Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MEMB123 Project Sem 2-11-12
Uploaded by
Maarij AnjumOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MEMB123 Project Sem 2-11-12
Uploaded by
Maarij AnjumCopyright:
Available Formats
MEMB123 Project (Semester 2 11/12)
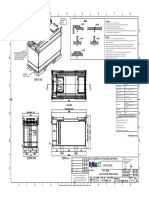
Project Objective: Design and built a model of a hoist support that can hold a load of 10N using a minimum of materials (cost effectiveness). Project Goals: The goals for this project are for students to: Learn the design process. See practical applications for trigonometry, physics, and statics. Improve skills associated with collecting data and drawing meaningful conclusions. Cultivate leadership within the team. Recognize the necessity of good communication skills for engineers by working in a team, completing memos, reports, drawings, and presentations. Project Grading: The grade for the project is broken down into the following categories: Model, Written Report and Oral Presentation Project Constraints: Size: Each team needs to design and build a prototype hoist with the following specifications shown in Figure 1. Minimum load that the hoist can support is 10N at 170 mm on the cantilever beam. Loading hook must be provided at 170mm on the cantilever beam to support the weight during the presentation of the model.
Figure 1
Hoist Support 1
Materials: Teams are encouraged to use as much creativity as possible, but are limited to the following materials: tongue depressor sticks A metal hook to carry the load glue guns and glue sticks string/masking tape Efficiency ratio = test load/weight of model Design Process: This project helps to integrate your engineering understanding, knowledge and skills to solve a real life problem. Your hoist support design process should include the following steps: 1. Problem definition. As a team, carefully read the problem statement and put it into your own words. Identify the functional requirements of the hoist support. Identify the constraints. Ensure that everyone in the team shares the same vision of the problem before proceeding. Also ensure that any questions regarding the project specification are resolved with the instructor. 2. Analysis/synthesis/conceptualization. Perform the hoist support component strength tests and discuss the results with other members of the team. Conceptualize alternative designs with your team. Brainstorm, mind mapping, toss around ideas that range from the ridiculous to the doable. Remember that a key element of brainstorming is to not get in the mode of being critical towards ideas. This comes later. You should never hear "That won't work!" at this stage in the planning. Document at least three alternatives with sketches and descriptions. You will need to write about these in the final report.
3. Prototype design and testing. Evaluate the proposed (alternative) designs and select the best approach. Justify and then develop the final design. Decide on design details such as materials, construction method, tools and dimensions. This is probably the most critical stage in your design process. Prepare a drawing of your design. 4. Design delivery. Communicate your team's hoist support design by writing and presenting the final report as a group
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- t80 A Pid 033800 All Symbology Rev C.Document19 pagest80 A Pid 033800 All Symbology Rev C.Maarij Anjum100% (2)
- Isometric View: Dymac GlobalDocument2 pagesIsometric View: Dymac GlobalMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- GDTP ApplicationInformationHandbookDocument10 pagesGDTP ApplicationInformationHandbookmanaswinNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Discontinuous Puf Panels Using Cyclopentane As A Blowing AgentDocument6 pagesProject Report On Discontinuous Puf Panels Using Cyclopentane As A Blowing AgentEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- DP158LCDocument4 pagesDP158LCyah jml100% (1)
- DP158LDDocument4 pagesDP158LDMichael ManzanoNo ratings yet
- D1146T G-DRIVE: Power RatingDocument2 pagesD1146T G-DRIVE: Power RatingGuillermo OchoaNo ratings yet
- Generator Sets Installation GuideDocument216 pagesGenerator Sets Installation Guidezinmerford92% (26)
- Hospital Cylindrical Silencers Reduce Noise 35 to 42 dBADocument1 pageHospital Cylindrical Silencers Reduce Noise 35 to 42 dBAMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- Form, 10.8 Engineering Document SubmittalDocument1 pageForm, 10.8 Engineering Document SubmittalMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- Pressure Losses in Fuel Pipeline: Work Order NoDocument14 pagesPressure Losses in Fuel Pipeline: Work Order NoMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- Form, 10.6 Engineering Calculation SheetDocument2 pagesForm, 10.6 Engineering Calculation SheetMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- Calculate tank wetted area with equationsDocument17 pagesCalculate tank wetted area with equationsShijumon KpNo ratings yet
- Form, 10.2 Document Release Control (PURC)Document1 pageForm, 10.2 Document Release Control (PURC)Maarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- DP158LCDocument4 pagesDP158LCyah jml100% (1)
