Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bits
Uploaded by
mkr518Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bits
Uploaded by
mkr518Copyright:
Available Formats
SSC Physics imp bits with answers
Student Name:. Ananda B.Tech Parents Signature:.. pluscoaching@ovi.com 98664 00174
PLUS COACHING CENTRE
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
1. MEASUREMENT OF LENGTH
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Smallest length that can be measured accurately using any scale is called _________________ Screw gauge works on the principle of ___________________ Screw gauge consists of __________and _________________scale Pitch of the screw (P) = ____________________ For a screw gauge, Least Count=______________________ If the zeroth division of the head scale is below the index line of Pitch scale, the error is said to be For a Positive zero error the correction is _________________ For a Positive zero error the correction is _________________ If the zeroth division of the head scale is above the index line of pitch scale, the error is said to be ______________________ For a negative zero error, the correction is _________________ Diameter of a wire or thickness of an object using screw gauge is ______________ The least count of a screw gauge whose head scale divisions are200,if itmoves5mm distance when the head is rotated through 5 revolutions is ________________ The Head of a screw gauge is divided into 50 divisions if it advances1m.m.when screw is turned through 2 rotations then the pitch of the screw is ________________ If the zeroth division of head scale coincides with the index line of pitch scale then the screw gauge has no ______________ While measuring the diameter of a nail using a screw gauge of L.C.0.01 mm, the H.S.R.is 18 and P.S.R. is found to be 1.5mm,then the diameter of the nail = ____________ The distance traveled by the tip of a screw for one complete rotation of its head is called the
16. 17. 18. 19.
The distance between two adjacent threads of a screw is ______________ The device used to measure thickness of a thin glass plate and the diameter of a thin wire which works on the principle of a screw in a nut is _______________ The least count of an ordinary scale is ______________ To find the accurate length of an object, the L.C. of the devise must be ___________
20. While measuring the diameter of a lead shot using screw gauge of l.c.0.01mm, the PSR is found to be 7.5mm, HSR is 48. Then the diameter of lead shot is ___________
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ++++++
ANSWERS
1) Least count 2) Screw in a nut 3) Pitch scale and Head Scale 4) Distance traveled by the Screw / No. of complete rotations made 5) Pitch of the screw / No of Head scale divisions 6) Positive Zero error 7) Negative 8) Negative zero error 9) Positive 10) PSR + (HSR X LC) 11) 0.0005CM 12) 0.5MM 13) Zero error 14) 1.68mm 15) Pitch of the screw 16) Screw gauge 17) Screw gauge 18) 1mm 19) Very low 20)7.98mm. http://pluscoaching.blogpsot.com
Student Name:. Ananda B.Tech pluscoaching@ovi.com Parents Signature:.. 98664 00174
PLUS COACHING CENTRE
+++++++++++++++CEEP + APRJC + Public++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
Our Universe
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
7.
Ptolemic theory is also known as ______________ Copernican theory is also known as _________________ According to Heliocentric theory, the ________________ is at the center of the universe. According to Ptolemic theory the ___________is at the center of the universe. The moon makes one revolution about the earth in_____________. The distance of the moon from the earth is about __________________
Every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force called ___________
8. 9. 10. 11.
The value of Universal Gravitational constant ______________________ Gravitational constant is applicable_______________________. The uniform acceleration produced in a freely falling body due to gravitational pull of the earth is known as _______________________ Units of acceleration due to gravity ,g; is _______________
12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19.
20.
The relation between G and g is _____________ Mass of the earth is ___________________ Radius of the earth is ___________________ Acceleration due to gravity is independent of ___________________ At a height equal to half the radius of earth, acceleration due to gravity approaches __ At the center of the earth, acceleration due to gravity is ____________ The value of g at the poles is _____________ The value of g at the equator is ____________________
The instrument used to measure small changes in the value of g at a given location is called _________
21.
The quantity of matter contained in a body is called the _________of the body
22. The _________of a body is the force with which it is attracted by the earth towards its center 23. Weight of a body _________ 24. The weight of a body on the moon is _________of its weight on the earth 25. The mass of a body is ____________any where in the universe. 26. The unit of weight in S.I. system ___________________ 27. The gravitational force acting on a stone of mass 10kg is ______________ 28. The weight of a stone of mass 400gms is __________________
29. The stretching of the spring is proportional to the applied force .This is called as ____________
30. ______________helps in the determination of the weight of a body 31. According to Keplers laws planets revolve around Sun in ________________orbits 32. The value of g on the moon is __________________ 33. The instrument used to determine the weight of a body is ________________ 34. The masses of two bodies are m1 and m2 and the distance between them is r. Then the force of attraction between them _____________________ Matching
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Mass of earth Distance between the earth and the moon ( A ) The value of G The value of g on earth Radius of the earth Geocentric theory Heliocentric theory force F= g= (H) (D) (B) (C) (G ) (I ) (E) A) 3.85x105k.m. B) 9.8m/sec2 C) 6.4x106m D) 6.67x10-11Nm2/Kg2 E) 6x1024Kg F) ma G) Ptolemy (F ) H) GM/r2
I) Copernicus
++++++ 1) Geocentric theory 2) Helio centric theory 3) Sun 4) Earth 5) 27.3dyas 6) 3.85 x 105 km. 7) Gravitational Force 8) 6.67 x 10-11 N m2Kg -2 9) Every where in the universe 10) Acceleration due to gravity (g) 11) m/sec2 12) F = GM/r2 13) 6 x 1024 kg 14) 6.4 x 106m 15) Mass 16) Zero 17) Zero 18) Maximum 19) Minimum 20) Gravity meter 21) Mass 22) Weight 23) w = mg 24) 1/6th 25) Constant 26) Newton 27) 9.8N 28) 3.92N 29) Hooks Law 30)Hooks law 31) Elliptical 32) 1.67m/sec2 33) Spring Balance 34) F = Gm1m2 / r2
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Choice Board 2Document1 pageChoice Board 2api-343289507No ratings yet
- The Planiverse PDFDocument272 pagesThe Planiverse PDFPino AffeNo ratings yet
- Name Class Date: G - N/KGDocument4 pagesName Class Date: G - N/KGDelosh TNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Physical Chemistry of FoodDocument192 pagesAn Introduction To The Physical Chemistry of FoodBishoyYousif100% (3)
- Lab Report Free Fall MotionDocument11 pagesLab Report Free Fall Motionalinaathirah04No ratings yet
- The Solar SystemDocument24 pagesThe Solar Systemapi-253632941No ratings yet
- Hkpo 2014 PDFDocument15 pagesHkpo 2014 PDFlagostinhaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsDocument7 pagesMechanics:-: AS Level Physics: Terms & DefinitionsJenniferNo ratings yet
- Quantum Signatures of BH Mass SuperpositionDocument7 pagesQuantum Signatures of BH Mass SuperpositionCemile ArabaciNo ratings yet
- What Kind of School Did You Go ToDocument11 pagesWhat Kind of School Did You Go ToHai Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- DFDocument3 pagesDFSagar KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Yearly Lesson Plan 2010Document26 pagesPhysics Form 4 Yearly Lesson Plan 2010Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- UTP - Unit 4 1Document34 pagesUTP - Unit 4 1Dasarathy A KNo ratings yet
- UFO PatentDocument23 pagesUFO PatentDj SavadaNo ratings yet
- Solution in English System: Hideclick Here To Show or Hide The SolutionDocument5 pagesSolution in English System: Hideclick Here To Show or Hide The SolutionJamie FederizoNo ratings yet
- Burn Time Calculator MFD TutorialDocument3 pagesBurn Time Calculator MFD Tutorialpoppy reversNo ratings yet
- 9th Race CBSE FoundationDocument124 pages9th Race CBSE FoundationArthar ThummarNo ratings yet
- Physics ATP NotesDocument39 pagesPhysics ATP NotesAmmara IftikharNo ratings yet
- 47fate of Beyond 2012Document242 pages47fate of Beyond 2012Aleksandar DjordjevicNo ratings yet
- Q1 3Document2 pagesQ1 3ROCHELLE CENIZALNo ratings yet
- Rainfall Mathematical ExplorationDocument14 pagesRainfall Mathematical ExplorationJordan Moshcovitis100% (1)
- As Physics Practical 3 - GPE To KEDocument2 pagesAs Physics Practical 3 - GPE To KERamcharantej24No ratings yet
- BBC Knowledge Magazine 2017Document97 pagesBBC Knowledge Magazine 2017Le Do Ngoc Hang100% (1)
- Gravitation (XII) Eng WADocument16 pagesGravitation (XII) Eng WAPrashantcool1999No ratings yet
- Script Sci6 q3 Week 1 Armando CortezDocument15 pagesScript Sci6 q3 Week 1 Armando CortezArman Berina CortezNo ratings yet
- Topic 10.2 - Fields at WorkDocument109 pagesTopic 10.2 - Fields at Workwevan98121No ratings yet
- Work Energy Power - 1Document10 pagesWork Energy Power - 1rahimuddinNo ratings yet
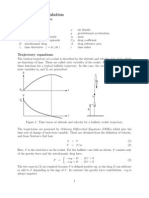
- Trajectory Calculation: Lab 2 Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesTrajectory Calculation: Lab 2 Lecture NotesDhillonvNo ratings yet
- Universal Law of Gravitation Ratio Student Sheet 10 27 1Document2 pagesUniversal Law of Gravitation Ratio Student Sheet 10 27 1api-373636400No ratings yet