Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics
Uploaded by
Shubham VermaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics
Uploaded by
Shubham VermaCopyright:
Available Formats
Question .1. State Newtons Second Law of motion both in words and in Equation form.
Under what condition does this equation becomes F = ma? Question .2. What is S I unit of force and how is it related to the CGS unit of force? Question .3. Differentiate between mass and weight. Question .4. Write the S I unit of mass and weight. Question .5. A force is applied on (i) a rigid body and (ii) non rigid body. How does the effect of force differ in the two cases ? Question .6. Define (i) Work (ii) Power and (iii) Energy. Question .7. Write the expression for the work done by constant force acting on a body, which gets displaced from its initial position in a direction different from the direction of force. Or, How can the work done be measured when force is applied at an angle to the direction of displacement ? Question .8. When a body moves in a circular path how much work is done ? Or, State the amount of work done by an object when it moves in a circular path for one complete rotation. Give reason to justify your answer.
Question .9. How is work done related to the applied force ? Question .10. What should the angle between force and displacement be to get the (i) minimum work (ii) maximum work ? Question .11. Give an example when work done by force acting on a body is zero even though the body gets displaced from its initial position by the application of the force. Question .12. A truck driver starts off with his loaded truck. What are the major energy changes that take place in setting the truck in motion ? Question .13. State the energy change in an oscillating pendulum. Q.14. What is the main energy transformation that occurs in : (i) Photosynthesis in green leaves (ii) Charging of battery. Question .15. Which physical quantity does the electron volt measure ? How is it related to the SI unit of this quantity ? Question .16. By what factor does the kinetic energy of a moving body change when its speed is reduced to half ? Question .17. Show that for the free fall of a body, the sum of the mechanical energy at any point in its path is constant. Question .18. Define the terms (i) mechanical advantage
(ii) velocity ratio (iii) efficiency of a machine. Write an expression to show the relationship between mechanical advantage, velocity ratioand efficiency for a simple machine. Question .19. What is the relationship between the mechanical advantage and velocity ratio of (i) An ideal machine and (ii) Practical machine ? Question .20. How do you distinguish between a lever of the first order from a second or a third order lever ? Question .21. The following are the examples of levers. State the class of lever to which each one belongs giving the relative position of load (L), Effort (E) and Fulcrum (F) (i) Scissors (ii) Sugar tongs (iii) Nut cracker and (iv) Pliers. Question .22. Fig below shows a weight less lever in equilibrium. Neglect friction at the fulcrum F. (i) State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever. (ii) Define mechanical advantage and calculate its value for the given lever. (iii) Name the type(s) of lever which has M.A.>1.
Question .23. Which class of levers has a mechanical advantage always greater than
one ? What change can be brought about in this lever to increase its mechanical advantage ? Question .24. Which class of levers has a mechanical advantage always less than one ? Explain briefly with a diagram why their mechanical advantage is less than one. Question .25. Why is the mechanical advantage of a lever of the third class always less than one ? Give one example of this class of lever. Question .26. To use a machine as a force multiplier, which class of lever should preferred ? Draw a sketch of such a lever. Or, Draw a labelled sketch of a class II lever. Give one example of such a lever.
Question .27. A pair of scissors and a pair of pliers belong to the same class of lever. (i) Which one has mechanical advantage less than one ? (ii) State the usefulness of such a machine whose mechanical advantage is less than one. . Question .28. Explain why scissors for cutting cloth may have blades much longer than the handles; but shears for cutting metals have short blades and long handles. Question .29. Give two reasons why the efficiency of a single movable pulley system is not 100%. Question .30. A combination of a movable pulley P1with a fixed pulley P2 is used for lifting up a load W. (i) State the function of the fixed pulley P2. (ii) If the free end of the string moves through a distance x, find the distance by which the load W is raised.
Question .31. Name a type of single pulley that can act as a force multiplier. Draw a labelled diagram of the above named pulley. Question .32. A block and tackle pulley system has a velocity ratio 3. (i) Draw a labelled diagram of this system. In your diagram, indicate clearly the points of application and the directions of the load and effort. (ii) Why should the lower block of this pulley system be of negligible weight ? Q.33. Define an inclined plane.
