Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phoenix Contact PSM ME RS232 RS485 P
Uploaded by
Prince AsifOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phoenix Contact PSM ME RS232 RS485 P
Uploaded by
Prince AsifCopyright:
Available Formats
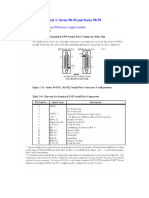
Interface Converter RS-232 (V.
24) / RS-485
The RS-485 standard is used when more than two participants have to communicate. Converting the RS-232 point-to-point interface to the bus-capable RS-485 standard allows up to 32 stations to be networked together using a 2-wire cable. The converters are used for converting an RS-232 interface into an RS-485 2-wire bus interface or vice versa. The RS-485 interface is capable of multipoint connections. The sample applications (see below) indicate the possible uses for the converters: Connection of an RS-232 master interface to an RS-485 2-wire bus system. Setting up a connection between up to 32 RS-232 interfaces. This structure is capable of multipoint connections. The converters operate irrespective of protocol and with code transparency, i.e. all bus stations have to support the same transmission protocol and speed. When several RS-232 stations are networked, it must also be possible to have software addressing of the stations. Half-duplex control of the RS-485 2wire interface requires one control line from the RS-232 interface. There is a choice of two design types depending on the installation location (whether in the switch cabinet or directly on the PC): 1. PSM Switch Cabinet Devices The interface converter PSM-EG.. carries out the function of interface conversion in an industrial version for the switch cabinet. In order to cope with the harsh EMC conditions to which bus systems are exposed, the RS-485 interface in the peripherals has high-grade galvanic isolation against both the RS-232 interface and the supply voltage with 2.5 kV. In addition, a protection circuit discharges transient interference to ground potential in a targeted fashion. The module is powered with 24 V DC ( 20 %) and converts the RS-232 TxD/RxD transmit and receive channel for transmission speeds of up to 64 kbit/s. The bus terminating resistor can be switched on using a coding switch. Data transmission takes place in half-duplex operation. The data flow direction of the RS-485 interface is changed over using one of the RS-232 control lines: - in DTE devices: RTS, - in DCE devices: CTS. (The DTE/DCE switch makes the adaptation so that one RS-232 1:1 connection is sufficient.) The logical allocation of control information corresponds to the following: An internal plug-in bridge also permits inverted control. Please contact us if the RS-232 interface does not provide this control line. We"ve got a solution as well. The connection can either be via a SUB-D plug connector or by means of pluggable screw terminal blocks. An integrated data indicator provides a dynamic display of transmit and receive data. 2. PSM Plug Modules PSM-V24... modules are directly attached to the 25-pin SUB-D connection of the RS-232 device interface. It is possible to select from male and female versions (types ...SB and ...BB). The 9/25-pin PSM-KAD... adapter cable is available for connecting to 9-pin interfaces. The integrated coding switch permits universal applicability on DTE or DCE interfaces. Data channels TxD/RxD are transmitted. The data flow direction of the RS-485 interface is changed over using RS-232 DTR control channel. The following logical allocation applies to PSM-V24/.../I modules: DTR log.1 (> +3V) = RS-485 transmit DTR log.0 (< -3V) = RS-485 receive All other plug modules operate with a control function which is the inverse of this one.
log. 1 (> +3V) = RS-485 transmit mode log. 0 (< -3V) = RS-485 receive mode The modules without electrical isolation are predominantly used for electrical adaptation over short distances. The use of electrical isolation is always recommended for transmission links in excess of 100 m. Such isolation is implemented in the PSM-V24/RS485-P... modules. All plug modules are powered via a separate plug-in power supply unit, or alternatively through the RS232 interface, pin 18/7.
