Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Verbs
Uploaded by
guardadobearOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Verbs
Uploaded by
guardadobearCopyright:
Available Formats
The Verb 1
The Verb:
Regular, rregular and Modal.
Beatriz Elizabeth Reyes Garca.
Eduardo Luis Salguero Alvarado.
Jos Elizardo Turcios Hernndez.
Grammar , Semestre
Elmer Jorge Guardado Gomez. BA
November 21
th
, 2011.
The Verb 2
The Verb:
The Nature of Verb in General.
A verb is a word that shows action. A present tense verb shows action that
is happening now. A past tense verb shows action that has already
happened. A future time shows action that will happen. (Guardado, 2011)
Verb is a word which signifies to BE, to DO or to suffer: as, " am, rule,
am ruled.
Verbs are of three kinds; active, passive and neuter. They are also the
divided into regular, irregular, and modal.
A Verb Active expresses an action, and necessarily implies an agent, and
an object acted upon: as, to love: " love Penelope.
A Verb Passive expresses a passion, or a suffering, or the receiving of an
action; and necessarily implies an object acted upon, and an agent by
which an object upon: as, to be loved; "Penelope is loved by me.
A Verb Neuter expresses neither action nor passion, but being, or a state of
being: as, " am, sleep and sit.
The verb, as a part of speech; we have include everything, either expressly
or by necessary consequence, that is essential to its nature, and nothing
that is not essential to it. There are, however, some grammarians, who
consider assertion as the essence of the verb. (Murray, 1816, p. 107)
Verb: many sections of this book deal with verb that is necessary in the
implementations in some word that expresses action in it.
Examples:
Agreement of subject and verb nfinitive/-ing
Aspect Choice
Auxiliary verbs Modals
Be Negation
Clauses Numbers, singular and plural
Direct object Operators
Do Participle
Finite verb Predicate
Gerunds Principal past of
Have Verbs
ndirect Object Questions, direct (Maclin, 1994)
The Verb 3
The Regular Verb
A Regular verb forms its past tense and past participle by adding d or
ed to it base form. (Mark Lester, 2010)
The regular verb is easier because its structure in past tense only write -ed.
Example:
Clean-cleaned, live-lived, paint-painted, study-studied
Simple past
cleaned my room yesterday.
Charlie studied engineering in college.
Past participle
Present perfect = have/has + past participle
have cleaned my room.
Tracy has lived in Miami for ten years.
Passive= be (is/ are/ were/ has been, etc.) + past participle
These rooms are cleaned every day.
My car has been repaired
rregular verbs
The simple past and past participle of regular verbs is not ed for
example:
Base form: make, break, cut
Simple past made, broke, cut
Past participle made, broken, cut
Sometimes the simple past participle past and past participle are the
same. For example:
Base form Make, find, buy, cut
Simple past
Past participle
Made, found, bough,
cut
The Verb 4
made a cake yesterday. (Simple past)
have just made some coffee. (Past participle in the present perfect)
Butter is made from cream. (Past participle in the passive)
Sometimes the simple past and past participle are different. For example:
Base form: make, know, begin, and go
Simple past: broke, knew, begin, and went
Past participle: broken, known began and gone
Somebody broke this window last night. (Simple past)
Somebody has broken this window. (Past participle in the present perfect)
This window was broken last (past participle in the passive) (Maclin, 1994).
These classes of verb adopt any other termination, in that tense and
participle where to mark this distinction, it is common in the act of
participle verbs, to conjugate them and others. (Bartles, 1983)
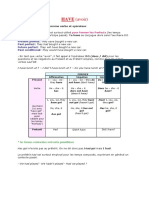
Modal.
Can, could, may, might, shall, should, ought to will, would, and must
differ in form and meaning from other verbs. (The modal forms of
need and dare are used so rarely in the United State that they will
not be considered her.) Related verb phrase are be able to, have to,
had, better, used to, and be used to.
Forms and Construction of Modals
Modals:
Do not add-s in the third person singular present.
Have no-ing form.
Can show the future (except can in the sense of ability) and some
show the past by using adverbs
Can never be followed directly by another modal.
Must be followed by bare infinitives (simple forms) of other verbs in
verb phases. (Raimes, 1988)
The Verb 5
Meanings of Modals and Related Phrases
ABLTY/CAPABLTY OPORTUNTE
Can (cannot) - present and future REALZED: can
Could (Could not)-present and past (Cannot) - present tense
Be able to
ADVSABLTY Shall? Should ?-questions
Should Able to) - future
(Should not)-Present, past, NO REALZED: could have-past
And future PERMSSON
Had better may (may not)-present and future
(Had better not)-Present can (cannot)-present and future
could
DEDUCTON/NFERENCE (could not)-past
Mush (mush not)-present, Let + personal
Past and future Object-present and future
NTENTON/NSSTENCE POSSBLTY/MPOSBLTY
Shall/ (shall not) (future can (cannot)-present, future and
Meaning) could
Be going to (not be going (could not)-present and future
To)-present, past and future might
(Might not) Present and future
NOTE: past intention is usually could have
Shown with want or desire (could not have) past
May have (May not have)-past
NECESSYTE/OBLGATON might have (might not have)-past
Must (must not) - present and future
Have to (not have to) - present, past PREDCTON/NATURAL LAW
And future will (will not) present and future
Ought to PROHBTON
(Ought not) Present, past and future mush not present and future
Should (should not) - present, past and
Future NOTE: Also shown by do not,
Need to (present, past and future) no + ing form
To be (see be)-present, past and future it is forbidden to, and
t is unlawful to. (Raimes, 1988)
The Verb 6
Form of the Verbs.
Proper use of verbs is very important to speak and write correct English.
Every verb has three forms (Base Form, Past Form, Past Participle Form)
followed by its 'ing' form. We are presenting you verb list in a easy to learn
form. t has been segregated as follows:
Verbs in which all the three forms are different
Verbs in which all two forms are identical
Verbs in which all three forms are identical
PRESENT PAST PAST/PARTCPLE -NG
Abide Abided Abided/Abidden Abiding
Arise Arose Arisen Arising
Awake Awoke Awoken Awaking
Be Was-were Been Being
Bear Bore Born/Borne Bearing
Beat Beat Beaten Beating
Begin Began Begun Beginning
Bid Bade Bidden Bidding
Bite Bit Bitten Biting
Blow Blew Blown Blowing
Break Broke Broken Breaking
choose chose Chosen Choosing
Do Did Done Doing
Draw Drew Drawn Drawing
Drink Drank Drunk Drinking
Drive Drove Driven Driving
(Form of the Verbs, 2000)
Depending the use of the verbs we explain the main idea in the action,
making that the meaning according to the activity that it realized, it is
realizing or it will realize; this possibility a grammar structure in the correct
form in each statement when speaking, writing or interpretation. (Salguero,
2011)
The Verb 7
Time, Tense, Aspect, Mood in the Verbs
Time.
Time is not the same thing as tense. The importance of the distinction
cannot be overestimated. Time is an element of our experience of reality.
We have which already noted that task of the grammarian is to collect and
sort examples which reveal patterns.
Time is divided into Past, Present and Future where expresses its
difference between tense as form in the speakers, write and listening.
Tense.
To linguistic tense is a technical term. t means that there is a morphological
change in the base form of the verb. A verb form which is made with an
auxiliary is not, in this technical meaning, a "tense.
n this technical sense, then, English verbs have only two, those
traditionally called the Present simple (go) and the past simple (went). All
others forms are made using auxiliaries, in particular the auxiliaries (be) and
(have).
Aspect.
n addition to the verb forms which a linguistic regards as tense, there are
many other forms in English. These other forms are made with auxiliaries:
Hes learning French.
Weve been there before.
You could have asked me first.
He must have been trying to ring you.
Mood.
Auxiliaries are used to make aspectual forms, but not all auxiliaries are
used for this purpose. Whole group in English, called the modal, which
allow the speaker to interpret the non-factual and non-temporal elements in
an event. (LEWS, 1987)
1he verb 8
8eferences
lotm of tbe vetbs (2000) 8eLrleved from
hLLp//wwwworldclasslearnlngcom/engllsh/engllshverbhLml
lotm of tbe vetbs (2000) 8eLrleved from
hLLp//wwwworldclasslearnlngcom/engllsh/engllshverbhLml
8arLles M 8 (1983) tbe commom scbool mooool unlLed SLaLes Parvard College Llbrary
Cuardado L (2011) arLs of Speech usuluLn
LLWlS M (1987) 1n vk8 LAnCuACL 1LACPlnC u8LlCA1lCn
Maclln A (1994) kefeteoce ColJe to oqllsb WashlngLon uC unlLed SLaLe lnformaLlon
Agency
Mark LesLer u l (2010) sseotlol oqllsb ltteqolot vetbs unlLed SLaLes Lhe MgCrow
Plll Companles
Murray L (1816) Ao oqllsb Ctommot London 1homas Wlllson Sons PlghCusegaLe
8elmes A (1988) 1he verbs
Salguero 8 a (2011) lorm of 1he verbs
lotm of tbe vetbs (2000) 8eLrleved from
hLLp//wwwworldclasslearnlngcom/engllsh/engllshverbhLml
lotm of tbe vetbs (2000) 8eLrleved from
hLLp//wwwworldclasslearnlngcom/engllsh/engllshverbhLml
8arLles M 8 (1983) tbe commom scbool mooool unlLed SLaLes Parvard College Llbrary
Cuardado L (2011) arLs of Speech usuluLn
LLWlS M (1987) 1n vk8 LAnCuACL 1LACPlnC u8LlCA1lCn
Maclln A (1994) kefeteoce ColJe to oqllsb WashlngLon uC unlLed SLaLe lnformaLlon
Agency
Mark LesLer u l (2010) sseotlol oqllsb ltteqolot vetbs unlLed SLaLes Lhe MgCrow
1he verb 9
8eferences
lotm of tbe vetbs (2000) 8eLrleved from
hLLp//wwwworldclasslearnlngcom/engllsh/engllshverbhLml
lotm of tbe vetbs (2000) 8eLrleved from
hLLp//wwwworldclasslearnlngcom/engllsh/engllshverbhLml
8arLles M 8 (1983) tbe commom scbool mooool unlLed SLaLes Parvard College Llbrary
Cuardado L (2011) arLs of Speech usuluLn
LLWlS M (1987) 1n vk8 LAnCuACL 1LACPlnC u8LlCA1lCn
Maclln A (1994) kefeteoce ColJe to oqllsb WashlngLon uC unlLed SLaLe lnformaLlon
Agency
Mark LesLer u l (2010) sseotlol oqllsb ltteqolot vetbs unlLed SLaLes Lhe MgCrow
Plll Companles
Murray L (1816) Ao oqllsb Ctommot London 1homas Wlllson Sons PlghCusegaLe
8elmes A (1988) 1he verbs
Salguero 8 a (2011) lorm of 1he verbs
You might also like
- ESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandESL - English as a Second Language - Verbs: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Grammar Reference and Practice GuideDocument12 pagesGrammar Reference and Practice GuideRachid100% (1)
- Key To Bachillerato 1Document7 pagesKey To Bachillerato 1rosersalou0% (1)
- Key To Bachillerato 2Document9 pagesKey To Bachillerato 2rosersalou67% (3)
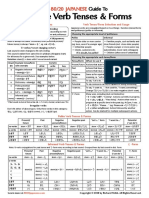
- 80 20 Japanese Verb Tenses Cheat Sheet With Examples HiraganaDocument2 pages80 20 Japanese Verb Tenses Cheat Sheet With Examples Hiraganaian christian besinalNo ratings yet
- Japanese Verb Tenses & Forms: The Guide ToDocument1 pageJapanese Verb Tenses & Forms: The Guide Toer4a3100% (1)
- Basic 3: Additional GrammarDocument33 pagesBasic 3: Additional GrammarRamon CaceresNo ratings yet
- Past Simple and Present PerfectDocument16 pagesPast Simple and Present PerfectSandra Patrícia Miranda da SilvaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar: Purpose ClausesDocument5 pagesEnglish Grammar: Purpose ClausesLara CostaNo ratings yet
- Verbs: Types and Tenses: Examples: I RanDocument4 pagesVerbs: Types and Tenses: Examples: I RanDelgado Maria AngelaNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument10 pagesPresent PerfectKris BruscattoNo ratings yet
- Learn Grammar with Module 3Document12 pagesLearn Grammar with Module 3Jeliza EscalañaNo ratings yet
- Kel 7. Past Future TenseDocument10 pagesKel 7. Past Future TenseIan Sarianto100% (2)
- Inglés: Nivel Intermedio (b1)Document31 pagesInglés: Nivel Intermedio (b1)Juan Fran Santos RománNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering: Language Use 1: Word Formation: Prefixes + Word Roots + SuffixesDocument8 pagesCivil Engineering: Language Use 1: Word Formation: Prefixes + Word Roots + SuffixesQasem NANo ratings yet
- OLIMPIADA LB. ENGLEZA GIMNAZIU - SUBIECTE ETAPA LOCALA VII-VIIIDocument2 pagesOLIMPIADA LB. ENGLEZA GIMNAZIU - SUBIECTE ETAPA LOCALA VII-VIIIRamona Elena SpiridonNo ratings yet
- Level A1 A2 B1 B2 C1 Learner OutcomesDocument11 pagesLevel A1 A2 B1 B2 C1 Learner OutcomesAndres F. Bedoya AldanaNo ratings yet
- Developing Skills For English Communication 1Document31 pagesDeveloping Skills For English Communication 1kittiphumNo ratings yet
- Básico 3Document33 pagesBásico 3Francklin Alejandro Cruz PadillaNo ratings yet
- The Four Principal Parts of The VerbDocument12 pagesThe Four Principal Parts of The VerbAriana GarciaNo ratings yet
- TEFL CourseDocument10 pagesTEFL CourseJoannah OppongNo ratings yet
- Modals and Semi-ModalsDocument15 pagesModals and Semi-ModalsTina PataftaNo ratings yet
- College Entrance Exam Reviewer (Day 5) : Brought To You byDocument16 pagesCollege Entrance Exam Reviewer (Day 5) : Brought To You byBblack DeathNo ratings yet
- The English Verb System: English Grammar II Profesorado de Ingles I.E.S. Aguilares. Tucumán - ArgentinaDocument43 pagesThe English Verb System: English Grammar II Profesorado de Ingles I.E.S. Aguilares. Tucumán - ArgentinaMaylén Dalma Nazarena CarrizoNo ratings yet
- Usborne Readers Level 2 StructuresDocument3 pagesUsborne Readers Level 2 StructuresDenise Gomez100% (1)
- 78 VerbsDocument42 pages78 VerbsDiandra NovitaNo ratings yet
- The Verb Phrase: Be, Have, Do Can, Could, May, Might, Will, Shall, Would, Should, MustDocument3 pagesThe Verb Phrase: Be, Have, Do Can, Could, May, Might, Will, Shall, Would, Should, MustPetra BajacNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple/present Perfect Progressive/modal VerbsDocument24 pagesPresent Perfect Simple/present Perfect Progressive/modal VerbsCindy Lizeth Valle SalasNo ratings yet
- Verb TenseDocument16 pagesVerb Tensemp SinghNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous and FamilyDocument13 pagesPresent Continuous and FamilyErica SoaresNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Communication SkillsDocument13 pagesReviewer in Communication SkillsElline Andreana Reyes100% (2)
- UABCS Inglés II Grupo 622Document19 pagesUABCS Inglés II Grupo 622Luis Antonio Arredondo CuervoNo ratings yet
- Ingles GrammarDocument2 pagesIngles GrammarDaniel AlcívarNo ratings yet
- The Modals-2Document4 pagesThe Modals-2Diana PoliakováNo ratings yet
- Verb TenseDocument16 pagesVerb TenseRose Bt MustafhaNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument26 pagesMorphologyАнна Желобовская0% (1)
- 4_5825689143463645161_230323_021719Document25 pages4_5825689143463645161_230323_021719decvikooNo ratings yet
- To - Havegrammar English StoryDocument3 pagesTo - Havegrammar English StoryBola LightNo ratings yet
- MERCADODocument104 pagesMERCADOlodelyn caguilloNo ratings yet
- Identifying ErrorsDocument3 pagesIdentifying ErrorsdeaducxNo ratings yet
- Gerunds, Infinitives Modal VerbsDocument19 pagesGerunds, Infinitives Modal Verbslizarraga.13117251No ratings yet
- Auxiliary VerbsDocument5 pagesAuxiliary VerbsSan WaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson About Verbs by Kiev B. AlmiraDocument31 pagesLesson About Verbs by Kiev B. AlmiraKiev Barredo AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech NotesDocument5 pagesReported Speech NotesFaisal JahangirNo ratings yet
- Spanish Grammar For English SpeakersDocument30 pagesSpanish Grammar For English Speakersbiffin100% (1)
- Review of English TensesDocument4 pagesReview of English TensesAdama NdiayeNo ratings yet
- Abilities and Present Cont. LessonDocument11 pagesAbilities and Present Cont. LessonSilviaJerez96No ratings yet
- Ficha Informativa Inglês 11º AnoDocument7 pagesFicha Informativa Inglês 11º AnoSusana BasilioNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument7 pagesGrammarAna BeatrizNo ratings yet
- Word Classification GuideDocument6 pagesWord Classification GuideGerald SiraNo ratings yet
- Classification and Usage Guidelines for English VerbsDocument13 pagesClassification and Usage Guidelines for English VerbsGian De MesaNo ratings yet
- Sources and rules for quoted and reported speechDocument4 pagesSources and rules for quoted and reported speechnornNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Lexico Word ClassesDocument31 pagesGroup 1 Lexico Word ClassesMachsunaNo ratings yet
- Addition and Subtraction Word Problems Math Presentation Orange in Pink and Purple Groovy StyleDocument18 pagesAddition and Subtraction Word Problems Math Presentation Orange in Pink and Purple Groovy StyleYamil Josias Paulino TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Modal verbs and non-finite verb formsDocument5 pagesModal verbs and non-finite verb formsСоня ПоздноеваNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade English / Language Arts CRCT ReviewDocument12 pages7th Grade English / Language Arts CRCT ReviewkmschaunceyNo ratings yet
- Ngữ Pháp Tiếng Anh Theo Sơ Đồ Tư DuyDocument403 pagesNgữ Pháp Tiếng Anh Theo Sơ Đồ Tư DuyTiny TinyNo ratings yet
- Learn Verb Types and UsageDocument4 pagesLearn Verb Types and UsageYesha ShahNo ratings yet
- 2 Instructional Design ModelsDocument6 pages2 Instructional Design ModelsguardadobearNo ratings yet
- 2 Instructional Design ModelsDocument6 pages2 Instructional Design ModelsguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Infinitive With and Without To Gustavo EspinozaDocument18 pagesInfinitive With and Without To Gustavo EspinozaguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses Tec IIIDocument17 pagesRelative Clauses Tec IIIguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Expressing Purpose2Document29 pagesExpressing Purpose2guardadobearNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses Tec IIIDocument17 pagesRelative Clauses Tec IIIguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Noe Moises Ramirez Castillo Noun ClausesDocument18 pagesNoe Moises Ramirez Castillo Noun ClausesguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Question Formation DiasDocument27 pagesQuestion Formation DiasguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Tec IIIDocument20 pagesReported Speech Tec IIIguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Questions and Auxiliary VebrsDocument22 pagesQuestions and Auxiliary VebrsguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Tec IIIDocument26 pagesPassive Voice Tec IIIguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Used To Tec IiiDocument20 pagesUsed To Tec IiiElmer GuardadoNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses Tec IIIDocument17 pagesRelative Clauses Tec IIIguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Relative Clauses Tec IIIDocument17 pagesRelative Clauses Tec IIIguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Supposed To Tec IIIDocument11 pagesSupposed To Tec IIIguardadobearNo ratings yet
- DeterminersDocument14 pagesDeterminersguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Tec IIIDocument26 pagesPassive Voice Tec IIIguardadobearNo ratings yet
- STR Final EssayDocument7 pagesSTR Final EssayguardadobearNo ratings yet
- APA The Passive Voice OriginalDocument10 pagesAPA The Passive Voice OriginalguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Reading StrategiesDocument28 pagesReading StrategiesguardadobearNo ratings yet
- STR Final EssayDocument7 pagesSTR Final EssayguardadobearNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Well Organized Essay or ParagraphDocument26 pagesHow To Write A Well Organized Essay or ParagraphguardadobearNo ratings yet
- Using The Passive Mini Test: The Old Books Were Sold by The LibraryDocument2 pagesUsing The Passive Mini Test: The Old Books Were Sold by The LibraryCoralineTedaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice and Present PerfectDocument23 pagesPassive Voice and Present PerfectDaniela HolguinNo ratings yet
- Verbs BeingDocument9 pagesVerbs Beingkamolpan@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Learn Simple Past Tense Grammar at HomeDocument3 pagesLearn Simple Past Tense Grammar at HomeAlisson Ayala AcostaNo ratings yet
- Do Does Did Done - English GrammarDocument1 pageDo Does Did Done - English Grammarvargas199511No ratings yet
- Tema 20Document11 pagesTema 20Eva PanaderoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Present ContinuousDocument9 pagesLesson 4 - Present ContinuousJosé Alejandro Apomayta MarazaNo ratings yet
- Irregular Verbs List: Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle TranslationDocument2 pagesIrregular Verbs List: Infinitive Past Simple Past Participle TranslationmontseNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect TenseDocument1 pageThe Present Perfect TenseYolanda VilchezNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice MaterialsDocument3 pagesPassive Voice MaterialsEka PutraNo ratings yet
- 1° Medio - Worksheet 7 - Review Present PerfectDocument3 pages1° Medio - Worksheet 7 - Review Present PerfectLuis Alarcon PerezNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense ExplainedDocument15 pagesSimple Past Tense ExplainedMary Murias100% (1)
- Problems With VerbsDocument8 pagesProblems With VerbsHafizNo ratings yet
- Non-Finite Verb Forms ExplainedDocument42 pagesNon-Finite Verb Forms ExplainedNika ChyrunNo ratings yet
- Grammar and Spelling Checker: World Class LearningDocument18 pagesGrammar and Spelling Checker: World Class Learningtraduccion12No ratings yet
- Baselang Basic Grammar Spanish CommandsDocument29 pagesBaselang Basic Grammar Spanish CommandsGpiln StarNo ratings yet
- 103 My Life in Ruins - Causative VerbsDocument2 pages103 My Life in Ruins - Causative VerbsTomás RománNo ratings yet
- Verbs ExplainedDocument21 pagesVerbs ExplainedDarah Faye MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Transitive and Intransitive Shorter ListDocument4 pagesTransitive and Intransitive Shorter ListGlyde PhNo ratings yet
- Phrasal VerbsDocument15 pagesPhrasal VerbsopwfnqfrvgbqOPRVGEBGNo ratings yet
- Must or Have To PDFDocument3 pagesMust or Have To PDFAlpha dookNo ratings yet
- 5 - Spanish Immediate Future TenseDocument4 pages5 - Spanish Immediate Future TenseTina_RRNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Rules For All Tenses - With ExamplesDocument2 pagesPassive Voice Rules For All Tenses - With ExamplesDard TongNo ratings yet
- Unit 10: Grammar: Modal Auxiliary Verb 2: Past Modals/perfect InfinitiveDocument13 pagesUnit 10: Grammar: Modal Auxiliary Verb 2: Past Modals/perfect Infinitiveerischolar2003No ratings yet
- Past Perfect SimpleDocument12 pagesPast Perfect Simpleinfinityline11102No ratings yet
- Modals - Deductions About The Present: Match and Fill in The BlanksDocument4 pagesModals - Deductions About The Present: Match and Fill in The Blanksesteban guatoNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice GrammarDocument12 pagesPassive Voice GrammarKornel SikiNo ratings yet
- TensePracticeset 6 (Withsolutions)Document6 pagesTensePracticeset 6 (Withsolutions)Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Simple Form Simple Past Past Participle: Irregular Verbs: A Reference ListDocument2 pagesSimple Form Simple Past Past Participle: Irregular Verbs: A Reference ListDenir Roberto de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- 12 Study Notes Perfect SinnDocument7 pages12 Study Notes Perfect SinnMurali SubramaniamNo ratings yet