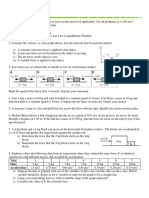
Numerical 1. A body of mass 1 kg is thrown vertically up with an initial speed of 15 ms-1. What is the magnitude and direction of the force due to gravity acting on the body when it is at the highest point ? Numerical 2. The weight of two bodies are 2.0 N and 2.0 kgf respectively. What is the mass of each body ? Numerical 3. Two balls of mass ratio 1 : 2 are dropped from the same height. (i) State the ratio between their velocities when they strike the ground and (ii) the ratio of the forces acting on them during motion. Numerical 4. A force of 100 N acts on a body for 5 seconds and produces a velocity of 50 ms-1. Find the mass of the body. Numerical 5. A cricket ball of mass 70 g, moving with a velocity of 0.5 m s-1 is stopped by a player in 0.5 s. What is the force applied by the player to stop the ball ?
Numerical 6. A man of mass 60 kg runs up a flight of 30 steps in 15 second. If each step is 20 cm high, calculate the power developed by the man. Take g =m 10 ms-2.
Numerical 7. How fast should a man weighing 60 kg run so that his kinetic energy is 750j Numerical 8. A block of mass 30 kg is pulled up a slope with a constant speed by applying a force of 200 N parallel to the slope. A and B are initial and final positions of the block. (i) Calculate the work done by the force in moving the block from A to B. (ii) Calculate the potential energy gained by the block. Numerical 9. A body of mass 1 kg falls from a height of 5 m. How much energy does it possess at any instant. Take g = 9.8 ms-2. Numerical 10. A bullet of mass 50 g is moving with a velocity of 500 ms-1. It penetrates 10 cm into a still target and comes to rest. (i) Calculate the KE possessed by the bullet. (ii) The average retarding force offered by the target. Numerical 11. An engine can pump 30000 litre of water to a vertical height of 45 m in 10 minutes (g = 9.8 ms-1). Calculate the work done by the machine and its power (density of water 1000kgm-3 and 1000 litre = 1 m3). Numerical 12. A machine raises a load of 750 N through a height of 16 m in 5 second. Calculate the power at which the machine works. Numerical 13. If power of a motor is 40 kW, at what speed can it raise a load of 20,000 N ? Numerical 14. A ball of mass 0.20 kg is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 20 ms-1. Calculate the maximum potential energy it gains as it goes up. Numerical 15. The work done by the heart is 1 joule per beat. Calculate the power of the heart if it beats 72 times in one minute.
Numerical 16. Two bodies, A and B of equal mass are kept at heights 20m and 30 m respectively. Calculate the ratio of their potential energies. Numerical 17. The diagram below shows the use of a lever. (a) State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever. (b) Give an example of this lever. (c) If FA = 10 cm, AB = 500 cm, calculate the minimum effort required to lift the load.
Numerical 18. The crow bar is a type of lever as shown below. A crowbar of length 150 cm has its fulcrum at a distance of 25 cm from the load. Calculate the mechanical advantage of this crowbar.
Numerical 19. A cook uses a fire tong of length 28 cm to lift a piece of burning coal of mass 250 g. If he applies his effort at a distance 7 cm from the fulcrum, what is the effort in SI unit ? Take g = 10 ms-2. Numerical 20. A woman draws water from a well using a fixed pulley. The mass of the bucket and water together is 6.0 kg. The force applied by the woman is 70 N. Calculate the mechanical advantage. (Take g = 10 ms-2). Numerical 21. Combination of a movable pulley P1with a fixed pulley P2used for lifting up a load 20 kgf. Calculate the effort applied at the free end of the string, neglecting the weight of the pulley P1 and friction. Numerical 22. In the arrangement of four pulleys, a load is attached to the movable lower block and an effort is applied at the free end of the string. Calculate the mechanical advantage of the system. Numerical 23. A block and tackle pulleys of 5 pulleys consists of 3 pulleys in the upper block and 2 pulleys in the lower block . If the load is raised by 1 m, through what distance will effort move ?