You might also like
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- RS232/RS485 Converter User GuideDocument2 pagesRS232/RS485 Converter User GuideKamal FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Communicationgfk 2220 ADocument35 pagesCommunicationgfk 2220 AvishartNo ratings yet
- C2-RS232-RS422-RS485-phan 3Document25 pagesC2-RS232-RS422-RS485-phan 3Duc Tri Bui100% (2)
- Silo - Tips Modbus Rtu Master CommunicationsDocument35 pagesSilo - Tips Modbus Rtu Master CommunicationsAhmed TalaatNo ratings yet
- HXSP-485 RS-232 RS-485 UserManual PDFDocument2 pagesHXSP-485 RS-232 RS-485 UserManual PDFAzito JumNo ratings yet
- Rs 232 & Rs 422 StandardDocument27 pagesRs 232 & Rs 422 Standardpalak parmar100% (3)
- Selecting and Using RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485 Serial Data StandardsDocument9 pagesSelecting and Using RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485 Serial Data StandardssoumyajitemdmNo ratings yet
- HXSP-485B DatasheetDocument1 pageHXSP-485B DatasheetErnane FreitasNo ratings yet
- Modbus Master Comm Manual GFK2220CDocument38 pagesModbus Master Comm Manual GFK2220Ckotia_sanjayNo ratings yet
- UT 201user ManualDocument1 pageUT 201user ManualIkhsan Cangkoi BurongNo ratings yet
- Phoenix ConverterDocument12 pagesPhoenix Convertereeng_nnabilNo ratings yet
- RS232 485 FundamentalDocument17 pagesRS232 485 Fundamentalknani9090100% (1)
- Modbus ProtocolDocument32 pagesModbus ProtocolwilliamIINo ratings yet
- DIAGRAMA Conversor R232 422Document5 pagesDIAGRAMA Conversor R232 422Gregg JamesNo ratings yet
- cs1520 Manual PDFDocument6 pagescs1520 Manual PDFJames AshNo ratings yet
- 398644875238424558571001109498an740 0Document8 pages398644875238424558571001109498an740 0api-27535945No ratings yet
- STM422 RS232 To RS485-RS422 Interface Converter User GuideDocument2 pagesSTM422 RS232 To RS485-RS422 Interface Converter User GuideMojixNo ratings yet
- Serial Port Pinout of GE PLCDocument15 pagesSerial Port Pinout of GE PLCAldo PerdomoNo ratings yet
- ATC-108 User's ManualDocument0 pagesATC-108 User's ManualMaitry ShahNo ratings yet
- RS232 485 FundamentalDocument47 pagesRS232 485 FundamentalSanket Karnik100% (3)
- Serial Port Pinout of GE PLCDocument15 pagesSerial Port Pinout of GE PLCAbde EsselamNo ratings yet
- ATC-277MM User's ManualDocument0 pagesATC-277MM User's ManualMaitry ShahNo ratings yet
- RS 485Document6 pagesRS 485Venkatesh Venkataramani100% (1)
- RS485 InglesDocument10 pagesRS485 InglesFernando PaladinoNo ratings yet
- CONV485E CONV485E/M: Rs-485 To Ethernet Tcp/Ip ConverterDocument3 pagesCONV485E CONV485E/M: Rs-485 To Ethernet Tcp/Ip Converter100limite2182No ratings yet
- HXSP-2108B RS-232/RS-485/RS-422 Converter Instruction: SpecificationDocument2 pagesHXSP-2108B RS-232/RS-485/RS-422 Converter Instruction: SpecificationAria SudarmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Serial Data CommunicationsDocument29 pagesChapter 6 - Serial Data CommunicationshuynhtrinhNo ratings yet
- RS-232 To RS-485: User ManualDocument6 pagesRS-232 To RS-485: User ManualEdward MainaNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between The RS-232 and RS-485 Serial Interfaces?Document7 pagesWhat's The Difference Between The RS-232 and RS-485 Serial Interfaces?santanu_sinha87100% (2)
- An 2Document7 pagesAn 2Carlos H. GojleviciusNo ratings yet
- Figure 3.2. RS-485 BusDocument42 pagesFigure 3.2. RS-485 BusMichal Cousins100% (1)
- RS 232 Specification StandardDocument9 pagesRS 232 Specification StandardTetsusaigaNo ratings yet
- RS 485Document5 pagesRS 485Vasily Ignatov100% (3)
- RS232-485 FundamentalDocument17 pagesRS232-485 Fundamentalh.torabyNo ratings yet
- I O PinoutDocument5 pagesI O PinoutDanang KartikaNo ratings yet
