Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Waterloo: V-JBTP
Uploaded by
David KimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Waterloo: V-JBTP
Uploaded by
David KimCopyright:
Available Formats
Waterloo
UnJ~tyoi
UDiversity of Waterloo Final Examination Winter TERM
(TemI)
2002
(Year)
iNSTRUcnONS:
PART A: 6 multiple-choice questionsword1S InarkBeach a) ANSWER CARDS Wll.L BE COLLBCI'ED AT 11:30 a.m.
I OUESTION GRADE
b) Mark. yourcardin darkpencil. Avoid a'asurcsby checking
IDIWas before marking them. EntrI: ~ ID# and the "K. ~tion" indicated above in the spaces provided. c) AnEMPT AU. QUESTIONS - there is no penalty for inco~t 1nSW0'S. However, credit may be denied if appropriateworlt is not shown in the spacebelow the qu~tions in this booklet. d) Numba:s in queltions may be takm as ~ to as many figures as you wish. but answersare rounded. 80 pick the closest one. PART B: 6 qUC8tions worth 12 marks ~h for. total of 102.
,
8
9 10 IJ 12
Partial credit is given for a correct approachprovided you show clearly what you are doing.
TOTAL
Diagramsare Dotto seale. USEFUL INFORMAnON:
I c 9.8 m/il c=3.00x IO'mls I cV-I.6x loot'} m,-I.67x 10-27 kg hc = 1240 eV.nm
DCIIaity air = 1.29kg/m3 of me-9.11 X 10-31 kg E. -136 eV (Bohr~ry
- -+n
Hearingthreshold 10.12 /m2 Io W h = 6.63 X 10-34 J.. e= 1.6x 10-19C for h)'dro&=)
.' co \,~ .
v-JBTP
B
Ru-1.09737x10'm-1
= bulk
- dcnsity
rnodulus
Velocity of sound in air V = 340 mil
Area of &pbe - 41tR2
Physics 125 Final Examination
Page2 of 10
Two springs, each with unstretchedlength 0.200 m but with different force constantskl and k2 are attachedto opposite ends of a block of massm on a level frictionless surface. The outer ends of the springs are now attachedto two pins PI and P20.1 m fi'om the original positions of the end of the springs.Let k. = 2.00 N/m and k2 - 6.00N/m. andm = 0.100 kg. At equilibrium how far
fi'omPIwill theleft face of~~
(8) .20
(b) .IS
Answer m. in
(c) .1
(d) .05
(e) noneof them
~J
'fa.
2.
Two sound soun;esemit sound waves in phase of wavelength 1... They are placed y" I..apart at an equal distance from the center of the circle. The circle has a radius of R ~ % 1... If the power of each source is P which equation descn"bcs intensity at point "B" in tcnns ofP and I..? the
(a) I =-::--:T
(b)J-~ .J.Z
p (c) 1 =A1
(d)
/- -pi 4d
(e) 1=
4p2 d
CARDSWilL BE COlLECTED AFrER 2 1/2HOURS
Physics 125 Final Examination
Page3 of 10
3.
A rod of glass of index 1.5 has one end ground and polished to a convex spherical surface of radius 7 cIn. The other end is flat and silvered to act as a flat minor. The distance between vertices V J and V 2 is 12 cm. An object is placed a very large distance from the convex end. Find the location of the final image from VI. Answer in cm. (8) 2.33 to the left ory I
(b) 2.33to dIeright orvi
(c) .4 to the left of V , (d) .4 to the right of V I (e) none of the above
4.
Monochromatic light ofwavelcogth A.= 600nm is incidenton a slit of width 2.4~. A screen is placed 3.0 m from the slit Find the intensity relative to central maximum of a point 20 cm away from the central maximum. (a) 1.86 (b) 1.06
(c) .8S1
(d) .786
(e) .531
-1
T~TI ';'~.OM.
~c.~
CARDSWll..L BE COU.EcrBD AFTER. 1/2HOURS 2
Physics 125 Final Examina~on
Page4 of 10
A coating of index of refraction n = 1.25 is depositedon a piece of glass of index n = 1.5. White
light is incident near nonnaJly on the coating. If a person does not like to see I.. = 400
DID and
I..= 7 00 n m transmitted through the coating but does not mind if wavelength of other values
transmit, bow thick mustthecoatingbe? Answerin om. (a) 500 (b) 700 (c) 1120
(d) 1210
(e) 1340
J.!L
CDo...J,.It\~
~~,
"1,$
'"'1'"~.
