Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Boilers Types
Uploaded by
Nazakat Ali KhosoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Boilers Types
Uploaded by
Nazakat Ali KhosoCopyright:
Available Formats
Boiler Types
Live steam models utilize many different varieties of boilers ranging from the simple pot to the locomotive type. Each boiler type can give excellent performance so long as it is operated within its design envelope. Copper is the best material for small boilers. Brass should never be used for a boiler barrel, but is satisfactory for fittings. Major boiler types are discussed as follows:
Pot Type
The pot boiler, show in Figure 2, is the simplest type and consists of a cylindrical copper tube with stayed end plates. The fire, which is typically from an alcohol burner, is applied to the external surface of the boiler. Its steaming ability can be significantly increased by the addition of a smoke tube and a stainless steel shield which encloses the burner and the lower portion of the boiler. Thus configured, the pot boiler can be a god steam generator in moderate temperatures and mild winds. Tank locomotives are good candidates for pot boilers since the tanks hide the fire shield. A suction fan and blower are not needed for firing since there is no necessity for a forced draft. Pot boilers have large water capacity and simple to steam. However, pot boilers tend to discolor since the burner flame is in direct contact with the outer barrel surface. Either a wick or vaporizing type burner can be used.
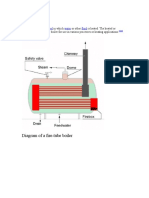
Water Tube Type (Smithies)
The water tube boiler was developed in the United Kingdom at the turn of the century by Mr. Fred Smithies. It consist of a copper inner barrel with stayed end plates and water tubes at the barrel's bottom, which extends from the front to the rear. This assembly slips into an outer casing which is shaped to resemble a locomotive boiler and firebox. There is an optimum sizing and arrangement for the water tubes, which depends on the boiler's dimensions. Typically, the tubes should be greater than 5 mm in diameter and should be space so as to allow plenty of room for a flame path between them. Increasing the number of tubes may not increase the boiler's ability to generate steam. If the flame path is restricted, the boiler cannot perform well since the draft cannot draw the flame forward toward the smoke box and increase flame temperature. The inner surface of the outer casing is insulated with a ceramic sheet. It is important that the insulation does not obstruct the flame path near the throat plate. Properly designed Smithies boilers perform well in adverse weather conditions. If the boiler should run dry, the lack of draft will automatically extinguish the fire. A Smithies boiler is simple to build and operate, but it does require a suction fan and a blower since it is a forced draft system. The biggest disadvantage of the Smithies boiler is the limited water capacity of its inner barrel as compared to other boiler types with similar external dimensions.
Vertical Type
The vertical boiler is a simple type which consists of a firebox at the bottom and a copper barrel with a smoke tube. It typically is used to drive stationary engines and boats. Firing is accomplished by alcohol or solid fuel pellets. More sophisticated versions of the vertical boiler contain many small tubes and are sometimes fired by coal or charcoal. (Fig. 3)
Center Flue Type
The center flue boiler, show in Figure 4, has a large water capacity and a low center of gravity which makes it ideal for model boats. The center flue is surrounded by water and sometimes has several cross tubes to improve circulations. This type of boiler is usually fired by a gas burner, because the flame is completely enclosed by the center flue. Therefore, the probability of an accidental fire is reduced. It is necessary to maintain the proper water level in this type of boiler to avoid damaging the center flue. It offers good performance capabilities in adverse weather conditions.
Smoke Tube Type
The smoke tube boiler, show in Figure 5, consists of a copper barrel with stayed end plates and several curved smoke tubes extending from the front tube sheet to the rear bottom surface of the barrel. Its chief advantage is a greater water capacity than a comparable Smithies boiler, while retaining good performance capability in adverse weather conditions. The sizing and number of tubes is a function of the area of the smoke box tube plate. It is more expensive to build than the Smithies type and requires a suction fan and blower, since it is a forced draft system.
Type C
The type C boiler, shown in Figurate 6, was developed by J. T. Van Riemsdijk. It consists of a copper barrel with stayed end plates and several tubes running the length of the boiler. A stainless steel fire box with a duct is attached to the rear of the barrel. A multi-wick burner provides the fire which is drawn backwards by the draft, up through the duct and into the tubes. The inner surface of the firebox and duct is lined with ceramic sheet. The outer surface of the duct can also be covered with ceramic sheet to reduce cab temperatures. The type C boiler has a good water capacity. It is easy to build and very strong. It requires a suction fan and blower since it is forced draft system. It has excellent performance capabilities in
adverse weather conditions. Its name from the fact that it is the follows two other small scale boilers developed by Van Riemsdijk, the type A (center flue) and type B (smoke tube).
Mixed Type (Smoke/Water Tubes)
The illustration above shows the Mixed Type of boiler developed by Dr. Seiichi Atonable. It has water tubes filled in the firebox of a locomotive type boiler in such as a way that the tubes acts a stays. This configuration also increases the heating area and provides better water circulation than a plan locomotive type boiler. The Aster JNR D 51 and JNR 9600 utilize this type of boiler.
Locomotive Type
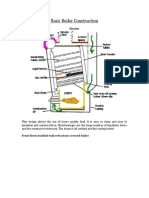
The Locomotive type boiler, shown in Figure 8, consists of a copper barrel and an outer and inner firebox attached to the rear of the barrel. Perfectly round pressure vessels carry pressure loads by developing hoop tension stresses in the wall of the boiler. In this case, there is no tendency for the
walls to bend. If a pressure vessel is not perfectly round, the walls will bend because the walls will bend attempting to form a perfect circle as it pressurizes. The results in a combined stress field with high stress levels. Since the firebox is not circular, it is necessary to provide additional structural members to strengthen non circular surfaces. This is the reason for stay bolts and structural beams in the firebox assembly. Thermal stresses also occur as a result of thermal expansion, therefore a boiler must be designed to carry both thermal and pressure loads. In a Belpaire type firebox, the outer wrapper and crown sheet may be stiffened by beams or girder stayed to each other. Both side plates of the outer firebox are cross stayed since they are flat. Flat surfaces on the back head and smoke box tube plate can be stiffened or stayed. Sometimes a combination of both is used resulting in a very strong boiler. If two or more stays are used, once can be hollow and used to route the blower line to the smoke box. Tubes extend from the front tube plate in the smoke box to the rear tube plate, which is located at the front of the fire box. This type of boiler can be fired by coal if grates are installed. Liquid fuel burners can also be employed. The locomotive type boiler is the most difficult to build but is very efficient and allows the realism of a coal fire. It requires a suction fan and a blower, since it is a forced draft system. Its water capacity may be less than a comparable type C boiler. The water level must be carefully maintained so that the crown sheet is always covered, otherwise the boiler will be damaged.
Saddle Type
The saddle type boiler, as shown in Figure 9, is used for the Aster Glaskasten. In order to provide a reasonable running period, it was necessary to have a boiler with a minimum water capacity of 100 cc. Since space was limited, a unique boiler shape was required. The saddle type boiler consists of a large diameter copper tube with end plates and a small cross tube. It uses features of the type C boiler as well as the Pot Type and Cross Water Tube Type. The inclined cross tube provides both extra water capacity and additional heating surface. They improve water circulation and also act as stays. The arc is filled a stainless steel firebox guiding the flame flow, so that the maximum heating area is realized.
You might also like
- Types of Boilers PDFDocument5 pagesTypes of Boilers PDFJosé RubioNo ratings yet
- Basic Boiler ConstructionDocument37 pagesBasic Boiler ConstructionSudarmarine SudharNo ratings yet
- Package Boiler Types and OperationDocument4 pagesPackage Boiler Types and Operationkuldeep mohiteNo ratings yet
- Chain Grate Boiler: Boilers/list - 2 - 1.htmlDocument1 pageChain Grate Boiler: Boilers/list - 2 - 1.htmljohanandrianNo ratings yet
- BoilerDocument14 pagesBoileryudhistharNo ratings yet
- Basic Boiler Construction GuideDocument8 pagesBasic Boiler Construction GuideIonescu FlorinNo ratings yet
