Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Layout of Power Plant Lab
Uploaded by
irsalan_shahidOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Layout of Power Plant Lab
Uploaded by
irsalan_shahidCopyright:
Available Formats
LAYOUT OF POWER PLANT LAB
List of apparatus:1) Nozzle study performance unit. 2) Air compressor study unit. 3) Single cylinder steam engine. 4) Rankine cycler. 5) Table. (i) (ii) (iii) Diesel engine (engine test bed) Petrol engine (engine test bed) Wankel engine model
6) Car sectioned model. 7) Table. (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Stirling cycle engine. 2-stroke petrol engine. 4 stroke petrol engine. Wankel engine model.
8) Table. (i) (ii) Turbo jet engine. Pressure gauge calibration apparatus.
9) Rack # 1. (i) (ii) 10) (i) Steam engine model. Steam turbine model. Rack # 2. Yamaha sectioned model.
(ii) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) 18)
Thermo electric engine. 2-shaft gas turbine. Marcet boiler. Steam motor set. Steam test bench. Engine test bed. Sloce speed diesel engine. Bio fuel engine project. Diesel generator.
Terms related to Power Plant: Enthalpy:
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure. Enthalpy is a thermodynamic potential. It is a state function and an extensive quantity. The unit of measurement in the International System of Units (SI) for enthalpy is the joule.
Entropy:
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that is a measure of the energy not available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when converting energy to work. During this work entropy accumulates in the system, but has to be removed by dissipation in the form of waste heat.
T-s diagram for steam:
There are four processes in the t-s diagram, these states are identified by number in the diagram to the right.
Process 1-2: The working fluid is pumped from low to high pressure, as the fluid is a liquid at this stage the pump requires little input energy.
Process 2-3: The high pressure liquid enters a boiler where it is heated at constant pressure by an external heat source to become a dry saturated vapor. The input energy required can be easily calculated using h-s chart or enthalpy-entropy chart also known as steam tables.
Process 3-4: The dry saturated vapor expands through a turbine, generating power. This decreases the temperature and pressure of the vapor, and some condensation may occur.
Process 4-1: The wet vapor then enters a condenser where it is condensed at a constant pressure to become a saturated liquid.
Dryness fraction:
If the water content of the steam is 5% by mass, then the steam is said to be 95% dry and has a dryness fraction of 0.95. Dryness fraction can be expressed as: = ws / (ww + ws) where = dryness fraction ww = mass of water (kg, lb) ws = mass of steam (kg, lb) (1)
Saturated steam dryness fraction x<1 Dry steam dryness fraction x=1 Superheated steam dryness fraction x=1
Description of power plant related apparatus
Single cylinder steam engine:A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. Steam engines are typically external combustion engines, although other external sources of heat such as solar power, nuclear power or geothermal energy may be used. The heat cycle is known as the Rankine cycle. The invention of reliable steam engines with reasonable efficiencies J. Watt, triggered the industrial revolution which shaped the world we live in.
RANKINE CYCLER:The Rankine Cycle is a cycle that converts heat into work. The heat is supplied externally to a closed loop, which usually uses water. This cycle generates about 80% of all electric power used throughout the world, including virtually all solar thermal, biomass, coal and nuclear power plants. It is named after William John Macquorn Rankine, a Scottish polymath.
These are the four main devices used in Rankine cycle.
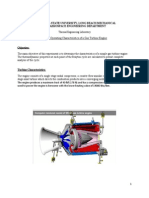
TURBO JET ENGINE:Turbojets consist of an air inlet, an air compressor, a combustion chamber, a gas turbine (that drives the air compressor) and a nozzle. The air is compressed into the chamber, heated and expanded by the fuel combustion and then allowed to expand out through the turbine into the nozzle where it is accelerated to high speed to provide propulsion.
In turbojet air is drawn into the engine through the front intake. The compressor squeezes the air to many times normal atmospheric pressure and forces it. The turbine extracts energy from the expanding gases to drive the compressor, which intakes more air. After leaving the turbine, the hot gases exit at the rear of the engine, giving the aircraft forward push.
STEAM TURBINE:A steam turbine is a mechanical device that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam, and converts it into rotary motion. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Parsons in 1884.
PRESSURE GAUGE CALIBRATION APPARATUS:Pressure gauges, like all measuring tools, have a tendency to wear over time and may become less accurate. Because pressure gauges are often manufactured to accurately read only the middle values (the low and high ends of the scale provide less accurate readings), just "zeroing" your pressure gauge may not ensure a good reading.
