Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Agent
Uploaded by
Mohini KhandelwalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Agent
Uploaded by
Mohini KhandelwalCopyright:
Available Formats
AgentAccording to section 182 of the Indian Contract Act,an agent is a person employed to do any act for another or to represent
another in dealing with third persons.The person for whom such act is done,or who is so represented,is called the principal.The relationship between the agent and the principal is called the agency.
Sub-agentSection 191 defines a sub-agent as a person employed by and acting under the control of the original agent in the business of the agency.Thus sub-agent is an agent appointed by an agent.The relation of the sub-agent to the original agent is as between themselves that of agent and principal.An agent who employs a sub-agent has the duties and liabilities of a principal to him.Sub-agent acts under the control of the original agent and the principal is not bound by his acts as there is no privity of contract between a sub-agent and principal.
Substituted AgentWhen an agent holding an express or implied authority to name another person to act in the business of the agency,has accordingly,named another person,such a person is not a sub-agent but a substituted agent. The substituted agent shall be taken as the agent of the principal for such part of the work as is entrusted to him(Section 194). Example: A directs B,his solicitor to sell his estate by auction and to employ an autioneer for the purpose. B names C an autioneer to conduct the sale. C is not a sub-agent. He is substituted agent of A.
Difference between Sub-agent and Substituted agentBoth sub-agent and the substituted agent are appointed by the original agent but they are not the same. The following points of difference may be noted:(1) A sub-agent works under the direct control of the original agent whereas a substituted agent works under the control of the principal. (2) The agent not only appoints the sub-agent but delegates all or some of his duties also. The agent does not delegate any part of his work to the substituted agent.
(3) There is a privity of contract between the principal and the substituted agent. But there is no such privity as between the principal and the sub-agent. The principal cannot sue the sub-agent or be sued by him. (4) A sub-agent is not liable to the principal except in case of fraud or wilful wrong. He is responsible only to the agent,whereas the substituted agent is responsible only to the principal and in no case to the agent. (5) The agent is responsible to the principal for the acts of the sub-agent but not so for the acts of substituted agent. (6) In case of sustituted agent,the duty of agent comes to an end. But in case of sub-agent he remain liable for his acts as long as sub-agency continues.
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Patent SearchesDocument2 pagesPatent Searchesapi-278561436No ratings yet
- IPR EngDocument3 pagesIPR EngJournalism TuitionNo ratings yet
- LEARNINGS .: 1 1St Module - Law of ContractDocument19 pagesLEARNINGS .: 1 1St Module - Law of ContractAsha RaiNo ratings yet
- Indivisibility Solidarity Concept DistinctionDocument3 pagesIndivisibility Solidarity Concept DistinctionlagurosangelicaNo ratings yet
- BG FormatDocument2 pagesBG FormatMitesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Veeam Propartner Agreement enDocument7 pagesVeeam Propartner Agreement enacmirazgcNo ratings yet
- Revised Corporation Code - SummaryDocument34 pagesRevised Corporation Code - SummaryAldrin ZolinaNo ratings yet
- Building Demolition Versova TextDocument6 pagesBuilding Demolition Versova TextpremkumalenNo ratings yet
- Mico Rodriguez's CounterclaimDocument237 pagesMico Rodriguez's CounterclaimgoodmoineNo ratings yet
- Ubject Nterpretation of TatutesDocument12 pagesUbject Nterpretation of TatutesJay Vardhan SihagNo ratings yet
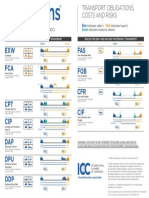
- Tabla INCOTERMSDocument1 pageTabla INCOTERMSCamila VerdeNo ratings yet
- Law299 Assignment Group 3 Am1104cDocument11 pagesLaw299 Assignment Group 3 Am1104caidryldanishNo ratings yet
- Leyte Geothermal Power Progressive Vs PNOC 2011 DigestDocument2 pagesLeyte Geothermal Power Progressive Vs PNOC 2011 DigestEmmanuel OrtegaNo ratings yet
- مصادر المعلومات التقليدية والالكترونيةDocument497 pagesمصادر المعلومات التقليدية والالكترونيةDoda DodiNo ratings yet
- Definitions Companies Act 2013 - Akanksha BohraDocument23 pagesDefinitions Companies Act 2013 - Akanksha BohraAkanksha BohraNo ratings yet
- LPR3115 - Dispute Resolution and RemediesDocument13 pagesLPR3115 - Dispute Resolution and RemediesLikumbi KasangaNo ratings yet
- One Pager Smart LifestyleDocument2 pagesOne Pager Smart LifestyleSam RamNo ratings yet
- OBLICON Defective Contracts MatrixDocument4 pagesOBLICON Defective Contracts Matrixdeeyanne1803100% (1)
- Corporate GuaranteeDocument14 pagesCorporate GuaranteeAkio ChingNo ratings yet
- CONTRACT FOR DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT SERVICES ... (PDFDrive) PDFDocument628 pagesCONTRACT FOR DESIGN, CONSTRUCTION AND CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT SERVICES ... (PDFDrive) PDFNam Do HoangNo ratings yet
- Reo Law On Credit TransactionsDocument5 pagesReo Law On Credit TransactionsCzarina JaneNo ratings yet
- KATHLEEN ObliCon Digests Baylon EndDocument14 pagesKATHLEEN ObliCon Digests Baylon EndDatu TahilNo ratings yet
- Carenado PA34T Emergency ProceduresDocument21 pagesCarenado PA34T Emergency ProceduresMikeParsonsNo ratings yet
- Contracts Reviewer For CPA AspirantsDocument13 pagesContracts Reviewer For CPA AspirantsMario CalvoNo ratings yet
- Answer Key - Preboard - Majorship - Filipino Volume 1Document1 pageAnswer Key - Preboard - Majorship - Filipino Volume 1dindoNo ratings yet
- Infringement. - Any Person Who Shall, Without The Consent of The Owner of TheDocument3 pagesInfringement. - Any Person Who Shall, Without The Consent of The Owner of TheDexterJohnN.BambalanNo ratings yet
- Termination OLFMDocument10 pagesTermination OLFMutkarhNo ratings yet
- University of Mindanao Vs Bangko Sentral NG PilipinasDocument5 pagesUniversity of Mindanao Vs Bangko Sentral NG PilipinasDarlene GanubNo ratings yet
- San Beda PartnershipDocument32 pagesSan Beda PartnershipLenard Trinidad79% (14)
- RF License Agreement - En-GbDocument0 pagesRF License Agreement - En-GbSudeep SharmaNo ratings yet