Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Homework Multiple Choice Questions on Genetics and Molecular Biology
Uploaded by
oceanblueeyesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Homework Multiple Choice Questions on Genetics and Molecular Biology
Uploaded by
oceanblueeyesCopyright:
Available Formats
Homework
MULTIPLECHOICE.Choosetheonealternativethatbestcompletesthestatementoranswersthequestion. 1)
Beadle and Tatum proposed the one gene-one enzyme concept. In its original form, this hypothesis could now be restated in which of the following ways? A) One DNA molecule contains the information to make one enzyme. B) A given sequence of DNA nucleotides contains the information to make one enzyme. C) Each gene contains the information to make one enzyme, one lipid, and one carbohydrate. D) Each gene is actually an enzyme that catalyzes the production of one protein. E) Each polypeptide is the result of the activity of one enzyme.
1)
Thefollowingquestionsrefertothefollowingsimplemetabolicpathway: enzymea A 2) B enzymeb C 2)
According to Beadle and Tatum's one gene-one enzyme hypothesis, how many gene(s) is (are) necessary for this pathway? A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 3 E) It cannot be determined from the pathway. A mutation results in a defective enzyme a. Which of the following would be a consequence of that mutation? A) an accumulation of A and no production of B and C B) an accumulation of A and B and no production of C C) an accumulation of B and no production of A and C D) an accumulation of B and C and no production of A E) an accumulation of C and no production of A and B One strain of a diploid organism is homozygous for a recessive allele coding for a defective enzyme a. Another strain is homozygous for a recessive allele coding for a defective enzyme b. Crossing those two strains will result in a strain that would grow on which of the following? A) a minimal medium supplemented with A B) a minimal medium supplemented with B C) a minimal medium supplemented with both A and B D) All of the above will support the growth of the new strain.
3)
3)
4)
4)
5)
The nitrogenous base adenine is found in all members of which of the following groups? A) proteins, triglycerides, and testosterone B) proteins, ATP, and DNA C) ATP, RNA, and genes D) alpha glucose, ATP, and DNA E) proteins, carbohydrates, and ATP If proteins were composed of only 12 different kinds of amino acids, what would be the smallest possible codon size in a genetic system with four different nucleotides? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 12
5)
6)
6)
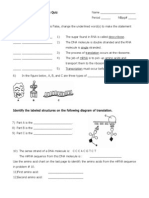
ThefollowingquestionsrefertoFigure17.1,atableofcodons.
Figure17.1 7)
A possible sequence of nucleotides in DNA that would code for the polypeptide sequence phe-leu-ile-val would be A) 5' TTG-CTA-CAG-TAG 3'. B) 3' AAC-GAC-GUC-AUA 5'. C) 5' AUG-CTG-CAG-TAT 3'. D) 3' AAA-AAT-ATA-ACA 5'. E) 3' AAA-GAA-TAA-CAA 5'. What amino acid sequence will be generated, based on the following mRNA codon sequence? 5'AUG-UCU-UCG-UUA-UCC-UUG A) met-arg-glu-arg-glu-arg B) met-glu-arg-arg-gln-leu C) met-ser-leu-ser-leu-ser D) met-ser-ser-leu-ser-leu E) met-leu-phe-arg-glu-glu
7)
8)
8)
9)
A peptide has the sequence NH2-phe-pro-lys-gly-phe-pro-COOH. What is the sequence in DNA that codes for this peptide? A) 3' UUU-CCC-AAA-GGG-UUU-CCC B) 3' AUG-AAA-GGG-TTT-CCC-AAA-GGG C) 3' AAA-GGG-TTT-CCC-AAA-GGG D) 5' GGG-AAA-TTT-AAA-CCC-ACT-GGG E) 5' ACT-TAC-CAT-AAA-CAT-TAC-UGA particular triplet of bases in the coding sequence of DNA is AGT. What is the corresponding triplet in the complementary strand of DNA? A) AGT B) UCA C) TCA D) GAC E) TCA in eukaryotes, but UCA in prokaryotes genetic code is essentially the same for all organisms. From this, one can logically assume all of the following except: A) A gene from an organism could theoretically be expressed by any other organism. B) All organisms have a common ancestor. C) DNA was the first genetic material. D) Codons usually translate into the same amino acids. E) Related organisms have many similar genes. of the following is true for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene expression? A) After transcription, a 3' poly(A) tail and a 5' cap are added to mRNA. B) Translation of mRNA can begin before transcription is complete. C) RNA polymerase may recognize a promoter region and begin transcription. D) mRNA is synthesized in the 3' 5' direction. E) The mRNA transcript is the exact complement of the gene from which it was copied. is the attachment site for RNA polymerase? A) structural gene region B) initiation region C) promoter region D) operator region E) regulator region of the following are transcribed from DNA except A) protein. B) exons. C) rRNA.
