Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BJT Ce Amp - Design
Uploaded by
నాంగిరి సురేష్Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BJT Ce Amp - Design
Uploaded by
నాంగిరి సురేష్Copyright:
Available Formats
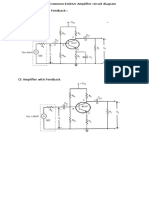
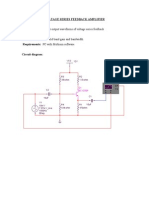
BJT CE AMPLIFIER
AIM: i) To design transistor CE amplifier for a given voltage gain. ii) To plot the frequency response. iii) To study the negative feedback effect on amplifier frequency response. APPARATUS: RSPS(0-30V) - 1No. CRO - 1No. BJT (BC107) - 1No. Resistors and Capacitors CIRCUIT DIAGRAM: CE AMPLIFIER
Fig.1 CE Amplifier
CE AMPLIFIER WITH CURRENT-SERIES FEED BACK
Fig.2 CE Amplifier with Current-Series Feedback CE AMPLIFIER WITH VOLTAGE-SHUNT FEED BACK
Fig.3 CE Amplifier with Voltage-Shunt Feedback
Designing of CE Amplifier: Biasing Let us design a CE amplifier with AV= 150, IC=2mA, Ic(min)=1.75mA; IC(max)=2.25mA.
Av
h fe
RC RL hie
For BC107B hfe(min)=180; hfe(max)=460
hie
VT h fe . I EQ
At room temperature VT=26mV and generally we select RL
such that RL RC i.e. RL=10RC. Using this data we can calculate RC then RL. Select VCE = 0.5VCC Now calculate
RE
VCC VCE IC I c (min)
min
RC
To Solve for stability factor S
S 11
=
max
Ic
I c (max)
max
I c (min) S 2
min
(1
max
, where S2 is the value of S when
1
Now calculate RB using
S2
(1
max
) 1
RB RE
max
RB RE
, where
RB
min
R1 R2
) I Cmin ,
V From the input loop equation R2
calculate
VBE
RB
RE (1
min
VR2
Vcc & R2 VR2 R1VR2 VCC VR2
R1
RB
Design of Capacitors: If the lower cut-off frequency is fL and the upper cut-off frequency is fH, then the value of the emitter bypass capacitor C2 can be calculated from
X C2
1 2 f L C2
hie 1 h fe
The coupling capacitor C1 can be calculated from
X C1
1 2 f LC1
Zi where Z i 10
R1 R2 hie
The value of the coupling capacitor C3 can be calculated from
X C3
1 2 f LC3
RL 10
PROCEDURE: CE Amplifier 1. Wire the circuit as shown in Fig.1 2. Adjust the input voltage to 10mv peak to peak and the frequency to 100 Hz. 3. Measure the peak to peak output voltage. 4. Vary the input frequency in steps 100Hz,200Hz, ..1kHz,2KHz, .10KHz,20KHz, 100KHz,200KHz, ,1MHz and take the corresponding output voltages and tabulate them in the below tabular form. 5. Plot the graph and calculate the bandwidth. Input voltage Vi =10mV PP S.No Frequency Output (Hz) Voltage (Vo) volts
Voltage gain= Vo/Vi
Gain in dB= 20log10(Vo/Vi)
CE Amplifier with Current-Series Feedback 1. Wire the circuit as shown in Fig.2 2. Adjust the input voltage to 10mv peak to peak and the frequency to 100 Hz. 3. Measure the peak to peak output voltage. 4. Vary the input frequency in steps 100Hz,200Hz, ..1kHz,2KHz, .10KHz,20KHz, 100KHz,200KHz, ,1MHz and take the corresponding output voltages and tabulate them in the below tabular form. 5. Plot the graph and calculate the bandwidth.