6.
Find the fractional change in cnct"gy(AEoergy/Encrgy of incident photon) for photons that arc
b~kSL:.~!tered (scattering angle +
10 pm. (1 pm = 10-12m) (a) .480
= 1800) via
Compton effect. Asswne incident wavelength to be
(b) .327
(c) .243
(d)
195
(e) Noneoftbose
CARDSWll.L BE COU.ECTEDAFrER 2 1/2HOURS
Physics 125 Final Examination
Page5 of 10
7.
A hannonic wave is traveling in the negative x direction. At t = 0 and x = 0 the displacementis zero and the particle speedis pointing upward. At t = I sec y(x,l) = IS CDS x), tin sec,x and (.3 yincm.
(a)
Detmnine the phasecoost. Determine the wavelength Detemline the angular frequency Write the general equation for the traveling wave.
+=
1..=
(1)=
rad
cm radii
(b)
For a point "x.' on the string detcm1inethe transversevelocity as a function of time.
(c)
Find the maximum transverse acceleration at t
=O,.x o. -
(d)
If the linear dcnsity of the stripg is J1 1.5 x 10-3kg/m determine the power at a given point x as a function of time.
CARDSWlll.. BE COU.BCTEDAFfER.2 1/2HOURS
Physics 125 Final Examination
Page 6 of 10
8.
An offshore station has a listening post under water. A boat with its engine rwming (vibrating) at 500 revolutions per minute emits a loud noise. The boat is fast approachingthe listening post at
SO km/hr.
W~t.d..
(a)
What~
(in Hz) is produced theboat'sengine? by
~ :r~'~':
I
. - -i
'
:~~~
- I
i
i
I ~~~.;
--;
-..
-.;..
.ll :
I 1\ I
, ,
s+a..,,",-~
; .1
I:
~I
-,
I'
I i '
'
I
!
'
:
'"'!-T'.!
:
-:
I
,
I
I
I
i
1
rI
:
,
-.. .
-1 1
... .,. ~_.i, 1 j!; ;
I!
-- - . -. I
'_1-,--'
.),.
:-I-!
i I
-I I-l I
. I
_\_!-__I~
,ot
I -, I I
- - - '. 1,
(b)
, If the speed of sound in water is 1450 m/s, what frequency would the under water listening post detect?
(c)
If there is a wind blowing toward the boat from the position of the station what frequency is heard by an observer at the station who is above the water level? (Assume the noise of the boat travels in air as well as water.)
(d)
If the IOtmd waves are reflected off the station, what beat frequency would the driver of the boat hear?
CARDS WILL BE COu.BCrBD AFrER 2 1/2 HOURS
Physics 125 Final Examination
Page 7 of 10
9.
Rays nom a distant object is incident on a converging lens (double convex 1008)of focallengtb 4Ocm.
(a)
How far from the lens would the image be found?
(b)
If a diverging lens of focal length f = -15 cm is placed 20 cm to the right of the converging lens where would the final image be funned for a distant object?
(c)
If the diverging lens is replaced by a thick piece of glass of n = 1.5, where would the final image be createdfor a distant object? Assume the glass is 2 cm thick..
~e.~ 4-+
object
CARDSwn.L BE COLLBCI'EDAFfER 2 1/2HOURS
Physics 125 Final Examination
Page8 of 10
10.
An air wedge is createdby inserting a thin sheet of paper between two flat pieces of glass along one edge. Light of wavelength of 450 om is incident normally on the glass plate. When viewed in reflection 15 dark fringes per centimetercan be seen. Is the point where the glassplates touch a bright spot or a dark spot? Explain.
(a)
(b)
Calculate the angle betweenthe glassplates.
(c)
Whenviewedin transmission, manydarkfringespercentimeter be ~? how can
(d)
When Justify your answer. spot? viewed in transmission is the point where the glass plates touch, a bright spot or a dark '
CARDS WllL BE COLLBcrED AFTER 2 In. HOURS
Physics 125 Final Examination
Page9 of 10
11.
In the photo electric effect experiment a light of wavelength A.= 400 om is shoneon one of the two elecb'Odes. There is a potential difference of 0.5 volts set up across the two electrodes (electrode #1 and electrode #2) to slow down or decelerate electrons that are ejected from the the first electrode. It is found that some electrons ovcroome this retarding forcc and arrive at the secondelectrodewith a kinetic energy of 0.6 eV. What is the stopping potential?