9)
10) A
10)
11) The
11)
12) Which
12)
13) Where
13)
14) All
14) D) tRNA. E) mRNA.
15) Which
of the following helps to stabilize mRNA by inhibiting its degradation? A) TATA box B) spliceosomes C) a modified guanosine triphosphate D) snRNPs E) poly(A) tail are the coding segments of a stretch of eukaryotic DNA called?
15)
16) What
16)
A) introns B) exons
codons D) replicons E) transposons
C) 17) All
of the following are found in prokaryotic messenger RNA except A) the AUG codon. B) the UGA codon. C) introns. D) uracil. E) cytosine. are significant to biological evolution because A) their presence increases the frequency of recombination. B) they protect the mRNA from degeneration. C) they are translated into essential amino acids. D) they maintain the genetic code by preventing incorrect DNA base pairings. E) they correct enzymatic alterations of DNA bases.
17)
18) Introns
18)
19) A
particular triplet of bases in the coding sequence of DNA is AAA. The anticodon on the tRNA that binds the mRNA codon is A) TTT. B) UUA. C) UUU. D) AAA. E) either UAA or TAA, depending on wobble in the first base. is an anticodon part of? A) DNA B) tRNA C) mRNA D) a ribosome E) an activating enzyme
19)
20) What
20)
21) What
type of bonding is responsible for maintaining the shape of the tRNA molecule? A) covalent bonding between sulfur atoms B) ionic bonding between phosphates C) hydrogen bonding between base pairs D) van der Waals interactions between hydrogen atoms E) peptide bonding between amino acids
21)
22) There
are 61 mRNA codons that specify an amino acid, but only 45 tRNAs. This is best explained by the fact that A) some tRNAs have anticodons that recognize two or more different codons. B) the rules for base pairing between the third base of a codon and tRNA are flexible. C) inosine can hydrogen-bond with U, C, or A. D) A and B are true. E) A, B, and C are true. is eukaryotic ribosomal RNA transcribed? Golgi apparatus B) ribosomes C) nucleoli D) X chromosomes E) prokaryotic cells only
A) the
22)
23) Where
23)
24) The
function of the ribosome in polypeptide synthesis is to A) hold mRNA and tRNAs together. B) catalyze the addition of amino acids from the tRNAs to the growing polypeptide chain. C) move tRNA and mRNA during the translocation process. D) do A and B. E) do A, B, and C. the following list, which is the first event in translation in eukaryotes? A) elongation of the polypeptide B) base pairing of activated methionine-tRNA to AUG of the messenger RNA C) binding of the larger ribosomal subunit to smaller ribosome subunits D) covalent bonding between the first two amino acids E) Both B and D occur simultaneously.
24)
25) From
25)
26) Choose
the answer that has these events of protein synthesis in the proper sequence. 1. An aminoacyl-tRNA binds to the A site. 2. A peptide bond forms between the new amino acid and a polypeptide chain. 3. tRNA leaves the P site and the P site remains vacant. 4. A small ribosomal subunit binds with mRNA. 5. tRNA translocates to the P site. A) 1, 3, 2, 4, 5 B) 4, 1, 2, 5, 3 C) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 D) 4, 1, 3, 2, 5 E) 2, 4, 5, 1, 3 are polyribosomes? A) groups of ribosomes reading the same mRNA simultaneously B) ribosomes containing more than two subunits C) multiple copies of ribosomes found associated with giant chromosomes D) aggregations of vesicles containing ribosomal RNA E) ribosomes associated with more than one tRNA to the signal hypothesis, ribosomes are directed to the ER membrane a specific characteristic of the ribosome itself, which distinguishes free ribosomes from bound ribosomes. B) by a signal-recognition particle that brings ribosomes to a receptor protein in the ER membrane. C) by moving through a specialized channel of the nucleus. D) by a chemical signal given off by the ER. E) by a signal sequence of RNA that precedes the start codon of the message.