Input voltage Vi =10mV PP S.No Frequency Output (Hz) Voltage (Vo) volts
Voltage gain= Vo/Vi
Gain in dB= 20log10(Vo/Vi)
CE Amplifier with Voltage-Shunt Feedback 1. Wire the circuit as shown in Fig.3 2. Adjust the input voltage to 10mv peak to peak and the frequency to 100 Hz. 3. Measure the peak to peak output voltage. 4. Vary the input frequency in steps 100Hz,200Hz, ..1kHz,2KHz, .10KHz,20KHz, 100KHz,200KHz, ,1MHz and take the corresponding output voltages and tabulate them in the below tabular form. 5. Plot the graph and calculate the bandwidth. Input voltage Vi =10mV PP S.No Frequency Output (Hz) Voltage (Vo) volts
Voltage gain= Vo/Vi
Gain in dB= 20log10(Vo/Vi)
Measurement of Input resistance & Output resistance 1. Connect a Resistor RA=10K as shown in the below figure. Now set input signal of 10mv PP and 1KHz. 2. Now measure the output voltage across RL which is Vo1. 3. Now remove RL and measure the output voltage across RL which is Vo2. 4. Calculate the input resistance using the expression
Ri
Vo1 RA Vo 2 Vo1
5. Now measure the load voltage across RL which is VFL and open the load resistor and measure voltage at the output which is VNL.
Ro
RL
VNL 1 VFL
6. Repeat the above four steps for measuring input & output resistances for Current-Series and Voltage-Shunt Feedback amplifiers.
You might also like
- EC Lab ManualDocument27 pagesEC Lab ManualMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- 18 CIRCUIT DIAGRAM MODEL GRAPH FREQUENCY RESPONSEDocument44 pages18 CIRCUIT DIAGRAM MODEL GRAPH FREQUENCY RESPONSEMurali DharanNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications QtyDocument0 pagesCommon Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications Qtyagama1188No ratings yet
- TransistorDocument8 pagesTransistorwei.cheng.auNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier LAbDocument17 pagesOperational Amplifier LAbAhmad DboukNo ratings yet
- AEC LabManualDocument30 pagesAEC LabManualPrateek PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Multistage Amplifier Configurations: ObjectiveDocument12 pagesDesign and Analysis of Multistage Amplifier Configurations: ObjectivePreet PatelNo ratings yet
- Ec FinalDocument46 pagesEc FinalManjunath YadavNo ratings yet
- ADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFDocument21 pagesADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFJk RinkuNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Multistage Amplifier Configurations: ObjectiveDocument19 pagesDesign and Analysis of Multistage Amplifier Configurations: ObjectivePreet PatelNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT #2 Frequency Response of Common Emitter AmplierDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT #2 Frequency Response of Common Emitter AmplierGhabriel Javier SembranoNo ratings yet
- Single Tuned Amplifier: Experiment:5Document2 pagesSingle Tuned Amplifier: Experiment:5hari007kmrNo ratings yet
- ADC Lab ManualDocument46 pagesADC Lab ManualDinesh Kumar A RNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response of CE AmplifierDocument4 pagesFrequency Response of CE AmplifierShees Nadeem100% (2)
- Laboratory Exercises 3aDocument9 pagesLaboratory Exercises 3aIan VillarojoNo ratings yet
- 2310 Lab07Document3 pages2310 Lab07tarottaurus54No ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document7 pagesAssignment 4Niraj Prasad YadavNo ratings yet
- ECII & Sim LabDocument49 pagesECII & Sim LabSivan LoveNo ratings yet
- RC Coupled AmplifierDocument4 pagesRC Coupled AmplifierSanyam Jain100% (1)
- The Operation Amplifier:: Level TranslatorDocument8 pagesThe Operation Amplifier:: Level TranslatorPrafull BNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions Unit 1,2 and 3Document22 pagesPractice Questions Unit 1,2 and 3gowshik ramNo ratings yet
- CE Amplifier Bandwidth, Gain & ImpedanceDocument3 pagesCE Amplifier Bandwidth, Gain & ImpedanceUday KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Electronics Chapter 1 ExercisesDocument12 pagesIntroduction to Electronics Chapter 1 Exercisesqw3rtytr3wqNo ratings yet
- AEC Lab ManualDocument70 pagesAEC Lab ManualRohan BoseNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Lab ManualDocument49 pagesAnalog Electronics Lab ManualReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- CMOS Comparator Design: TSMC 0.25 Um TechnologyDocument15 pagesCMOS Comparator Design: TSMC 0.25 Um TechnologySharath_Patil_7623No ratings yet
- 1voltage Series Feedback AmplifierDocument7 pages1voltage Series Feedback AmplifierManjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 Common Emitter Amplifier AIM: Fig 1. Circuit DiagramDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 4 Common Emitter Amplifier AIM: Fig 1. Circuit Diagrampandiyarajan142611No ratings yet
- Fet Common Source Amplifier: Experiment No: 2Document5 pagesFet Common Source Amplifier: Experiment No: 2hari007kmrNo ratings yet
- Assign 1Document3 pagesAssign 1anij9825No ratings yet
- Assign 1 PDFDocument3 pagesAssign 1 PDFtanishk jainNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 Study of Voltage Gain and Frequency Response of Common Emitter Amplifier AIMDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 4 Study of Voltage Gain and Frequency Response of Common Emitter Amplifier AIMBinita SedhaiNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument8 pagesSolutionPallavi SahuNo ratings yet
- Linear Electronics Lectures Frequency Response and FeedbackDocument56 pagesLinear Electronics Lectures Frequency Response and FeedbackkbkkrNo ratings yet
- Lic ManualDocument68 pagesLic ManualVanitha RNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response of A Single Stage RC Coupled AmplifierDocument26 pagesFrequency Response of A Single Stage RC Coupled AmplifierkanchankonwarNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 1-8Document31 pagesLab Manual 1-8Vengat Raman Manohar100% (1)
- 9 CE AmplifierDocument5 pages9 CE AmplifierAnsh PratapNo ratings yet
- RC Coupled Amplifier Design and AnalysisDocument7 pagesRC Coupled Amplifier Design and AnalysisShweta GadgayNo ratings yet
- RC Coupled Transistor AmplifierDocument7 pagesRC Coupled Transistor AmplifierIshratNo ratings yet
- AEC Manuel For AutnomusDocument24 pagesAEC Manuel For Autnomusanon_648461124No ratings yet
- Lab10 2011Document5 pagesLab10 2011Venkat RamananNo ratings yet
- Ee 3401 Lab 9 ReportDocument8 pagesEe 3401 Lab 9 ReportHayan FadhilNo ratings yet
- EDC II Lab ManualDocument46 pagesEDC II Lab Manualshreeyak841No ratings yet
- Long Report Lab 7Document15 pagesLong Report Lab 7Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift Oscillator and RC Coupled Ce Amplifier - Lab ExperimentDocument8 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillator and RC Coupled Ce Amplifier - Lab ExperimentMani BharathiNo ratings yet
- BJT Fet QuestionDocument12 pagesBJT Fet Questiondearprasanta6015No ratings yet
- RC Coupled AmplifierDocument4 pagesRC Coupled AmplifierSayan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- EC1 Lab Exp3 PDFDocument2 pagesEC1 Lab Exp3 PDFRitu RoyNo ratings yet
- Long ReportDocument14 pagesLong ReportNur Hadi NorazmanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Operation of A RF Class-A Tuned AmplifierDocument7 pagesLab Report Operation of A RF Class-A Tuned AmplifierKugaa NesvaranNo ratings yet
- Voltage Series Feedback AmplifierDocument5 pagesVoltage Series Feedback AmplifierRavi Teja71% (7)
- Homework #9 Derive Equations and Design Cascade AmplifiersDocument4 pagesHomework #9 Derive Equations and Design Cascade AmplifierskbkkrNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CH 3Document33 pagesTutorial CH 3gebretsadkan abrhaNo ratings yet
- Electronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesFrom EverandElectronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Audio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandAudio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- MH1Document18 pagesMH1నాంగిరి సురేష్No ratings yet
- Lec 05Document38 pagesLec 05నాంగిరి సురేష్No ratings yet
- AnalogElectronics - Low and High Frequency Model of CE BJTDocument16 pagesAnalogElectronics - Low and High Frequency Model of CE BJTనాంగిరి సురేష్No ratings yet
- ECE Department's Electronic Circuits CourseDocument27 pagesECE Department's Electronic Circuits CourseklnayaagiNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument7 pagesFull Wave RectifierShafiqur Rahman ParvejNo ratings yet
- Am OpampDocument2 pagesAm Opampనాంగిరి సురేష్No ratings yet
- Light Emitting Diode (Led) 1Document51 pagesLight Emitting Diode (Led) 1piyush_chawla18No ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument11 pagesRectifiersనాంగిరి సురేష్No ratings yet
- TM View Software User - S ManualDocument190 pagesTM View Software User - S ManualLuis SánchezNo ratings yet
- Calculation For Short Circuit Current Calculation Using IEC / IEEE StandardDocument11 pagesCalculation For Short Circuit Current Calculation Using IEC / IEEE StandardibmmoizNo ratings yet
- General Physics1 Q2 W8 Module8 ThermodynamicsDocument23 pagesGeneral Physics1 Q2 W8 Module8 ThermodynamicsRegine Ann ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Forrester Roi StudyDocument30 pagesForrester Roi StudymcgettsNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Power Grid InertiaDocument47 pagesPresentation On Power Grid InertiajorjijonNo ratings yet
- Compact GSM II: Installation and Application ManualDocument22 pagesCompact GSM II: Installation and Application ManualleonardseniorNo ratings yet
- Business Analyst TrainingDocument3 pagesBusiness Analyst TrainingMuniswamaiah Mohan100% (1)
- Tut 5. Two-Column Hammerhead Pier PDFDocument35 pagesTut 5. Two-Column Hammerhead Pier PDFOscar Varon BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Insertion Appointment of Complete Dentures: Lec 17 4 GradeDocument15 pagesInsertion Appointment of Complete Dentures: Lec 17 4 GradeSaif Hashim100% (1)
- L - 1 - INTRO - Well LoggingDocument47 pagesL - 1 - INTRO - Well LoggingSaaeed Ali100% (1)
- Cics Class 05Document18 pagesCics Class 05HarithaNo ratings yet
- Using Topcon GR-3 GPS for Topographic SurveysDocument4 pagesUsing Topcon GR-3 GPS for Topographic SurveysFranco BaldiNo ratings yet
- Jm-10 Operation Manual Rev02 UnlockedDocument121 pagesJm-10 Operation Manual Rev02 UnlockedAlan Jimenez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Control of 2-DOF Robot ArmDocument8 pagesModeling and Control of 2-DOF Robot ArmOtter OttersNo ratings yet
- Saravel Air Hanling UnitDocument92 pagesSaravel Air Hanling UnitClaire ApapNo ratings yet
- ASME - Performance Test CodesDocument1 pageASME - Performance Test CodesanoopkntpcNo ratings yet
- ME4111 Engineering and Mechanical PrinciplesDocument5 pagesME4111 Engineering and Mechanical PrinciplesEdvard StarcevNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Interpret Technical DrawingDocument5 pagesPrepare and Interpret Technical DrawingDwin Rosco75% (4)
- Probability DPP (1 To 7) 13th WADocument16 pagesProbability DPP (1 To 7) 13th WARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- The Big Bang Never HappenedDocument3 pagesThe Big Bang Never HappenedIvan Vule Fridman100% (1)
- Tools - For - Problem - Solving (Appendix B), R.K. Malik's Newton Classes PDFDocument48 pagesTools - For - Problem - Solving (Appendix B), R.K. Malik's Newton Classes PDFMoindavis DavisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2LolmasterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document18 pagesLecture 01priyasonu049No ratings yet
- Thesis On Multilevel ModelingDocument6 pagesThesis On Multilevel Modelingsashajoneskansascity100% (2)
- Impact of GIC On Power TransformersDocument141 pagesImpact of GIC On Power TransformersAkash Verma100% (1)
- Gas-Insulated Switchgear: Type 8DN8 Up To 170 KV, 63 Ka, 4000 ADocument33 pagesGas-Insulated Switchgear: Type 8DN8 Up To 170 KV, 63 Ka, 4000 APélagie DAH SERETENONNo ratings yet
- SE 2003&2008 Pattern PDFDocument799 pagesSE 2003&2008 Pattern PDFBenigno Tique Jonasse100% (1)
- 3-Lecture 03 Translational Mechanical System3-SDocument23 pages3-Lecture 03 Translational Mechanical System3-SHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- UMTS Chap6Document33 pagesUMTS Chap6NguyenDucTaiNo ratings yet