Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Peds Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
twils033Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Peds Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
twils033Copyright:
Available Formats
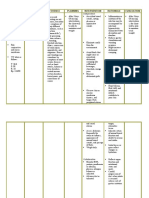
NURSING CARE PLAN Clients initials S.E.
Age 5
Nursing System Educative Supportive
ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS PLANNING IMPLEMENTATON EVALUATION
DATA COLLECTION
SCD
COLLABORATIVE PROBLEM
GOAL/OBJECTIVES
NURSING ORDERS
RATIONAL FOR
NURSING ORDERS
METHODS OF NRSG
ASSISTANCE
GOAL MET, NOT
MET, PARTIALLY
MET
SUBJECTIVE DATA
Dx. Asthma
History unsteady gait and
hallucinations
Clients states she does not
have to go to the bathroom.
Also stated last bowel
movement was 3 days ago
OBJECTIVE DATA
BP 105/60, Temp 36.8 C,
RR 22, HR 98, O2 94,
blood sugar level 89,
weight 34.4kg, height 125
Patient appears to be the
stated age
Oriented to selI, place, and
time
Cardio: regular rate and
rhythm without murmur.
Lungs: wheezing
Skin is intact.
Abdomen is distended,
bowel sounds present in all
4 quadrants
\
PRIORITY #2 Alteration in
bowel elimination:
constipation related to
immobility secondary to
unsteady gait as evidence by
defecation occurring less
than 3 times per week
RATIONALE PRIORITY #2
According to Maslow`s
Hierarchy oI Needs excretion
oI bodily Iluids is a
physiological need that must
be met
GOAL:
1. Patient will have a
bowel movement
within 24 hours
2. Patient will
verbalize an
understanding of
methods of
preventing
constipation within
24 hours
OB1ECTIVES:
1. Client will increase
intake of food high in
fiber
2.Client will do
activities of daily
living and exercise as
able
3. Client will increase
her intake of fluids
1.1 Encourage
consumption oI whole
grains
1.2 Encourage
consumption oI Iruits
high in Iiber
1.3 Limit intake oI
carbohydrates (without
Iiber)
2.1 Encourage client to
perIorm ADLs
2.2 Assist client in
ambulating
2.3Demonstrate in bed
exercises
3.1 Encourage Iluid
intake oI 1500 ml/day
3.2 Limit intake oI
carbonated beverages
and citric Iluids
3.3 implement
psychosocial Iactors to
help stimulate
micturation
1. A Iunction oI the
nurse is to assist
clients with diet and
bowel preparation
(Kozier & Erb, 2008)
2. Nursing strategies
include administering
cathartics and
antidirrheals;
administering
cleansing,
carminative, or
retention enemas;
applying protective
skin agents;
monitoring Iluid and
electrolyte imbalance;
and instructing clients
in ways to promote
normal deIecation.
(Kozier & Erb, 2008)
Monitored patients
Iluid input and output.
Encouraged an increase
in daily Iluid intake.
Placed the client in low
Ilower`s position.
Provided ice water.
Encouraged the patient
to change positions
while in bed and sit in a
chair to eat breakIast
and lunch. Encourage
patient to comb hair,
brush teeth, and wash
Iace upon waking up.
Demonstrated range oI
motion exercises the
patient could do while
in bed.
1. Goal not met
as evidence by
patient not
having a bowel
movement and
did not verbalize
ways to prevent
constipation.
Patient needs
more time to
Iully achieve
goals. Nursing
care should be
continued until
goals are met.
NORFOLK STATE UNIVERSITY Student Tessa Wilson
DEPARTMENT OF NURSING Date 10/15/2011
NURSING CARE PLAN Clients initials S.E. Age 5
Nursing System Educative Supportive
ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS PLANNING IMPLEMENTATON EVALUATION
DATA COLLECTION
SCD
COLLABORATIVE PROBLEM
GOAL/OBJECTIVES
NURSING ORDERS
RATIONAL FOR
NURSING ORDERS
METHODS OF NRSG
ASSISTANCE
GOAL MET, NOT
MET, PARTIALLY
MET
SUBJECTIVE DATA
Dx. Asthma
History unsteady gait and
hallucinations
Sister reported patient
exhibited 'hallucinations
in the middle oI the night.
Patient reports being tired
OBJECTIVE DATA
BP 105/60, Temp 36.8 C,
RR 22, HR 98, O2 94,
blood sugar level 89,
weight 34.4kg, height 125
Patient appears to be the
stated age. Skin is intact.
Oriented to selI, place, and
time. Cardio: regular rate
and rhythm without
murmur. Lungs: wheezing,
normal depth, parallel chest
expansion, patient breaths
through mouth.
PRIORITY #1 At risk for
ineffective breathing pattern
due to inflammation
secondary to asthma as
evidence by fatigue and
labored breathing
RATIONALE PRIORITY #1
According to Maslow`s
Hierarchy oI Needs breathing
is a physiological need that is
required Ior survival
GOAL:
1. Client will verbalize
an increase in comfort
from labored breathing
in 1 hour
2. Client will verbalize
ways to help achieve an
adequate breathing
pattern within 24 hours
OB1ECTIVES:
1. Client`s breathing
pattern will be
maintained as evidence
by eupnea in 1 hour
2.Client will understand
and verbalize factors
that will worsen
patients pulmonary
condition
3. Client will have an
absence of cyanosis
1.1 encourage Iluid intake
oI 1,500 ml/ day
1.2 Teach patient how to
count own respirations and
relate respiratory rate to
activity tolerance
1.3Explain to the patient the
signs oI respiratory
compromise
2.1 Provided therapeutic
environment
2.2 Discuss possible
precipitating Iactors which
may worsen condition
2.3 Discussed
environmental Iactors (e.g.
pollen) that may worsen
patients condition
3.1 Encouraged deep
breathing
3.2 Follow prescribed
pharmacological regimen
3.3 Prevent patient Irom
taking out her nasal cannula
1. Nursing
interventions to
promote oxygenation
include promoting
healthy breathing and
a healthy heart, deep
breathing and
coughing, and
hydration. (Kozier &
Erb, 2008)
2. The nurse teaches
the client about home
care activities to
maintain a patient
airway and gas
exchange and to
promote healthy
breathing. (Kozier &
Erb, 2008)
Encouraged an increase
in daily Iluid intake.