Numerical 24. A uniform metre scale is kept in equilibrium when supported at the 60 cm mark and a mass M is suspended from the 10 cm mark. State with reason whether the weight of the scale is greater than, less than or equal to the weight of mass M.
Question .1. State Snells law of refraction. Question .2. The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined as
g
a = sin i / sin r
(i) Write down a similar expression for a g in terms of angle i and angle r. (ii) In (i) above, if angle r = 90 what is the corresponding angle i called ? (iii) What is the physical significance of i in part (ii) above ? Question .3. What is meant by (i) Critical angle (ii) Total internal reflection. Question .4. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate how a ray of light incident obliquely on one face of a rectangular glass slab of uniform thickness emerges parallel to its original direction. Mention which pairs of angles are equal. Question .5. Water in a pond appears to be only three quarter of its actual depth. (i) What property of light is responsible for this observation ? (ii) Illustrate your answer with the help of a ray diagram. Question .6. (i) With the help of a well labelled diagram show that the apparent depth of an object, such as a coin, in water is less than its real depth. (ii) How is the refractive index of water related to the real depth and the apparent depth of a column of water ?
Question .7. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the bending of a stick in water. Question .8. What is an optical fibre ? Give one practical use of an optical fibre. Question .9. Explain briefly what causes the twinkling of stars at night. Question .10. What is meant by the statement, the critical angle for diamond is 24 ? How is the critical angle of the material related to its refractive index ? Question .11. A glass slab is placed over a page on which the word VIBGYOR is printed with each letter in its corresponding colour. (i) Will the image of all the letters be in the same place ? (ii) If not, state which letter will be raised to the maximum. Give a reason for your answer. Question .12. What is meant by refraction ? Question .13. Express the refractive index of a medium (i) in terms of the velocity of light; (ii) in terms of the angle of incidence i in air and the angle of refraction r in a denser medium. Question .14. If a ray of light passes from medium I to medium II without any change of direction, what can be said about the refractive indices of these media (angle i is not 0) ? Question .15. Mention two properties of a wave: one property which varies and the other which remains constant when the wave passes from one medium to another. Question .16. A prism deviates a monochromatic ray of light through an angle when the angle of incidence on the surface of the prism is i:
(i) Draw a diagram showing the variation of with i. On your graph show the angle of minimum deviation. (ii) What is the relation between the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence when the ray suffers minimum deviation ? Question .17.Mention one difference between reflection of light from a plane mirror and total internal reflection of light from a prism. Numerical 1. The velocity of light in diamond is 121,000 km s-1. What is its refractive index ? (velocity of light in vacuum/air = 3 105 m s-1). Numerical 2. Calculate the velocity of light in a glass block of refractive index1.5. (velocity of light in air = 3 108 m s-1). Numerical 3. If the refractive indices for a ray passing from air to water and from water to air, are denoted by symbols aw and wa respectively, write down the relation between aw and wa. If wa = 0.75, what will be the magnitude of aw. Numerical 4.A glass-slab 2.5 cm thick is placed over a coin. If the refractive index of glass is 3/2, find the height through which coin is raised. Numerical 5. If the speed of light in vacuum is 3 108 m s-1 and refractive index of water is 4/3, calculate the speed of light in water ?
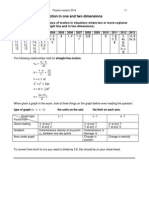
Question .1. An object is placed in front of a lens between its optical cenre and the focus. The image formed is virtual, erect and diminished . (i) Name the lens which forms this image. (ii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image with the above characteristics.
Question .2. An object AB is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens as shown in figure below. Copy the diagram. Using three rays starting from B and the properties of the points marked F1, O and F2 obtain the image formed by the lens.