A) by
26)
27) What
27)
28) According
28)
29) Which
of these statements represents a common misconception regarding point mutations? A) They involve changes in one base pair. B) They can cause drastic changes in polypeptide structure. C) They always produce a change in the amino acid sequence of a protein. D) They can lead to the shortening of the mutated polypeptide. E) They could result in a frameshift mutation. frameshift mutation could result from A) a base insertion only. B) a base deletion only. C) a base substitution only. D) deletion of three consecutive bases. E) either an insertion or a deletion of a base.
29)
30) A
30)
31) When
a nucleotide pair is lost from the middle of a gene during the process of transcription, what happens? A) snRNPs splice and then remove incorrect amino acids. B) Normal termination does not occur; transcription continues indefinitely. C) The reading frame is shifted, producing a nonfunctional polypeptide. D) A signal-recognition particle moves in to correct coding errors. E) There is little effect on the protein being synthesized due to redundancy of the genetic code.
31)
You might also like
- AP Biology Unit 5 ExamDocument13 pagesAP Biology Unit 5 ExamLana Sage CummingsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Gene Expression From Gene To ProteinDocument18 pagesChapter 17 Gene Expression From Gene To Protein蔡旻珊100% (1)
- 107普生期末Document4 pages107普生期末Rose FuNo ratings yet
- Replication, Transcription & Translation Exam ReviewDocument6 pagesReplication, Transcription & Translation Exam ReviewAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Quiz Chapter 8 Microbial GeneticsDocument5 pagesQuiz Chapter 8 Microbial GeneticsshishashaneNo ratings yet
- Microbiology With Diseases by Body System 2nd Edition Bauman Test BankDocument11 pagesMicrobiology With Diseases by Body System 2nd Edition Bauman Test Bankjamesgregoryfzwjdynogt100% (32)
- Exam2A.F2015-KEYDocument6 pagesExam2A.F2015-KEYKathy PhamNo ratings yet
- CH 07Document11 pagesCH 07Brian Blocks100% (2)
- DNA SamplexDocument6 pagesDNA SamplexNelica RotoniNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledRobert FaganNo ratings yet
- Bio 2 Study GuideDocument17 pagesBio 2 Study GuideJahnik KurukulasuriyaNo ratings yet
- Chem 121 Chapter 22. Nucleic AcidsDocument14 pagesChem 121 Chapter 22. Nucleic Acidsnurain IsmailNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument8 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritancePriyanshu ShivamNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis Eleventh EditionDocument18 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Genetic Analysis Eleventh Editiondaonhatc2ddrq100% (25)
- MCDB 1A Midterm 1 Scantron InstructionsDocument10 pagesMCDB 1A Midterm 1 Scantron InstructionsKenji SoaresNo ratings yet
- Ls3 Midterm I Exam: InstructionsDocument8 pagesLs3 Midterm I Exam: InstructionsArmaanGurayaNo ratings yet
- Mader Chap012 10eTBDocument17 pagesMader Chap012 10eTBDr. Michael DavidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiotechnologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To BiotechnologyChemengNo ratings yet
- Midterm 2 Review QuestionsDocument23 pagesMidterm 2 Review QuestionshamoudyelmouallemNo ratings yet
- B.SC - III Zoology (GBK)Document7 pagesB.SC - III Zoology (GBK)Naveen ShiwalNo ratings yet
- NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE INTRO BIOINFORMATICS EXAMDocument9 pagesNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE INTRO BIOINFORMATICS EXAMjunie9201No ratings yet
- Genetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition Sanders Test BankDocument16 pagesGenetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition Sanders Test Bankbrandonrodriguezmpscxofkzy100% (15)
- 4. Molecular basis of inheritanceDocument9 pages4. Molecular basis of inheritanceVINOD KUMAR M TNo ratings yet
- Test Bank MetabolismDocument6 pagesTest Bank MetabolismWanga CharleneNo ratings yet
- BISC403 Sample Exam 4 W - Answers 20SpDocument5 pagesBISC403 Sample Exam 4 W - Answers 20SpGrace MillsNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics MCQ PDFDocument11 pagesMolecular Genetics MCQ PDFJunghoon LeeNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis QuizDocument6 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis QuizJeremy Guggenheim100% (2)