- ATC-105 User's ManualDocument0 pagesATC-105 User's ManualMaitry Shah100% (1)
- Serial Port InterfacingDocument5 pagesSerial Port Interfacingyampire100% (1)
- All IBM PC and Compatible Computers Are Typically Equipped With Two Serial Ports and One Parallel PortDocument16 pagesAll IBM PC and Compatible Computers Are Typically Equipped With Two Serial Ports and One Parallel Port452bobNo ratings yet
- RS485 To RS232 Converter - AquaticusDocument5 pagesRS485 To RS232 Converter - AquaticusSarai LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Parallel To Serial or Serial To Parallel Converter: Model 232SPS2Document1 pageParallel To Serial or Serial To Parallel Converter: Model 232SPS2vjNo ratings yet
- PSM-ME-RS232/RS485-P: Interface Converter RS-232 For RS-485 2/4-Wire or RS-422Document16 pagesPSM-ME-RS232/RS485-P: Interface Converter RS-232 For RS-485 2/4-Wire or RS-422Dario AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Using The Series 8130 RTU With FMDocument14 pagesUsing The Series 8130 RTU With FMАлександрNo ratings yet
- UMSN101ADocument4 pagesUMSN101AClaudiuNo ratings yet
- Comms WiresDocument10 pagesComms WiresBDNo ratings yet
- Max 232Document1 pageMax 232vvinodkumarvNo ratings yet
- ATC-277SM User's ManualDocument2 pagesATC-277SM User's ManualMaitry ShahNo ratings yet
- Rs-232 Interface: Computer TerminalDocument4 pagesRs-232 Interface: Computer TerminalJames MojicaNo ratings yet
- RS-422 and RS-485 Application Note: Balanced Line DriversDocument23 pagesRS-422 and RS-485 Application Note: Balanced Line DriversMarinel123No ratings yet
- Application Guide: Data Communications ReferenceDocument2 pagesApplication Guide: Data Communications Referencekamran719No ratings yet
- Universal Isolated Interface Converter: Eurotherm OntrolsDocument4 pagesUniversal Isolated Interface Converter: Eurotherm OntrolszacriasNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Electrical Interface and ModemDocument71 pagesTopic 2 Electrical Interface and ModemsuhailiNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference FOR RS485, RS422, RS232 AND RS423Document3 pagesQuick Reference FOR RS485, RS422, RS232 AND RS423Radharaman Das100% (1)
- Microcontroller Programming: D.Thulasi Contract Lecturer ECE Quli Qutubshah Government PolytechnicDocument11 pagesMicrocontroller Programming: D.Thulasi Contract Lecturer ECE Quli Qutubshah Government Polytechnicsairam dastariNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Serial RS485 and RS232Document7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Serial RS485 and RS232jackNo ratings yet
- VPI-VSI Communications ManualDocument39 pagesVPI-VSI Communications ManualIasm1neNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between The RS-232 and RS-485 Serial Interfaces?Document7 pagesWhat's The Difference Between The RS-232 and RS-485 Serial Interfaces?Pranjali patil100% (1)
- 3202 SPD 703 1.PDF&IsFromRegistration 1Document2 pages3202 SPD 703 1.PDF&IsFromRegistration 1senthil_bsnl06No ratings yet
- RS 485 WikipediaDocument6 pagesRS 485 Wikipediamarcos_visNo ratings yet
- Communication Media & Protocol Selection: DCE and DTE DevicesDocument6 pagesCommunication Media & Protocol Selection: DCE and DTE Devicesmohed_kamal100% (1)
- 2t Per Hour Horizontal Mixer and Hammer Mill Group1Document2 pages2t Per Hour Horizontal Mixer and Hammer Mill Group1Prince AsifNo ratings yet
- Valuka Feeds Crab ReportDocument2 pagesValuka Feeds Crab ReportPrince AsifNo ratings yet
- Valuka Feeds Crab ReportDocument2 pagesValuka Feeds Crab ReportPrince AsifNo ratings yet
- Company A Plus Industries LTDDocument11 pagesCompany A Plus Industries LTDPrince AsifNo ratings yet
- General Member: Dyeing-Printing-FinishingDocument14 pagesGeneral Member: Dyeing-Printing-FinishingPrince AsifNo ratings yet