(a)
(b)
What is the work function of the electrode#1?
(c)
If the intensity of the ray incident on the first e lecb'odcis 2 W 1m2Wbat would the m aximum kinetic energyof the photoelectron be?
(d)
If a 0.7 percent of the incident photons produce photoelectrons. how many photoelectronsper secondare emitted off an areaof I cm2of the electrode?
CARDSWll1.. BE COu..EcrED AFrER.2 1/2 HOURS
Pb.)lSics FinalExamination 125
Page 10of 10
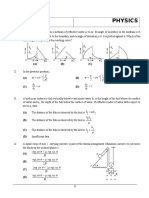
12.
A plane wave (wavelength 1..) incident on a double slit syStem. "a" is the width of each slit and is "d" is the separationbetween the two slits. L is a converging lens and the screenS is placed at d1efocal plane of the lens (a = 0.030 mm, d = 4a, 1.. 480 DID and assumefocaileDgdl of the lens = is large comparedto "dj.
(a)
Supposeslit S2 is blocked off so that light passesonly through S,. Find the angularposition 9, of the seconddiffraction minimum with respectto the horizontal axis CO.
(b)
Find the angular position ~ of the second diffraction minimum with respectto axis CO for light passingthrough ~ whm 8, is blocked off..
(c)
Supposelight is allowedto passthroughboth St and S2- DeteIDline numberof ~mplete the fringe maxima which are located within the central diffraction maximum.
(d)
In the arrangement part (c) find the intensityof light at a point P on ~ of 9 = 0.500 tennsof the intensity the light at 9 = O. in of
S for which
CARDS WILL BE COu.EcrED
AFI'ER 2 1/2 HOURS
You might also like
- Physics Comedk 2009 Question PaperDocument9 pagesPhysics Comedk 2009 Question PaperpremsempireNo ratings yet
- National University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIDocument11 pagesNational University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIYuhua SunNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios9 PDFDocument4 pagesEjercicios9 PDFapolo1711No ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Document36 pagesChapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Zulkarnain AgosNo ratings yet
- Allen: Aieee - 2012 Test Paper With Answer (Held On Sunday 29 APRIL, 2012)Document5 pagesAllen: Aieee - 2012 Test Paper With Answer (Held On Sunday 29 APRIL, 2012)rishabhk28995No ratings yet
- JEE MAINS Solved Paper 2012Document30 pagesJEE MAINS Solved Paper 2012chithrasajeev100% (1)
- NUS Physics Fundamentals Term TestDocument10 pagesNUS Physics Fundamentals Term TestYuhua SunNo ratings yet
- 10 12 Physics CBSE Paper SolutionDocument20 pages10 12 Physics CBSE Paper SolutionnafehakhanNo ratings yet
- M.SC - Physics - 2017 PDFDocument20 pagesM.SC - Physics - 2017 PDFjaswinder singhNo ratings yet
- JEE MAINS Solved Paper 2013Document24 pagesJEE MAINS Solved Paper 2013chithrasajeev67% (3)
- Phys102 182 Final Exam Zero VersionDocument12 pagesPhys102 182 Final Exam Zero VersionNano SuyatnoNo ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument6 pagesWave OpticsKoyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- PCG2009 PDFDocument31 pagesPCG2009 PDFvraj patelNo ratings yet
- National University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIDocument11 pagesNational University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIKatto - Darling in the PianoNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2014 Answer Key Online 11-04-2014Document11 pagesJEE Main 2014 Answer Key Online 11-04-2014anushrikocher1450% (2)
- CBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper - SolutionDocument15 pagesCBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper - SolutionMichelle DennisNo ratings yet
- Paper of PieasDocument44 pagesPaper of Pieaslovelyosmile25333% (3)
- Physics MCQ Model Test 1Document82 pagesPhysics MCQ Model Test 1ap cpianNo ratings yet
- Wave Optics (QB)Document12 pagesWave Optics (QB)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Final ExamA1Document3 pagesFinal ExamA1LÂN HỒ THANHNo ratings yet
- Important InstructionsDocument31 pagesImportant InstructionsAshish_AAABNo ratings yet