STEAM ENGINE MODEL:Steam engine is explained above. This model shows the complete function of the parts of the steam engines. The model is shown in figure below.
Two shaft gas turbine:Gas turbines are becoming increasingly used as power plants for a wide variety of applications around the world. Originally they were developed solely for aircraft propulsion where their inherent low specific weight (i.e. mass/unit power) made them essential for high speed flight. For this particular purpose they have been developed to a high degree of efficiency both thermodynamically and mechanically.
Marcet Boiler (Model: HE 169):The market boiler is a bench top unit designed to demonstrate the thermodynamic basic principal of boiling phenomenon. The unit consists of a stainless steel pressure vessel fitted with a high pressure immersion electrical heater. The unit also comes with a safety valve, glass thermometer and Bourdon type pressure gauge. Water inlet valve and discharge valve are also installed.
You might also like
- Steam TurbineDocument47 pagesSteam Turbinegone gangasagarNo ratings yet
- Steam EngineDocument13 pagesSteam EngineMuhammad Bin RiazNo ratings yet
- Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesRankine Cyclerr1819No ratings yet
- Jasper Van B Arrieta Bsme-IvDocument6 pagesJasper Van B Arrieta Bsme-IvJasper Van ArrietaNo ratings yet
- PASGT-Propulsion Ancillary Systems and Gas Turbine STCW ’78 as amended 2010 Table A-III/1 & Table A-III/2Document100 pagesPASGT-Propulsion Ancillary Systems and Gas Turbine STCW ’78 as amended 2010 Table A-III/1 & Table A-III/2Kyle100% (1)
- JJ308 REPORT Layout and Piping of The Steam Power Plant SystemDocument9 pagesJJ308 REPORT Layout and Piping of The Steam Power Plant SystemAh Tiang86% (7)
- A Gas Turbine UnitDocument9 pagesA Gas Turbine UnitTITU NATHNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document11 pagesLab Report 3Samsung Note 9No ratings yet
- Exp#4-Gas TurbineDocument9 pagesExp#4-Gas TurbineLilo17xiNo ratings yet
- Producing Power from Heat: The Rankine CycleDocument55 pagesProducing Power from Heat: The Rankine CyclemjunaidNo ratings yet
- Bhel TrainingDocument41 pagesBhel TrainingArun AroraNo ratings yet
- AES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byDocument25 pagesAES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byIrfan UllahNo ratings yet
- Heat Engines ME111Document43 pagesHeat Engines ME111Arct John Alfante ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power StationsDocument83 pagesThermal Power StationschdiNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbines FundamentalsDocument51 pagesSteam Turbines Fundamentalssevero97100% (1)
- Heat Engines: Devices that Convert Heat into WorkDocument23 pagesHeat Engines: Devices that Convert Heat into WorkSHek Hxni100% (1)
- TurbinesDocument34 pagesTurbinesDipesh Patle100% (2)
- Heatpump PDFDocument17 pagesHeatpump PDFJulio RicardoNo ratings yet
- Growth of The STEAM-ENGINEDocument76 pagesGrowth of The STEAM-ENGINENauman KhanNo ratings yet
- Automotive Turbocharged Gas Turbine.Document48 pagesAutomotive Turbocharged Gas Turbine.Santanu ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Power CyclesDocument23 pagesChapter 2-Power CyclesbaseakelNo ratings yet
- How the Rankine cycle converts heat into electricityDocument7 pagesHow the Rankine cycle converts heat into electricitydeepakkesri260% (1)
- Power Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineDocument7 pagesPower Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineMonglafru MogNo ratings yet
- GENERATING ELECTRICITYDocument34 pagesGENERATING ELECTRICITYAdeniji OlusegunNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant ProcessesDocument53 pagesThermal Power Plant ProcessesAaryaveerNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument11 pagesGas Turbine Power PlantCK Godinez100% (1)
- Thermodynamics - Steam TurbineDocument8 pagesThermodynamics - Steam TurbineSaiful ZakwanNo ratings yet
- Brayton CycleDocument4 pagesBrayton CycleIRMABFNo ratings yet
- Fawley Power Station Efficiency and Renewable Fuel ConversionDocument2 pagesFawley Power Station Efficiency and Renewable Fuel ConversionShrey Tyagi0% (3)
- Design and Selection-DriverDocument6 pagesDesign and Selection-DrivermuazmaslanNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: HistoryDocument9 pagesSteam Turbine: HistoryrikumohanNo ratings yet
