Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JM
Uploaded by
Guillermo ArdenaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JM
Uploaded by
Guillermo ArdenaCopyright:
Available Formats
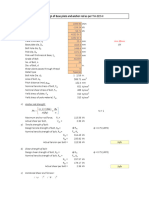
Problem 1
Assume that a 20-mm-diameter rivet joins the plates that are each 110 mm wide. The allowable stresses are 120 MPa for bearing in the plate material and 60 MPa for shearing of rivet. Determine (a) the minimum thickness of each plate; and (b) the largest average tensile stress in the plates.
Solution: Part (a): From shearing of rivet:
From bearing of plate material:
answer Part (b): Largest average tensile stress in the plate:
answer
Problem 2
Given: Diameter of each rivet = 3/4 inch Maximum allowable shear stress of rivet = 14 ksi Maximum allowable bearing stress of plate = 18 ksi The figure below:
Required: The maximum safe value of P that can be applied Solution: Based on shearing of rivets:
Based on bearing of plates:
Safe load
answer
Problem 3
Given: Load P = 14 kips Maximum shearing stress = 12 ksi Maximum bearing stress = 20 ksi The figure below:
Required: Minimum bolt diameter and minimum thickness of each yoke Solution:
For shearing of rivets (double shear)
diameter of bolt answer For bearing of yoke:
thickness of yoke answer
Problem 4
Given: Shape of beam = W18 86 Shape of girder = W24 117 Shape of angles = 4 3- 3/8 Diameter of rivets = 7/8 inch Allowable shear stress = 15 ksi Allowable bearing stress = 32 ksi Required: Allowable load on the connection
Solution: Relevant data from the table (Appendix B of textbook): Properties of Wide-Flange Sections (W shapes): U.S. Customary Units Designation Web thickness W18 86 0.480 in W24 117 0.550 in Shearing strength of rivets: There are 8 single-shear rivets in the girder and 4 double-shear (equivalent to 8 single-shear) in the beam, thus, the shear strength of rivets in girder and beam are equal.
Bearing strength on the girder: The thickness of girder W24 117 is 0.550 inch while that of the angle clip 0.375 inch, thus, the critical in bearing is the clip. is or
Bearing strength on the beam: The thickness of beam W18 86 is 0.480 inch while that of the clip angle is 2 0.375 = 0.75 inch (clip angles are on both sides of the beam), thus, the critical in bearing is the beam.
The allowable load on the connection is Problem 5 Given: Diameter of bolt = 7/8 inch Diameter at the root of the thread (bolt) = 0.731 inch Inside diameter of washer = 9/8 inch Tensile stress in the nut = 18 ksi Bearing stress = 800 psi Required: Shearing stress in the head of the bolt Shearing stress in threads of the bolt Outside diameter of the washer Solution:
answer
Tensile force on the bolt:
Shearing stress in the head of the bolt:
answer Shearing stress in the threads:
answer Outside diameter of washer:
answer
Problem 6
Given: Allowable shear stress = 70 MPa Allowable bearing stress = 140 MPa Diameter of rivets = 19 mm
The truss below:
Required: Number of rivets to fasten member BC to the gusset plate Number of rivets to fasten member BE to the gusset plate Largest average tensile or compressive stress in members BC and BE Solution: At Joint C:
(Tension) Consider the section through member BD, BE, and CE:
(Compression) For Member BC: Based on shearing of rivets: Where A = area of 1 rivet number of rivets, n
say 5 rivets
Based on bearing of member:
Where Ab = diameter of rivet thickness of BC number of rivets, n
say 7 rivets use 7 rivets for member BC answer For member BE: Based on shearing of rivets: Where A = area of 1 rivet number of rivets, n
say 5 rivets Based on bearing of member:
Where Ab = diameter of rivet thickness of BE number of rivets, n
say 3 rivets use 5 rivets for member BE answer Relevant data from the table (Appendix B of textbook): Properties of Equal Angle Sections: SI Units Designation Area L75 75 6 864 mm2 L75 75 13 1780 mm2
Tensile stress of member BC (L75 75 6):
answer
Compressive stress of member BE (L75 75 13):
answer
Different Kinds of Centrifugal fans and their Advantages: Radial Blade (RB) Lower volume Higher pressure
Static Efficiency to 70% Good material handling capabilities Lower operating RPMs (per sp) Overloading type horsepower curve Higher noise Higher Volume lower pressure Static Efficiency to 80% More durable than airfoil Use with light material when frequent cleaning is acceptable Non-overloading horsepower curve Lower noise Higher volume lower pressure Static Efficiency to 84% Clean air only Non-overloading horsepower curve Lowest noise Higher volume lower pressure Static Efficiency to 84% Clean air only Non-overloading horsepower curve Lowest noise Medium volume higher pressure Static Efficiency to 78% Moderate material handling capabilities Lower operating RPMs Overloading type horsepower curve Higher noise
Backward Inclined (BI)
Backward Curved (BC)
Airfoil (AF)
Radial Tip (RT)
Forward Curve (FC) Highest volume lower pressure Static efficiency to 65%
Clean air only Overloading type horsepower curve Low noise
Theory of Centrifugal fans
Industrial fans and blowers are designed to move air and/or powders in industrial and commercial settings. HVAC fans and blowers are used to move air through heating, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. Pressure blowers and fans are used to create and sustain a positive pressure for inflatable structures, clean rooms, laboratories, and medical facilities. Material handling and pneumatic conveying blowers move air through an enclosed system to transport materials. Centrifugal pumps consist of a set of rotating vanes, enclosed within a housing or casing, that are used to impart energy to a fluid through centrifugal force. Electronic cooling fans move air to cool electronic devices. Fan repair services and blower repair services maintain, refurbish and repair fans and blowers.