Monitored patient`s
vital signs.
Demonstrated deep
breathing exercises.
Placed patient in high
Iowlers position.
Monitored patient`s
level oI consciousness.
Administered
medication as
prescribed. Monitor
respiratory rate, depth
and eIIort. Monitor
client`s behavior and
mental status Ior the
onset oI restlessness.
Remind the client to
breathe through her
nose and not her mouth
1. Goal not met
as evidence by
presence oI
labored breathing
and inability to
achieve comIort.
Patient needs
more time to
Iully achieve
goals. Nursing
care should be
continued until
goals are met.
You might also like
- Biographical Data - InfantDocument3 pagesBiographical Data - Infantmitsuki_sylphNo ratings yet
- AmbroxolDocument1 pageAmbroxolPrecious CarmelaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocument14 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type IIElay PedrosoNo ratings yet
- Gary Fending For HimselfDocument3 pagesGary Fending For HimselfPrincess Levie CenizaNo ratings yet
- NCP PryllDocument6 pagesNCP PryllpjcolitaNo ratings yet
- Somera Case 1928Document68 pagesSomera Case 1928jrkalbo75% (4)
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Document3 pagesSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- NCP For ConcussionDocument3 pagesNCP For Concussiontamtam_antonio100% (1)
- NCP AnemiaDocument2 pagesNCP AnemiaAriaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Document3 pagesSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Milagros FloritaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan With Other ReferncesDocument3 pagesDischarge Plan With Other ReferncesApril Joy PrestoNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan DyspneaDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan DyspneaMae JavierNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection - NCPDocument3 pagesRisk For Infection - NCPHamil BanagNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Infection and Bleeding PrecautionsDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan for Infection and Bleeding Precautionshayascent hilarioNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Nursing Interventions Evaluation Standard Criteria Subjective: Short Term GoalDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Nursing Interventions Evaluation Standard Criteria Subjective: Short Term GoalmitchNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For Imbalance Body TemperatureDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Risk For Imbalance Body TemperatureCarl J.No ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJoevelyn LaynoNo ratings yet
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP HemothoraxMichael John F. NatividadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Omeprazole CompressDocument2 pagesDrug Study Omeprazole CompressAngelica TolledoNo ratings yet
- NCP - ERDocument5 pagesNCP - ERAnnelore ArcayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For LYING inDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For LYING inKarissa CiprianoNo ratings yet
- University of Negros Occidental Student Clinical Training ReportDocument3 pagesUniversity of Negros Occidental Student Clinical Training ReportAzhly AntenorNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPKarell Eunice Estrellado Gutierrez100% (1)
- Case For NCPDocument5 pagesCase For NCPSarah Jane MaganteNo ratings yet
- Improving Dental Hygiene in Grade III StudentsDocument3 pagesImproving Dental Hygiene in Grade III Studentsx483xDNo ratings yet
- NCP ErDocument4 pagesNCP ErljarseniornNo ratings yet
- NCP 4Document1 pageNCP 4marohunkNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On SepsisDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan On SepsisleoNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment On GERD PatientDocument8 pagesPhysical Assessment On GERD PatientRobert Medina100% (1)
- Rebamipide drug guide: Dosage, uses, side effectsDocument1 pageRebamipide drug guide: Dosage, uses, side effectsmarsh155No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Gen 017 - Sas Lesson #1Document2 pagesGen 017 - Sas Lesson #1Faith CalimlimNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM) 2Document1 pageDiabetes Mellitus (DM) 2Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing System Review ChartDocument2 pagesNursing System Review ChartifancyouuuNo ratings yet
- R.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document2 pagesR.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Karen Joy ItoNo ratings yet
- #27 - Web 2.0, Blogs, WikisDocument19 pages#27 - Web 2.0, Blogs, WikisMissy PNo ratings yet
- You Are Caring For A Patient With An NG Feeding TubeDocument2 pagesYou Are Caring For A Patient With An NG Feeding TubeWen Silver100% (1)
- Learning FeedbackDocument2 pagesLearning FeedbackDeejay L. RaramaNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- CS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPDocument2 pagesCS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Document4 pagesDischarge Plan For Dengue Fever 1Cecille Ursua0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Patient with PruritusDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan for Patient with PruritusJachel Kathleen LaguioNo ratings yet
- FCP (Gorres)Document3 pagesFCP (Gorres)Kaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- GERD and PUD Nursing CareDocument6 pagesGERD and PUD Nursing CareDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- NafarinDocument2 pagesNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- Essential care universally available at affordable cost defined as primary health careDocument11 pagesEssential care universally available at affordable cost defined as primary health careAngelina Janiya NicoleNo ratings yet
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeDocument2 pagesTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- NCP (Acute Pain)Document2 pagesNCP (Acute Pain)jennilois100% (1)
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument25 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurejohnleeeNo ratings yet
- Ugib NCPDocument5 pagesUgib NCPJhuRise Ann Mangana100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument23 pagesNursing Care PlanLorielle HernandezNo ratings yet
- Care Plan 2Document11 pagesCare Plan 2api-28474004567% (3)