- AIIMS - 2005: Solved PaperDocument16 pagesAIIMS - 2005: Solved PaperIndomie GorengNo ratings yet
- Iut Admission Xest 20I7.2 ('I8 Question Paper: Set ADocument10 pagesIut Admission Xest 20I7.2 ('I8 Question Paper: Set APho3nixNo ratings yet
- GUJCET Physics and Chemistry Question Paper 1Document31 pagesGUJCET Physics and Chemistry Question Paper 1Piyush GoreNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Usp SP by AneeshDocument4 pages12 Physics Usp SP by AneeshSweetu NancyNo ratings yet
- Physics Tutioral Sheet 2014Document13 pagesPhysics Tutioral Sheet 2014INDRA JEET YADAVNo ratings yet
- 1.physics (Aieee) Model PaperDocument26 pages1.physics (Aieee) Model PaperDeep Agarwal100% (1)
- Model Question Paper Higher Secondary - Second Year - PhysicsDocument6 pagesModel Question Paper Higher Secondary - Second Year - Physicsbindum_9No ratings yet
- Short Questions on Interference and DiffractionDocument11 pagesShort Questions on Interference and DiffractionNishi SinghalNo ratings yet
- Topper Sample Paper 3 Class XII-Physics Solutions: Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70Document14 pagesTopper Sample Paper 3 Class XII-Physics Solutions: Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70coolspanky_227053No ratings yet
- KCET 2014 Previous Year Paper For PhysicsDocument58 pagesKCET 2014 Previous Year Paper For PhysicsVeeresh badigerNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper - 12th ClassDocument6 pagesModel Question Paper - 12th ClassIMRAN ANSARINo ratings yet
- Xii-Iit GT-9 - Code - A - Final QP-23.12.2023Document11 pagesXii-Iit GT-9 - Code - A - Final QP-23.12.2023pasupathyshivavNo ratings yet
- 12 Rev MCQ Ans KeyDocument9 pages12 Rev MCQ Ans Keyselva.nishanth2006No ratings yet
- 2008 Test 1Document6 pages2008 Test 1Elias SigüenzaNo ratings yet
- Ques 44Document1 pageQues 44Vijay PrakashNo ratings yet
- Class 12Document6 pagesClass 12Sanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Term Ii XiiDocument4 pagesTerm Ii XiiJanmenjoy BiswalNo ratings yet
- Fundamentos de Fisica Hoolliday Parcial SolucionarioDocument5 pagesFundamentos de Fisica Hoolliday Parcial SolucionarioAlejandro Zambrano ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- AWS - 07 - PhysicsDocument5 pagesAWS - 07 - Physicsteju1996coolNo ratings yet
- Modern Middle East Physics ExamDocument9 pagesModern Middle East Physics ExamNazneen AliNo ratings yet
- Eklavya (NEET) Sample Paper - 1Document58 pagesEklavya (NEET) Sample Paper - 1arja keerthanaNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam - 1 + Answers Winn F10Document13 pagesPractice Exam - 1 + Answers Winn F10Billy PozehlNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet Engineering PhysicsDocument13 pagesTutorial Sheet Engineering PhysicsTusharSharmaNo ratings yet
- ENEL2PAH1 - Physical Electronics 1Document5 pagesENEL2PAH1 - Physical Electronics 1qanaqNo ratings yet
- Paper - 5Document16 pagesPaper - 5Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- ISAT-2011 Previous Year Question PaperDocument30 pagesISAT-2011 Previous Year Question Paperktktkt01No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument11 pagesPhysicsgopichandpaleti720No ratings yet
- ch32 PDFDocument14 pagesch32 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE 2005 Mains Paper With Answer KeyDocument12 pagesIIT-JEE 2005 Mains Paper With Answer KeyNarmadha RameshNo ratings yet
- Phy 2015Document5 pagesPhy 2015ANASNo ratings yet
- PB XII Phy QP Nov 2022Document8 pagesPB XII Phy QP Nov 2022Ayushi KayalNo ratings yet
- G12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsDocument25 pagesG12 Physics Pre Board - 1 QP With SolutionsSreshta ReddyNo ratings yet
- Pre Board 1 22-23Document7 pagesPre Board 1 22-23VAIBHAW VAIBHAWNo ratings yet
