Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Importance of Organic Matter
Uploaded by
api-37377450 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views6 pagesstudy
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentstudy
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views6 pagesImportance of Organic Matter
Uploaded by
api-3737745study
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Write down the importance of organic matter.
The importance of soil organic matter is relation to soil fertility and
physical condition is widely recognized. However, organic matter
contributes to the fertility or productivity of the soil through its positive
effects on the chemical, physical and biological properties of the soil.
The role of organic matter in soil is so varied and extensive that it
makes one think of the claims printed on old time patent machine labels;
fortunately these for organic matter are all true.
1. Organic matter influence the soil color due to presence
of adequate amount of organic matter in soil, the color
will be brown to dark brown or black.
2. Organic matter binds soil particles (sand, silt and clay)
into structural units called aggregates. Hence organic
matter has a profound effect on the improvement of
soil structure and thereby soil maintains favorable
condition of aeration and permeability.
3. The rate of infiltration and percolation of water is
enhanced by the application of organic matter in the
soil.
4. Water holding capacity is increased by the application
of organic matter. The amount of available water in
sandy and loamy soils increase with the application of
organic matter.
5. Organic matter reduces plasticity, cohesion, stickiness
etc. in soils containing appreciable amounts of clay.
6. Organic matter increases the ability of the soil to resist
erosion.
7. Organic matter affects the bulk density of soil which in
turn influences the soil porosity favorably.
8. Organic matter reduces losses of surface soil by wind
erosion by forming granules with soil particles.
9. During decomposition or organic matter various
organic acids and CO2 liberate in the soil which help to
reduce alkalinity of soil.
10. Organic matter also acts as a buffering agent. Due to
such buffering effect it reduces the likelihood of
damage to plant roots from excessive acids, alkalis or
added to it in the form of fertilizers and thus stabilizes
the soil pH.
11. Organic matter has solubilizing effect on some mineral
compounds present in the soil.
12. Organic matter can be considered as a store house of
various nutrients essential to plant growth. Organic
matter is the source of 90-95% of the nitrogen in
unfertilized soil. In addition, organic matter supplies
available phosphorus, sulfur and some other
micronutrients like Fe, Mn, Cu, and Zn to the soil and
thereby increases the nutrient as well as improves the
soil health.
13. Organic matter temporarily absorbs heavy metal
pollutants which are usually derived from applied
waste waters used for irrigation. Adsorption of
pollutants helps clean contaminated water.
14. Organic matter serves as a source of energy for both
macro and micro organisms and helps in performing
various beneficial functions in soil.
15. Organic matter acts as a chelate. Chelate is any organic
compound that can bound to a metal more than one
bond and from a ring or cyclic structure by that
bonding.
16. Various organic substances like vitamins, antibiotics
and growth promoting compounds namely auxin are
produced by different micro-organism during
decomposition of various organic matter.
17. Organic matter interact with organic pesticides and it
can absorb N and S oxides from the atmosphere with
have implications with respect to both the yield of crop
plants and the quality of the environmental
respectively.
Harmful effects of organic matter:
Many beneficial effects or organic matter in the soil are
counter balanced by harmful influence under certain conditions. A few
harmful effects are given below:
1. Organic matter is an energy anti carbon source fro
many diseases organism ensuring their longer periods
of survival in soils.
2. Excessive amounts of organic matter create a problem
for mixing the soil thoroughly and abstract easy
planting.
3. Various organic residues produce different
phytotoxins during their decomposition which make
them undesirable as organic matter. Alleopathy is also
active. Alleopathy is any direct or indirect harmful
effect of one plant on another through the production
and release of toxic substance into the environment.
Describe the sample and products of organic matter decomposition:
As a result of enzymic action of organic matter and
consequent formation of humus simple end products are formed
immediately. The simple end products are either used by plants or
microorganisms or readily lost, if not utilized and sink to minimum unless
fresh tissues are frequently added.
