Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHF, HPN and CAP
Uploaded by
Jhune VillegasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHF, HPN and CAP
Uploaded by
Jhune VillegasCopyright:
Available Formats
Pamantasan ng Lungsod ng Pasig Alcalde Jose St.
, Kapasigan, Pasig City COLLEGE OF NURSING
Case Presentation (Medicine Ward)
Submitted by: Jhune Emmanuel S. Villegas BSN III Nightingale
Submitted to: Professor Elena Mabini
Introduction
Congestive Heart failure Inability of the heart to keep up with the demands on it and, specifically, failure of the heart to pump blood with normal efficiency may be due to failure of the right or left or both ventricles This can include shortness of breath (dyspnea), cardiac asthma, pooling of blood (stasis) in the systemic circulation or in the liver's circulation, swelling (edema), cyanosis, and enlargement of the heart as signs and symptoms
Hypertension Generally defined as a persistent elevation of systolic a persistent elevation of systolic blood pressure of 140mm of Hg or blood pressure of 140mm of Hg or above and diastolic pressure of above and diastolic pressure of 90mm of Hg or above. Blood pressure is determined by the amount of blood your heart pumps and the amount of resistance to blood flow in your arteries. The more blood your heart pumps and the narrower your arteries, the higher your blood pressure. Persistent hypertension is one of the risk factors for strokes, heart attacks, heart failure and arterial aneurysm, and is a leading cause of chronic kidney failure
Uncontrolled and prolonged elevation of blood pressure can lead to a variety of changes in the myocardial structure, coronary vasculature, and conduction system of the heart. These changes can lead to the development of left ventricular hypertrophy, coronary artery disease, various conduction system diseases, and systolic and diastolic dysfunction of the myocardium, which manifest clinically as angina or myocardial infarction, cardiac arrhythmias, and congestive heart failure. Thus, hypertensive cardiovascular disease is a term applied generally to heart diseases, such as LVH, coronary artery disease, cardiac arrhythmias, and CHF, caused by direct or indirect effects of elevated BP. Although these diseases generally develop in response to
chronically elevated BP, marked and acute elevation of BP can also lead to accentuation of an underlying predisposition to any of the symptoms traditionally associated with chronic hypertension
Community-Acquired Pneumonia It occurs outside of hospitals and other health care settings. Most people get CAP by breathing in germs (especially while sleeping) that live in the mouth, nose, or throat. It is the most common type of pneumonia. Most cases occur during the winter. About 4 million people get this form of pneumonia each year. About 1 out of every 5 people who has CAP needs to be treated in a hospital. most common causes of CAP differ depending on a person's age, but they include Streptococcus pneumoniae, viruses, the atypical bacteria, and Haemophilus influenzae
Nursing Theory THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK NOLA PENDERS THEORY: HEALTH PROMOTION MODEL
The health promotion model is a competence- or approach-oriented model in which the motivational source for behavior change is based in the individuals subjective value of the changethat is, how our client perceives the benefits of changing the given health behavior.
The importance of an individuals unique personal factors or characteristics and experiences will depend on the target behavior for health promotion. Prior related behavior includes previous experience, knowledge, and skill in health-promoting actions.
Individuals who made a habit of a previous health-promoting behavior and received a positive benefit as a result will engage in future health-promoting behaviors.
In contrast, a person with a history of barriers to achieving the behavior remembers the hurdles, which creates a negative effect.
Nurse can assist by focusing on the positive benefits of the behavior, teaching them how to overcome the hurdles and providing positive feedback for their successes.
Our interventions usually focus on factors that can be modified. We also focus on factors that cannot be changed, such as family history. Like our client who has a family history of hypertension, he may neglect self-care practices.
He may do this out of fear or just feeling that with his family history, it is inevitable that he also had hypertension. Nurses should recognize this and direct more support and information to this especially offer more hope for a cure.
Health-promoting behavior is directed toward attaining positive health outcomes for the client. Health-promoting behaviors should result in improved health, enhanced functional ability, and better quality of life at all stages of development.
To promote the health of our client, plan of activities is necessary for implementation. It includes diet modification specifically Low Salt Low Fat Diet, deep breathing exercise for pain management and coughing exercise,frequent positioning and elevation of bed for improvement of ventilation.
