Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Me Is Is
Uploaded by
Yian PangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Me Is Is
Uploaded by
Yian PangCopyright:
Available Formats
Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis is the cell division in which a cell will divide into two daughter cells that are identical to the original cell.
Meiosis is the cell division that results in the formation of gametes. Meiosis reduces the chromosome number from diploid to haploid. The products (haploids) formed from meiosis will have a complete set of chromosomes, and that each haploid is genetically different from each other.
Mitosis
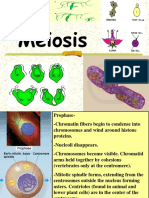
Prophase Sister chromatids condense and become more visible and thicker. Kinetochores develop in the centromere regions The nucleolus disappears The nuclear envelope disappears Metaphase Chromosomes line up on the center of the cell (equatorial plate). They were moved to the center by the spindles coming from the opposite ends of the cell, where the centrioles are.
Anaphase
The centromeres of each of the chromosome are pulled by the spindle fibers. The sister chromatids are separated. They are now referred to as daughter chromosomes. Telophase New nuclei form around the chromosomes from each end of the cell The chromosomes uncoil and become less visible Spindle breaks apart After mitosis, cytokinesis takes place and the cell is split into two cells.
Meiosis
Prophase I Chromosomes thicken and become more visible Homologous chromosomes pair Four sister chromatids form a tetrad Crossing over, or the exchange of genetic materials at the chiasmata, occurs This will increase variability Nucleoli disappear Nuclear envelope disappear Spindle forms Metaphase I Chromosome pairs are lined up at the center of the cell (equatorial plate).
Anaphase I
The homologous chromosomes separate The daughter nuclei will contain one set of chromosomes, and each chromosome has two chromatids Telophase I This doesnt occur in all organisms If this stage occurs in an organism, then the nuclear envelope will form. Then cytokinesis occurs.
Prophase II The chromosomes condense and become visible The nuclear envelope and nucleoli disappear Metaphase II The chromosomes, containing two chromatids, are lined up at the equatorial plate
Anaphase II The sister chromatids separate Telophase II The haploid daughter cells start to form The nuclear envelope starts to form After Telophase II, cytokinesis takes place and produces 4 haploid daughter cells.
There are differences between meiosis II and mitosis:
DNA will not replicate before meiosis II The sister chromatids in meiosis II will likely not be identical due to crossing over The number of chromosomes at the center of the cell in meiosis II is half the number of chromosomes in mitosis. Meiosis results in 4 genetically different haploid nuclei]
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Economic CommunityDocument5 pagesEconomic CommunityYian PangNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Akemi Uchi Pop Card FormatDocument1 pageAkemi Uchi Pop Card FormatYian PangNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Folio Biology Form 4 Chapter 8 and 9Document28 pagesFolio Biology Form 4 Chapter 8 and 9Yian PangNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Plant Cell Animal CellDocument3 pagesPlant Cell Animal CellYian PangNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Bishop Study Guide 5Document16 pagesBishop Study Guide 5Yian PangNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Bio 5Document17 pagesBio 5Prince SanjiNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Cells AssignmentDocument18 pagesCells AssignmentMuqadasNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Module 4-The Cell's Life CycleDocument5 pagesModule 4-The Cell's Life CycleGoogle BackupNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Test Bank For Human Heredity Principles and Issues 10Th Edition Michael Cummings 1133106870 9781133106876 Full Chapter PDFDocument31 pagesTest Bank For Human Heredity Principles and Issues 10Th Edition Michael Cummings 1133106870 9781133106876 Full Chapter PDFkelly.rhodes162100% (12)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- PHA611 LEC 1st ShiftingDocument225 pagesPHA611 LEC 1st ShiftingGAILE MEIZTY MOSADANo ratings yet
- Cell Divisions - MCQDocument6 pagesCell Divisions - MCQKerem TezmenNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- General Biology1 (Answer Key)Document15 pagesGeneral Biology1 (Answer Key)Olive PelayoNo ratings yet
- 01 02 Cytoskeleton PDFDocument12 pages01 02 Cytoskeleton PDFsigninNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Superior Science Academy Test 5 Bio 9th ClassDocument2 pagesSuperior Science Academy Test 5 Bio 9th ClassNaeem AmjidNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- CSEC Biology Jan 2021 P2 - OCRDocument28 pagesCSEC Biology Jan 2021 P2 - OCRJonathan RamsundarNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Remedial Activity - Science-8 4TH QuarterDocument3 pagesRemedial Activity - Science-8 4TH Quartermylyn ceraficaNo ratings yet
- SPM Bio F4 C5Document8 pagesSPM Bio F4 C5Wenan Chooi Wen HanNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Ch11 Test File-The Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument43 pagesCh11 Test File-The Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDollar'sCornerNo ratings yet
- Checked - Unit 2 Cells, Development, Biodiversity and Conservation - Exam - MSDocument10 pagesChecked - Unit 2 Cells, Development, Biodiversity and Conservation - Exam - MSEllane leeNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology GCSE Unit 41 Cell Biology Revision MatDocument4 pagesAQA Biology GCSE Unit 41 Cell Biology Revision MatkhawlaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Heredity AND Variation: Cell DivisionDocument21 pagesHeredity AND Variation: Cell Divisionshahadah_rahimNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Siklus Sel - Bruce Albert (SEND)Document27 pagesSiklus Sel - Bruce Albert (SEND)Rahmah Khairunnisa QonitaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Cancer Test Review Sheet: Name: DateDocument5 pagesCell Cycle & Cancer Test Review Sheet: Name: DateAnicia ToscanoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cancer ReviewDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cancer ReviewEivor LynNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis Quiz - KEYDocument2 pagesMitosis Vs Meiosis Quiz - KEYJanecil A. BonzaNo ratings yet
- Free Online Guide - Class 12 Biology Viva Voce Questions For Practical Experiments and Projects - 1-13Document2 pagesFree Online Guide - Class 12 Biology Viva Voce Questions For Practical Experiments and Projects - 1-13anam sadiq100% (2)
- 'The Cell Cycle' ScriptDocument3 pages'The Cell Cycle' ScriptLLCaplan100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Chapter 5 Bio f4Document20 pagesChapter 5 Bio f4Madyha AzmiNo ratings yet
- Bakery Technology - Yeast and Sourdough PDFDocument1 pageBakery Technology - Yeast and Sourdough PDFZoran MiladinovićNo ratings yet
- CN 6 BioDocument2 pagesCN 6 BioJanna PaduaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science SOL Review - New One Answer KeyDocument30 pagesEarth Science SOL Review - New One Answer KeyXiandan AyjNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesClass 10 Biology - Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionGreatAkbar1No ratings yet
- Acp1 ActDocument6 pagesAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 03.10.21 Cell Cycle Part 02Document53 pages03.10.21 Cell Cycle Part 02Atharv PatidarNo ratings yet
- 7.3: Mitotic Phase - Mitosis and CytokinesisDocument4 pages7.3: Mitotic Phase - Mitosis and CytokinesisMartinoKhanzaniaNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)