As the enzymatic changes of soil organic matter proceed,
simple end products begin to manifest themselves. Some of them especially
carbon dioxide and water appear immediately. Others are nitrate nitrogen
etc. accumulate only after the peak of two vigorous decomposition stage is
over, and the general purpose decay organisms decrease in number.
The common simple products which are formed due to
the activity of soil micro organisms are:
I. Carbon base components: CO2, CO3²ˉ,HCO3ˉCH4, C (elemental
carbon).
II. Nitrogen base compounds: NH4+, NO2+, NO3ˉ, N(gaseous)
III. Sulfur base compounds: S, H2S, SO3²ˉ, SO4²ˉ, CO2
IV. Phosphorus base compounds: H2PO4, HPO4²ˉ, PO4³ˉ(in acidic
soil)
V. Other sample products: H2O, H+, OHˉ, O2, H2, Na+, K+, Ca²+,
Mg²+, Fe²+, Zn, Mn, Ge etc.
Distinguish between peat and muck:
Peat Muck
1. An organic soil that contains more 1. An organic soil that contain 20-
than 50% organic matter & the 50% organic matter & the organic
organic matter is partially decayed or matter is completely decomposed, is
non-decayed, is called peat. called muck.
2. The kind of plant in the peat can 2. The plant materials of muck
be identified. cannot be identified.
3. Peat soils are coarse/fine textured 3. Muck soils are quite fine textured
depending on the nature of deposited as the original plant materials are
plant residues. broken down.
4. Light in color 4. Light in color
• Describe the influence of organic matter on soil properties.
Or
*Describe in detail the importance of soil organic matter in soil fertility.
Or
• Write down the function of soil organic matter on soil properties.
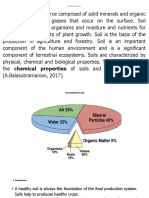
Organic matter is an essential part of a productive soil.
Although it remains in the soil in a small amount it is a store house of
plant nutrients in the soil. It influence on the physical, chemical and
biological properties of the soil, the functions of organic matter are
described as below
Effect of physical properties of soil
1. Effect of organic matter on soil erosion:
Coarse organic matter on the soil surface reduces impact
of the falling raindrop and permits clear water to seep gently into the soil. As
a result surface run off of water and erosion are reduced. And there is more
available water for plant growth. Coarse organic matter on the soil surface
reduced losses of soil by wind erosion.
2. Effect of organic matter on soil temperature:
Organic matter makes a soil black colored. Black colored
soil absorbs more heat than lighter colored soil. This
temperature is necessary for seed germination. On the
other hand surface mulches lower soil temperatures in the
summer and keep the soil warmer in winter.
3. Effect of organic matter on soil evaporation:
Evaporation losses of water are reduced by organic
matter.
4. Effect of organic matter on soil structure:
Decomposing organic matter produces slimes and
microbial gums which help to form and to stabilize
desirable soil structure.
5. Effect of organic matter on decay of plant root:
When the plant roots decay they provide channels,
through which new plant roots grow. These channels are
effective in transmitting water and plants use this water
from the channels.
6. Effect of organic matter on water holding capacity:
Organic matter increases water holding capacity in the
soil. It holds water fairly tightly, thus the permanent
wilting percentage is increased.
• Effect on chemical properties in soil:
1. Effect of organic matter on nutrient availability:
Upon decomposition organic matters supply some
of all nutrients needed by growing plants. When
external condition are favorable for rapid plant
growth. The same conditions favor a rapid release
of nutrients from the organic matter. Most of the
soil nitrogen occurs in organic combination which
releases nitrogen in the soil for plant.
2. Effect of organic matter on ion exchange:
Humus as well as organic matter is store house for
the exchangeable and available cations such as K+,
Ca²+. Mg²+, etc. temporary it holds NH4+ ion in an
exchangeable and available form. It increases ion
exchange capacity of the soil.
