Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syst ECG Rely
Uploaded by
RaafiqOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Syst ECG Rely
Uploaded by
RaafiqCopyright:
Available Formats
SYSTEMATIC EVALUATION OF THE ECG
1. GENRAL: Check PX ID; dates; place in sequence 2. CALIBRATION: Std; std; chair; NB generalised small complexes DDX: Obesity; COPD; pericardial effusion; hypothyroidism 3. RYTHM & RATE: RR-interval if constant - regular (Rate = 300/no. of blocks), else irregular (Rate = no. of complexes x 6) 4. P-WAVE: Precede every QRS-complex?; size and morphology 5. PR-INTERVAL: Length 6. QRS-COMPLEX: Axis; width; height; Q-wave morphology 7. ST-SEGMENT: Position about iso-electric axis (depression and elevation) 8. T-WAVE MORPHOLOGY: Size, shape 9. QT-INTERVAL: Length 10. PATTERNS: Pulmonary embolism; mitral valve lesions (MS, MInc.); hyper/hypokalaemia; hyper/hypocalcaemia;ischemia; dysrhytmias 11. LOCALISATION: Localisation of infarcts
ST-SEGMENT
ST-elevation
ST-depression
Myocardial Ischemia NSTEMI Post. infarct Digoxin VH with systolic pverload Reciprocal changes of infarct
INFARCTION
Leads
II; III; aVF II; III; aVF; V5; V6 V1-V3 I; aVL; V1-V6 V4-V6 I; aVL V1-V3 (mirror image) V4r; V5r; V6r
Location
Inferior Inferolateral Anteroseptal Wide anterior Lateral High Lateral True posterior (R) ventrivle
Artery
RCA or circumex Circumex or RCA LAD (L)Main stem/ LAD Circumex 1st Diagn. of LAD Circumex RCA
T P Q
QT
MI Pericarditis Prinzmental angina Ventricular anuerysm
T-WAVE MORPHOLOGY
Inverted T-waves
T-waves are usually (+)ve, Inversion may be normal in SII; aVR; V1
Peaked T-waves
Hyper acute MI Hyper kalaemia
Flattened T-waves
Ischemia Pericarditis Myocarditis Hypercalcaemia
QRS-COMPLEX Axis
BBB MI Myocardial myopathy VH WPW Syndrome Ventricular rhythms May be normal in septal region of black patients
Pathalogical Q-waves No electrical activity Shows electrical activity in opposing wall
SI
aVF
(N): -30<axis<90
(L) Axis DDX
[-90<axis<-30]
(R) Axis DDX
QT-INTERVAL
[90<axis<180]
(N): QT<11 blocks
ST-elevation: ST straighten Elimination of ST-junction Slope elevaion J-point elevates T-inversion T amplitude increase Giant peaked T ST-elevation T (N) 2/52 post MI
deep Q; inf. infarct (L) ant. hemi block Primum ASD WPW Syndrome
RVH antero-lat. infarct WPW Syndrome (L) post. hemi block
QT-interval Congenital defects of K+ channel (Long QT-syndr.) K+; Mg++; Ca++
Drugs Ischemia/ Infarction QT-interval Ca++
TACHYARRHYTHMIAS DDX P-WAVE MORPHOLOGY
Left atrial enlarement
BRADYARRHYTHMIAS BRADYCARDIAS Sinus bradycardia Intermittend cond. Slow escape rhythms HEARTBLOCKS
SII
V1
Width
V1
V6
(N): QRS<2 blocks
RBBB
LBBB
Right atrial enlarement
Bi-fascicular block
P-mitrale [SII] Biphasic-P [V1] P-Pulmonale [SII]
Combination of RBBB & LBBB + (L) axis deviation
V6
RVH
Amplitude V1 PR-INTERVAL
(N): 3<PR<5 (blocks)
PR: Pre-excitation (WPW)
ectopic atrial focus
Tall R in V1: DDx RVH; RBBB; WPW; true post. infarct; Duchennes MD
Pathological (infarct) if present in two or more adjacent leads.
BROAD
LVH
Tall R [V6] + deep S [V1] 35mm + T-inversion [V5-V6] = Systolic overload
(N): width < 1 block height < 3 blocks
Large R in V1 + (R) axis; T-inversion [V1-V3]
NARROW
Tall slurred R [V1] Deep slurred S [V6; SII] Inverted T [V1-V3]
Negative QRS [V1-V3] Broad, M-shaped QRS [V6]
REGULAR
Sinus tachy Ectopic atrial tachy Atrial utter AVNRT AVRT VT SVT + BBB SVT + Ab-cond SVT + Ec-cond Ventricular pacemaker
IRREGULAR
AF Atrial utter with var. block MAT
MVT Torsade de Point AF with BBB VF
SA Block/arrest AV Blocks: 1 2 - Mobitz 1
(Wenckebach)
Qwave
PR: 1 AV Block
- Mobitz 2 3
Pulmonary Embolism Sinus tachy Atrial arrythmias incl. AF (R) VH (R) BBB S1Q3T3 pattern
PATTERNS
COPD Gen. small complexes P-pulmonale (R) axis deviation (R) VH (R) BBB
Mitral Stenosis (L) AH, if sinus rhythm AF commonly present (R) VH (R) axis deviation
Mitral Incompetence (L) AH, if sinus rhythm AF commonly present (L) VH (R) VH due to PHTN
K+ Flat/ absent P-waves Broad QRS-complex Larger, peaked T Arrhythmias
K+ Flat T-waves Prominent U-waves 1 or 2 block ST-depression
Ca++ QT
Ca++ QT
Ischemia NNB: Horizontal STdepression ST-segment becomes horizontal
ST-elevation (Prinz ST-T junction mental angina) becomes angular T becomes symmetric T attened/ inverted T apex becomes sharp May cause a BBB ST displaced down
You might also like
- Essential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachFrom EverandEssential Cardiac Electrophysiology: The Self-Assessment ApproachNo ratings yet
- ECG Brief NotesDocument5 pagesECG Brief NotesKalpani Malsha UdawelagedaraNo ratings yet
- Ecg Interpretation:: The BasicsDocument40 pagesEcg Interpretation:: The BasicsRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Basic EKG 2: Dr. Wattana Wongtheptien M.D. Cardiologist Chiangrai Regional HospitalDocument79 pagesBasic EKG 2: Dr. Wattana Wongtheptien M.D. Cardiologist Chiangrai Regional HospitalVeerapong Vattanavanit0% (1)
- PDF DocumentDocument40 pagesPDF DocumentsalikiqbalNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument40 pagesECG InterpretationMuhammad BadrushshalihNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument6 pagesEcgMohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Ecg 1Document40 pagesEcg 1doctorhanifNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiograms (Ecgs)Document86 pagesElectrocardiograms (Ecgs)nana wandhanaNo ratings yet
- THE Electrocardiogram (Ecg / Ekg) : By: DR Yasir MansouriDocument83 pagesTHE Electrocardiogram (Ecg / Ekg) : By: DR Yasir Mansourirofi modiNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiograms (Ecgs)Document80 pagesElectrocardiograms (Ecgs)heena solankiNo ratings yet
- Adi Bestara EKG at A Glance NewestDocument113 pagesAdi Bestara EKG at A Glance Newestkarpax21100% (1)
- Basics of ECG: By-Pallavi ChicholikarDocument115 pagesBasics of ECG: By-Pallavi ChicholikarBhakti WashilkarNo ratings yet
- Basics of Ecg: DR Shyama Assistant Professor General Medicine Aiims, PatnaDocument117 pagesBasics of Ecg: DR Shyama Assistant Professor General Medicine Aiims, PatnaSimran KothariNo ratings yet
- EKG Abnormal 1 - UnisbaDocument52 pagesEKG Abnormal 1 - UnisbanovylatifahNo ratings yet
- ECG Lecture 4Document44 pagesECG Lecture 4asdasdasdasNo ratings yet
- Deborah Goldstein Georgetown University Department of Internal MedicineDocument66 pagesDeborah Goldstein Georgetown University Department of Internal MedicineAltama L. SidartaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah EKG II Unswagati 2016Document77 pagesKuliah EKG II Unswagati 2016iikNo ratings yet
- ECG ExaminationDocument70 pagesECG ExaminationPercy Caceres OlivaresNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAMDocument63 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAMMbah GapinbissiNo ratings yet
- 5 Ekg PM Eng PDFDocument70 pages5 Ekg PM Eng PDFfgxNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument95 pagesECG InterpretationNur Rahmat Wibowo100% (9)
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHYDocument75 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAPHYMeliaNo ratings yet
- Physician Assistant Certification and Recertification Exam Review - PANRE - PANCEDocument14 pagesPhysician Assistant Certification and Recertification Exam Review - PANRE - PANCEThe Physician Assistant Life100% (3)
- Ekg Normal Dan Acs Sudin TimurDocument59 pagesEkg Normal Dan Acs Sudin TimurArum MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi ECG Dr. SallyDocument66 pagesInterpretasi ECG Dr. SallyRichard GunawanNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation: UNS Cardiovascular Dept Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocument85 pagesEKG Interpretation: UNS Cardiovascular Dept Medical Student Lecture Seriesandina rosmalianti100% (1)
- Cardiology/EKG Board Review: Michael J. Bradley D.O. DME/Program Director Family Medicine ResidencyDocument87 pagesCardiology/EKG Board Review: Michael J. Bradley D.O. DME/Program Director Family Medicine ResidencyummimalikihamidNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument168 pagesECG InterpretationPavi YaskarthiNo ratings yet
- ECG AbnormalDocument60 pagesECG Abnormalvidishmalaviya300No ratings yet
- Basic ECG Lecture - NewDocument148 pagesBasic ECG Lecture - NewAradhanaRamchandaniNo ratings yet
- ECGDocument198 pagesECGKatrina Maravilla100% (1)
- Ecg Basics - NAVEENDocument65 pagesEcg Basics - NAVEENNaveen MathieuNo ratings yet
- Kuliah EKG Blok Kegawatdaruratan September 2018Document122 pagesKuliah EKG Blok Kegawatdaruratan September 2018khanzaisdiharanaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Ekg UnswagatiDocument75 pagesKuliah Ekg UnswagatiiikNo ratings yet
- Superimposed ECG PDFDocument93 pagesSuperimposed ECG PDFEdalyn CapiliNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument169 pagesElectrocardiogramjitendra magarNo ratings yet
- Ecg Presentation 2013Document40 pagesEcg Presentation 2013Samuel FpNo ratings yet
- Cardio INTERPRETATION OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAMDocument74 pagesCardio INTERPRETATION OF THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAMkrisnoNo ratings yet
- Suatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisDocument78 pagesSuatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisAnonymous 3LwVkUsdNo ratings yet
- Suatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisDocument78 pagesSuatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisMohammad AlmuhaiminNo ratings yet
- Kursus Ekg DR Ismi-1Document78 pagesKursus Ekg DR Ismi-1Sekar Ayu WulandariNo ratings yet
- Dr. Anas Yasin - MDDocument58 pagesDr. Anas Yasin - MDMahfouzNo ratings yet
- Simple Guide To Ecg InterpretationDocument53 pagesSimple Guide To Ecg Interpretationedy suyantoNo ratings yet
- Suatu Alat LaboratorisDocument78 pagesSuatu Alat LaboratorisHematology 2016No ratings yet
- 35ekg 1Document103 pages35ekg 1Veerapong Vattanavanit100% (2)
- Basic ECG For ParamedicDocument82 pagesBasic ECG For ParamedicMaza AmfoterikNo ratings yet
- ECG Kursus FKUSU DR A.majid 05 Juni 2007Document37 pagesECG Kursus FKUSU DR A.majid 05 Juni 2007Shinta LissevaNo ratings yet
- Ecg BSTDocument204 pagesEcg BSTAnusha Verghese100% (1)
- The Normal ElectrocardiogramDocument63 pagesThe Normal ElectrocardiogramPuravin Crishan VeerasamyNo ratings yet
- Abnoramal ECGDocument20 pagesAbnoramal ECGImmanuelNo ratings yet
- ECG Praktis Sesi 1 RestutiDocument49 pagesECG Praktis Sesi 1 RestutiKaisun TeoNo ratings yet
- Basics of ECG: DR Subroto Mandal, MD, DM, DC Associate Professor, CardiologyDocument206 pagesBasics of ECG: DR Subroto Mandal, MD, DM, DC Associate Professor, CardiologyRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- DrAbnet ECG - BasicsDocument99 pagesDrAbnet ECG - BasicsAbnet WondimuNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG Interpretation: Cardiology and Vascular Department Medical Faculty of Hasanuddin UniversityDocument61 pagesBasic ECG Interpretation: Cardiology and Vascular Department Medical Faculty of Hasanuddin UniversityHayat Hamzah DawiNo ratings yet
- ECG1Document123 pagesECG1ayeshaNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi ElektrokardiografiDocument60 pagesInterpretasi ElektrokardiografiYogi GustriansyahNo ratings yet
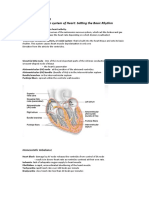
- Intrinsic Conduction System of Heart: Setting The Basic RhythmDocument3 pagesIntrinsic Conduction System of Heart: Setting The Basic RhythmDeniebev'z OrillosNo ratings yet
- Adult and Pediatric Emergency DrugsDocument4 pagesAdult and Pediatric Emergency DrugsRubille ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanCindy Mae Quinga100% (2)
- Emergency TrolleyDocument22 pagesEmergency TrolleyAaron Wallace100% (1)
- Neonatal LupusDocument19 pagesNeonatal Lupusyogeshraval368No ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms 2011 PDFDocument6 pagesACLS Algorithms 2011 PDFmaya_fitrianaNo ratings yet
- Precourse Als PDF Cardiopulmonary ResuscitatiDocument2 pagesPrecourse Als PDF Cardiopulmonary ResuscitatiΡαφαελλα ΣτυλιανουNo ratings yet
- Ekg BasicDocument24 pagesEkg BasicGhica CostinNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Docx Grand CaseDocument10 pagesDRUG STUDY - Docx Grand CaseAntonette PereyraNo ratings yet
- Complaint Emergency HandbookDocument306 pagesComplaint Emergency HandbookUsman Amjad100% (3)
- Drug Study CardinalDocument21 pagesDrug Study CardinalDrei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Icd 10 KamusDocument174 pagesIcd 10 KamusaininadiaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular NotesDocument20 pagesCardiovascular NotesJus ThomNo ratings yet
- ACLS AHA Guidelines 2006 PosterDocument1 pageACLS AHA Guidelines 2006 PosterJeane SuyantoNo ratings yet
- Basicpacingconceptsppt2017-171221084227 2Document101 pagesBasicpacingconceptsppt2017-171221084227 2Bob RiouxNo ratings yet
- Heart RhythmsDocument68 pagesHeart Rhythmsyasahswi91No ratings yet
- Nebivolol Hydrochlorothiazide Prescribing InformationDocument7 pagesNebivolol Hydrochlorothiazide Prescribing InformationRaihan RakibNo ratings yet
- Sample ChartingDocument4 pagesSample Chartinggreen_archer100% (1)
- Bioset 9000Document34 pagesBioset 9000Pavel RashkovNo ratings yet
- Ekg Primeri PDFDocument21 pagesEkg Primeri PDFStevanovic StojaNo ratings yet
- Ecg QuizDocument46 pagesEcg QuizAchmad Jauhar FirdausNo ratings yet
- Morgan 2012Document5 pagesMorgan 2012aixacamila3No ratings yet
- ECG in Emergency MedicineDocument228 pagesECG in Emergency MedicineBobbyGustafsonNo ratings yet
- Symptoms Respiratory System Cardiovascular System DiagnosisDocument2 pagesSymptoms Respiratory System Cardiovascular System DiagnosisAdelina RinataNo ratings yet
- Harrison Self-Assessment and Board Review (1) - 403-490Document88 pagesHarrison Self-Assessment and Board Review (1) - 403-490Cristobal Andres Fernandez Coentrao100% (2)
- Memorias LavecDocument288 pagesMemorias Lavecsbc27No ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmia: Prepared By: Charina Gail O. Baloy, RPH, Msc. (C.)Document44 pagesCardiac Arrhythmia: Prepared By: Charina Gail O. Baloy, RPH, Msc. (C.)Chinenye Akwue100% (1)
- Rhythm EKG Rate (BPM) Rhythm EKG InterventionsDocument6 pagesRhythm EKG Rate (BPM) Rhythm EKG InterventionsRawabi rawabi1997No ratings yet
- Acls Topic Wise McqsDocument40 pagesAcls Topic Wise McqsRuh ullah67% (6)
- SpringhDocument22 pagesSpringhMary Hiromi MizushimaNo ratings yet