yet
- Mango Business ProfileDocument30 pagesMango Business ProfilerafiyemNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis Using Wireshark Cookbook: Chapter No. 13 "Troubleshooting Bandwidth and Delay Problems"Document22 pagesNetwork Analysis Using Wireshark Cookbook: Chapter No. 13 "Troubleshooting Bandwidth and Delay Problems"Packt PublishingNo ratings yet
- Reliance CommunicationsDocument120 pagesReliance CommunicationsMadhav LavaniaNo ratings yet
- Success With Business - Preliminary - AK - 0Document54 pagesSuccess With Business - Preliminary - AK - 0BiancaNo ratings yet
- PUMA Signed Mercedes Caps T&CsDocument7 pagesPUMA Signed Mercedes Caps T&CsMorganeheyneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Intro To EbankingDocument18 pagesLecture 1 - Intro To Ebankingtagashii100% (3)
- Isp Agreement / Service Order For Broadband Service: Bank & BranchDocument2 pagesIsp Agreement / Service Order For Broadband Service: Bank & Branchsidharthsud28No ratings yet
- VAIO Digital Studio™ Computer User GuideDocument94 pagesVAIO Digital Studio™ Computer User GuidePatrick HensleyNo ratings yet
- Smooth Wall HowtoDocument22 pagesSmooth Wall HowtoSharjeel Sayed100% (5)
- To All ChatanoogaDocument17 pagesTo All Chatanoogadon504No ratings yet