3. Effect of organic matter on availability of phosphorus:
Fresh organic matter has a special function in
making available soil phosphorus in acid soil.
Upon decomposition organic matter releases
citrates, oxalates, tetrahedral and lactates, which
combine with iron and aluminum more readily
than does phosphorus. As a result the availability
of phosphorus ion increased.
4. Effect of organic matter on solubility of soil minerals:
Upon decomposition of organic matter, reduced
various kinds of acids and carbon dioxide which
reacts with soil minerals and dissolve it and
releases plant nutrient elements.
5. Effect of organic matter on buffering:
Organic matter as well as humus contains various
kinds of exchangeable cations which resist the soil
pH after making a small amount of acid and alkali.
6. Effect of organic matter on reclamations of alkalinity:
After decomposition of organic matter and
inorganic acids are released. These acids help to
reduce alkalinity of soil.
* Effect of biological properties of soil:
1. Effect of organic matter on the source of food and energy of
microorganisms.
Soil organic matter is the main food and energy
source of soil microorganisms. Through decomposition of organic matter
microorganisms take up their food elements. So organic matter serves as a
source of energy for the growth of soil micro-organisms.
You might also like
- Group JDocument3 pagesGroup Jusman abdulkarimNo ratings yet
- Unit JDocument22 pagesUnit JY. NARASHIMHA VITTALNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 SoilDocument34 pagesLecture 5 SoilMudassar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of Soil: Minerals, Organic Matter & MoreDocument8 pagesChemical Properties of Soil: Minerals, Organic Matter & MoreMahnoor FarooqNo ratings yet
- Soil Resources: Earth Science'SDocument59 pagesSoil Resources: Earth Science'SJoshua Glenn EbronNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Use of CompostDocument12 pagesPreparation and Use of Compostronalit malintadNo ratings yet
- Study of SoilsDocument39 pagesStudy of Soilsjumajumbe150No ratings yet
- Unit 4. The Soil ChemistryDocument104 pagesUnit 4. The Soil ChemistryMorena EmorNo ratings yet
- New Soil FertilityDocument16 pagesNew Soil FertilitySarahNo ratings yet
- Soil Fertility Factors Affecting Soil FeDocument13 pagesSoil Fertility Factors Affecting Soil FeUmme HaniNo ratings yet
- GEOGRAPHY A LEVEL (FORM SIX) NOTES - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY 1.5 - STUDY OF SOIL - EcoleBooksDocument63 pagesGEOGRAPHY A LEVEL (FORM SIX) NOTES - PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY 1.5 - STUDY OF SOIL - EcoleBooksMukasa NajibNo ratings yet
- Agricultural ScienceDocument4 pagesAgricultural ScienceNadia HammondNo ratings yet
- Organic matter's role in soil and plant healthDocument5 pagesOrganic matter's role in soil and plant healthCall'me Mo MayNo ratings yet
- MICROCLIMATEDocument14 pagesMICROCLIMATERyza MartizanoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Soil Organic Matter On Physical Properties of SoilDocument6 pagesEffect of Soil Organic Matter On Physical Properties of Soiljohnronaldmiranda93No ratings yet
- Soil PropertiesDocument3 pagesSoil Propertiesnyandengthomas7No ratings yet
- Determination of Organic Content in Different Boreholes in Various Regions in Khulna DivisionDocument12 pagesDetermination of Organic Content in Different Boreholes in Various Regions in Khulna DivisionSuvashis PaulNo ratings yet