- Form, 10.7 Bill of Materials (Cover Page)Document1 pageForm, 10.7 Bill of Materials (Cover Page)Maarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- Silex: Super Critical Cylindrical SilencersDocument1 pageSilex: Super Critical Cylindrical SilencersMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- HVAC T-Chart - Surface AreaDocument4 pagesHVAC T-Chart - Surface AreaMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- Check ValvesDocument4 pagesCheck ValvesALP69No ratings yet
- Reduce Engine Noise with Engine Exhaust SilencersDocument28 pagesReduce Engine Noise with Engine Exhaust SilencersMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- ANSI B16.9 ElbowDocument3 pagesANSI B16.9 ElbowLuna LukaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Metrology Engineering Metrology: N. Sinha Mechanical Engineering Department IIT KanpurDocument32 pagesEngineering Metrology Engineering Metrology: N. Sinha Mechanical Engineering Department IIT KanpurRishi Raj100% (1)
- Autocad Tutorial 4 PDFDocument7 pagesAutocad Tutorial 4 PDFMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Standard ChannelsDocument2 pagesData Sheet Standard Channelsmanan_mansoorNo ratings yet
- Datcon PDFDocument88 pagesDatcon PDFYean Carlos Silva Herrera100% (1)
- Iso GD&TDocument39 pagesIso GD&TSanjay Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Fit Calculation For Alternator ShaftDocument2 pagesFit Calculation For Alternator ShaftMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- Calculation and Design of Exhaust Noise Mufflers For Power Engineering EquipmentDocument10 pagesCalculation and Design of Exhaust Noise Mufflers For Power Engineering EquipmenthenrengNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Bevel Proposal - Line 3 PDFDocument2 pagesMechanical Bevel Proposal - Line 3 PDFMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- ASME GDTP Pricing Structure FY18Document1 pageASME GDTP Pricing Structure FY18Ravi Kiran MeesalaNo ratings yet
- KiteDocument1 pageKiteMaarij AnjumNo ratings yet
- English For Academic Purposes (EAP) : Lecture 5: Past SimpleDocument11 pagesEnglish For Academic Purposes (EAP) : Lecture 5: Past Simplealmastar officeNo ratings yet
- 04 LimeDocument32 pages04 LimeGoogle user100% (1)
- Reading in Philippine History (Chapter 3)Document14 pagesReading in Philippine History (Chapter 3)AKIO HIROKINo ratings yet
- Monthly Business ReviewDocument36 pagesMonthly Business Reviewmdipu5_948971128No ratings yet
- Graphic Organizers for Organizing IdeasDocument11 pagesGraphic Organizers for Organizing IdeasMargie Tirado JavierNo ratings yet
- Project Report VajDocument15 pagesProject Report VajTamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- Sexual & Reproductive Health of AdolocentsDocument8 pagesSexual & Reproductive Health of AdolocentsSourav HossenNo ratings yet
- Template - Time in ManufacturingDocument2 pagesTemplate - Time in ManufacturingVero RoaNo ratings yet
- User Manual LCD Signature Pad Signotec SigmaDocument15 pagesUser Manual LCD Signature Pad Signotec SigmaGael OmgbaNo ratings yet
- EDIBLE VACCINES: A COST-EFFECTIVE SOLUTIONDocument21 pagesEDIBLE VACCINES: A COST-EFFECTIVE SOLUTIONPritish SareenNo ratings yet
- J-Garlic in CheeseDocument12 pagesJ-Garlic in CheeseMary GinetaNo ratings yet
- History of English Prose PDFDocument21 pagesHistory of English Prose PDFMeisyita QothrunnadaNo ratings yet
- TOS 22402 Winter 19th I SCHEME Paper Model Answer PaperDocument25 pagesTOS 22402 Winter 19th I SCHEME Paper Model Answer Paperirshadmirza753No ratings yet
- Measures of CentralityDocument13 pagesMeasures of CentralityPRAGASM PROGNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instruções Iveco Eurocargo Euro 6Document226 pagesManual de Instruções Iveco Eurocargo Euro 6rsp filmes100% (1)
- Activity 2Document5 pagesActivity 2Kier VillegasNo ratings yet
- Topic1 Whole NumberDocument22 pagesTopic1 Whole NumberDayang Siti AishahNo ratings yet
- Active Disturbance Rejection Control For Nonlinear SystemsDocument8 pagesActive Disturbance Rejection Control For Nonlinear SystemsTrần Việt CườngNo ratings yet
- Project Planning and Management Unit 1Document13 pagesProject Planning and Management Unit 1Savant100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University: Emester ViDocument4 pagesGujarat Technological University: Emester ViPradeep SutharNo ratings yet
- Joel Werner ResumeDocument2 pagesJoel Werner Resumeapi-546810653No ratings yet
- Occupant Load CalculationsDocument60 pagesOccupant Load CalculationsKAIVALYA TIWATNENo ratings yet
- Chams 1Document78 pagesChams 1Das RavindraNo ratings yet
- The Clàsh The 0nly Band That MatteredDocument255 pagesThe Clàsh The 0nly Band That MatteredNikos VaxevanidisNo ratings yet
- Turabian Sample PaperDocument9 pagesTurabian Sample Paperemme_lopez908133% (3)
- Food Science, Technology & Nutitions - Woodhead - FoodDocument64 pagesFood Science, Technology & Nutitions - Woodhead - FoodEduardo EstradaNo ratings yet
- Pmls 1 Final Exam Reviewer: Clinical Chemistry ContDocument14 pagesPmls 1 Final Exam Reviewer: Clinical Chemistry ContPlant in a PotNo ratings yet
- D2DDocument2 pagesD2Dgurjit20No ratings yet
- Philip Larkin: The Art of Poetry 30Document32 pagesPhilip Larkin: The Art of Poetry 30Telmo RodriguesNo ratings yet