Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Global System For Mobile Communications
Uploaded by
Sayan HaldarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Global System For Mobile Communications
Uploaded by
Sayan HaldarCopyright:
Available Formats
Global System for Mobile Communications
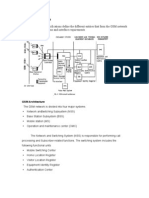
The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is an international standard for voice and data transmission over a wireless phone. Utilizing three separate components of the GSM network, this type of communication is truly portable.A user can place an identification card called a Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) in the wireless device, and the device will take on the personal configurations and information of that user. This includes telephone number, home system, and billing information. Although the United States has migrated toward the PCS mode of wireless communication, in large part the rest of the world uses GSM. The architecture used by GSM consists of three main components: a mobile station, a base station subsystem, and a network subsystem.These components work in tandem to allow a user to travel seamlessly without interruption of service, while offering the flexibility of having any device used permanently or temporarily by any user. The mobile station has two components: mobile equipment and a SIM.The SIM, as mentioned, is a small removable card that contains identification and connection information, and the mobile equipment is the GSM wireless device.The SIM is the component within the mobile station that provides the ultimate in mobility.This is achieved because you can insert it into any GSM compatible device and, using the identification information it contains, you can make and receive calls and use other subscribed services.This means that if you travel from one country to another with a SIM, and take the SIM and place it into a rented mobile equipment device, the SIM will provide the subscriber intelligence
back to the network via the mobile GSM compatible device.All services to which you have subscribed will continue through this new device, based on the information contained on the SIM. For security and billing purposes, SIM and the terminal each have internationally unique identification numbers for independence and identification on the network.The SIMs identifier is called the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI).The mobile unit has what is called an International Mobile Equipment Identifier (IMEI). In this way a users identity is matched with the SIM via the IMSI, and the position of the mobile unit is matched with the IMEI.This offers some security, in that a suspected stolen SIM card can be identified and flagged within a database for services to be stopped and to prevent charges by unauthorized individuals. The base station subsystem, like the mobile station, also has two components: the base transceiver station and the base station controller.The base transceiver station contains the necessary components that define a cell and the protocols associated with the communication to the mobile units.The base station controller is the part of the base station subsystem that manages resources for the transceiver units, as well as the communication with the mobile switching center (MSC).These two components integrate to provide service from the mobile station to the MSC. The network subsystem is, in effect, the networking component of the mobile communications portion of the GSM network. It acts as a typical class 5 switching central office. It combines the switching services of the core network with added functionality and services as requested by the customer.The main component of this subsystem is the MSC. The MSC coordinates the access to the POTS network, and acts similarly to any other switching node on a POTS network. It has the added
ability to support authentication and user registration. It coordinates call hand-off with the Base Station Controller, call routing, as well as coordination with other subscribed services. It utilizes Signaling System 7 (SS7) network architecture to take advantage of the efficient switching methods.There are other components to the network subsystem called registers: visitor location register (VLR) and home location register (HLR). Each of these registers handles call routing and services for mobility when a mobile customer is in their local or roaming calling state.The VLR is a database consisting of visitor devices in a given systems area of operation.The HLR is the database of registered users to the home network system.
General Packet Radio Service
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), also called GSM-IP, sits on top of the GSM networking architecture offering speeds between 56 and 170 Kbps. GPRS describes the bursty packet-type transmissions that will allow users to connect to the Internet from their mobile devices. GPRS is nonvoice. It offers the transport of information across the mobile telephone network. Although the users are always on like many broadband communications methodologies in use today, users pay only for usage. This provides a great deal of flexibility and efficiency.This type of connection, coupled with the nature of packet-switched delivery methods, truly offers efficient uses of network resources along with the speeds consumers are looking for.The data rates offered by GPRS will make it possible for users to partake in streaming video applications and interact with Web sites that offer multimedia, using compatible mobile handheld devices. GPRS is based on Global System for Mobile (GSM) communication
and as such will augment existing services such as circuit-switched wireless phone connections and the Short Message Service (SMS).
Short Message Service
Short Message Service (SMS) is a wireless service that allows users to send and receive short (usually 160 characters or less) messages to SMScompatible phones. SMS, as noted earlier, is integrated with the GSM standard. SMS is used either from a computer by browsing to an SMS site, entering the message and the recipients number, and clicking Send, or directly from a wireless phone.
www.syngress.com
You might also like
- Unit-4 (Wireless Communication)Document15 pagesUnit-4 (Wireless Communication)Anonymous EjQbY1CNo ratings yet
- GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Document3 pagesGSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Pulkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- GSM Cellular Network: 1 Principles of GSM Mobile Communication TechnologyDocument17 pagesGSM Cellular Network: 1 Principles of GSM Mobile Communication TechnologyTuan-Anh BuiNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument35 pagesGSM Network ArchitectureIkobayo AdewaleNo ratings yet
- GSM Network Architecture: GSM (Global System For Mobile)Document5 pagesGSM Network Architecture: GSM (Global System For Mobile)mard gharibNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction and Motivation: Evolving of Technology To 4G WirelessDocument13 pages1 - Introduction and Motivation: Evolving of Technology To 4G WirelessSalma SwaidanNo ratings yet
- 3.3) Basics of GSMDocument13 pages3.3) Basics of GSMRobin SinghNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Document7 pagesTelecommunication: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Simum100% (1)
- Global System For Mobile (GSM)Document17 pagesGlobal System For Mobile (GSM)Barhav SarbastNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Global System For Mobile CommunicationsDocument25 pagesOverview of The Global System For Mobile Communicationszaid_asiaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Unit 4Document10 pagesWireless Communication Unit 4Lavanya R GowdaNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Global System For Mobile CommunicationsDocument25 pagesOverview of The Global System For Mobile Communicationsaytacerd0% (1)
- Course Material (Lecture Notes) : Sri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology, VirudhunagarDocument17 pagesCourse Material (Lecture Notes) : Sri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology, VirudhunagarArun SharmaNo ratings yet
- GSM Mobile Services: Project Report ONDocument67 pagesGSM Mobile Services: Project Report ONRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument5 pagesGSM Network Architecturekataz2010No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of GSMDocument16 pagesFundamentals of GSMKalai SelvanNo ratings yet
- GSM System OverviewDocument12 pagesGSM System Overviewvemala vandanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Wireless & Mobile Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument17 pagesUnit 2 - Wireless & Mobile Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inprateek bharadwajNo ratings yet
- Forensics and The GSM Mobile Telephone System: International Journal of Digital Evidence Spring 2003, Volume 2, Issue 1Document17 pagesForensics and The GSM Mobile Telephone System: International Journal of Digital Evidence Spring 2003, Volume 2, Issue 1BEALogicNo ratings yet
- Overview of The GSM CommunicationsDocument18 pagesOverview of The GSM CommunicationsronyiutNo ratings yet
- Network Switching SubsystemDocument24 pagesNetwork Switching SubsystemAIC DSNo ratings yet
- Mobile TechnologyDocument18 pagesMobile TechnologyLady BugNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument5 pagesGSM Network ArchitecturePrashant KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4Nandhini PNo ratings yet
- A GSM Network Is Composed of Several Functional EntitiesDocument3 pagesA GSM Network Is Composed of Several Functional EntitiesNauman ChaudaryNo ratings yet
- G.S.M Modem/MobileDocument9 pagesG.S.M Modem/MobileJilly ArasuNo ratings yet
- Telecom AssignmentDocument5 pagesTelecom Assignmentikra khanNo ratings yet
- How We Make A CallDocument4 pagesHow We Make A CallAbuzarNo ratings yet
- GSM OverviewDocument6 pagesGSM OverviewSudeepta SahaNo ratings yet
- Future Developments in Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP ApplicationsDocument12 pagesFuture Developments in Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP ApplicationsJournal of Mobile, Embedded and Distributed Systems (JMEDS)No ratings yet
- Global System Mobility (GSM)Document28 pagesGlobal System Mobility (GSM)Zain ABNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Notes Unit IIIDocument13 pagesMobile Computing Notes Unit IIIkimNo ratings yet
- Archtecture of GSMDocument8 pagesArchtecture of GSMMjrtMQNo ratings yet
- Mobile Financial Services Terms Explained: Source: Mobey Forum Collected and Maintained By: Dr. Hosam Abou EldahabDocument18 pagesMobile Financial Services Terms Explained: Source: Mobey Forum Collected and Maintained By: Dr. Hosam Abou EldahabA MohsenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GSM GSM Network Components Mobile Services Switching Centre-MscDocument11 pagesIntroduction To GSM GSM Network Components Mobile Services Switching Centre-MscDenaiya Watton LeehNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 MCDocument17 pagesUnit-2 MCJohnpaulNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GSM: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Document12 pagesIntroduction To GSM: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications)Anuj KuradeNo ratings yet
- GSM ArchitectureDocument8 pagesGSM ArchitectureAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- GSM OverviewDocument18 pagesGSM Overviewchandunandamuri8940No ratings yet
- GSM NW ArchitectureDocument3 pagesGSM NW ArchitectureSreepad BharanNo ratings yet
- Entities of The GSM SystemDocument18 pagesEntities of The GSM Systemhieuvnp3No ratings yet
- Anti-Theft Tracking System For Automobiles: (Autogsm)Document3 pagesAnti-Theft Tracking System For Automobiles: (Autogsm)sravyareddyNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument19 pagesUnit IKiran janjalNo ratings yet
- John Scourias: A Brief Overview of GSM, byDocument14 pagesJohn Scourias: A Brief Overview of GSM, bymohsinakram1No ratings yet
- Network Switching SubsystemDocument7 pagesNetwork Switching SubsystemraufthegreatNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Global System For MobileDocument16 pagesOverview of The Global System For MobilevenkateshmukharjiNo ratings yet
- CC CC CC: C CC CC CC CDocument19 pagesCC CC CC: C CC CC CC Cpk_babuaNo ratings yet
- 2G Network: Elecom EtworkDocument13 pages2G Network: Elecom Etworkpg5555No ratings yet
- MC - Unit 2Document31 pagesMC - Unit 2Hrudhai SNo ratings yet
- The GSM System History: NextDocument19 pagesThe GSM System History: NextJoseph DavisNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing5thDay5.08.2019Document61 pagesMobile Computing5thDay5.08.2019Kalyan DasNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument11 pagesGSM Network ArchitectureYe YintNo ratings yet
- Appraisal of Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM) in NigeriaDocument6 pagesAppraisal of Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM) in NigeriaAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Rappaport GSMDocument18 pagesRappaport GSMUsman100% (1)
- Program: B.E Subject Name: Mobile Computing Subject Code: EC-8003 Semester: 8thDocument17 pagesProgram: B.E Subject Name: Mobile Computing Subject Code: EC-8003 Semester: 8thNidhi ChavanNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument5 pagesGSM Network Architecturenarayanan07No ratings yet
- Second Generation (2G) Cellular Radio SystemsDocument40 pagesSecond Generation (2G) Cellular Radio SystemsMd. Golam Sarwar JoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 v1 DFP6033Document40 pagesChapter 3 v1 DFP6033Vimalan RamanathanNo ratings yet
- Apply For A U.S. VisaDocument2 pagesApply For A U.S. VisaShiva ShivaNo ratings yet
- Windows PowerShell Tutorial For BeginnersDocument47 pagesWindows PowerShell Tutorial For BeginnersPranav SinghNo ratings yet
- Stephen CardotDocument2 pagesStephen CardotphillosisNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Act, 2000Document5 pagesInformation Technology Act, 2000Jeeva SkNo ratings yet
- Risks and Benefits of Business Intelligence in The CloudDocument10 pagesRisks and Benefits of Business Intelligence in The CloudElena CanajNo ratings yet
- Foreign Investment ApplicationDocument3 pagesForeign Investment ApplicationragunatharaoNo ratings yet
- Hot Info Details: No.: 4944 R Eleased: O Perating Systems: ProductsDocument3 pagesHot Info Details: No.: 4944 R Eleased: O Perating Systems: ProductsimmortalNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Test - October 2021: Solve All 15 Questions. Each Question Carries 2 MarksDocument6 pagesAptitude Test - October 2021: Solve All 15 Questions. Each Question Carries 2 MarksAbhishek KoundalNo ratings yet
- Detection of Internet Scam Using Logistic Regression: Mehrbod Sharifi Eugene Fink Jaime G. CabonellDocument5 pagesDetection of Internet Scam Using Logistic Regression: Mehrbod Sharifi Eugene Fink Jaime G. CabonellAdityaNo ratings yet
- An Implementation of Secure Data Exchange Ensuring Authentication and Authorization Using Color DropsDocument3 pagesAn Implementation of Secure Data Exchange Ensuring Authentication and Authorization Using Color DropsseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- Health Care System DfdsDocument95 pagesHealth Care System Dfdssamee530100% (1)
- ET712078973IN SpeedPost Track ConsignmentDocument2 pagesET712078973IN SpeedPost Track ConsignmentvaseenandanNo ratings yet
- Ee LABDocument6 pagesEe LABSafiullah MangrioNo ratings yet
- MIS5206 Week 12 Quiz Solutions1Document6 pagesMIS5206 Week 12 Quiz Solutions1Ashish JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Brain FingerprintingDocument16 pagesBrain FingerprintingVemula Lohith KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Profile SummaryDocument8 pagesComputer Profile SummaryFatimah Dinda AfifahNo ratings yet
- Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) GlossaryDocument17 pagesCertified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC) GlossarySyed100% (1)
- Faqs On Magnetic Stripe DeactivationDocument2 pagesFaqs On Magnetic Stripe Deactivationdfz138No ratings yet
- 勒索软件建立安全备份作为你的最后一道防线Document13 pages勒索软件建立安全备份作为你的最后一道防线青葱冯No ratings yet
- AL ScanWatch ServiceOverviewDocument2 pagesAL ScanWatch ServiceOverviewCan dien tu Thai Binh DuongNo ratings yet
- Harijana KmariyammaDocument2 pagesHarijana Kmariyammavenkateswarlu gollaNo ratings yet
- IEC 61508 AssessmentDocument21 pagesIEC 61508 Assessmentajinkya.patilNo ratings yet
- Ethical HackingDocument30 pagesEthical HackingMukesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Dell Sonicwall™ Sonicos 5.8.4.2: Release NotesDocument22 pagesDell Sonicwall™ Sonicos 5.8.4.2: Release NotesmarciosouzajuniorNo ratings yet
- Account Statement From 1 Apr 2020 To 31 Mar 2021: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalanceDocument5 pagesAccount Statement From 1 Apr 2020 To 31 Mar 2021: TXN Date Value Date Description Ref No./Cheque No. Debit Credit BalancesayanNo ratings yet
- Pract1 ProductCipherDocument7 pagesPract1 ProductCipherVailantan FernandesNo ratings yet
- AdminguideDocument202 pagesAdminguideClaudia Carolina Vasquez AcostaNo ratings yet
- Fetching Data Directly From ECC System in BEX Query Using RRIDocument11 pagesFetching Data Directly From ECC System in BEX Query Using RRIwaiting4addNo ratings yet
- Yvraine: M Ws Bs A W LD SVDocument3 pagesYvraine: M Ws Bs A W LD SVRicNo ratings yet
- Prosafe RSDocument3 pagesProsafe RSDavide ContiNo ratings yet