- Physical study of the Steam-Generating UnitDocument12 pagesPhysical study of the Steam-Generating UnitIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant 1Document30 pagesThermal Power Plant 1ckissyou04No ratings yet
- Gas TrubineDocument17 pagesGas Trubinemn_sundaraamNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine: Navigation SearchDocument21 pagesGas Turbine: Navigation SearchluffydsiniNo ratings yet
- Engine Analysis-Capstone ReportDocument13 pagesEngine Analysis-Capstone ReportAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Power CycleDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Power CycleBese Mat100% (1)
- Gas Turbine: "Microturbine" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument20 pagesGas Turbine: "Microturbine" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeRyanNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine: Photograph A Monument, Help Wikipedia and Win!Document3 pagesGas Turbine: Photograph A Monument, Help Wikipedia and Win!justin2552No ratings yet
- Gas Turbine TheoryDocument3 pagesGas Turbine Theoryjustin2552No ratings yet
- Gas Turbine TheoryDocument3 pagesGas Turbine Theoryjustin2552No ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument16 pagesSteam TurbineUtkarsh VermaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Rankine Cycle ExplainedDocument8 pagesThermodynamic Rankine Cycle ExplainedsupriyasarkarNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineDocument7 pagesPower Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineMonglafru MogNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument15 pagesGas Turbine Power Plantrahul100% (1)
- Heat EngineDocument8 pagesHeat Enginekhaoula.ikhlefNo ratings yet
- Stirling Engine & Applications Project SeminarDocument32 pagesStirling Engine & Applications Project SeminarLASINNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Gas Turbine:: Land Based Gas Turbines Are of Two TypesDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Gas Turbine:: Land Based Gas Turbines Are of Two TypesTahir MuneebNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document36 pagesChapter 1sanky reddyNo ratings yet
- THERMO BS II NotesDocument8 pagesTHERMO BS II Notesm.waseemNo ratings yet
- Gas TurbineDocument14 pagesGas TurbineLarry SmithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Steam Power Plant Cycle PDFDocument31 pagesChapter 3. Steam Power Plant Cycle PDFJohn Carlo LEBRILLANo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment#1 PDFDocument21 pagesThermodynamics Assignment#1 PDFArslan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Rankine Cycle:: (Citation Needed)Document11 pagesRankine Cycle:: (Citation Needed)bnida99No ratings yet
- Turbine Is A Rotary Machine With Vanes or Blades Around ItDocument10 pagesTurbine Is A Rotary Machine With Vanes or Blades Around ItTalha AhmadNo ratings yet
- Gas and Oil Engines, Simply Explained: An Elementary Instruction Book for Amateurs and Engine AttendantsFrom EverandGas and Oil Engines, Simply Explained: An Elementary Instruction Book for Amateurs and Engine AttendantsNo ratings yet
- Lower SurfaceDocument2 pagesLower Surfaceirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Modeling-Coordinates (Version 1) .XLSBDocument71 pagesModeling-Coordinates (Version 1) .XLSBirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Green Globes Building Rating System ExplainedDocument3 pagesGreen Globes Building Rating System Explainedirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Channel Flow and Heat Transfer ParametersDocument1 pageChannel Flow and Heat Transfer Parametersirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- CFX Particle TransportDocument3 pagesCFX Particle Transportirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Testing of Vapour Chamber Used in Electronics CoolDocument11 pagesTesting of Vapour Chamber Used in Electronics Coolirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Andheri Raat Ke Musafir by Naseem Hijazi Part 1 PDFDocument247 pagesAndheri Raat Ke Musafir by Naseem Hijazi Part 1 PDFirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Current Copy: I Softwarefolderview 07-Nov-17 11:17:55 Am Current Version: 7.0.0 Old Version: V.0 KashifrazaDocument1 pageCurrent Copy: I Softwarefolderview 07-Nov-17 11:17:55 Am Current Version: 7.0.0 Old Version: V.0 Kashifrazairsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- MPDocument1 pageMPirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text Documentirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Catalog NortonIndustrial 7362 2015 BookmarkedDocument316 pagesCatalog NortonIndustrial 7362 2015 Bookmarkedirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- VIOLI Straightening Brochure Low 012ukDocument4 pagesVIOLI Straightening Brochure Low 012ukirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Workbench Tutorial AirfoilDocument10 pagesWorkbench Tutorial Airfoilfab1991No ratings yet