- Stmarysmazindejuu Ac TZ Gallery DjuM 1512281451309814Document13 pagesStmarysmazindejuu Ac TZ Gallery DjuM 1512281451309814Venance Mubisehi MukulansaboNo ratings yet
- Soil Microbiology: Sana'a University Faculty of Science Biology DepartmentDocument38 pagesSoil Microbiology: Sana'a University Faculty of Science Biology DepartmentNesma NsrNo ratings yet
- Soil Organic Matter Benefits and ManagementDocument2 pagesSoil Organic Matter Benefits and ManagementYash rautNo ratings yet
- 17 - 18 Carbon Cycle - Humus Formation PDFDocument10 pages17 - 18 Carbon Cycle - Humus Formation PDFshubhamNo ratings yet
- G7 SoilDocument43 pagesG7 SoilJamika ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1st Mid PartDocument13 pages1st Mid PartAbdullah Al Mamun100% (1)
- Organic MatterDocument5 pagesOrganic MatterPc NdujiNo ratings yet
- Notes of Soil MicrobiologyDocument60 pagesNotes of Soil MicrobiologyJagdish Donde89% (54)
- Soil Components: Chemistry For Engineers (Chem 114E) Bpsu Science ClusterDocument15 pagesSoil Components: Chemistry For Engineers (Chem 114E) Bpsu Science ClusterJohn Andrei Q. PadillaNo ratings yet
- Yr 10 WK 6 & 8 NoteDocument6 pagesYr 10 WK 6 & 8 Notesedrick ocheNo ratings yet
- CARRENDocument4 pagesCARRENMIKI RULOMANo ratings yet
- Soil - Components, Properties and Processes (1Document12 pagesSoil - Components, Properties and Processes (1Tiffany RishiNo ratings yet
- PProb6 176819212 Notes of Soil MicrobiologyDocument60 pagesPProb6 176819212 Notes of Soil MicrobiologyjacjiNo ratings yet
- Chemical & Biological Properties of The SoilDocument122 pagesChemical & Biological Properties of The SoilJoshua StevenNo ratings yet
- Roles and sources of organic matterDocument4 pagesRoles and sources of organic matterEyeVanNo ratings yet
- Unit2 - Ecological Factors Soil and WatarDocument39 pagesUnit2 - Ecological Factors Soil and WatarSejal PrasadNo ratings yet
- Soil PreparationDocument48 pagesSoil PreparationVincent Paul BillonedNo ratings yet
- Module+19+-+UNIT+IV Chemistry+of+the+Soil+ (Part+1)Document8 pagesModule+19+-+UNIT+IV Chemistry+of+the+Soil+ (Part+1)Gema Rose llenadoNo ratings yet
- HANNA - Soil Test HandbookDocument16 pagesHANNA - Soil Test HandbookMukul SinghNo ratings yet
- Build Rich Soil with Organic AmendmentsDocument16 pagesBuild Rich Soil with Organic AmendmentsSyafinaz WanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. The Organic Matter and The Soil Organic MatterDocument22 pagesChapter 6. The Organic Matter and The Soil Organic MattercyrillakinanNo ratings yet
- Soil Pollution Diaconu Vasile Grupa 7401Document7 pagesSoil Pollution Diaconu Vasile Grupa 7401Adelina GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Soil Resources Definition of Soil Factors Brief Introduction To Soil ClassificationDocument10 pagesSoil Resources Definition of Soil Factors Brief Introduction To Soil Classificationkhatrishivam7864No ratings yet
- Chem101 Ho10Document9 pagesChem101 Ho10Claire TaborNo ratings yet
- Soil Sience - Awoke E.Document77 pagesSoil Sience - Awoke E.awokeNo ratings yet
- Understanding Soil ChemistryDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Soil ChemistryJhess GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Fungsi TanahDocument5 pagesFungsi TanahM. Ilham Tegar YunusNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 10 Organic Matter DecompositionDocument3 pagesEXERCISE 10 Organic Matter DecompositionKobe Conrad AbelleraNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Chemical and Organic FarmingDocument4 pagesDifferences Between Chemical and Organic FarmingRahul N Shripati100% (2)
