Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cerebral Circulation AFIFI
Uploaded by
henriquegmeloCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cerebral Circulation AFIFI
Uploaded by
henriquegmeloCopyright:
Available Formats
vascularlzao arLerlal Lncefalo Aflfl
1
Ceiebial Ciiculation
Indice
SCu8CLS Cl SuL? 2
lnLernal CaroLld ArLery 2
A CP1PALMlC A81L8? 2
8 An1L8lC8 CPC8CluAL A81L8? 3
C An1L8lC8 CL8L88AL A81L8? 3
u MluuLL CL8L88AL A81L8? 4
L CS1L8lC8 CCMMunlCA1lnC A81L8? 3
verLebral ArLery 3
A CS1L8lC8 SlnAL A81L8? 3
8 An1L8lC8 SlnAL A81L8? 6
C CS1L8lC8 lnlL8lC8 CL8L8LLLA8 A81L8? (lCA) 6
8asllar ArLery 6
A A8AMLulAn LnL18A1lnC A81L8lLS 6
8 SPC81 Cl8CuMlL8Ln1lAL A81L8lLS 6
C LCnC Cl8CuMlL8Ln1lAL A81L8lLS 6
u CS1L8lC8 CL8L88AL A81L8lLS (llgures 273 and 1726) 7
Cl8CLL Cl WlLLlS 7
CCnuuC1lnC Anu LnL18A1lnC vLSSLLS 8
PlS1CLCC? Cl CL8L88AL vLSSLLS 8
CCLLA1L8AL Cl8CuLA1lCn 8
1he consLanLly acLlve braln requlres a rlch blood supply Lo susLaln lLs ongolng acLlvlLy
lrreverslble braln damage (braln deaLh) resulLs lf Lhe blood supply Lo Lhe braln ls
lnLerrupLed for more Lhan a few mlnuLes consclousness ls losL lf Lhe blood supply ls
lnLerrupLed for abouL 3 s Leslons of Lhe nervous sysLem due Lo lnLerrupLlon of blood
supply consLlLuLe Lhe mosL common Lype of cenLral nervous sysLem dlsorders
lL ls esLlmaLed LhaL abouL 13 percenL of cardlac ouLpuL reaches Lhe braln abouL 20
percenL of oxygen uLlllzaLlon of Lhe body ls consumed by Lhe adulL braln and as much
as 30 percenL by Lhe lnfanL braln 1he blood flow Lhrough Lhe human braln ls esLlmaLed
Lo be 800 ml/mln or approxlmaLely 30 ml/100 g of braln Llssue per mlnuLe 1hls
average value lncreases wlLh an lncrease ln funcLlonal acLlvlLy of Lhe braln or reglons
vascularlzao arLerlal Lncefalo Aflfl
2
wlLhln lL 1he blood flow ls markedly lncreased ln Lhe sensory moLor area on vlgorous
exerclse of Lhe conLralaLeral llmb Cerebral blood flow ls fasLer ln gray maLLer (70 Lo 80
ml/100 g per mln) Lhan ln whlLe maLLer (30 ml/100 g per mln) lrreverslble braln
damage wlll occur lf Lhe cerebral blood flow ls less Lhan 13 ml/100 g per mln
SUURCES UF SUPPLY
1he braln recelves lLs blood supply from four arLerlal Lrunks Lwo lnLernal caroLld
arLerles and Lwo verLebral arLerles Cn Lhe rlghL slde Lhe brachlocephallc Lrunk glves
rlse Lo Lhe rlghL subclavlan and rlghL common caroLld arLerles 1he rlghL subclavlan
arLery glves rlse Lo Lhe rlghL verLebral arLery and Lhe rlghL common caroLld arLery
blfurcaLes lnLo Lhe rlghL lnLernal and exLernal caroLld arLerles Cn Lhe lefL slde Lhe
verLebral arLery arlses from Lhe lefL subclavlan arLery and Lhe lnLernal caroLld arLery
arlses from Lhe lefL common caroLld arLery A knowledge of normal cerebral vascular
anaLomy ls essenLlal for undersLandlng and locallzlng cerebrovascular dlsorders 1hls
chapLer wlll focus on blood supply of Lhe cerebral corLex lL ls worLh noLlng LhaL
nomenclaLure of Lhe varlous branches of cerebral vessels varles from auLhor Lo auLhor
8lood supplles of Lhe splnal cord and braln sLem are dlscussed ln Lhelr respecLlve
chapLers ChapLers 3 3 7 9 11 13 and 13
Internal Carotid Artery
1he lnLernal caroLld arLerles arlse aL Lhe blfurcaLlon of Lhe common caroLld arLerles ln
Lhe neck (llgure 271) ascend ln fronL of Lhe Lransverse processes of Lhe upper Lhree
cervlcal verLebrae and enLer Lhe base of Lhe skull Lhrough Lhe caroLld canal WlLhln
Lhe cranlum Lhe lnLernal caroLld arLery lles ln Lhe cavernous slnus lL Lhen plerces Lhe
dura Lo begln lLs subarachnold course 1he lnLernal caroLld arLery glves rlse Lo Lhe
ophLhalmlc anLerlor choroldal anLerlor cerebral mlddle cerebral and posLerlor
communlcaLlng branches WlLhln Lhe cavernous slnus Lhe lnLernal caroLld arLery lles
close Lo Lhe medlal wall lmmedlaLely ad[acenL Lo Lhe abducens nerve (Cn vl) CLher
cranlal nerves ln Lhe slnus slLuaLed along Lhe laLeral wall lnclude Lhe oculomoLor (Cn
lll) Lrochlear (Cn lv) ophLhalmlc and maxlllary dlvlslons of Lhe Lrlgemlnal (Cn v)
lrom lLs slLe of orlgln from Lhe common caroLld arLery Lo lLs slLe of blfurcaLlon lnLo Lhe
anLerlor and mlddle cerebral arLerles Lhe lnLernal caroLld arLery ls dlvlded lnLo four
segmenLs (1) Lhe cervlcal segmenL exLends from Lhe orlgln of Lhe lnLernal caroLld
arLery from Lhe common caroLld Lo Lhe slLe where lL enLers Lhe caroLld canal (2) Lhe
lnLrapeLrosal segmenL ls Lhe parL of Lhe arLery as lL courses Lhrough Lhe peLrous
porLlon of Lhe Lemporal bone (3) Lhe lnLracavernous segmenL courses Lhrough Lhe
cavernous slnus and (4) Lhe cerebral (supracllnold) segmenL exLends from Lhe slLe of
exlL of Lhe arLery from Lhe cavernous slnus Lo lLs blfurcaLlon lnLo Lhe anLerlor and
mlddle cerebral arLerles 1he lnLracavernous and cerebral segmenLs are collecLlvely
known as Lhe caroLld slphon because of Lhelr characLerlsLlc Sshaped conflguraLlon All
Lhe ma[or branches of Lhe lnLernal caroLld arLery arlse from Lhe cerebral segmenL
A. UPHTHALMIC ARTERY
1he ophLhalmlc arLery ls Lhe flrsL lnLracranlal branch of Lhe lnLernal caroLld as lL
courses Lhrough Lhe cavernous slnus (llgure 271) 1he ophLhalmlc arLery supplles Lhe
vascularlzao arLerlal Lncefalo Aflfl
3
opLlc nerve and glves rlse Lo Lhe cenLral arLery of Lhe reLlna 1hus lnLerrupLlon of Lhe
blood supply from Lhe lnLernal caroLld sysLem may resulL ln dlsLurbances ln vlsual
aculLy 1he ophLhalmlc arLery ls also of lmporLance because of lLs anasLomoLlc
connecLlons wlLh branches of Lhe exLernal caroLld sysLem Lhls anasLomoLlc
relaLlonshlp ls essenLlal ln esLabllshlng collaLeral clrculaLlon when Lhe lnLernal caroLld
sysLem ls occluded ln Lhe neck
. ANTERIUR CHURUIDAL ARTERY
1he anLerlor choroldal arLery arlses from Lhe lnLernal caroLld arLery afLer lL emerges
from Lhe cavernous slnus (llgure 271) lL passes venLral Lo Lhe opLlc LracL and supplles
Lhe opLlc LracL cerebral peduncles laLeral genlculaLe body posLerlor parL of Lhe
posLerlor llmb of Lhe lnLernal capsule Lall of Lhe caudaLe nucleus uncus amygdala
anLerlor hlppocampus chorold plexus of Lhe Lemporal horn and someLlmes Lhe globus
pallldus 1he anLerlor choroldal arLery ls prone Lo occluslon by Lhrombus because of lLs
small callber
C. ANTERIUR CERERAL ARTERY
1he anLerlor cerebral arLery (llgures 271 llgures 272 and 1726) orlglnaLes from Lhe
lnLernal caroLld arLery laLeral Lo Lhe opLlc chlasm and courses dorsal Lo Lhe opLlc nerve
Lo reach Lhe lnLerhemlspherlc flssure where lL curves around Lhe genu of Lhe corpus
callosum and conLlnues as Lhe perlcallosal arLery dorsal Lo Lhe corpus callosum As Lhe
Lwo anLerlor cerebral arLerles approach Lhe lnLerhemlspherlc flssure Lhey are [olned
by Lhe anLerlor communlcaLlng arLery 1he followlng are among lLs ma[or branches
O 8ecurrenL ArLery of Peubner (Medlal SLrlaLe ArLery) (llgure 272)
1hls arLery arlses from Lhe anLerlor cerebral arLery elLher proxlmal or dlsLal Lo Lhe
anLerlor communlcaLlng arLery lL supplles Lhe anLerlor llmb and genu of Lhe lnLernal
capsule and parLs of Lhe head of Lhe caudaLe rosLral puLamen and globus pallldus lL
also provldes blood supply Lo Lhe posLerlor porLlons of Lhe gyrus recLus and
orblLofronLal corLex 1hus occluslon of Lhls arLery wlll resulL ln subcorLlcal and corLlcal
lnfarcLs 1he recurrenL arLery of Peubner varles ln number from one Lo Lhree
O 2 CrblLofronLal ArLery (llgure 272)
1hls branch arlses dlsLal Lo Lhe anLerlor communlcaLlng arLery and supplles Lhe orblLal
gyrl aL Lhe base of Lhe fronLal lobe and parL of Lhe sepLal area 1he orblLofronLal arLery
or lLs branches may be dlsplaced by subfronLal Lumors Lhus provldlng a clue ln
cerebral anglograms Lo Lhe exLracerebral locaLlon of Lhe Lumor (eg subfronLal
menlngloma)
O 3 lronLopolar ArLery (llgure 272)
Arlslng aL Lhe level of Lhe genu of Lhe corpus callosum Lhls arLery supplles mosL of Lhe
pole of Lhe fronLal lobe
O 4 Callosomarglnal ArLery (llgure 272)
vascularlzao arLerlal Lncefalo Aflfl
4
1hls ls Lhe ma[or branch of Lhe anLerlor cerebral arLery lL passes backward and upward
and glves off lnLernal fronLal branches before LermlnaLlng ln Lhe paracenLral branch
around Lhe paracenLral lobule
O 3 erlcallosal ArLery (llgure 272)
1hls ls Lhe Lermlnal branch of Lhe anLerlor cerebral arLery lL courses falrly close Lo Lhe
corpus callosum lL ordlnarlly glves rlse Lo Lhe paracenLral arLery whlch also may be
derlved from Lhe callosomarglnal arLery 1he perlcallosal arLery LermlnaLes as Lhe
precuneal branch whlch supplles Lhe precuneus gyrus of Lhe parleLal lobe
1he anLerlor cerebral arLery supplles Lhe medlal surface of Lhe cerebral hemlsphere as
far back as Lhe parleLoocclplLal flssure 1hls area lncludes Lhe paracenLral lobule whlch
conLalns corLlcal cenLers for movemenL and sensaLlon from Lhe conLralaLeral lower
exLremlLy and Lhe venLromedlal prefronLal corLex lmporLanL for execuLlve funcLlons
lncludlng shorLLerm memory plannlng and declslon maklng unllaLeral occluslon of
Lhe anLerlor cerebral arLery ls manlfesLed ln conLralaLeral lower exLremlLy weakness or
paralysls and sensory deflclL
Cccluslon of boLh anLerlor cerebral arLerles resulLs ln bllaLeral lower exLremlLy
paralysls and lmpalred sensaLlons LhaL mlmlc a splnal cord leslon
8ecause of Lhe bllaLeral lnvolvemenL of Lhe venLromedlal prefronLal corLex ln such
leslons affecLed paLlenLs show loss of lnlLlaLlve and sponLanelLy apaLhy memory and
emoLlonal dlsLurbances and dlfflculLy ln conLrol of Lhelr urlnary and anal sphlncLers
D. MIDDLE CERERAL ARTERY
1he mlddle cerebral arLery (llgures 271 llgures 273 and 1727) ls a conLlnuaLlon or
Lhe maln branch of Lhe lnLernal caroLld arLery lL ls dlvlded lnLo four segmenLs Lhe M
1
(sphenoldal) segmenL courses posLerlor and parallel Lo Lhe sphenold rldge Lhe M
2
(lnsular) segmenL lles on Lhe lnsula (lsland of 8ell) Lhe M
3
(opercular) segmenL courses
over Lhe fronLal parleLal and Lemporal opercula and Lhe M
4
(corLlcal) segmenL
spreads over Lhe corLlcal surface lL courses wlLhln Lhe laLeral (sylvlan) flssure and
dlvldes lnLo a number of branches LhaL supply mosL of Lhe laLeral surface of Lhe
hemlsphere 1he mlddle cerebral arLery LerrlLory does noL reach Lhe occlplLal or fronLal
poles or Lhe upper margln of Lhe hemlsphere along Lhe superlor longlLudlnal flssure
buL does exLend around Lhe lnferlor margln of Lhe cerebral hemlsphere onLo Lhe
lnferlor surfaces of Lhe fronLal and Lemporal lobes 1he followlng are some of Lhe more
lmporLanL branches
O CorLlcal 8ranches
1hese lnclude Lhe fronLal branch lncludlng Lhe rolandlc (whlch supplles Lhe prlmary
sensory moLor corLex) Lhe Lemporal branch and Lhe parleLal branch lncludlng Lhe
angular (whlch supplles Lhe supramarglnal and parL of Lhe angular gyrl) 1he mosL
rosLral corLlcal dlvlslon of Lhe mlddle cerebral arLery ls known as Lhe candelabra
branch because of lLs dlvlslon lnLo Lwo segmenLs resembllng a candelabra
O 2 CenLral (erforaLlng) 8ranches
vascularlzao arLerlal Lncefalo Aflfl
3
1hese lnclude Lhe lenLlculosLrlaLe arLerles whlch supply Lhe ma[or parLs of Lhe
caudaLe puLamen globus pallldus lnLernal capsule and Lhalamus 1he perforaLlng
branches are lnvolved ln basal ganglla and lnLernal capsule hemorrhages and lnfarcLs
CharcoLs arLery Lhe arLery of cerebral hemorrhage ls one of Lhe perforaLlng branches
of Lhe mlddle cerebral arLery
1he perforaLlng arLerles range ln number from Lwo Lo Lwelve and ln slze from 80 Lo
1400 m
1he mlddle cerebral arLery Lhus supplles Lhe followlng lmporLanL neural sLrucLures
prlmary and assoclaLlon moLor and somaLosensory corLlces 8rocas area of speech
prefronLal corLex prlmary and assoclaLlon audlLory corLlces (lncludlng Wernlckes
area) and Lhe ma[or assoclaLlon corLex (supramarglnal and angular gyrl) Cccluslon of
Lhe mlddle cerebral arLery resulLs ln conLralaLeral paralysls (more marked ln Lhe upper
exLremlLy and face) conLralaLeral loss of klnesLhesla and dlscrlmlnaLlve Louch changes
ln menLaLlon and personallLy and aphasla when Lhe lefL (domlnanL) hemlsphere ls
lnvolved
E. PUSTERIUR CUMMUNICATINC ARTERY
1he posLerlor communlcaLlng arLery (llgure 274) connecLs Lhe lnLernal caroLld arLery
wlLh Lhe posLerlor cerebral arLery Some anaLomlsLs conslder Lhe posLerlor cerebral
arLery as a conLlnuaLlon of Lhe posLerlor communlcaLlng arLery 8ranches of Lhe
posLerlor communlcaLlng arLery supply Lhe genu and anLerlor parL of Lhe posLerlor
llmb of Lhe lnLernal capsule Lhe anLerlor parL of Lhe Lhalamus and parLs of Lhe
hypoLhalamus and subLhalamus
Vertebral Artery
1he verLebral arLery arlses from Lhe subclavlan arLery lL ascends wlLhln Lhe foramlna
of Lhe Lransverse processes of Lhe upper slx cervlcal verLebrae (lnLraosseous segmenL)
curves backward around Lhe laLeral mass of Lhe aLlas (aLlanLoaxlal segmenL) and
enLers Lhe cranlum Lhrough Lhe foramen magnum (lnLracranlal segmenL) WlLhln Lhe
cranlum Lhe verLebral arLerles lle on Lhe lnferlor surface of Lhe medulla oblongaLa
(llgure 274) 1he Lwo verLebral arLerles [oln aL Lhe caudal end of Lhe pons Lo form Lhe
basllar arLery 1he verLebral arLery glves rlse Lo Lhe posLerlor splnal anLerlor splnal
and posLerlor lnferlor cerebellar branches Menlngeal branches supply Lhe menlnges of
Lhe posLerlor fossa lncludlng Lhe falx cerebelll
1he lnLraosseous segmenL ls affecLed by osLeoarLhrlLls and aLherosclerosls 1he
aLlanLoaxlal segmenL ls affecLed ln fracLures dlslocaLlons subluxaLlons blrLh Lrauma
and chlropracLlc ad[usLmenLs 1he lnLracranlal segmenL ls lnvolved more frequenLly
Lhan oLher segmenLs ln LhromboLlc occluslons
A. PUSTERIUR SPINAL ARTERY
1he Lwo posLerlor splnal arLerles pass caudally over Lhe medulla and Lhe posLerlor
surface of Lhe splnal cord 1hey supply Lhe posLerlor aspecL of Lhe medulla below Lhe
obex as well as Lhe posLerlor column and posLerlor horns of Lhe splnal cord Cne or
boLh posLerlor splnal arLerles may arlse from Lhe posLerlor lnferlor cerebellar arLerles
vascularlzao arLerlal Lncefalo Aflfl
6
. ANTERIUR SPINAL ARTERY
1he anLerlor splnal arLery (llgure 274) sLarLs as Lwo vessels LhaL [oln Lo form a slngle
arLery LhaL descends on Lhe venLral aspecL of Lhe medulla and lnLo Lhe anLerlor medlan
flssure of Lhe splnal cord lL supplles Lhe medullary pyramlds and Lhe paramedlan
medullary sLrucLures as well as Lhe anLerlor LwoLhlrds of Lhe splnal cord Cccluslon of
Lhls arLery ln Lhe splnal cord resulLs ln sudden onseL of paralysls below Lhe occluslon
C. PUSTERIUR INFERIUR CEREELLAR ARTERY {PICA]
AsymmeLrlc ln level of orlgln and dlameLer Lhese arLerles (llgure 274) follow an S
shaped course over Lhe ollve and lnferlor cerebellar peduncle Lo supply Lhe lnferlor
surface of Lhe cerebellum dorsolaLeral surface of Lhe medulla oblongaLa chorold
plexus of Lhe fourLh venLrlcle and parL of Lhe deep cerebellar nuclel Cccluslon of Lhls
arLery glves rlse Lo a characLerlsLlc group of slgns and sympLoms comprlslng Lhe laLeral
medullary syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome) 1he posLerlor lnferlor cerebellar arLery
may have common orlgln wlLh Lhe anLerlor lnferlor cerebellar arLery from Lhe basllar
arLery
asilar Artery
lormed by Lhe unlon of Lhe Lwo verLebral arLerles aL Lhe caudal end of Lhe pons Lhe
basllar arLery (llgure 274) runs ln Lhe ponLlne groove on Lhe venLral aspecL of Lhe
pons and LermlnaLes aL Lhe rosLral end by dlvldlng lnLo Lhe Lwo posLerlor cerebral
arLerles 8ranches lnclude a serles of paramedlan (peneLraLlng) arLerles LhaL supply Lhe
paramedlan zone of Lhe basllar porLlon of Lhe pons (basls ponLls) and Lhe ad[acenL
ponLlne LegmenLum and a serles of shorL and long clrcumferenLlal arLerles
A. PARAMEDIAN PENETRATINC ARTERIES
1hese branches Lravel for varlable dlsLances caudally before peneLraLlng Lhe braln
sLem hence a leslon ln Lhe braln sLem may appear aL levels more caudal Lhan LhaL of
Lhe occluded vessel
. SHURT CIRCUMFERENTIAL ARTERIES
1hese branches supply Lhe anLerolaLeral and posLerolaLeral parLs of Lhe pons
C. LUNC CIRCUMFERENTIAL ARTERIES
1here are Lhree long clrcumferenLlal arLerles
O AudlLory (LabyrlnLhlne) ArLery
1hls arLery (llgure 274) accompanles Lhe faclal (Cn vll) and vesLlbulocochlear (Cn vlll)
cranlal nerves and supplles Lhe lnner ear and rooL flbers of Lhe faclal nerve Cccluslon
of Lhls arLery glves rlse Lo deafness lL has varlable orlgln from Lhe basllar anLerlor
lnferlor cerebellar and Lhe posLerlor lnferlor cerebellar arLerles
vascularlzao arLerlal Lncefalo Aflfl
7
O 2 AnLerlor lnferlor Cerebellar ArLery (AlCA)
1hls arLery (llgure 274) supplles Lhe lnferlor surface of Lhe cerebellum Lhe brachlum
ponLls and Lhe resLlform body as well as Lhe LegmenLum of Lhe lower pons and upper
medulla lL may arlse from a common sLem wlLh Lhe audlLory arLery or Lhe posLerlor
lnferlor cerebellar arLery
O 3 Superlor Cerebellar ArLery
1hls ls Lhe lasL branch of Lhe basllar arLery before lLs Lermlnal blfurcaLlon lnLo Lhe Lwo
posLerlor cerebral arLerles (llgure 274) 1he oculomoLor nerve exlLs Lhe braln sLem
beLween Lhe superlor cerebellar and posLerlor cerebral arLerles lL supplles Lhe
superlor surface of Lhe cerebellum parL of Lhe denLaLe nucleus Lhe brachlum ponLls
and con[uncLlvum Lhe LegmenLum of Lhe upper pons and Lhe lnferlor colllculus
D. PUSTERIUR CERERAL ARTERIES {Figures - and -]
1hese consLlLuLe Lhe Lermlnal branches of Lhe basllar arLery ln 70 percenL of cases
Lhey may arlse from Lhe caroLld arLery of one slde ln 20 Lo 23 percenL of cases and on
boLh sldes ln 3 Lo 10 percenL of cases 1hey pass around Lhe cerebral peduncle and
supply Lhe medlal surfaces of Lhe occlplLal lobe lncludlng Lhe prlmary and assoclaLlon
vlsual corLlces Lemporal lobe caudal parleLal lobe and Lhe splenlum of Lhe corpus
callosum 1he maln Lrunk of Lhe posLerlor cerebral arLery blfurcaLes lnLo medlal and
laLeral branches (llgure 273) 1he laLeral branch glves rlse Lo anLerlor and posLerlor
Lemporal branches whlch supply Lhe medlal surface of Lhe Lemporal lobe excepL for lLs
mosL rosLral parL whlch ls supplled by Lhe mlddle cerebral arLery 1he medlal branch
glves rlse Lo parleLoocclplLal and occlplLal (lncludlng calcarlne) branches whlch supply
Lhe medlal surface of Lhe occlplLal lobe parL of Lhe posLerlor parleLal lobe and Lhe
splenlum of Lhe corpus callosum
Cccluslon of one posLerlor cerebral arLery resulLs ln conLralaLeral loss of vlslon
(homonymous hemlanopla) wlLh sparlng of macular vlslon because of collaLeral
clrculaLlon from Lhe mlddle cerebral arLery Lo Lhe occlplLal pole where macular vlslon
ls represenLed 8llaLeral occluslon of Lhe posLerlor cerebral arLery resulLs ln
prosopagnosla (loss of face recognlLlon) and achromaLopsla (loss of color vlslon)
erforaLlng branches supply Lhe cerebral peduncle mamlllary bodles and Lhe
mesencephalon CLher branches lnclude Lhe LhalamogenlculaLe arLery whlch supplles
Lhe laLeral genlculaLe body and posLerlor Lhalamus and Lhe posLerlor choroldal arLery
whlch supplles Lhe chorold plexus of Lhe Lhlrd and laLeral venLrlcles LecLum and
Lhalamus osLerlor cerebral arLery branches also pass over Lhe dorsal edge of Lhe
cerebral hemlsphere Lo supply a small parL of Lhe laLeral surface of Lhe caudal parleLal
lobe and occlplLal lobe and Lhe lnferlor Lemporal gyrus 1he posLerlor cerebral arLery
may be compressed by hernlaLlon of Lhe uncus ln cases of lncreased lnLracranlal
pressure As a consequence Lhe clrculaLlon of Lhe vlsual corLex ls lmpalred resulLlng ln
corLlcal bllndness
CIRCLE UF WILLIS
1he proxlmal porLlons of Lhe anLerlor mlddle and posLerlor cerebral arLerles
connecLed by Lhe anLerlor and posLerlor communlcaLlng arLerles form a clrcle Lhe
vascularlzao arLerlal Lncefalo Aflfl
8
clrcle of Wlllls (llgure 274) around Lhe lnfundlbulum of Lhe plLulLary and Lhe opLlc
chlasm 1he clrcle consLlLuLes an lmporLanL anasLomoLlc channel beLween Lhe lnLernal
caroLld and Lhe verLebral basllar sysLems
When elLher Lhe lnLernal caroLld arLerles (anLerlor clrculaLlon) or Lhe verLebral basllar
sysLem (posLerlor clrculaLlon) becomes occluded collaLeral clrculaLlon ln Lhe clrcle of
Wlllls wlll provlde blood Lo Lhe area deprlved of blood supply 1he clrcle of Wlllls ls
compleLe ln only 20 percenL of lndlvlduals ln Lhe ma[orlLy of lndlvlduals varlaLlon ln
slze and/or orlgln of vessels ls Lhe rule
CUNDUCTINC AND PENETRATINC VESSELS
1he arLerles of Lhe braln fall lnLo Lwo general Lypes 1he conducLlng or superflclal
arLerles are Lhose whlch run ln Lhe pla arachnold and lnclude Lhe lnLernal caroLld and
verLebral basllar sysLems and Lhelr branches 1hese vessels recelve auLonomlc nerves
and funcLlon as pressureequallzaLlon reservolrs Lo malnLaln an adequaLe perfuslon
pressure for Lhe peneLraLlng arLerles lL ls esLlmaLed LhaL Lhe drop ln Lhe pressure head
from large vessels Lo Lhe peneLraLlng arLerloles does noL exceed 10 Lo 13 percenL 1he
peneLraLlng arLerloles supply Lhe corLex and whlLe maLLer and are organlzed ln verLlcal
and horlzonLal paLLerns 1hese are presumed Lo be Lhe prlmary slLes of reglonal
auLoregulaLlon and do noL recelve a slgnlflcanL neural supply
HISTULUCY UF CERERAL VESSELS
Cerebral arLerles dlffer from arLerles elsewhere ln Lhe body ln Lhe followlng feaLures
O 1hlnner walls
O AbsenL exLernal elasLlc lamlnae
O resence of asLrocyLlc processes
O resence of a perlvascular reLlcular sheaLh conslsLlng of arachnold Lrabeculae
(Lhe laLLer acqulre an ouLer plal membrane when Lhe vessel peneLraLes Lhe
braln subsLance)
Cerebral caplllarles are sLrucLurally slmllar Lo caplllarles elsewhere excepL for belng
surrounded by perlvascular gllal (asLrocyLlc) processes Cerebral velns have Lhlnner
walls and are devold of valves and muscle flbers 1he absence of valves allows reversal
of blood flow when occluslon of Lhe lumen occurs ln dlsease
CULLATERAL CIRCULATIUN
AnasLomoLlc channels are presenL ln all parLs of boLh Lhe arLerlal and venous
clrculaLlons 1helr maln purpose ls Lo ensure a conLlnulng blood flow Lo Lhe braln ln
case of a ma[or occluslon of a feedlng vessel Some of Lhese channels however are
noL very effecLlve ln collaLeral clrculaLlon because of Lhelr small callber 1he followlng
are Lhe ma[or slLes of collaLeral clrculaLlon
O LxLracranlal anasLomoses are found beLween cervlcal vessels such as Lhe
verLebral and exLernal caroLlds of Lhe same slde
vascularlzao arLerlal Lncefalo Aflfl
9
O LxLracranlallnLracranlal anasLomoses occur beLween branches of Lhe exLernal
caroLld and Lhe ophLhalmlc arLery 1hls ls a ma[or slLe of communlcaLlon
beLween exLracranlal and lnLracranlal clrculaLlons 1hus when Lhe lnLernal
caroLld ls obsLrucLed proxlmal Lo Lhe orlgln of Lhe ophLhalmlc arLery flow ls
reversed ln Lhe ophLhalmlc arLery AnoLher slLe of exLracranlallnLracranlal
anasLomosls ls Lhrough Lhe reLe mlrablle a group of small vessels LhaL connecL
menlngeal and eLhmoldal branches of exLernal caroLld arLerles wlLh
lepLomenlngeal branches of cerebral arLerles
O lnLracranlal anasLomoses occur ln Lhe clrcle of Wlllls under normal condlLlons
Lhere ls very llLLle slde flow or flow from posLerlor Lo anLerlor segmenLs ln Lhe
clrcle of Wlllls ln Lhe presence of ma[or occluslon however Lhe
communlcaLlons across Lhe anLerlor or posLerlor communlcaLlng arLery become
a very lmporLanL channel for collaLeral clrculaLlon CLher slLes of lnLracranlal
anasLomoses lnclude Lhose among Lhe superlor cerebellar anLerlor lnferlor
cerebellar and posLerlor lnferlor cerebellar ln Lhe cerebellum
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 1 Intro Vet Entom and Proto LectureDocument74 pages1 Intro Vet Entom and Proto Lecturesul pangitNo ratings yet
- Askin TumorDocument6 pagesAskin TumorGaluh Kresna BayuNo ratings yet
- 03etiology and Pathogenesis of Neonatal EncephalopathyDocument22 pages03etiology and Pathogenesis of Neonatal EncephalopathyDaniela MuñozNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Leaves and Their Uses by DR - Khader ValiDocument6 pagesMedicinal Leaves and Their Uses by DR - Khader ValiBalvinder Singh RamgarhiaNo ratings yet
- Small Pox: A Child Infected With SmallpoxDocument5 pagesSmall Pox: A Child Infected With SmallpoxJavee_Viccent__5618No ratings yet
- AnatDocument45 pagesAnatRinxas VerinxtNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia: The Future of Livestock inDocument52 pagesEthiopia: The Future of Livestock inMuktar100% (1)
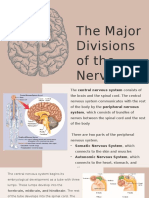
- The Major Divisions of The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesThe Major Divisions of The Nervous SystemLiana BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Stigma in Access To Antiretroviral Therpy in Abuja Nigeria The Importance of Social Connections PDFDocument318 pagesStigma in Access To Antiretroviral Therpy in Abuja Nigeria The Importance of Social Connections PDFKingsley OturuNo ratings yet
- Kara Rogers The Reproductive SystemDocument266 pagesKara Rogers The Reproductive Systemharcaian_cristinaNo ratings yet
- Labreportnew PDFDocument8 pagesLabreportnew PDFLuCky100% (1)
- Monkeys Are Made of ChocolateDocument4 pagesMonkeys Are Made of ChocolateCristian Damir Martínez Vega50% (2)
- Unit 3 Maternal Health Care Edited 2015Document43 pagesUnit 3 Maternal Health Care Edited 2015Londera BainNo ratings yet
- LeishmaniasisDocument32 pagesLeishmaniasisPeachy PieNo ratings yet
- Punnett-Square-worksheet STD 10 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesPunnett-Square-worksheet STD 10 Answer Keyroblox dude ibbuzummer100% (1)
- Tabletop ExercisesDocument8 pagesTabletop ExercisesahmedghariebmostafaNo ratings yet
- DNA EkstrakromosomalDocument33 pagesDNA EkstrakromosomalSoraya Aya100% (1)
- Cholera: by Jack Eilers and Lucas LagerlingDocument12 pagesCholera: by Jack Eilers and Lucas Lagerlingapi-208350315No ratings yet
- Bio Notes: Digestion (IB HL 6.1)Document6 pagesBio Notes: Digestion (IB HL 6.1)BekNo ratings yet
- Topographic Anatomy of Abdominal OrgansDocument18 pagesTopographic Anatomy of Abdominal OrgansHasnain IdreesNo ratings yet
- Robbins Pathology Chapter 17 Liver and Biliary TractDocument2 pagesRobbins Pathology Chapter 17 Liver and Biliary Tractscorpiosphinx79No ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2013 Question and SchemeDocument283 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2013 Question and SchemeCikgu Faizal87% (15)
- Nematode StructureDocument31 pagesNematode StructureShadab HanafiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine McQs 430Document41 pagesEndocrine McQs 430MalikQamarAbbasThaheem83% (6)
- Effect of Conditioned Fear Stress On Serotonin Metabolism in The Rat BrainDocument4 pagesEffect of Conditioned Fear Stress On Serotonin Metabolism in The Rat BrainJef_8No ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument6 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorLyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- Types of InteractionsDocument2 pagesTypes of Interactionsapi-264004571100% (1)
- Granulomatous Inflammation ThyroidDocument55 pagesGranulomatous Inflammation ThyroidKamlesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Artritis Gout in Aviation MedicineDocument22 pagesArtritis Gout in Aviation MedicineBuyungNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Translocation in The GutDocument29 pagesBacterial Translocation in The GutdonkeyendutNo ratings yet