- Basic Boiler Construction: Front Fired Studded Wall Refractory Covered BoilerDocument12 pagesBasic Boiler Construction: Front Fired Studded Wall Refractory Covered BoilerAnand JinoNo ratings yet
- BoilerDocument48 pagesBoilerAbdallah Mansour100% (2)
- In Simple A Boiler May Be Defined As A Closed Vessel in Which Steam Is Produced From Water by Combustion of FuelDocument9 pagesIn Simple A Boiler May Be Defined As A Closed Vessel in Which Steam Is Produced From Water by Combustion of FuelJomari Tobes SatorreNo ratings yet
- Basic Boiler ConstructionDocument8 pagesBasic Boiler ConstructionLuthfi Yulian FikriNo ratings yet
- Steam Boilers ME 1103 Introduction To MeDocument27 pagesSteam Boilers ME 1103 Introduction To MePriyadarshee ShaswatNo ratings yet
- Materials: Pressure Vessel Steel Wrought Iron Stainless Steel Live Steam Copper Brass Fireboxes Steam LocomotivesDocument10 pagesMaterials: Pressure Vessel Steel Wrought Iron Stainless Steel Live Steam Copper Brass Fireboxes Steam LocomotivesVelampalli AshokNo ratings yet
- Design and Thermal Analysis of CFB and Simple BoilersDocument89 pagesDesign and Thermal Analysis of CFB and Simple Boilersbharathkumar0310No ratings yet
- Boiler: MaterialsDocument10 pagesBoiler: MaterialssarojpapuNo ratings yet
- Modern Boiler ConstructionDocument7 pagesModern Boiler ConstructionMeghanath AdkonkarNo ratings yet
- Boiller Types Sabic PDFDocument40 pagesBoiller Types Sabic PDFMuhammad Hamza NaveedNo ratings yet
- BoilersDocument76 pagesBoilers58-Sanket TupkarNo ratings yet
- Materials: Vessel Water FluidDocument8 pagesMaterials: Vessel Water FluidJinith MahajanNo ratings yet
- Compact Package Boilers ExplainedDocument4 pagesCompact Package Boilers ExplainedSANJOYNo ratings yet
- Steam Generators (Boilers) : SubhankarDocument24 pagesSteam Generators (Boilers) : Subhankarশুভঙ্কর মুখার্জীNo ratings yet
- Fire Tube Boilers PDFDocument16 pagesFire Tube Boilers PDFG.SWAMI67% (3)
- Water-Tube Boiler: ApplicationsDocument6 pagesWater-Tube Boiler: Applicationssabya512No ratings yet
- Boiler: For The Limp Bizkit Song, SeeDocument12 pagesBoiler: For The Limp Bizkit Song, SeeMahesh G RajuNo ratings yet
- Crucible FurnacesDocument10 pagesCrucible FurnacesZara SaeedNo ratings yet
- Types of BoilersDocument30 pagesTypes of BoilersGnana Subramanian ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Crucible FurnacesDocument10 pagesCrucible FurnacesZara Saeed0% (1)
- BoilerDocument10 pagesBoilerAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- 2.10. Furnace Design Considerations: Fig. 2.5 Fig. 2.6Document8 pages2.10. Furnace Design Considerations: Fig. 2.5 Fig. 2.6vatsal07No ratings yet
- Unit-1 Boilers and AcessoriesDocument55 pagesUnit-1 Boilers and AcessoriestamilvananirttNo ratings yet
- Boiler Design Development: A Historical PerspectiveDocument8 pagesBoiler Design Development: A Historical PerspectiveYashNo ratings yet
- G.L. Bajaj Boilers ClassificationDocument39 pagesG.L. Bajaj Boilers ClassificationAbhay TrivediNo ratings yet
- Meg 5-LF-29-30 Types of Aux BoilersDocument54 pagesMeg 5-LF-29-30 Types of Aux BoilersAkash KandwalNo ratings yet
- General Marine EngineeringDocument67 pagesGeneral Marine EngineeringSailorprof100% (3)
- 11 Steam Generators 3-2Document26 pages11 Steam Generators 3-2Omar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Navigation Search Merged Discuss: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesNavigation Search Merged Discuss: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaHarjot SinghNo ratings yet
- Fire Tube BoilerDocument2 pagesFire Tube Boilerarif99pakNo ratings yet
- Marine Boiler and Steam Engineering: Prepared by P.Thanga Sabari AP, Marine MSECDocument169 pagesMarine Boiler and Steam Engineering: Prepared by P.Thanga Sabari AP, Marine MSECrickNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Steam Generators: Mechanics of Steam BoilersDocument7 pagesLecture 7 - Steam Generators: Mechanics of Steam BoilersIjazzzAliNo ratings yet
- Boilers PrintDocument66 pagesBoilers PrintsuswagatNo ratings yet
- Boiler: Diagram of A Fire-Tube BoilerDocument4 pagesBoiler: Diagram of A Fire-Tube BoilerMd ShahidNo ratings yet
- Boiler House Management Course Final PDFDocument107 pagesBoiler House Management Course Final PDFPaul StuttNo ratings yet
- 7 Years of Service for First Posiflow BDocument8 pages7 Years of Service for First Posiflow BKarthick VelayuthamNo ratings yet
- Boilers NotesDocument16 pagesBoilers Notesjust randomNo ratings yet
- Model Boilers: A Booklet Flanging Boiler EndsDocument20 pagesModel Boilers: A Booklet Flanging Boiler EndsSravanthi SallaNo ratings yet
- Boilers 1Document87 pagesBoilers 1ahsanNo ratings yet
- Scotch BoilerDocument52 pagesScotch Boilerrajishrrr100% (1)
- What Is A BoilerDocument7 pagesWhat Is A BoilerAhmad MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Doosan Posiflow technology improves boiler efficiency and reliabilityDocument12 pagesDoosan Posiflow technology improves boiler efficiency and reliabilityKarthick VelayuthamNo ratings yet
- BoilersDocument47 pagesBoilersAshish RawatNo ratings yet
- Boilers: A Simplified GuideDocument9 pagesBoilers: A Simplified GuideKeanu EspinaNo ratings yet
- CLM Series Steam and Water Boiler: Bryan "Flexible Water Tube"Document10 pagesCLM Series Steam and Water Boiler: Bryan "Flexible Water Tube"Alexánder Muñoz FerrerNo ratings yet
- Properties of BoilerDocument17 pagesProperties of BoilerSohail Aziz Ahmad MalikNo ratings yet
- Boiler TypesDocument5 pagesBoiler TypesJhansi YerraboluNo ratings yet
- Industrial BoilersDocument32 pagesIndustrial BoilersNipun SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Fire tube boiler design guideDocument2 pagesFire tube boiler design guideTan LatoNo ratings yet
- Chimneys & Fireplaces: They Contribute to the Health Comfort and Happiness of the Farm Family - How to Build ThemFrom EverandChimneys & Fireplaces: They Contribute to the Health Comfort and Happiness of the Farm Family - How to Build ThemNo ratings yet
- Nazakat Ali P20 May 2016Document8 pagesNazakat Ali P20 May 2016Nazakat Ali KhosoNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Singer Sewing Machine No. 66Document29 pagesInstruction Manual: Singer Sewing Machine No. 66Andy100% (5)
- Prep. Process For Weaving: Fabric Manufacturing - II by Dr. Nazakat Ali Buitems Lec-ADocument11 pagesPrep. Process For Weaving: Fabric Manufacturing - II by Dr. Nazakat Ali Buitems Lec-ANazakat Ali KhosoNo ratings yet
- No. 15 Instruction ManualDocument36 pagesNo. 15 Instruction ManualAndy80% (5)
- Rapier WeftDocument14 pagesRapier WeftSarah Asghar100% (1)
- Sewing Machine 3Document75 pagesSewing Machine 3Nazakat Ali KhosoNo ratings yet
- SingerDocument26 pagesSingerOmar Burgos MercadoNo ratings yet
- Sewing Machines 5Document16 pagesSewing Machines 5Nazakat Ali KhosoNo ratings yet
- No. 15 Instruction ManualDocument36 pagesNo. 15 Instruction ManualAndy80% (5)
- Water Research Myp Nov09Document55 pagesWater Research Myp Nov09Nazakat Ali KhosoNo ratings yet
- 5934 CH04Document65 pages5934 CH04Nazakat Ali KhosoNo ratings yet
- Membrane Technology: Source: Zaini Ujang Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaDocument55 pagesMembrane Technology: Source: Zaini Ujang Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaNazakat Ali KhosoNo ratings yet
- Fabric Abrasion Test Scores & Observations Under 40 CharactersDocument1 pageFabric Abrasion Test Scores & Observations Under 40 CharactersNazakat Ali KhosoNo ratings yet
- Smart TextilesDocument2 pagesSmart TextilesNazakat Ali KhosoNo ratings yet
- PDI Quality Manual Rev 4 - 1.0 Table of ContentsDocument1 pagePDI Quality Manual Rev 4 - 1.0 Table of ContentslouieNo ratings yet
- PunchesDocument25 pagesPunchesJhoanne NagutomNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Epithelium: Human Histology Lecture Chapter 17 Ï The Respiratory SystemDocument16 pagesRespiratory Epithelium: Human Histology Lecture Chapter 17 Ï The Respiratory SystemEvandie OngNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - TRANSMUTATION - Louise Peralta - 11 - FairnessDocument2 pagesLESSON 2 - TRANSMUTATION - Louise Peralta - 11 - FairnessLouise Joseph PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Oral Dislocation Rehabilitation Program - FirstDocument2 pagesOral Dislocation Rehabilitation Program - FirstPriyaki SebastianNo ratings yet
- Caffeine's Effect on Daphnia Heart RateDocument2 pagesCaffeine's Effect on Daphnia Heart RateMianto NamikazeNo ratings yet
- WILLIEEMS TIBLANI - NURS10 Student Copy Module 15 Part1Document32 pagesWILLIEEMS TIBLANI - NURS10 Student Copy Module 15 Part1Toyour EternityNo ratings yet
- Metals and Metallurgy: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument43 pagesMetals and Metallurgy: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- High Voltage - WikipediaDocument7 pagesHigh Voltage - WikipediaMasudRanaNo ratings yet
- Badhabits 2022Document53 pagesBadhabits 2022Sajad KhaldounNo ratings yet
- A.686 (17) Cod AlarmeDocument39 pagesA.686 (17) Cod Alarmeciocioi iancuNo ratings yet
- 4th QUARTER EXAMINATION IN TLE 8Document3 pages4th QUARTER EXAMINATION IN TLE 8judy ann sottoNo ratings yet
- Spez KR QUANTEC Prime enDocument155 pagesSpez KR QUANTEC Prime enDave FansolatoNo ratings yet
- Waste Management: Spoilage of LandscapeDocument7 pagesWaste Management: Spoilage of Landscapeshauryasahu2004No ratings yet
- NECC Sri Lanka May 2017 An Open Appeal To UN and International Community PDFDocument18 pagesNECC Sri Lanka May 2017 An Open Appeal To UN and International Community PDFThavam RatnaNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Vegan DietsDocument3 pagesPros and Cons of Vegan DietsCristian AsmazaNo ratings yet
- Courses at NeevDocument10 pagesCourses at NeevDr Mohan SavadeNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Medicines ReportDocument28 pagesVeterinary Medicines Reportvikram chhabraNo ratings yet
- Cooking - Sauces and Marinade RecipesDocument96 pagesCooking - Sauces and Marinade Recipesagape_1st7100% (3)
- Chapter 1 EconomicsDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Economicsjordan cedeñoNo ratings yet
- Carbon Steel Alloys Steel, Pipe Dimension With Weight Test Pressures According To ANSI B36, 10 For ASTM A53/A 106/API 5L/A335/ SpecificationDocument6 pagesCarbon Steel Alloys Steel, Pipe Dimension With Weight Test Pressures According To ANSI B36, 10 For ASTM A53/A 106/API 5L/A335/ SpecificationsanjibkrjanaNo ratings yet
- Technical PaperDocument10 pagesTechnical Paperalfosoa5505No ratings yet
- High Flyers / Answer Key G / Unit 4: GrammarDocument8 pagesHigh Flyers / Answer Key G / Unit 4: GrammarDian Novyta AriantiNo ratings yet
- wk4 Stdconferencereflection ElmoreajaDocument4 pageswk4 Stdconferencereflection Elmoreajaapi-316378224No ratings yet
- Ethics Zoo EssayDocument2 pagesEthics Zoo EssayChanel SalinasNo ratings yet
- (Tertiary Level Biology) R. J. Wootton (Auth.) - Fish Ecology-Springer Netherlands (1992)Document218 pages(Tertiary Level Biology) R. J. Wootton (Auth.) - Fish Ecology-Springer Netherlands (1992)John Davi JonesNo ratings yet
- Rhodes-Solutions Ch2 PDFDocument16 pagesRhodes-Solutions Ch2 PDFOscar GarzónNo ratings yet
- An Interview - ExercisesDocument3 pagesAn Interview - ExercisesCarmen GloriaNo ratings yet
- The Human Excretory System: A 40-Character GuideDocument3 pagesThe Human Excretory System: A 40-Character GuideMelvel John Nobleza AmarilloNo ratings yet
- Research Journal DNA PolymeraseDocument12 pagesResearch Journal DNA PolymeraseMauhibahYumnaNo ratings yet