- 01 Soils 221015 (Revised) KopieDocument30 pages01 Soils 221015 (Revised) KopieAlberto CamachoNo ratings yet
- Soil Organic Matter PDFDocument13 pagesSoil Organic Matter PDFBishwaksen BaidyaNo ratings yet
- 212 Master Gardener Living SoilDocument6 pages212 Master Gardener Living SoilAlex KreiterNo ratings yet
- Mini Project HarshithaDocument18 pagesMini Project HarshithaGurram AmarsaiNo ratings yet
- Senesi 1989Document22 pagesSenesi 1989Vikas GoyalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Chemistry of The Environment The Soil Chemistry: Learning ObjectivesDocument17 pagesUnit 4 - Chemistry of The Environment The Soil Chemistry: Learning ObjectivesNiña Viaña BinayNo ratings yet
- C2017 06SoilOrganicMatterDocument4 pagesC2017 06SoilOrganicMatterGabriel OrregoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry and AnalysisDocument12 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry and Analysissubhajit29in100% (1)
- Activity 5 - Produce Organic FertilizersDocument2 pagesActivity 5 - Produce Organic FertilizersAbby AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Components of SoilDocument6 pagesComponents of SoilRyanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Soil: Functions, Importance and PhasesDocument28 pagesIntroduction to Soil: Functions, Importance and PhasesYosephNo ratings yet
- Causes & Effects of Soil PollutionDocument5 pagesCauses & Effects of Soil PollutionHaiper CT100% (1)
- Digging in II Understanding Soil Nutrients PDFDocument25 pagesDigging in II Understanding Soil Nutrients PDFPRASOON PSNo ratings yet
- Soil Health : Understanding and Enhancing Soil Biology and NutrientsFrom EverandSoil Health : Understanding and Enhancing Soil Biology and NutrientsNo ratings yet
- PracDocument31 pagesPracapi-3737745100% (1)
- PracDocument31 pagesPracapi-3737745100% (1)
- 307 Lab ReportDocument12 pages307 Lab Reportapi-3737745No ratings yet
- Soil 302Document20 pagesSoil 302api-3737745100% (3)
- Soil AmmendmentDocument4 pagesSoil Ammendmentapi-3737745No ratings yet
- Soil ReactionDocument18 pagesSoil Reactionapi-3737745100% (3)
- Soil Organic MatterDocument46 pagesSoil Organic Matterapi-3737745100% (1)
- 305 Lab ReportDocument12 pages305 Lab Reportapi-3737745No ratings yet
- PotassiumDocument14 pagesPotassiumapi-3737745No ratings yet
- NitrificationDocument3 pagesNitrificationapi-3737745No ratings yet
- Ion Exchange 2Document26 pagesIon Exchange 2api-3737745100% (3)
- My CollectionsDocument3 pagesMy Collectionsapi-3737745No ratings yet
- LimeDocument19 pagesLimeapi-3737745100% (1)
- Largest Earthquakes by MagnitudeDocument11 pagesLargest Earthquakes by MagnitudeNickCanabeNo ratings yet
- MELC-Earth Life ScienceDocument5 pagesMELC-Earth Life ScienceAnNaMAyAbarracoso-Babon75% (4)
- List of Active Volcano in MindanaoDocument3 pagesList of Active Volcano in MindanaoVikki AmorioNo ratings yet
- The Potential For Giant Tsunamigenic Earthquakes in The Northern Bay of BengalDocument5 pagesThe Potential For Giant Tsunamigenic Earthquakes in The Northern Bay of BengalNathan VincentNo ratings yet
- Earth's Interior Structure and Properties QuizDocument6 pagesEarth's Interior Structure and Properties Quizknickpoint waterfallNo ratings yet
- Geol 222 Stratigraphy & Historical Geology: MRS RoferosDocument16 pagesGeol 222 Stratigraphy & Historical Geology: MRS RoferosMary Rose Soria Roferos100% (1)