- FEtch ExecuteDocument5 pagesFEtch Executeirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Stepper - Mcppi CallertableDocument1 pageStepper - Mcppi Callertableirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Tut Failure TheoriesDocument39 pagesTut Failure TheoriesKamil Hakan TuranNo ratings yet
- MineDocument12 pagesMineirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Mohr's Circle: Academic Resource CenterDocument23 pagesMohr's Circle: Academic Resource CentersyedamiriqbalNo ratings yet
- GearDocument2 pagesGearirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- Heating and Cooling Load CalculationDocument7 pagesHeating and Cooling Load Calculationirsalan_shahidNo ratings yet
- PETREL 1 Structural Modeling PDFDocument42 pagesPETREL 1 Structural Modeling PDFKuala Tambora100% (1)
- PGZ Schwenken EnglDocument36 pagesPGZ Schwenken EngljonNo ratings yet
- A VecFaraday1Document10 pagesA VecFaraday1zorrinNo ratings yet
- PVT Experiment IndividualDocument36 pagesPVT Experiment IndividualnursyakirahrahimNo ratings yet
- AbbrebiationDocument8 pagesAbbrebiationMahade Hasan DipuNo ratings yet
- Divine Particles Pressnote by Sanatan SansthaDocument4 pagesDivine Particles Pressnote by Sanatan SansthaHaindava KeralamNo ratings yet
- Numerical Investigation and Design of Aluminum Alloy Circular HollowDocument13 pagesNumerical Investigation and Design of Aluminum Alloy Circular HollowDjordjeDjNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument5 pagesWater CycleCathy McPherson HuffNo ratings yet
- 7th Semester UET TaxilaDocument4 pages7th Semester UET TaxilaRameez AnwarNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 4 PPT Q3 - Interactive Quiz - Heat, Light, SoundDocument50 pagesSCIENCE 4 PPT Q3 - Interactive Quiz - Heat, Light, SoundRe ChelNo ratings yet
- Accessible Design LightingDocument8 pagesAccessible Design LightingArch AmiNo ratings yet
- B.Tech. 1st Term Q15 PDFDocument10 pagesB.Tech. 1st Term Q15 PDFDEBAPRASAD PALNo ratings yet
- Kathrein 80010761Document2 pagesKathrein 80010761Sego Megono100% (1)
- Earthing CalculationDocument4 pagesEarthing Calculationanandpurush100% (1)
- Engineering Management: Assignment Chapter 8Document4 pagesEngineering Management: Assignment Chapter 8Aftab AliNo ratings yet
- Coanda Effect Air-LiftDocument19 pagesCoanda Effect Air-LiftJúlio Cesar RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Complete Resonance MathematicsDocument701 pagesComplete Resonance MathematicsRajendra Bisoi100% (6)
- Physics Duty Chapter SevenDocument23 pagesPhysics Duty Chapter SevenScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- IR Drop PDFDocument3 pagesIR Drop PDFarammartNo ratings yet
- Physics 114 - Graphical Analysis of Motion 2015-2Document4 pagesPhysics 114 - Graphical Analysis of Motion 2015-2barackNo ratings yet
- Armor Rods: NomenclatureDocument8 pagesArmor Rods: NomenclatureArturo Tipacti QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment of Existing Bridge StructuresDocument262 pagesRisk Assessment of Existing Bridge StructuresShadi0% (1)
- Electrochemical Reactivation (EPR) For Detecting Sensitization of AISI Type 304 and 304L Stainless SteelsDocument9 pagesElectrochemical Reactivation (EPR) For Detecting Sensitization of AISI Type 304 and 304L Stainless SteelsAndres Carmona100% (1)
- TDS PH MacTexMXL May2014Document1 pageTDS PH MacTexMXL May2014Catherine MagnayeNo ratings yet
- CIS221-Design of Concrete Structures: BY Dr. Abdallah MostafaDocument20 pagesCIS221-Design of Concrete Structures: BY Dr. Abdallah Mostafamagdy makramNo ratings yet
- Dual DegreeDocument19 pagesDual DegreekhananuNo ratings yet
- MCQ's Concrete Technology - Fawad AhmadDocument10 pagesMCQ's Concrete Technology - Fawad AhmadFawad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Thermoelectric Mini Fridge & WarmerDocument37 pagesThermoelectric Mini Fridge & WarmerDinu RamanattukaraNo ratings yet
- Materials Finer Than 75 - : Standard Test Method For M (No. 200) Sieve in Mineral Aggregates by WashingDocument3 pagesMaterials Finer Than 75 - : Standard Test Method For M (No. 200) Sieve in Mineral Aggregates by WashingLuis Alejandro Sánchez LópezNo ratings yet