As a nurse, one must reinforce clients personal and family health-promoting behaviors. And by assisting them to develop and choose health-promoting options.
Next Anatomy and physiology dko mahanap eh
Nephrons tend to react on sympathetic response of the body STRESS Increased renal absorption of sodium and water Increase sympathetic nervous system activity related to dysfunction
Normal Elastic Function of blood vessels
Increase Fluid volume
Constriction of veins
Increase of ReninAngiotensinAldosterone activity (kidneys)
Dysfunction of Vascular endothelium that leads to decrease vasodilation
Increase Preload CARDIAC OUTPUT Increases (Heart)
Increase Contractility
Hypertrophy
Functional Constrictions
PERIPHERAL RESISTANCE Increases
Ineffective Autoregulation
HYPERTENSION Elevation of Blood Pressure
Presence of Cardiovascular Disease (Atherosclerosis of coronary arteries, cardiomayopathy valvular disorders,coronary artery disease) Hypertension (Elevated Blood Pressure)
Ventricular Overload
Decrease Ventricular Contraction
Stimulate release of epinephrine and norepinephrine
Decrease Renal Perfusion
Stimulates Renin-AngiotensinAldosterone System for sodium and water retention
Tachycardia Myocardial Hypertrophy Increase Osmotic Pressure Decrease Ventricular Filling
Decrease CARDIAC OUTPUT Invading Organisms: (Staphylococcus Pneumoniae) Capillaries small blood vesselsprotein Enters the become leaky and in the Cause fluid seeps in the alveoli rich Oxygen Deprivation lungs(Capillaries)
Fluid Overload Edema
Mucus productionoccurs Solidification Alveolar walls and Infection of of spaces within the Consolidation and leaky capillariesto quantities fluid debris may linge the mucus lung due further of the lings AlveoliParenchymawith fluid and debris fill (Hollow air) with blood
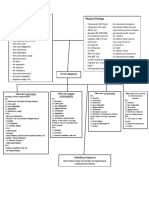
Nursing Health History Biographical Data 1. Patient X 2. Bayabas St., Napico, Manggahan, Pasig City 3. 49 years old 4. Male 5. Filipino 6. Married 7. Company worker 8. Roman Catholic 9. Office loan as source of health finances Chief Complaint: Client verbalizes, Nalulunod ako, Di ako makatulog. He stated that he was unable to sleep for three consecutive days prior to admission because of shortness of breath. Presence of fever for three days and cough with yellowish phlegm. HEALTH HISTORY A. History of Present Illness Mr. B is known of having hypertension 5 years ago but not taking any maintenance drug. He was admitted to ER last July 18, 2010 due to difficulty of breathing. He has cough with yellowish phelgm and with (+) crackle and SCE. B. Past History Mr. B had childhood illnesses like chickepox, measles,mumps when he ws young. He has no known allegies to food, drugs, animals, insects or environmental agents. He had a gunshot accident before. He has previous hospitalization last 2000 due to peptic ulcer disease. C. Past History of Illness Mr. B stated that in his family, there was none of the diseasa conditions similar with other patients of the hospitals. His family history was only about asthma with her wife and hypertension from his dad. Her two chikdren also asthma, the eldest and youngest.
PAIN ASSESSMENT
The client stated that prior to confinement he experiened some pain. It was pain during coughing under the diaphram and upper abdomen. And when cough is prevented from doing so, it became more worst pain. He rated it 7 out of 10 and to relieve the pain he usually position himself prone.
FUNCTIONAL HEALTH PATTERN 1. Health Perception and Health Management Pattern According to Mr. B, he is feeling well even though he is not yet for discharge and they are still waiting for more clarified reason of being healthily discharge. He said it is easy to follow the instructions that his doctors and nurses may tell him. He thinks that his codition right now is brought about by overworking and lack of proper food choices. He has stop smoking since 2000 after he was hospitalized of having peptic ulcer disease.
2. Nutrition and Metabolic Pattern Mr. B said that before, his typical type of foods are galunggong and pinakbet but because he is working, the typical foods he eats are chickens, porks, beef and oily foods. He also said thateating too much fatty foods might be one of the reason why he became a CHF patient. He also loose weight in 1 months , because before, he weighs 92 kilograms and now, its only 76.2 kilograms. He has two decaying teeth but he doesnt want it to be removed for it is not aching anyway.