- Deep Sea Sediment Gravity Flow Deposits in Gulf of Tomini, SulawesiDocument9 pagesDeep Sea Sediment Gravity Flow Deposits in Gulf of Tomini, SulawesiSubhan ArifNo ratings yet
- Major Tectonic Plates & Boundaries ExplainedDocument5 pagesMajor Tectonic Plates & Boundaries ExplainedDaniela AndradeNo ratings yet
- Ramos, 2009 - Geological - JournalDocument24 pagesRamos, 2009 - Geological - Journalfrancarlos de la cruz chuquimangoNo ratings yet
- 10 Natural Hazard - Mass MovementDocument58 pages10 Natural Hazard - Mass MovementMary Angelie IlaganNo ratings yet
- Seismic SlidesDocument116 pagesSeismic SlidesGul E ZahraNo ratings yet
- Paper - Origin and Evolution of Sedimentary Basins Their Energy and Mineral Resources With Reference To International Issues in The Mediterranean Sea State of The ArtDocument151 pagesPaper - Origin and Evolution of Sedimentary Basins Their Energy and Mineral Resources With Reference To International Issues in The Mediterranean Sea State of The ArtResky ArdianNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document13 pagesTutorial 4shalvinNo ratings yet
- IGCP BrazilDocument116 pagesIGCP BrazilZildaPenaNo ratings yet
- Geological Society of America Memoir 162 1984: Jurassic La Quinta Formation in the Sierra de Perija, VenezuelaDocument20 pagesGeological Society of America Memoir 162 1984: Jurassic La Quinta Formation in the Sierra de Perija, VenezuelaEdgar Castiblanco OrtizNo ratings yet
- Relationships Between Undrained Shear Strength, Liquidity Index, and Water Content Ratio of ClaysDocument12 pagesRelationships Between Undrained Shear Strength, Liquidity Index, and Water Content Ratio of ClaysArham SheikhNo ratings yet
- Mr. Rolando DC. Nicolas JRDocument28 pagesMr. Rolando DC. Nicolas JRSharlaine TandinganNo ratings yet
- 2nd Ishihara Lecture SPT and CPT Based RelationshipDocument12 pages2nd Ishihara Lecture SPT and CPT Based Relationshipabel100% (1)
- SSC Petrology: Classification of Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic RocksDocument11 pagesSSC Petrology: Classification of Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic RocksArianne Mae De Vera GallonNo ratings yet
- Igneous Layering in Basaltic Magma ChambersDocument78 pagesIgneous Layering in Basaltic Magma ChambersCristian GomezNo ratings yet
- Diagram of Subduction ProcessDocument48 pagesDiagram of Subduction ProcessThea Rusia100% (1)
- BCL Drilling Services: Borehole LogDocument7 pagesBCL Drilling Services: Borehole LogDennis SagaoNo ratings yet
- Geologic Processes and Hazards ExplainedDocument16 pagesGeologic Processes and Hazards ExplainedAlexa Fatima100% (1)
- Science Quarter 1 Week 1.1: Not For SaleDocument5 pagesScience Quarter 1 Week 1.1: Not For SaleWesley M. PerezNo ratings yet
- DRRR - Parallel-Assessment-Q3 AnneDocument6 pagesDRRR - Parallel-Assessment-Q3 Anneangelica barruelaNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering IDocument19 pagesGeotechnical Engineering IJanina MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- Week 1B Melc 13 Science 9 Q3 Las - Anna Liza D. MacoDocument7 pagesWeek 1B Melc 13 Science 9 Q3 Las - Anna Liza D. MacoaljemerNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Sixth GradeDocument15 pagesPlate Tectonics: Sixth GradenicNo ratings yet
- Volcano Case StudyDocument3 pagesVolcano Case StudyJosephat MugumbaNo ratings yet
- Minggu 2 Mekanika Tanah 2Document47 pagesMinggu 2 Mekanika Tanah 2Nur CahyoNo ratings yet