Question .1. Write down the following and fill in the blanks spaces with appropriate colours : (a) Green + Magenta = ___________. (b) Red + _________ = Yellow. (c) Red + Blue = _____________. (d) Blue + _________ = Cyan. (e) Yellow + Blue = _________ . (f) Magenta + ___________ = White. (g) _______ + Red = White. (h) Red + ________ + Green = White. (i) A red rose appears ________ when seen in green light. (j) A piece of red cloth appears red in white light because it _________ blue and green and ______ only red. Question .2. Write down the colour spectrum produced when white light is passed through a prism. Which of these colours is deviated most ? Question .3. What is the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave whose frequency is 1012 Hz ? Name this electromagnetic wave. question .4. Show the effect of mixing two primary colours through labelled colour triangle. Question .5. Give one useful and one harmful effect of ultra violet radiation on the human body. Question .6. Define a pair of complementary colours. Name the colours in one such pair. Question .7. Define dispersion of light. Question .8. Explain briefly how white light gets dispersed by a prism. Question .9. Draw a diagram to show that white light can be split up into different colours.
Draw another diagram to show how the colours can be combined to give the effect of white light .
Question .10. Name the extreme colours in a pure spectrum of light. Question .11. State the equation for the relation between frequency and wavelength of light in vacuum. Question .12. Name any four regions of electromagnetic spectrum (other than visible light) in increasing order of wavelength. Question .13. Name any two electromagnetic waves which have a frequency higher than that of violet light. State one use of each. Question .14. Give one use each of the electromagnetic radiation given below : (i) microwave (ii) ultra violet radiation (iii) infrared radiation. Question .15. How would you show the presence of UV and IR rays in the spectrum? Question .16. When yellow paint and blue paint are mixed we get green colour. When yellow light and blue light are mixed, white light is obtained. Give reasons. Question .17. A green shirt is observed in blue light. What colour it will appear to be and why ? Question .18. Explain why in day light an object appear red when seen through a
red glass and black when seen through a blue glass ?
Question .19. Write the names of a pair of colours which combine to give white light. What is the name given to such a pair of colours ? Question .20. A flag is made up of three strips of cloth of yellow, white and cyan colours. Name the colour of a particular light in which this flag will appear to be of a single colour. Question .21. (i) White light is passed through a yellow filter. What colour is (colours are) seen on a screen plated at the end ? (ii) If the light emerging from the yellow filter is then passed through a red filter, what will be seen on the screen placed at the end ? Question .22. What will be the colour of an object which appears green in white light and black in red light ? Question .23. Give the approximate range of wavelengths in vacuum associated with UV rays and visible light. Question .24. A TV station transmits waves of frequency 200 MHz. Calculate the wavelength of the waves if their speed in air is 3.0 108 m s-1. Question .25. Why are infrared radiations preferred over ordinary visible light for taking photograph in fog ? Question .26. (i) What will be the colour of a blue flower when it is seen in magenta coloured light? (ii) Name another secondary colour of light in which the flower will show the same colour as it shows in the magenta coloured light
Question .27. (i) A particular type of high energy invisible electromagnetic rays help us to study the structure of crystals. Name these rays and give another important use of these rays. (ii) How does the speed of light in glass change on increasing the wavelength of light ? Question .28. A room has window pans made of a special glass which can reflect green light, transmit red light, scatter blue light and absorb all the other colours of light. The room is illuminated with white light from inside. What colour will the window pane appear when seen from (i) inside the room, (ii) outside the room ?
Question .3. Figure below shows an object AB placed on the principal axis of a convex lens placed in air. F1 and F2 are the two foci of the lens. Copy the diagram : (i) Draw a ray of light starting from B and passing through O. Show the same ray after refraction by the lens. (ii) Draw another ray from B which passes through F2 after refraction by the lens. (iii) Locate the final image formed. (iv) Is the image formed real and inverted ?
Question .4. Is it possible to burn a piece of paper using a convex lens in day light without using matches or any direct flame ? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate your answer. Question .5. Figure below shows an object AB placed on the principal axis of a lens L. The two foci of the lens are F1 and F2. The image formed by the lens is erect, virtual and diminished. Copy the diagram and answer the following questions : (i) Draw the outline of lens L used. (ii) Draw a ray from B, and passing through O. Show the ray after refraction by the lens. (iii) Draw a ray of light starting from B, which after passing parallel to the principal axis, is incident on the lens and emerges after refraction from it. (iv) Locate the final image formed.