- AQA Biology Topic 8.3 Structures of Ribonucleic AcidDocument4 pagesAQA Biology Topic 8.3 Structures of Ribonucleic AcidfNo ratings yet
- 8 - Biochemistry MCQs Neuclic AcidsDocument6 pages8 - Biochemistry MCQs Neuclic Acidswanna learnNo ratings yet
- Replikasi 1: IncorrectDocument5 pagesReplikasi 1: IncorrectSuci Ummi Roziqotul QudsiyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 & 3: D. Structural Gene of The Prokaryotes Is Split GeneDocument3 pagesChapter 2 & 3: D. Structural Gene of The Prokaryotes Is Split Genenanang eko yuliantoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Practice Exam 1Document5 pagesBiotechnology Practice Exam 1crazybobblaskeyNo ratings yet
- Buenasher Learning Academy IncDocument8 pagesBuenasher Learning Academy IncEl CruzNo ratings yet
- BIL 255 Exam Questions on DNA-Protein SynthesisDocument31 pagesBIL 255 Exam Questions on DNA-Protein SynthesisMax ArmourNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Principles and Explorations 7th Edition Black Test BankDocument19 pagesMicrobiology Principles and Explorations 7th Edition Black Test Bankeugenephedrayy2bfk100% (29)
- Exam 4 Study Guide Spring 2023Document5 pagesExam 4 Study Guide Spring 2023Masai PaceNo ratings yet
- Full download Test Bank For Microbiology With Diseases By Taxonomy 6Th Edition Robert W Bauman pdfDocument24 pagesFull download Test Bank For Microbiology With Diseases By Taxonomy 6Th Edition Robert W Bauman pdfstephanie.jackson490100% (7)
- Mmoi BC SbaDocument15 pagesMmoi BC SbaYoon YoonNo ratings yet
- HL Paper1Document13 pagesHL Paper1JennyNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA MCQDocument6 pagesRecombinant DNA MCQChaze WaldenNo ratings yet
- Final MolecularDocument13 pagesFinal Molecularpharmadr2024No ratings yet
- 2020 Midterm 2 Questions W AnswersDocument12 pages2020 Midterm 2 Questions W AnswersKingsley ZhengNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology An Introduction 13th by Tortora DownloadDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology An Introduction 13th by Tortora Downloadchristinemays21121993bgw100% (24)
- RNA and Protein Synthesis Problem SetDocument6 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis Problem Setpalms thatshatterNo ratings yet
- E03 Abaila 1Document9 pagesE03 Abaila 1Warisha RanaNo ratings yet
- Oc NucleotidesDocument9 pagesOc NucleotidesLê KhanhNo ratings yet
- 105期末Document7 pages105期末Rose FuNo ratings yet
- Genetics Questions - MCQDocument4 pagesGenetics Questions - MCQManisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis Problems KEYDocument4 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis Problems KEYnona wayne dela peña100% (1)
- Kahoot MCQ - StudentDocument12 pagesKahoot MCQ - Studentnewyork0218No ratings yet
- Encode SequenceDocument212 pagesEncode SequenceRaj Naithik100% (1)
- Genetics Exam Multiple Choice and Short Answer QuestionsDocument9 pagesGenetics Exam Multiple Choice and Short Answer QuestionsQuốc ViệtNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis Problem SetDocument4 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis Problem SetEMMA FACCIONo ratings yet
- Chbe 473/594B Homework #1 Spring 2013 (Due Jan. 31, 2011 in Class) 1. Multiple Choice (Only One Correct Answer) (3' For Each Problem)Document6 pagesChbe 473/594B Homework #1 Spring 2013 (Due Jan. 31, 2011 in Class) 1. Multiple Choice (Only One Correct Answer) (3' For Each Problem)HouIn CheongNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Polypeptide End Product TranslationDocument5 pagesAmino Acid Polypeptide End Product TranslationAcep AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Test 3Document11 pagesCell Biology Test 3Carol HathawayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Genomes and Their EvolutionDocument8 pagesChapter 21 Genomes and Their Evolution蔡旻珊No ratings yet