- 8 Copies Ncert Part-1 12th PhyDocument7 pages8 Copies Ncert Part-1 12th PhyAbin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample PaperDocument1 pagePhysics Sample PaperKrishnaNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- SmajeffreysmarteducationresourceDocument25 pagesSmajeffreysmarteducationresourceapi-284321672No ratings yet
- Professional Ethics in Civil EngineeringDocument44 pagesProfessional Ethics in Civil EngineeringMohiminulIslamFardinNo ratings yet
- Importance of peer groups and self-fulfilling propheciesDocument3 pagesImportance of peer groups and self-fulfilling propheciesCee BeeNo ratings yet
- Sahasranamavali of Lord Vishnu - IIDocument92 pagesSahasranamavali of Lord Vishnu - IIHetal PatelNo ratings yet
- 75 Ways To Politely Interrupt A ConversationDocument5 pages75 Ways To Politely Interrupt A Conversationrevathy varatharajahNo ratings yet
- Final Demo Lesson Plan in MAPEH 9Document10 pagesFinal Demo Lesson Plan in MAPEH 9Giezelle Leopando100% (4)
- Johor Leadership Camp 2015Document16 pagesJohor Leadership Camp 2015Amirul Harith100% (1)
- 03 - Gee2 - WK9 - Analysis, Application and ExplorationDocument2 pages03 - Gee2 - WK9 - Analysis, Application and ExplorationAeri Shim NoonxrNo ratings yet
- Slavoj Žižek - Surplus-Enjoyment - A Guide For The Non-Perplexed (2022, Bloomsbury Academic) - Libgen - LiDocument511 pagesSlavoj Žižek - Surplus-Enjoyment - A Guide For The Non-Perplexed (2022, Bloomsbury Academic) - Libgen - LiMateusz Kanabrodzki100% (1)
- PM620 Unit 4 DBDocument3 pagesPM620 Unit 4 DBmikeNo ratings yet
- Kragh 2018 - Chronotopic Narratives of Seven Gurus and Eleven Texts PDFDocument25 pagesKragh 2018 - Chronotopic Narratives of Seven Gurus and Eleven Texts PDFpechawaNo ratings yet
- Clinical LeadershipDocument31 pagesClinical LeadershipDedy Hartantyo100% (2)
- Ae 5Document3 pagesAe 5api-410774615No ratings yet
- Ltu Ex 2012 36549405Document153 pagesLtu Ex 2012 36549405Nighat ImranNo ratings yet
- Understanding Foundations of Leadership ModelsDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Foundations of Leadership ModelsChing ChongNo ratings yet
- Cost & Management Accounting For MBA 13, Binder 2014Document213 pagesCost & Management Accounting For MBA 13, Binder 2014SK Lashari100% (1)
- A Separate Peace Teacher GuideDocument44 pagesA Separate Peace Teacher GuideSwagat Sukumar Sahoo100% (3)
- Modeling A Fixed Bed Using Comsol Multiphysics and CFD Worcester Polytechnic InstituteDocument24 pagesModeling A Fixed Bed Using Comsol Multiphysics and CFD Worcester Polytechnic InstituteSriparthanNo ratings yet
- Shree Satya Narayan Kath ADocument3 pagesShree Satya Narayan Kath Asomnathsingh_hydNo ratings yet
- Power of MantraDocument15 pagesPower of Mantraphani1978No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and WinemakingDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis and WinemakingKathleen Claire MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Even Zohar Polysystems Revisited 2005Document11 pagesEven Zohar Polysystems Revisited 2005Carla Murad100% (2)
- Teaching Methods and Principles ExplainedDocument25 pagesTeaching Methods and Principles Explainedlittle large2100% (1)
- Writing Gone Wilde - Ed CohenDocument14 pagesWriting Gone Wilde - Ed CohenElisa Karbin100% (1)
- A New Concept For Tilted-Component Telescopes: by Erwin HerrigDocument4 pagesA New Concept For Tilted-Component Telescopes: by Erwin HerrigbirbiburbiNo ratings yet
- Misuse of Domestic Violence Laws CaseDocument36 pagesMisuse of Domestic Violence Laws CaseLatest Laws Team100% (4)
- Hegel's Concept of Mutual Recognition - The Limits of Self-DeterminationDocument9 pagesHegel's Concept of Mutual Recognition - The Limits of Self-DeterminationLaura Berenice Romero GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Teaching English For Elementary Grades PDFDocument252 pagesTeaching English For Elementary Grades PDFJess Bernaldez100% (2)
- "Yoga Therapy at The Wall" - IntroductionDocument36 pages"Yoga Therapy at The Wall" - IntroductionLaura Goellner96% (25)
- Kragt 2017Document7 pagesKragt 2017zhrieeNo ratings yet