Question .6. Write the name of the (i) most sensitive and (ii) most insensitive part of the retina.
Question .7. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the action of a convergent lens as reading glasses or magnifying glass. Question .8. In an optical camera, state (i) the nature of lens used (ii) what is meant by f-number (iii) two characteristics of the image formed by the lens. Question .9. An erect, diminished and virtual image is formed when an object is placed between the optical centre and the principal focus of a lens. (i) Name the type of lens, which forms the above image. (ii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image with the above characteristics. Question .10. State two similarities between the photographic camera and the human eye. Question .11. Name any two essential parts of a single lens photographic camera. Question .12. A ray of light after refraction through a concave lens emerges parallel to the principal axis. Draw a ray diagram to show the incident ray and its and its corresponding emergent ray. Question .13. State the characteristics of the image of an extended source, formed by a concave lens. & Question .14. The diagram given below shows an object O and its image I. Copy the diagram and draw suitable rays to locate the lens and its focus. Name the type of lens in this case.
Question .15. An object is placed in front of a convex lens such that the image formed has the same size as that of the object. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this. & Question .16. Mention one similarity and one difference between the lens of a photographic camera and that of the human eye. Question .17. Draw outline ray diagram to show the formation of images through an eye in the following cases : (i) from a distance object for a short-sighted person and (ii) from the normal point of distinct vision for a long sighted person.
You might also like
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hydraulics Reviewer For Civil Engineering StudentsDocument2 pagesHydraulics Reviewer For Civil Engineering StudentsKing BangngayNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetDocument12 pagesWork Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetAnonymous LZmFaXc100% (2)
- Advances in Critical Buckling Load Assessment For Tubular Inside WellboresDocument9 pagesAdvances in Critical Buckling Load Assessment For Tubular Inside WellboresPeaceMaker AmirahNo ratings yet
- Circulo de Morh PytelDocument51 pagesCirculo de Morh PytelJohn Royer Araúz FuentesNo ratings yet
- G11 Work Energy and PowerDocument3 pagesG11 Work Energy and PowerpranitNo ratings yet
- Viskozimetri PDFDocument9 pagesViskozimetri PDFabasakNo ratings yet
- Engineering PhysicsDocument4 pagesEngineering PhysicsMadhu DasariNo ratings yet
- Acfrogcotthiaaw5ijplyyv4xwwtz7k8a6rjmi5tglxbnapq Kvubt p69mzhkhpnx7gbztj8xixdcvnehh0m2tay9zo5-Bx5eslder28mpvqp-Kwj5ajqsdgi7xbnzi6axuvuyibu5uvdpporzDocument6 pagesAcfrogcotthiaaw5ijplyyv4xwwtz7k8a6rjmi5tglxbnapq Kvubt p69mzhkhpnx7gbztj8xixdcvnehh0m2tay9zo5-Bx5eslder28mpvqp-Kwj5ajqsdgi7xbnzi6axuvuyibu5uvdpporzFalak SetaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 2013 Class - XI Subject - : Time: 3Hrs M.M. 70Document4 pagesSample Paper - 2013 Class - XI Subject - : Time: 3Hrs M.M. 70Shankar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Icse X Work, Power & Energy Question BankDocument5 pagesIcse X Work, Power & Energy Question BankanimeshtechnosNo ratings yet
- Model Questiones For Engineering Mechanics 1 Year All BranchesDocument10 pagesModel Questiones For Engineering Mechanics 1 Year All BranchesFeolo Riel TarayNo ratings yet
- Imp. Question Vol 1 XI 2017 18Document5 pagesImp. Question Vol 1 XI 2017 18akash kalraNo ratings yet
- Machines QBDocument6 pagesMachines QBAnsh KediaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 2011 Class - XI Subject - Physics Time: 3 Hrs. MM: 70 General InstructionsDocument4 pagesSample Paper - 2011 Class - XI Subject - Physics Time: 3 Hrs. MM: 70 General InstructionsMini PGNo ratings yet
- Section A and B MechanicsDocument7 pagesSection A and B MechanicsJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- Conceptual QuestionsDocument4 pagesConceptual QuestionssmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- General Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityZiyad MohammedNo ratings yet