- Topical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2From EverandTopical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 3 Part 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Annual Plant Reviews, Plant MitochondriaFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Plant MitochondriaDavid C. LoganNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Biotechnology: The Science, Technology and Medical ApplicationsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Biotechnology: The Science, Technology and Medical ApplicationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- MAN0012656 Genomic DNA Purification UGDocument4 pagesMAN0012656 Genomic DNA Purification UGranaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering Fundamentals - Parte 1Document60 pagesBiochemical Engineering Fundamentals - Parte 1Jose Suarez0% (1)
- Gene Therapy (Group 2)Document27 pagesGene Therapy (Group 2)Nikoh Anthony EwayanNo ratings yet
- SAFC Biosciences - Technical Bulletin - The Science of LONG®R3IGF-I: Features and BenefitsDocument4 pagesSAFC Biosciences - Technical Bulletin - The Science of LONG®R3IGF-I: Features and BenefitsSAFC-GlobalNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules of Cell: DR G V RamanaDocument24 pagesBiomolecules of Cell: DR G V RamanaSATYAJIT SAHUNo ratings yet
- Genetic MutationDocument27 pagesGenetic MutationKathleen JOy BiasUraNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Worksheet-PrintDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet-PrintmuraliMu0% (1)
- OEB50 Assignment1Document17 pagesOEB50 Assignment1Adrian GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Feinberg AP Et Al. 2016 Epigenetic Modulators, Modifiers and Mediators in Cancer Aetiology and ProgressionDocument16 pagesFeinberg AP Et Al. 2016 Epigenetic Modulators, Modifiers and Mediators in Cancer Aetiology and ProgressionJasmyn KimNo ratings yet
- 106 Incourse Test 2009 PDFDocument22 pages106 Incourse Test 2009 PDFc107896No ratings yet
- DNA Review Questions KEYDocument26 pagesDNA Review Questions KEYLaura AkamNo ratings yet
- G26interno BrochureDocument6 pagesG26interno BrochurecyberwmxNo ratings yet
- Karakterisasi Molekulerelaeidobius Kamerunicusfaust. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) Asal Sumatera Utara Menggunakan MetodeDocument13 pagesKarakterisasi Molekulerelaeidobius Kamerunicusfaust. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) Asal Sumatera Utara Menggunakan MetodeShinta Naurah RahmadhiaNo ratings yet
- Krebs Cycle: Jan Allen U. Fernandez 11 Stem EfrjDocument15 pagesKrebs Cycle: Jan Allen U. Fernandez 11 Stem EfrjTurn2ndTurN P.ONo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - DNADocument14 pagesLesson 1 - DNAOmar ElhosaryNo ratings yet
- IB DP Biology 1.4 Membrane Transport QuestionDocument19 pagesIB DP Biology 1.4 Membrane Transport QuestionikaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chap 2 (Biological Molecules) F.SC 1st Year Biology Helping Notes PDFDocument10 pages12 Chap 2 (Biological Molecules) F.SC 1st Year Biology Helping Notes PDFZainab fatimaNo ratings yet
- Full PDFDocument9 pagesFull PDFAle TabaskoNo ratings yet
- Opposite and Coordinated Rotation of Amphitrichous Flagella Governs Oriented Swimming and Reversals in A Magnetotactic SpirillumDocument8 pagesOpposite and Coordinated Rotation of Amphitrichous Flagella Governs Oriented Swimming and Reversals in A Magnetotactic SpirillumFernandoNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Test Serie S 2Document7 pagesMolecular Biology Test Serie S 2ANIL KUMARSBMTNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument12 pagesLab ReportJISAS CLIMAXNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle WorksheetHarold SagumNo ratings yet
- Wednesday 20 January 2021: BiologyDocument40 pagesWednesday 20 January 2021: BiologyMilka RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Case BasedDocument2 pagesChapter 11 Case BasedRishabh ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Notes MsDocument28 pagesMeiosis Notes Msapi-44119921No ratings yet
- Development of A Quantitative Real-Time PCR For Myrtle Rust 2018Document12 pagesDevelopment of A Quantitative Real-Time PCR For Myrtle Rust 2018amir-scribdNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Genetic EngineeringDocument66 pagesEarth and Life Science Genetic EngineeringJisho 恐怖 Lomotos75% (4)
- Plant Biotechnology Homework NotesDocument1 pagePlant Biotechnology Homework Notesshoyou9100% (1)
- 04 Lecture AnimationDocument66 pages04 Lecture AnimationJoshua VidalNo ratings yet
- 3 Enzymes As BiologyDocument35 pages3 Enzymes As BiologyADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet