Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nitrogen Cycle
Uploaded by
dhawana2Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nitrogen Cycle
Uploaded by
dhawana2Copyright:
Available Formats
Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrates are taken out of the soil by plants, they are washed out of the soil (leaching) and de-nitrifying bacteria turn nitrates back into nitrogen gas. This happens mostly in anaerobic conditions, e.g. waterlogged marshes. Nitrogen fixing bacteria are bacteria which are in the roots of legumes, and are used in crop rotation because they are very useful for turning nitrogen in the air. decomposers: breaks downs proteinsfrom dead animal and ureas. denitrifying bacteria: they are found on waterloggs and they converts back nitrates into nitrogen gas. nitrifying bacteria: turns ammonuim compounds into nitrates , so that it can be absorbed by plants.
Making nitrogen into compounds is called fixing. Fixing occurs naturally by the action of certain bacteria in soil. Lightning can cause nitrogen to react with oxygen in the air forming nitrous oxides. This also occurs in petrol engine pollution. More than half of nitrogen fixing occurs through natural processes. The Haber Process accounts for about 30%. Nitrogen compounds in the soil are essential for plant growth see fertilisers.
Nitrogen - higher only Plants and animals need nitrogen to make proteins. But they cannot get nitrogen directly from the air because, as a gas, nitrogen is fairly unreactive. Plants are able to take up nitrogen compounds such as nitrates and ammonium salts from the soil. Nitrogen fixation Making nitrogen compounds from nitrogen in the air is called nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation happens in three ways:
The energy in lightning splits nitrogen molecules into individual nitrogen atoms. These react with oxygen to form nitrogen oxides. Nitrogen oxides are washed to the ground by rain, where they form nitrates in the soil.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria found in the soil and in the root nodules of leguminous plants, such as peas, beans and clover, fix nitrogen gas into nitrogen compounds. The Haber process is used by industry to produce ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. Ammonia is used to make nitrogen compounds that are used as fertiliser by farmers.
Nitrogen compounds Nitrogen compounds in living things are returned to the soil through: excretion and egestion by animals the decay of dead plants and animals Denitrifying bacteria present in soil break down nitrogen compounds and release nitrogen gas into the air.
The Nitrogen Cycle As a result of these processes, nitrogen is cycled continually through the air, soil and living things. This is called The Nitrogen Cycle. This animation summarises the main features of the nitrogen cycle.
Carbon cycle
Plants take the CO2 in the air and turn it into fats carbohydrates and proteins. These are then used for respiration in the plant (by which they are turned into CO2 ). The fats, proteins and carbohydrates can then either decay when the plant dies, be turned into products by humans or be eaten by animals. If they are eaten then some of the carbon compounds are used in respiration by the animal which has eaten the plant (which gives off carbon dioxide). The rest are then brought into the soil when the animal dies, and the CO2 is released by microbes and fungi when the animal decomposes. Sometimes however, this carbon dioxide is not released and fossil fuels are formed
If they are turned into a product this product is then burnt which releases carbon dioxide, and if the tree dies the carbon dioxide is created by decomposers.
You might also like
- Unit 2 Notes PDFDocument13 pagesUnit 2 Notes PDFdhawana2No ratings yet
- Student Edexce Moles Workbook Unit 1 PDFDocument112 pagesStudent Edexce Moles Workbook Unit 1 PDFdhawana20% (1)
- Specifications Notes Unit 2Document12 pagesSpecifications Notes Unit 2dhawana2No ratings yet
- 3H and 4H Mark Schemes and Reports May 05Document30 pages3H and 4H Mark Schemes and Reports May 05dhawana2100% (2)
- Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry AnswersDocument57 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Chemistry AnswersMelissa Iacovidou90% (20)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Soda 2520ash Material 2520 BalanceDocument5 pagesSoda 2520ash Material 2520 BalanceEng RaaNo ratings yet
- AMI - Moisture IndicatorsDocument2 pagesAMI - Moisture IndicatorssalamrefighNo ratings yet
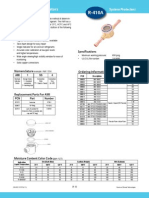
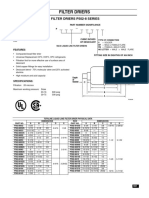
- Totaline® Liquid Line Filter Driers P502-8 SeriesDocument48 pagesTotaline® Liquid Line Filter Driers P502-8 SeriesDianaNo ratings yet
- Opteon Freon General Replacement GuideDocument2 pagesOpteon Freon General Replacement GuideaNo ratings yet
- TonisitasDocument6 pagesTonisitasPutri PajarianaNo ratings yet
- Ek Series Hermetic Liquid Line Filter Driers Catalog en Us 1620596Document4 pagesEk Series Hermetic Liquid Line Filter Driers Catalog en Us 1620596agus sutiawanNo ratings yet
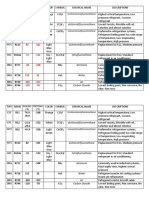
- Important Refrigerants and Its PropertiesDocument2 pagesImportant Refrigerants and Its PropertiesNyle BertNo ratings yet
- The Nitrogen Cycle: Processes, Players, and Human ImpactDocument8 pagesThe Nitrogen Cycle: Processes, Players, and Human ImpactKesto LoriakNo ratings yet
- SC13-11 (Structural Beam For Fertilizer Plant)Document1 pageSC13-11 (Structural Beam For Fertilizer Plant)lucidbaseNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant Selection ConsiderationsDocument27 pagesRefrigerant Selection Considerationsme12m113No ratings yet
- Salt Lake: Properties List See Also References External LinksDocument4 pagesSalt Lake: Properties List See Also References External Linkstsvmpm1765No ratings yet
- A5. Thermophysical Properties of RefrigerantsDocument10 pagesA5. Thermophysical Properties of Refrigerantsalikaya12002No ratings yet
- Community-Based Groundwater Management for Rubber Nursery IrrigationDocument7 pagesCommunity-Based Groundwater Management for Rubber Nursery IrrigationAdelia JbrNo ratings yet
- 1862-17 2018 Ammonia Symposium Preliminary Program FlyerDocument2 pages1862-17 2018 Ammonia Symposium Preliminary Program FlyerMaged HegabNo ratings yet
- Review of Brackish Water Treatment into Clean Water Using Reverse Osmosis MembraneDocument11 pagesReview of Brackish Water Treatment into Clean Water Using Reverse Osmosis Membranemuhammad arfanNo ratings yet
- Aarav Lalan - Unit 3 Stoichiometry Challenge Lab - 18971803Document4 pagesAarav Lalan - Unit 3 Stoichiometry Challenge Lab - 18971803AaravNo ratings yet
- Lista Compresores 2 - de - AgostoDocument11 pagesLista Compresores 2 - de - Agostojuan luis loaiza correaNo ratings yet
- Untitled 12Document20 pagesUntitled 12Jehana NaolNo ratings yet
- LP Hitachi PrimairyDocument1 pageLP Hitachi PrimairyAlexandru ChirilaNo ratings yet
- RCF Corp Diary-2014Document53 pagesRCF Corp Diary-2014Mohamed Salman KhatriNo ratings yet
- Studi Kandungan Merkuri Dan Arsen Dalam 4bc896d9Document11 pagesStudi Kandungan Merkuri Dan Arsen Dalam 4bc896d9bayu kenzieNo ratings yet
- Vengaikurichi 393 SurveyDocument181 pagesVengaikurichi 393 SurveyR.sunder R.sunderNo ratings yet
- 25 CompressorsDocument8 pages25 CompressorsDekkiNo ratings yet
- Carbon CycleDocument27 pagesCarbon CycleYana TvNo ratings yet
- Richfield Fertilisers PVT LTD Maharashtra IndiaDocument10 pagesRichfield Fertilisers PVT LTD Maharashtra IndiaRichfield Fertilisers Pvt Ltd.No ratings yet
- The Nitrogen Cycle - WorksheetDocument11 pagesThe Nitrogen Cycle - WorksheetAmrita HarrilalNo ratings yet
- Catalogue 301: Catalogue Condensé Des Produits Sporlan Mars 2011Document64 pagesCatalogue 301: Catalogue Condensé Des Produits Sporlan Mars 2011Israel DekoleadenuNo ratings yet
- Process for Secondary Production of Sodium Carbonate from Waste LiquorDocument11 pagesProcess for Secondary Production of Sodium Carbonate from Waste LiquorRima AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Soda Ash ReportDocument13 pagesSoda Ash ReportKaranNo ratings yet
- Catalogo GS 2018 PDFDocument116 pagesCatalogo GS 2018 PDFOcma MallidaNo ratings yet