- QuestionDocument8 pagesQuestionHimanshuTripathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - The Trio of ScalarsDocument6 pagesChapter 7 - The Trio of ScalarsNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Physics - 11Document11 pagesPhysics - 11Ishika GuptaNo ratings yet
- ICSE X FORCE REMEDIAL REVISION-mergedDocument8 pagesICSE X FORCE REMEDIAL REVISION-mergedanimeshtechnosNo ratings yet
- Work Energy WorksheetDocument3 pagesWork Energy Worksheetasmit sahooNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Mechanics Revision SheetDocument7 pagesTopic 2 Mechanics Revision SheetJNo ratings yet
- Assignment I: Statics of Particles and Rigid BodiesDocument8 pagesAssignment I: Statics of Particles and Rigid BodiesmNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 ExercisesDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document52 pagesWa0003.Atharva DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 4Document3 pagesWork Sheet 4Afaan OromooNo ratings yet
- Cbse Xi Physics Test PapersDocument14 pagesCbse Xi Physics Test PapersBhavesh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Uploads563856384743unit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions 2019 PDFDocument6 pagesUploads563856384743unit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions 2019 PDFRolando TorresNo ratings yet
- Em MAY JUNE 2010Document0 pagesEm MAY JUNE 2010Bala SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Problem Set 2016Document6 pagesTopic 2 Problem Set 2016ellie du123No ratings yet
- PDF 1698809991381Document2 pagesPDF 1698809991381riyele3191No ratings yet
- Unit 4 ExercisesDocument4 pagesUnit 4 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument10 pagesAssignmentTanmay dograNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Work WSDocument5 pagesWork WSalhanunNo ratings yet
- HW5 SheetDocument6 pagesHW5 SheetWissam HatimNo ratings yet
- Physics Set I PDFDocument4 pagesPhysics Set I PDFAdityaSinghNo ratings yet
- EM ModelDocument4 pagesEM ModelArunGopal PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- 11th PT-1Document6 pages11th PT-1ABHISHEK PANDANo ratings yet
- Em - QB - V UnitDocument10 pagesEm - QB - V UnitVEERAMANIKANDANNo ratings yet
- Physics 11Document9 pagesPhysics 11NasimaNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Assignment-1Document3 pagesWork and Energy Assignment-1Aditi KumariNo ratings yet
- Practice Assignment Work Energy and PowerDocument3 pagesPractice Assignment Work Energy and PowerAyush GogiaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentAishley MatharooNo ratings yet
- XI (2018-19) Physics Quarterly Exam QPDocument7 pagesXI (2018-19) Physics Quarterly Exam QPD SamyNo ratings yet
- Work - Energy - PowerDocument9 pagesWork - Energy - PowermaryNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument3 pagesLaws of Motionmili groupNo ratings yet
- A V Classes: Class: Xi Physics Assignment No. Iv Unit: Iv, Chap: Work Energy & Power 1 Mark TypeDocument1 pageA V Classes: Class: Xi Physics Assignment No. Iv Unit: Iv, Chap: Work Energy & Power 1 Mark TypeAtul VermaNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstDocument34 pagesPROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstMarj Ladica MangaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Force and MotionDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Force and MotionJerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks 70 General Instructions: Sample Paper - 08 Class - XI Subject - Physics (Theory)Document4 pagesTime: 3 Hours Max. Marks 70 General Instructions: Sample Paper - 08 Class - XI Subject - Physics (Theory)Arjun PrasadNo ratings yet
- FWM Prefinals 2023Document5 pagesFWM Prefinals 2023kumarardash86No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Review 3Document15 pagesUnit 2 Review 3highschoolresources7No ratings yet
- Ch.5lawsofmotionDocument4 pagesCh.5lawsofmotionsamahadadilkhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Motion Summary 2014Document58 pages1 Motion Summary 2014api-248740887No ratings yet
- AP Physics ProblemsDocument11 pagesAP Physics ProblemsjoacoXDNo ratings yet
- Pisiks 71 Prob SetsDocument8 pagesPisiks 71 Prob SetsAndroNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy AsDocument4 pagesWork Power Energy Asdhruvrawat0409No ratings yet
- High Power Fiber LaserDocument4 pagesHigh Power Fiber LaserShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- Econ Cheat SheetDocument1 pageEcon Cheat SheetShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- What Is Your On Life?: OutlookDocument8 pagesWhat Is Your On Life?: OutlookShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- 006.chapter6 Practice MC SetC and AnswersDocument4 pages006.chapter6 Practice MC SetC and AnswersShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- Eece.2160sp19 Lec1 IntroDocument21 pagesEece.2160sp19 Lec1 IntroShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- t A. Find the average power absorbed by the 50-Ω resistorDocument2 pagest A. Find the average power absorbed by the 50-Ω resistorShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- Labs Open Lab Hours WeeklyDocument2 pagesLabs Open Lab Hours WeeklyShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- 7 5 PDFDocument1 page7 5 PDFShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- Problem 7.21: SolutionDocument1 pageProblem 7.21: SolutionShubham VermaNo ratings yet
- 2 Velocity and AccelerationDocument28 pages2 Velocity and AccelerationAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Shaft ReportDocument51 pagesShaft ReportbalajiNo ratings yet
- Week 14 Plastic Deformation BeamDocument34 pagesWeek 14 Plastic Deformation BeamdarshanNo ratings yet
- L6-8 - Forward Kinemetics - Revised PDFDocument34 pagesL6-8 - Forward Kinemetics - Revised PDFAnirudh GoyalNo ratings yet
- 16 TrefilageDocument10 pages16 TrefilageYahyaMoummouNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Angles & Their MeasureDocument6 pages6.1 Angles & Their MeasureMiles BaldersNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Yeild Line AnalysisDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Yeild Line Analysisdebebe girmaNo ratings yet
- First Law of Thermodynamics For A Control VolumeDocument28 pagesFirst Law of Thermodynamics For A Control VolumeTushyNo ratings yet
- M-900 Robot Working Range: 330 KG 3203 MMDocument1 pageM-900 Robot Working Range: 330 KG 3203 MMjosjcrsNo ratings yet
- Contact Stress Calculation PDFDocument23 pagesContact Stress Calculation PDFRanjit Kumar TANo ratings yet
- Chapter 25Document57 pagesChapter 25Rawan Z NemerNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-04-26 at 6.58.53 AMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-04-26 at 6.58.53 AM25hshalabiNo ratings yet
- SPX Curve BookDocument38 pagesSPX Curve BookCarlos Alberto Ramirez GarciaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Soil Yielding and Shear Failure of Soil - QuoraDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Soil Yielding and Shear Failure of Soil - QuoraVinithaNo ratings yet
- Gate MCQ Mechanical Engineering by NodiaDocument47 pagesGate MCQ Mechanical Engineering by NodiaPriyank GabaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanical VibrationDocument1 pageIntroduction To Mechanical VibrationDomingo Joshua Eduard C.No ratings yet
- Lab 6 ConservationDocument3 pagesLab 6 Conservationajit2150No ratings yet
- Syllabus For EGR 233: Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument4 pagesSyllabus For EGR 233: Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDamn NationNo ratings yet
- Fizik Tingkatan 4Document2 pagesFizik Tingkatan 4download notesNo ratings yet
- Physical Pharmacy Principles ReviewerDocument7 pagesPhysical Pharmacy Principles ReviewerAntonio CharismaNo ratings yet
- Aryan+Patel+ +Impulse+and+Momentum - Pdf.kamiDocument2 pagesAryan+Patel+ +Impulse+and+Momentum - Pdf.kamiAryan PatelNo ratings yet
- AGARDAG328Document200 pagesAGARDAG328ENo ratings yet
- FHSC1014 Additional Tutorial 5Document5 pagesFHSC1014 Additional Tutorial 5Zheng Kit OoiNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Plastic Analysis of StructuresDocument17 pagesUnit Iii Plastic Analysis of StructuresrajNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument24 pagesAtomic PhysicsReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet