Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7
Uploaded by
alexcw92Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7
Uploaded by
alexcw92Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table
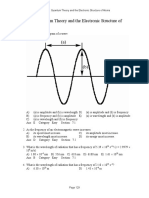
MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A photon of light has a frequency of 3.26 1015 hertz (hertz =1/s). What is its wavelength? The speed of light is 3.00 108 m/s. a. 1.09 107 nm b. 9.78 1014 nm c. 978 nm d. 109 nm e. 92.0 nm ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: 7.1 Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter
2. Light has a frequency of 7.21 1013 hertz. What is its wavelength? The speed of light is 3.00 108 m/s. a. 2.16 109 nm b. 2.40 105 nm c. 4.16 103 nm d. 2.40 104 nm e. 4.16 106 nm ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: 7.1 Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter
3. Light has a wavelength of 444 nm. What is its frequency? The speed of light is 3.00 108 m/s. a. 1.48 106 Hz b. 1.48 1015 Hz c. 1.48 102 Hz d. 6.76 1014 Hz e. 6.76 104 Hz ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: 7.1 Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter
4. Light has a wavelength of 582 nm. What is its frequency? The speed of light is 3.00 108 m/s. a. 1.75 1020 Hz b. 5.15 1014 Hz c. 1.94 1013 Hz d. 1.94 103 Hz e. 1.75 102 Hz ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: 7.1 Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter
5. Which of the following statements is/are correct? I. The frequency of light is the number of waves that pass a given point in a second. II. The shorter the wavelength of light, the greater its energy. III. The wavelength of light increases as the frequency increases. a. b. c. d. e. I only II only III only I and II II and III
ANS: D
PTS: 1
TOP: 7.1 Electromagnetic Radiation and Matter
6. Arrange the following four electromagnetic spectral regions in order of decreasing energy. visible X-ray microwave radio a. microwave, radio, X-ray, visible b. microwave, visible, X-ray, radio c. radio, visible, X-ray, microwave d. X-ray, radio, visible, microwave e. X-ray, visible, microwave, radio ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: 7.2 Planck's Quantum Theory
7. Which wavelength of light is the fastest? a. 418.6 nm b. 554.9 nm c. 626.1 nm d. 563.8 nm e. All have the same speed. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: 7.2 Planck's Quantum Theory
8. What is the phenomenon that occurs when excited gaseous elements emit only a few colored lines? a. Planck's constant b. photoelectric effect c. line spectrum d. quantum theory e. electromagnetic spectrum ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: 7.2 Planck's Quantum Theory
9. Which statement about light is true? a. It oscillates back and forth between wave and particle-like behavior. b. It exhibits both wave and particle-like behavior at the same time. c. It has neither wave nor particle-like behavior. d. It behaves as a particle only. e. It behaves as a wave only. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: 7.2 Planck's Quantum Theory
10. Determine the energy of a photon that has a frequency of 5.23 1014 Hz. Given: h = 6.63 1034 J s. a. 1.27 1048 J b. 1.16 1027 J c. 3.47 1019 J d. 1.04 1010 J e. 7.87 1047 J ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: 7.2 Planck's Quantum Theory
11. Determine the energy of a photon that has a wavelength of 488 nm. The speed of light is 3.00 108 m/s and h = 6.63 1034 J s. a. 1.63 1015 J b. 4.08 1019 J c. 9.71 1023 J d. 4.08 1028 J
e. 4.52 1036 J ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: 7.2 Planck's Quantum Theory
12. What is a photon? a. light that comes from a cathode ray tube b. a high speed electron that gives off light when it strikes an object c. very high frequency light d. very long wavelength light e. a massless "particle" or bundle of energy that moves at the speed of light ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: 7.2 Planck's Quantum Theory
13. Which of the following is not a characteristic of the Bohr model of the atom? a. Orbits have any radii. b. An electron is restricted to specific energy levels around the nucleus. c. Each orbit has a discrete energy associated with it. d. An electron is located in an orbit around the nucleus. e. Orbits have a defined circumference. ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: 7.3 The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom
14. According to the Bohr model for the hydrogen atom, the energy necessary to excite an electron from n = 2 to n = 3 is ________ the energy necessary to excite an electron from n = 3 to n = 4. a. equal to b. less than c. more than d. either less than or equal to e. either more than or equal to ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: 7.3 The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom
15. What is a major shortcoming of the Bohr model? a. It explains the spectral characteristics of hydrogen. b. It accounts for the existence of line spectra. c. It requires that the energy in the atom be quantized. d. It implies that a one electron system can have four colors of light in its line spectrum. e. It does not deal with multielectron atoms. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: 7.3 The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom
16. Which idea was proposed by Louis de Broglie? a. Electrons are located in orbits. b. Small particles, such as electrons, move in waves. c. Energy in the atom is quantized. d. Electrons have clockwise or counter-clockwise spins. e. Excited state orbits have higher energy than ground state orbits. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: 7.4 Beyond the Bohr Model: The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom 17. Which idea was proposed by Werner Heisenberg? a. Certain metals emit electrons when illuminated by light with low enough wavelength. b. Light waves passing through a diffraction parting produce a diffraction pattern. c. Light waves have particle properties, and particles of matter have wave-like properties. d. Photons used to determine the location of electrons have no measurable effect on
electrons. e. Simultaneously determining the exact momentum and exact position of an electron is impossible. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: 7.4 Beyond the Bohr Model: The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom 18. Which statement regarding an orbital is false? a. An orbital is three dimensional. b. Only one electron is allowed per orbital. c. An electron shell consists of a collection of orbitals with the same principal quantum number. d. An orbital may be designated with the letters s, p, d, f. e. An orbital boundary surface would need to be infinitely large to guarantee that an electron would always be found inside the orbital. ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 19. Match the names of the four quantum numbers with their symbols. Orbital magnetic principal spin a. n, l, ml, ms b. l, ms, n, ml c. ml, ms, l, n d. l, ml, n, ms e. ml, l, n, ms ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 20. Which word or phrase least applies to the quantum number represented by the symbol n? a. shell b. size c. principal d. distance from nucleus e. shape ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 21. Which word or phrase least applies to the quantum number represented by the symbol l? a. subshell b. s, p, d, f c. azimuthal d. orientation e. shape ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 23. Which azimuthal (orbital) quantum numbers can exist for n = 3? a. l = 0 b. l = 0, 1 c. l = 0, 1, 2 d. l = 0, 1, 2, 3
e. l = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 24. If l = 2, what value can ml have? a. ml = 0, +1, +2 b. ml = +1 c. ml = +2 d. ml = 2, 1, 0, +1, +2 e. ml = 1, 0, +1 ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 25. How many electrons can the third principal quantum level hold? a. 2 b. 8 c. 16 d. 18 e. 32 ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 26. How many orbitals are contained in the 4d subshell? a. 2 b. 5 c. 6 d. 10 e. 14 ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 27. How many electrons can be contained in the 2p subshell? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4 e. 6 ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 28. Which statement is true? a. The 3d orbitals have lower energy than the 2p orbitals. b. The 4p orbitals hold more electrons than the 3d orbitals. c. The 2p orbitals hold up to 6 electrons. d. Two electrons in the 1s orbital will have the same spin. e. The p orbitals occur in groups of 5. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 29. The d orbitals occur in groups of __________ and hold up to __________ electrons.
a. b. c. d. e.
3, 6 4, 8 5, 10 6, 12 7, 14
ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 30. Which set of quantum numbers is not allowed? a. n = 0, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +1/2 b. n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +1/2 c. n = 2, l = 1, ml = 1, ms = +1/2 d. n = 3, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = +1/2 e. n = 4, l = 3, ml = 0, ms = 1/2 ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: 7.5 Quantum Numbers, Energy Levels and Atomic Orbitals 31. Which type of atomic orbital has two lobes of electron density? a. s b. p c. d d. s and p e. p and d ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: 7.6 Shapes of Atomic Orbitals
32. What is the correct electron configuration for beryllium (Be)? a. 1s22s2 b. 1s22s22p1 c. 1s22s22p2 d. 1s22s22p4 e. 1s22s22p6 ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: 7.7 Atom Electron Configurations
33. What is the correct electron configuration for aluminum? a. 1s22s1 b. 1s22s22p43s23p3 c. 1s22s22p63s23p1 d. 1s22s22p23s23p23d24s1 e. 1s22s22p23s23p24s25s1 ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: 7.7 Atom Electron Configurations
34. What is the correct electron configuration for gallium? a. 1s22s22p63s23p1 b. 1s22s22p63s23p64s24p1 c. 1s22s22p63s23p64s24d104p1 d. 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p1 e. 1s22s22p63s23p63d104p3 ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: 7.7 Atom Electron Configurations
35. Give the element that has the electron configuration:
a. b. c. d. e.
1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p65s2 In Pd Fe Ni Sr PTS: 1 TOP: 7.7 Atom Electron Configurations
ANS: E
36. Which of the following corresponds to the electron configuration of a noble gas? a. 1s22s2 b. 1s22s22p4 c. 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p2 d. 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p3 e. 1s22s22p63s23p6 ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: 7.7 Atom Electron Configurations
37. What is the correct shorthand notation for the electron configuration given? 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s2 a. [Ar]5s2 b. [Ar]3s23p63d104p65s2 c. [Ca]3d104p65s2 d. [Kr]5s2 e. [Rb]5s1 ANS: D PTS: 1 TOP: 7.7 Atom Electron Configurations
38. What is the electron configuration of arsenide ion, As3? a. 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 b. 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s2 c. 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p6 d. 1s22s22p63s23p64s24d10 e. 1s22s22p63s23p64s24d104p6 ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: 7.8 Ion Electron Configurations
39. What is the electron configuration of O2? a. 1s22s22p5 b. 1s22s22p6 c. 1s22s22p4 d. 1s22s22p2 e. 1s22s22p3 ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: 7.8 Ion Electron Configurations
40. What is the electron configuration of Li+? a. 1s1 b. 1s2 c. 1s22s1 d. 1s22s2 e. 1s22s22p1 ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: 7.8 Ion Electron Configurations
41. What is the electron configuration of Al3+?
a. b. c. d. e.
1s22s22p5 1s22s22p4 1s22s22p2 1s22s22p6 1s22s22p63s23p1 PTS: 1 TOP: 7.8 Ion Electron Configurations
ANS: D
42. Which one of the following does not have the electron configuration [Ne]3s23p6? a. Ar b. Br c. Ca2+ d. Cl e. K+ ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: 7.8 Ion Electron Configurations
43. Substances that have the same electron configuration are: a. paramagnetic. b. diamagnetic. c. ferromagnetic. d. lanthanides. e. isoelectronic. ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: 7.8 Ion Electron Configurations
44. Arrange the elements given in order from largest to smallest atomic radii. K Ne Ar Na P a. Ar > K > Na > Ne >P b. K > Ar > P > Na > Ne c. Ar > P > Na > Ne > K d. Ne > Ar > P > Na > K e. K > Na > P > Ar > Ne ANS: E PTS: 1 TOP: 7.9 Periodic Trends: Atomic Radii
45. Which of the following has the largest ionic radius? a. Na+ b. F c. P3 d. K+ e. Cl ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: 7.10 Periodic Trends: Ionic Radii
46. Which statement is false? a. Br is larger than Kr. b. Cl is smaller than S2. c. K+ is smaller than Ar. d. Mg2+ is smaller than Ca2+. e. N3 is larger than Ne. ANS: C PTS: 1 TOP: 7.10 Periodic Trends: Ionic Radii
47. Which element has the largest first ionization energy? a. Be b. Ca c. Mg d. Sr e. Ba ANS: A PTS: 1 TOP: 7.11 Periodic Trends: Ionization Energies
48. Arrange the following in order of increasing ionization energy. Ar Cl Li Na P a. P < Cl < Ar < Li < Na b. Na < Li < P < Cl < Ar c. Ar < Cl < Na < Li < P d. Cl < Ar < Na < Li < P e. P < Cl < Ar < Na < Li ANS: B PTS: 1 TOP: 7.11 Periodic Trends: Ionization Energies
You might also like
- ExChEL Group Study Session 13 - Day 1 ExaminationDocument15 pagesExChEL Group Study Session 13 - Day 1 ExaminationRochelle Louise SampagaNo ratings yet
- MCQ CharacterizationDocument18 pagesMCQ CharacterizationAmjed AL-KAHTEEB100% (2)
- Quiz Bootcamp08practicelightelectronconfigurationfa18 1Document5 pagesQuiz Bootcamp08practicelightelectronconfigurationfa18 1api-233552637No ratings yet
- ExamQuestionsTroChapter7 8 TrimmedDocument8 pagesExamQuestionsTroChapter7 8 TrimmedAli TarekNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Chemical Reactivity 9th Edition Kotz Test Bank DownloadDocument15 pagesChemistry and Chemical Reactivity 9th Edition Kotz Test Bank DownloadTodd Dean100% (23)
- CentralDocument10 pagesCentralwondimuNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2Nd Edition by Zumdahl Isbn 1305079248 9781305079243 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2Nd Edition by Zumdahl Isbn 1305079248 9781305079243 Full Chapter PDFmarc.herman362100% (12)
- Chang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 7Document10 pagesChang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 7haha_le12No ratings yet
- Review - 2018 - Final ExamDocument3 pagesReview - 2018 - Final ExamQuang LinhNo ratings yet
- EDocument13 pagesESultan Hadi PrabowoNo ratings yet
- CH Atomic StructureDocument30 pagesCH Atomic StructureOP HBSNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Ch. 7: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument26 pagesPractice Questions For Ch. 7: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionPaolo PepsNo ratings yet
- Question Bank CHEM 1201Document12 pagesQuestion Bank CHEM 1201SHASHANK VISHWAKARMANo ratings yet
- WS Chap11 ParkDocument6 pagesWS Chap11 ParkporesNo ratings yet
- WS - Honors Atomic Theory WSDocument9 pagesWS - Honors Atomic Theory WSsquattingm0nkeysNo ratings yet
- Problems 42Document12 pagesProblems 42Maurice KingNo ratings yet
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch36 Test BankDocument10 pagesWolfson Eup3 Ch36 Test BankifghelpdeskNo ratings yet
- Correct Answer: ADocument10 pagesCorrect Answer: ALara AminNo ratings yet
- Chapter 38 - Photons and Matter WavesDocument12 pagesChapter 38 - Photons and Matter WavesVV Cephei100% (1)
- 12U Quantum Mechanics P-SetDocument5 pages12U Quantum Mechanics P-SetTariq ZaitounNo ratings yet
- Support Material Class 11 L-2Document8 pagesSupport Material Class 11 L-2Sarnitha RaghunathNo ratings yet
- Horizons Exploring The Universe Enhanced 13th Edition Seeds Test Bank 1Document15 pagesHorizons Exploring The Universe Enhanced 13th Edition Seeds Test Bank 1vincenza100% (41)
- Horizons Exploring The Universe Enhanced 13Th Edition Seeds Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument46 pagesHorizons Exploring The Universe Enhanced 13Th Edition Seeds Test Bank Full Chapter PDFelizabeth.hayes136100% (13)
- Test Bank Chapter 7Document8 pagesTest Bank Chapter 7aya.alkhateeb28No ratings yet
- CH 07Document36 pagesCH 07LAVTOLNo ratings yet
- Chem Basic FB Answer Key CH 05 (06.13.16)Document6 pagesChem Basic FB Answer Key CH 05 (06.13.16)amalieroNo ratings yet
- CHM 420 Question (Chapter 3) Atomic Structure & Quantum Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pagesCHM 420 Question (Chapter 3) Atomic Structure & Quantum Electromagnetic WavesFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Exam1 PracticeDocument9 pagesExam1 PracticeTruong Cai100% (1)
- MSE160 Custom Textbook SolutionsDocument541 pagesMSE160 Custom Textbook Solutionstal4444No ratings yet
- 02 Smith 2e CH 02Document2 pages02 Smith 2e CH 02Sidney TyNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet OneDocument3 pagesWork Sheet Onekaleb asegdewNo ratings yet
- Rays From Copper Is - What Is The EnergyDocument1 pageRays From Copper Is - What Is The Energysaifi_786No ratings yet
- Homework Set3 ParticlenatureofmatterDocument2 pagesHomework Set3 Particlenatureofmatteryobrosky0% (1)
- One Mark QuestionsDocument4 pagesOne Mark Questionshari95No ratings yet
- Chem 11 2016 WorksheetDocument4 pagesChem 11 2016 Worksheettemesgenor21No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 10th Edition Ebbing Test BankDocument38 pagesGeneral Chemistry 10th Edition Ebbing Test Bankrickeybrock6oihxNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 10Th Edition Ebbing Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument42 pagesGeneral Chemistry 10Th Edition Ebbing Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDebraPricemkw100% (12)
- CH 2 Question Upto Quantum NumberDocument6 pagesCH 2 Question Upto Quantum NumberibtihazaryanNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Physics Chapter 5 - Teacher'sDocument12 pagesForm 5 Physics Chapter 5 - Teacher'sPavithiran100% (5)
- Chemistry - I - 1, 2, 4,11,12Document78 pagesChemistry - I - 1, 2, 4,11,12SubhanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Chapter 7Document8 pagesTest Bank Chapter 7teafNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation and Electronic StructureDocument3 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation and Electronic StructureAjay NaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 Atomic Physics: The Hydrogen Atom The Bohr Model Electron Waves in The AtomDocument64 pagesChapter 28 Atomic Physics: The Hydrogen Atom The Bohr Model Electron Waves in The Atomvivekrajbhilai5850No ratings yet
- Chapter 42 - Nuclear PhysicsDocument14 pagesChapter 42 - Nuclear PhysicsVV Cephei100% (3)
- Chemistry Teacher Book Chapter 5.1Document6 pagesChemistry Teacher Book Chapter 5.1BryceWallsNo ratings yet
- CHM 111 QuestionsDocument22 pagesCHM 111 QuestionsBABATIMILEYIN OLLANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Atomic Structure - ExercisesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Atomic Structure - ExercisesHÂN ĐOÀN HUỲNH NGỌCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Quantum Mechanics-4Document3 pagesChapter 7 - Quantum Mechanics-4Larry MolinerosNo ratings yet
- Atoms in Electrons Practice TestDocument11 pagesAtoms in Electrons Practice TestFlowery SamaranayakeNo ratings yet
- Akaki Adventist School Work Sheet For Grade 12 Chemistry From Grade 11chemistry Unit Two Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument4 pagesAkaki Adventist School Work Sheet For Grade 12 Chemistry From Grade 11chemistry Unit Two Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableYonilo memeloNo ratings yet
- Supplementary ProblemsDocument30 pagesSupplementary ProblemsMike PatenaudeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document18 pagesChapter 7roxy8marie8chanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Exercises by ResonanceDocument35 pagesAtomic Structure Exercises by Resonancechiragjn12086% (7)
- Chapter 8 The Quantum Mechanical AtomDocument18 pagesChapter 8 The Quantum Mechanical Atomsadaf yousafzaiNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Six of The Eight Questions. Only The RST Six Solutions Will Be GradedDocument11 pagesAnswer Any Six of The Eight Questions. Only The RST Six Solutions Will Be Gradedsaliya_kumaraNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure WorksheetDocument7 pagesAtomic Structure WorksheetXB44.SouraTanay RoyNo ratings yet
- hss17c0400t Ir ReviewDocument5 pageshss17c0400t Ir ReviewLara AminNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Important Question Answer of Chapter 2 (Structure of Atom) &chapter 3 (Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument38 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Important Question Answer of Chapter 2 (Structure of Atom) &chapter 3 (Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Propertiessriram.j.athreyaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Structure of Atom Important Questions With AnswersDocument16 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Structure of Atom Important Questions With AnswersPriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Optics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandOptics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Kinetics Prelim Take Home Exam December 25 2017Document2 pagesKinetics Prelim Take Home Exam December 25 2017Michelle Mendoza100% (1)
- Hydrolysis-Condensation Processes of The Tetra-Alkoxysilanes TPOS, TEOS and TMOS in Some Alcoholic SolventsDocument13 pagesHydrolysis-Condensation Processes of The Tetra-Alkoxysilanes TPOS, TEOS and TMOS in Some Alcoholic SolventssorescuNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal Oxide Nanoparticles As Efficient Catalysts in OxidationDocument30 pagesTransition Metal Oxide Nanoparticles As Efficient Catalysts in Oxidationdoctorji1925No ratings yet
- Optical Lithography PDFDocument16 pagesOptical Lithography PDFprashn80No ratings yet
- Thermal Physics IB Physics: Topic 3 & Option CDocument55 pagesThermal Physics IB Physics: Topic 3 & Option CMoiz Dhanerawala100% (1)
- Knowledge For Global DevelopmentDocument138 pagesKnowledge For Global Developmentsedinst100% (1)
- 01 - What Is The S3 ScannerDocument4 pages01 - What Is The S3 ScannerViet PhanNo ratings yet
- The Colloidal State: (I) Crystalloids (Ii) ColloidsDocument12 pagesThe Colloidal State: (I) Crystalloids (Ii) Colloidssrimant kumarNo ratings yet
- F 2129 - 04 - RjixmjkDocument8 pagesF 2129 - 04 - RjixmjkPrakash MakadiaNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Chemistry Unit 2 NotesDocument18 pagesAQA A Level Chemistry Unit 2 NotesMuadh Chati100% (2)
- Industrial Refrigeration TrainerDocument2 pagesIndustrial Refrigeration TrainerEugine BalomagaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Thermofluid MechanicsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Thermofluid MechanicsLaki ENNo ratings yet
- Salt Analysis 2 - Al2 (SO4) 3Document3 pagesSalt Analysis 2 - Al2 (SO4) 3mystical moonbeamNo ratings yet
- Ijertv2is80230 6Document13 pagesIjertv2is80230 6emad hayekNo ratings yet
- PH MeterDocument5 pagesPH MeterMd.Tanvirul EhsanNo ratings yet
- H2SO4 AspenDocument6 pagesH2SO4 AspenMohammadTahaAmmarNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Temperature, Pressure and Density As Function of The Height Above Sea LevelDocument53 pagesAtmospheric Temperature, Pressure and Density As Function of The Height Above Sea LevelMustafa TıraşNo ratings yet
- Working With Non-Ideal Gases PDFDocument3 pagesWorking With Non-Ideal Gases PDFpolaris44No ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Modern PhysicsDocument88 pagesChapter - 3 Modern PhysicsMehedi Hasan FoysalNo ratings yet
- Quantum DotDocument127 pagesQuantum DotmelprvnNo ratings yet
- Tasco Q&aDocument386 pagesTasco Q&aMai PhamNo ratings yet
- Ions and Radicals TextDocument3 pagesIons and Radicals Textameerfati76No ratings yet
- Furfuryl Alcohol A Versatile, Eco Sustainable Compound in PerspectiveDocument17 pagesFurfuryl Alcohol A Versatile, Eco Sustainable Compound in PerspectiveTalha Nibras AliNo ratings yet
- 7 AtmosphereDocument38 pages7 AtmosphereNaveen PillaiNo ratings yet
- Curing Characteristics of Low Emission Urea-Formaldehyde Adhesive in The Presence of WoodDocument13 pagesCuring Characteristics of Low Emission Urea-Formaldehyde Adhesive in The Presence of WoodNam Phạm VănNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Mixture 5 - 6 10-1Document3 pagesCharacteristics of Mixture 5 - 6 10-1Jeanette Saligo AlvarNo ratings yet
- CHE506 - Lab Report On Plug Flow ReactorDocument25 pagesCHE506 - Lab Report On Plug Flow Reactorfiorella50% (2)
- Lean Oil Absorption 02Document14 pagesLean Oil Absorption 02Shri JrNo ratings yet
- Study On The Heat Load Characteristics of Underground StructuresDocument9 pagesStudy On The Heat Load Characteristics of Underground StructureskylealamangoNo ratings yet