Theory of Blowers
Material handling and pneumatic conveying blowers move air through an enclosed system to transport materials. Industrial fans and blowers are designed to move air and/or powders in industrial and commercial settings. HVAC fans and blowers are used to move air through heating, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. Pressure blowers and fans are used to create and sustain a positive pressure for inflatable structures, clean rooms, laboratories, and medical facilities. Fan repair services and blower repair services maintain, refurbish and repair fans and blowers. Regenerative blowers are low pressure, high volume blowers that generate centrifugal airflow. Pneumatic Fittings are specifically designed for use in compressed air lines.
Reference: http://www.illinoisblower.com/node/38 http://productsearch.machinedesign.com/mdproducts/centrifugal_fan_theory http://productsearch.machinedesign.com/mdproducts/pneumatic_conveying_blower_theory
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Properties of Engineering MaterialsDocument4 pagesProperties of Engineering MaterialsArchi KumariNo ratings yet
- Design of Replaceent Scheme of Inadequate GussetDocument9 pagesDesign of Replaceent Scheme of Inadequate GussetPartha GangopadhyayNo ratings yet
- 2015thermal PDFDocument26 pages2015thermal PDFBenAmmareImed0% (1)
- Fem in Fracture PDFDocument464 pagesFem in Fracture PDFamitpatel100% (2)
- VESSEL SPECIFICATION FOR OVERHEAD ACCUMULATORDocument2 pagesVESSEL SPECIFICATION FOR OVERHEAD ACCUMULATORMustafa AhsanNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Kme 501Document2 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Kme 501ANKIT JHANo ratings yet
- Weaver (1976) - On Flow Induced Vibrations in Hydraulic Structures and Their AlleviationDocument12 pagesWeaver (1976) - On Flow Induced Vibrations in Hydraulic Structures and Their AlleviationEmerson Borges Santana100% (1)
- Chemical Reaction Engineering-Octave LevenspielDocument24 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering-Octave Levenspielfekremariam AmbawNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow - Bernoulli's Energy TheoremDocument12 pages1.2 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow - Bernoulli's Energy TheoremTeodolfo Delos Trino Balanay100% (1)
- Tutorial Week 11 - Gas-Phase Pressurized CSTRDocument16 pagesTutorial Week 11 - Gas-Phase Pressurized CSTRsiti azilaNo ratings yet
- Viscoelastic Damping 101: Reducing Vibration through Passive DampingDocument3 pagesViscoelastic Damping 101: Reducing Vibration through Passive DampingvdertiNo ratings yet
- Appendix A: Dimensionless Groups: By. Robert B. HeimannDocument2 pagesAppendix A: Dimensionless Groups: By. Robert B. HeimannGusti Ayoe NurjanahNo ratings yet
- Electric Submersible Pump FundamentalsDocument26 pagesElectric Submersible Pump FundamentalsSoko JeanNo ratings yet
- Donaldson Indust Water Process ChillersDocument6 pagesDonaldson Indust Water Process ChillersJeEJyZaNo ratings yet
- FTDDocument188 pagesFTDsharath1199No ratings yet
- Contact Pressure and Yield StressDocument2 pagesContact Pressure and Yield StressthisisjineshNo ratings yet
- Monopole Base Plate - TIADocument2 pagesMonopole Base Plate - TIAAnonymous D2iC3RtKONo ratings yet
- FEDERAL ENERGY MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Data Center Rack Cooling Saves EnergyDocument4 pagesFEDERAL ENERGY MANAGEMENT PROGRAM Data Center Rack Cooling Saves EnergyRohit RwtNo ratings yet
- Short Introduction Into Rheology: Basics, Testing in Rotation, Creep and Oscillation, Extensional RheologyDocument44 pagesShort Introduction Into Rheology: Basics, Testing in Rotation, Creep and Oscillation, Extensional RheologyHafiezul HassanNo ratings yet
- ME 450/550 Computational Fluid Dynamics: CFD Lab 3Document12 pagesME 450/550 Computational Fluid Dynamics: CFD Lab 3api-273690515No ratings yet
- CD T.PM 04.15 Lackey PDFDocument10 pagesCD T.PM 04.15 Lackey PDFjose03No ratings yet
- GAPDocument3 pagesGAPSASHIN ServiSoftNo ratings yet
- Downhole Gas SeperatorDocument210 pagesDownhole Gas SeperatorNourden AlNo ratings yet
- Z Graph ReportDocument14 pagesZ Graph ReportS Kiong TingNo ratings yet
- Deep Foundations - CVX9416Document9 pagesDeep Foundations - CVX9416siyamsankerNo ratings yet
- Fluent Multiphase 19.0 L01 Introduction PDFDocument24 pagesFluent Multiphase 19.0 L01 Introduction PDFNishant VermaNo ratings yet
- Conduction 1 Dimension 08Document29 pagesConduction 1 Dimension 08bobysuryaNo ratings yet
- Quiz ChemistryDocument3 pagesQuiz ChemistryMohd imtiazNo ratings yet
- Materi Ujian Komprehensif: Teknik Reservoir IDocument2 pagesMateri Ujian Komprehensif: Teknik Reservoir IdoubleulandNo ratings yet
- Microchannel Heat Exchanger As EvaporatorDocument11 pagesMicrochannel Heat Exchanger As EvaporatorAbhilash TilakNo ratings yet