Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LMDT
Uploaded by
hassnainiqbal11Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LMDT
Uploaded by
hassnainiqbal11Copyright:
Available Formats
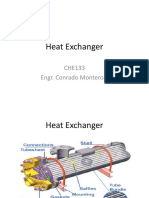
HEAT TRANSFER LOG MEAN TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCE (LMTD) METHOD The rate of heat transfer is a heat exchanger can
be expressed as q UA Tm Where Tm is the log mean temperature difference given as T T1 T2 m T ln 1 T2 Parallel Flow Heat Exchanger
HEAT EXCHANGER LMTD METHOD Counter Flow Heat Exchanger
Multipass and Cross flow heat exchangers In these heat exchangers, the correction factor is used where the log mean temperature difference is expressed as Tlm F Tlm ,CF F is the correction factor Tlm ,CF is the log mean temperature difference for a counter flow heat exchanger Tlm is the actual log mean temperature difference
The correction factor is determined from charts in Figure 1318
HEAT EXCHANGER LMTD METHOD
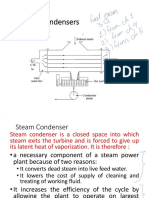
Figure 1318 Correction factor F charts for common shell-and-tube and cross-flow h eat exchangers (from Bowman, Mueller, and Nagle) HEAT EXCHANGER LMTD METHOD Questions 1. Steam in the condenser of a power plant is to be condensed at a temperature of 30C with cooling water from a nearby lake, which enters the tubes of the conde nser at 14C and leaves at 22C. The surface area of the tubes is 45 m2, and the overall heat transfer coefficient is 2100 W/m2 K. Det ermine the mass flow rate of the cooling water needed and the rate of condensati on of the steam in the condenser. (Ans: 1087 kW, 32.5 kg/s, 0.45 kg/s) 2. A counter-flow double-pipe heat exchanger is to heat water from 20C to 80C at a rate of 1.2 kg/s. The heating is to be accomplished by geothermal water available at 160C at a mass flow rate of 2 kg/s. The inner tube is thin-walled an d has a diameter of 1.5 cm. If the overall heat transfer coefficient of the heat exchanger is 640 W/m2 K, determine the length of the heat exchanger required to achieve the desired heating. (Ans: 108 m) 3. A 2-shell passes and 4-tube passes heat exchanger is used to heat glycerin f rom 20C to 50C by hot water, which enters the thin-walled 2-cm- diameter tubes at 80C and leaves at 40C. The total length of the tubes in the heat exchanger is 60 m. The convection heat transfer coefficient is 25 W/m2 K on the glycerin (shell) side and 160 W/m2 K on the water (tube) side. Determine the rate of heat transfer in the heat exchanger (a) before any fouling occurs and (b) after fouling with a fouling factor of 0.0006 m2 K/ W occ urs on the outer surfaces of the tubes. 3
(Ans 1830 W, 1805 W)
HEAT EXCHANGER
4 LMTD METHOD 4. A test is conducted to determine the overall heat transfer coefficient in an automotive radiator that is a compact cross-flow water-to-air h eat exchanger with both fluids (air and water) unmixed. The radiator has 40 tub es of internal diameter 0.5 cm and length 65 cm in a closely spaced plate-finned matrix. Hot water enters the tubes at 90C at a rate of 0.6 kg/s and leaves at 65C . Air flows across the radiator through the interfin spaces and is heated from 20C to 40C. Determine the overall heat transfer coefficient Ui of thi s radiator based on the inner surface area of the tubes. Data: specific heat cap acity of water is 4184 J / kg K (Ans 3341 W/m2 K)
HEAT EXCHANGER LMTD METHOD
You might also like
- Tutorial 5 TFP260S PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial 5 TFP260S PDFHundzukani Ngobeni100% (1)
- Basic Training For Oil and Chemical Tankers CargoDocument140 pagesBasic Training For Oil and Chemical Tankers CargoCamilla Alba100% (8)
- Hydraulic Engineering Experiment H6: Flow Measurement in Closed ConduitsDocument20 pagesHydraulic Engineering Experiment H6: Flow Measurement in Closed ConduitsKS Chong100% (1)
- ME 307: Heat Transfer Equipment Design: (Arpachi-Ex-7.9)Document5 pagesME 307: Heat Transfer Equipment Design: (Arpachi-Ex-7.9)mz_haqNo ratings yet
- MEHB323 Example Question On Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesMEHB323 Example Question On Heat ExchangerAkmal RosliNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger MathDocument8 pagesHeat Exchanger MathMasum ParvezNo ratings yet
- Tablet FormulationDocument9 pagesTablet FormulationChintan Deepakkumar Kabir100% (2)
- 3 Avaliacao Grupo1 PDFDocument3 pages3 Avaliacao Grupo1 PDFPedro Henrique Fauro De AraujoNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 6 Heat ExchangerDocument4 pagesTUTORIAL 6 Heat ExchangerFikri Rahim50% (2)
- Prob Sheet Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesProb Sheet Heat ExchangerAnonymous mXicTi8hB0% (1)
- Ihte Que BankDocument2 pagesIhte Que BankNikunj PatelNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness Ntu MethodDocument4 pagesEffectiveness Ntu MethodBen Musimane100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Tutorial 1 PDFDocument2 pagesHeat Exchanger Tutorial 1 PDFNitin BuZz100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Tutorial Sheet 5Document4 pagesHeat Exchanger Tutorial Sheet 5Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Tutorial Sheet 5Document4 pagesHeat Exchanger Tutorial Sheet 5Charlotte BNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lab ManualDocument43 pagesHeat Transfer Lab ManualNarasimharajan ManiNo ratings yet
- PS Chapter11Document6 pagesPS Chapter11x비No ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions On Heat Ex ChangersDocument3 pagesTutorial Questions On Heat Ex ChangersPuneet Garg100% (1)
- Tut 4 Heat ExchangersDocument2 pagesTut 4 Heat ExchangersGomolemo BaarxxNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesTutorial Heat ExchangerAhmad Nor Fahmi WalidNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger (New)Document38 pagesHeat Exchanger (New)Rochie DiezNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document3 pagesTutorial 8CHANDAN RAJNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2-Pressure DropDocument2 pagesSheet 2-Pressure Dropmohelg83No ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger ReportDocument8 pagesHeat Exchanger Reportarslan shahidNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document1 pageAssignment 5olenbearNo ratings yet
- Tugas 2 TMK 3Document2 pagesTugas 2 TMK 3Arif Fuji HariyantoNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger 2Document64 pagesHeat Exchanger 2John Louie GresulaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Revised SolutionDocument11 pagesTutorial 3 - Revised Solutionngoc.nguyenlamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chap5Document1 pageTutorial Chap5Aman RedhaNo ratings yet
- Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger Manual NewDocument9 pagesShell & Tube Heat Exchanger Manual NewNikhil DhimanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 SlideDocument21 pagesChapter 4 Slidecanva proNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document3 pagesTutorial 6Hoài ThươngNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument3 pagesExamBiyadgie AlebelNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation of Heat TransfeRDocument20 pagesExperimental Investigation of Heat TransfeRsurajNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IVDocument4 pagesAssignment - IVdivyanshu.221ch018No ratings yet
- Tutorial 10 CengelDocument1 pageTutorial 10 Cengelsakinah azizanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-1 - Heat Exchanger CalculationsDocument50 pagesLecture 3-1 - Heat Exchanger CalculationsBilal AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Process Heat Transfer (CDB2023)Document4 pagesAssignment - Process Heat Transfer (CDB2023)qrunchyNo ratings yet
- Basic Design MethodologyDocument4 pagesBasic Design MethodologySatya SuryaNo ratings yet
- Prob Set Heat and MassDocument15 pagesProb Set Heat and MassCheng PasionNo ratings yet
- MHM 420 - 780 2019 Assignment 5 PDFDocument2 pagesMHM 420 - 780 2019 Assignment 5 PDFTatenda NyabadzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Power 2021 QFir1Document39 pagesChapter 5 Power 2021 QFir1leena aljabrNo ratings yet
- Numerical Problems LMTDDocument4 pagesNumerical Problems LMTDKhalidNo ratings yet
- MEHB323 Tutorial Assignment Ch11Document2 pagesMEHB323 Tutorial Assignment Ch11Lufy HahaNo ratings yet
- Design of HEDocument35 pagesDesign of HESaurabh SengarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Heat Exchanger Sem 1 2019 2020 PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial Heat Exchanger Sem 1 2019 2020 PDFmimie azideeNo ratings yet
- Me8693 Heat and Mass Transfer - QBDocument5 pagesMe8693 Heat and Mass Transfer - QBmeckup123No ratings yet
- EKC 216 Wk13 Chapter 10 - Heat Exchanger L1 2017.keyDocument52 pagesEKC 216 Wk13 Chapter 10 - Heat Exchanger L1 2017.keySyazwan WanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - HMTDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank - HMTSUNDARAMAHALINGAM ANo ratings yet
- 4 25293 730Document12 pages4 25293 730elsa fitrianti pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems For Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesPractice Problems For Heat ExchangerFour AyesNo ratings yet
- HMT 113401 Anna UnivDocument5 pagesHMT 113401 Anna Univsathiya_ramNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger ProblemsDocument4 pagesHeat Exchanger ProblemsmiraNo ratings yet