- IT Requirements Paper For Library Management System TemplateDocument23 pagesIT Requirements Paper For Library Management System TemplateSaadi FaidNo ratings yet
- CERT-PH Incident Reporting and Technical Assistance Request GuidelinesDocument13 pagesCERT-PH Incident Reporting and Technical Assistance Request GuidelinesJaico DictaanNo ratings yet
- Iridium Openport ManualDocument44 pagesIridium Openport ManualZakaria ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 51talk Training Reminders (Self-Access NTT + Live NTT) PDFDocument6 pages51talk Training Reminders (Self-Access NTT + Live NTT) PDFMary GraceNo ratings yet
- II Unit 26Document1 pageII Unit 26LOLEKNo ratings yet
- Hwi D121HDocument5 pagesHwi D121HRicardo HolleroNo ratings yet
- JACE 8000 DS New TridiumDocument6 pagesJACE 8000 DS New TridiumMyke KingNo ratings yet
- Infinera Ds TM 3000 - II ChassisDocument3 pagesInfinera Ds TM 3000 - II Chassism3y54mNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Certbus AZ-300 2019-11-15 by Macolm Sing 266Document19 pagesMicrosoft Certbus AZ-300 2019-11-15 by Macolm Sing 266Evan0% (1)
- Sprint DG OMADM ATcommandsDocument7 pagesSprint DG OMADM ATcommandssichale13No ratings yet
- BACnet Aplication GuideDocument502 pagesBACnet Aplication GuideLaercio Marques100% (3)
- Building Mod Auth Radius 2.0Document2 pagesBuilding Mod Auth Radius 2.0Zeljko PetakNo ratings yet
- Gmail - Harish Crackers-Thank You For Your OrderDocument2 pagesGmail - Harish Crackers-Thank You For Your OrderARAVINDH RNo ratings yet
- Puteractive Issue656,26April9May2023Document76 pagesPuteractive Issue656,26April9May2023Keith PlummerNo ratings yet
- SINAMICS DC Converter ManualDocument706 pagesSINAMICS DC Converter Manualmostafa3133% (3)
- SLM FlowchartDocument1 pageSLM FlowchartDurgaprasad PandaNo ratings yet
- Router and VPN Client For Public Internet On A Stick Configuration ExampleDocument9 pagesRouter and VPN Client For Public Internet On A Stick Configuration ExamplenthecuongNo ratings yet
- Daddy Finger Where Are You Finger Family Song + More Nursery Rhymes & Kids Songs - GoBooBoo - YouTubeDocument1 pageDaddy Finger Where Are You Finger Family Song + More Nursery Rhymes & Kids Songs - GoBooBoo - YouTubeNaomi TampubolonNo ratings yet
- BASIC 5 - Final ExamDocument5 pagesBASIC 5 - Final ExamEdrickNo ratings yet
- Oma TS MLP V3 - 3 20091001 CDocument134 pagesOma TS MLP V3 - 3 20091001 CCamilo jimenezNo ratings yet
- Deeply Fully WhollyDocument4 pagesDeeply Fully WhollypilgrimNo ratings yet
- Word Files Email InfoDocument1 pageWord Files Email Infoapi-3700469No ratings yet
- Hyderabad International Convention CentreDocument31 pagesHyderabad International Convention CentreHarshini PNo ratings yet
- Country Study: Ethiopia. This Source Contains An Entire Book Dedicated To The Role ofDocument6 pagesCountry Study: Ethiopia. This Source Contains An Entire Book Dedicated To The Role ofapi-318870684No ratings yet
- Negative Impacts of Social Media.. HafsaDocument4 pagesNegative Impacts of Social Media.. HafsaMorning QueensNo ratings yet
- MOSXApp Programming GuideDocument92 pagesMOSXApp Programming Guideferkys77No ratings yet
- HE - LOCAL-GUIDING - GR12 - Q1 - MODULE 5 For TeacherDocument18 pagesHE - LOCAL-GUIDING - GR12 - Q1 - MODULE 5 For TeacherNhatz Gallosa Marticio100% (4)
- Suda Lexico - Suida Lexicon PDFDocument1,316 pagesSuda Lexico - Suida Lexicon PDFde Damasco100% (1)
- Campus Network Design Using Cisco Packet Tracer: Mini Project-2 (2020-21)Document35 pagesCampus Network Design Using Cisco Packet Tracer: Mini Project-2 (2020-21)arya0% (1)
- Advanced Mobile Marketing - Section 7 SlidesDocument91 pagesAdvanced Mobile Marketing - Section 7 SlidesSAURABH BHANDARINo ratings yet