- 09 - Heat Transfer EquipmentDocument22 pages09 - Heat Transfer EquipmentsanelisofuturemoyoNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument1 pageHeat ExchangerArpit GoyalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 SolutionDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 Solutionngoc.nguyennhuNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Topico 3 Moreta HenryDocument6 pagesEjercicios Topico 3 Moreta HenrystearimofyNo ratings yet
- Concentric Tube Heat Exchanger ReportDocument19 pagesConcentric Tube Heat Exchanger Reportillyzl100% (1)
- Double Pipe Heat ExchangerDocument3 pagesDouble Pipe Heat ExchangerSayyeda Neha FatimaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1877705815030623 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S1877705815030623 MainJOAM MANUEL RINCÓN ZULUAGANo ratings yet
- Context Clues: "Using Context Clues in The Sentences or Paragraph"Document4 pagesContext Clues: "Using Context Clues in The Sentences or Paragraph"Rizki fitriana dewiNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA EllaDocument3 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA EllaElla IntanNo ratings yet
- Ame101 LecturenotesDocument5 pagesAme101 Lecturenotesagrocel_bhvNo ratings yet
- 2-Electrochemistry: Week 3 - Topic 2Document65 pages2-Electrochemistry: Week 3 - Topic 2ClarkNo ratings yet
- CLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 17 Stars and Solar SystemDocument7 pagesCLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 17 Stars and Solar SystemSurbhi NayarNo ratings yet
- Cto Coal To OlefinsDocument50 pagesCto Coal To OlefinsJUAN ANTONIO HERNANDEZ SOSANo ratings yet
- Jgeot.21.00089 OffprintDocument11 pagesJgeot.21.00089 OffprintBrian SheilNo ratings yet
- Demystifying Quantum MechanicsDocument10 pagesDemystifying Quantum Mechanicsmrbubos0% (1)
- Exercise 5 Organic Components: Proteins and LipidsDocument2 pagesExercise 5 Organic Components: Proteins and LipidsHanna Joy BringuelaNo ratings yet
- DLP n0. 2 in Science Super Duper FinalDocument5 pagesDLP n0. 2 in Science Super Duper FinalMichelle ManilaNo ratings yet
- Constant Head Permeability TestDocument14 pagesConstant Head Permeability Testfuji0% (1)
- SCIENCE-10 Q4 MOD3 Biomolecules-Carbohydrates-Lipids BookletDocument12 pagesSCIENCE-10 Q4 MOD3 Biomolecules-Carbohydrates-Lipids BookletRetep Aren100% (2)
- Determination of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Using Flame Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument4 pagesDetermination of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA) in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Using Flame Atomic Absorption SpectrosSoumyadeep SainNo ratings yet
- DLL Science (Week 6)Document5 pagesDLL Science (Week 6)Dianne S. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationDocument1 pageRepublic of The Philippines Department of EducationMaria Shiela Cantonjos MaglenteNo ratings yet
- Tin Mill Products, Electrolytic Tin Plate, Single Reduced: Standard Specification ForDocument5 pagesTin Mill Products, Electrolytic Tin Plate, Single Reduced: Standard Specification Forist93993No ratings yet
- Fencing Drawing-Proposal As On 15.02.2023Document1 pageFencing Drawing-Proposal As On 15.02.2023Bittudubey officialNo ratings yet
- Are A Class of Organic Compounds That Have An OxygenDocument6 pagesAre A Class of Organic Compounds That Have An OxygenArianne MontañoNo ratings yet
- A 2010 Hydrometallurgical Separation of Rare Earth Elements, Cobalt and Nickel From Spent Nickel-Metal-Hydride Batteries PDFDocument7 pagesA 2010 Hydrometallurgical Separation of Rare Earth Elements, Cobalt and Nickel From Spent Nickel-Metal-Hydride Batteries PDFJokin HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic 2019-2: Nedher Sánchez RamírezDocument47 pagesThermodynamic 2019-2: Nedher Sánchez RamírezGenesis FloresNo ratings yet
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 06 For Board Exam 2023 1 PDFDocument7 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper Test 06 For Board Exam 2023 1 PDFSahasra YeruvaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Mechanical SystemsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Mechanical SystemsEEE ACEECNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument44 pagesLipidsMilena De CresentNo ratings yet
- BS en 10211-2013Document22 pagesBS en 10211-2013Federico De MartiniNo ratings yet
- A. Velocity B. Length C. Density D. Temperature E. AreaDocument3 pagesA. Velocity B. Length C. Density D. Temperature E. AreaFitria Istikomah DewiNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Learning Activity 1 Short Quiz 1Document39 pagesWeek 1: Learning Activity 1 Short Quiz 1yagami100% (1)