3. Elimination Pattern Mr. B said that he has none of eliminating problems as well as urinating. He described it as normal frequent urination.
4. Activity-Exercise Pattern Perceived ability for: Feeding Bathing Toileting Bed mobility 4 4 5 5 Grooming General Mobility Cooking Home Maintenance 4 4 4 4
Dressing Mr. B.
Shopping
5. Sleep- Rest Pattern Mr. B said that there is difficulty for him to sleep due to cough he still have. He also said that he takes siesta by 1pm to 6pm. And for him, to relieve the diffucultly hes in, he use to change position from supine to sitting and to prone.
6. Cognitive-Perceptual Pattern He has no colorblindness experiencing as well as hearing impairment. He also said that he learns more easily when the topic is beng lactured to him and he take notes of those informations and listens actively. Aside from that, Mr. B didnt say anything.
7. Self- Perception and Self- Concept Pattern Mr. B, described himselfes Dati malakas ako, di naman ako nahahapo, ngayon lagi na ko nahahapo. Para akong nalulunod,hinahingal agad ako. The client states that he feels less capable of doing things he usually do. Especially those tasks hes doing at work. He missed his job he said; he wants to be discharge early so that he can go back to work and have the assignment in their working places.
8. Sexuality- Reproductive Pattern Mr. B, admitted that he is sexually active only with his wife and they use contraceptives.
9. Role- Relationship Pattern He descibed his role as a fullfiling one for he said, he was the only breadwinner of the family. But now that he was in the hospital, he was uncapable to find job and give income to his family. He stated,Kapag nakareover ako, babalik ako sa trabaho.
10. Stress- Tolerance Pattern He said that his primary stressors are his daughters. Because if he ask for favors, his daughters take some more time before dong it and he also said that his children were hardheaded and very
noisy. But he always think that he was highblood so he usually rejects the emotion of being angry. He want to calm down himself to prevent elevated blood pressure that he might have.
11. Value- Beliefs Pattern He said that the most important things for him were enough income to support his childrens studies as well as his family for everyday trials. His family were all Roman Catholics but they usually listens to Ely Soriano. He said, it is important to have faith cause it is where he takes his strength to go on and keep on struggling. The client believes that God will always be beside us. He is a God-fearing person. And according to him, religion is very important.
Next P.E wala ako eh dko na mahanap Tapos NCP dko din mahanap NCP nito eh
GENERIC NAME Furosemide 40 mg IV now then 40 mg IV q 8BP check
BRAND NAME Lasix, Delone, Detu e
ACTION
DRUG INTERACTION Drug study Congestive heart failure, liver disease, or kidney disease. Hypertension
ADVERSE EFFECT
NURSING CONSIDERATION
A "water pill"
(diuretic) that increases the amount of urine you make, which causes your body to get rid of excess water. Lowering high blood pressure helps prevent strokes, heart attacks, and kidney problems. It also reduces swelling/fluid retention (edema) and can help to improve symptoms such as trouble breathing. blocking the absorption of sodium, chloride, and water from the filtered fluid in the kidney tubules, causing a profound increase in the output of urine (diuresis) blood vessels that supply the areas of the heart where there is not enough oxygen thereby delivering oxygen to the heart tissue that needs it most. Used in the management of angina pectoris (heart pain).
Drugs that can affect
hearing/balance (e.g., aminoglycoside antibiotics such as gentamicin, tobramycin), amphotericin B, cholestyramine, cisplatin, colestipol, corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone), digoxin, lithium, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, indomethacin ), large doses of aspirin and aspirin-like drugs (salicylates), sucralfate.
Dizziness, lightheadedness, headache, blurred vision, loss of appetite, stomach upset, diarrhea, or constipation serious symptoms of dehydration or mineral loss: muscle cramps or weakness, confusion, severe dizziness, drowsiness, unusual dry mouth or thirst, nausea or vomiting, fast/irregular heartbeat, unusual decrease in the amount of urine, fainting, seizures
Before using this
medication ask for medical history, especially of: kidney disease, liver disease, untreated mineral imbalance (e.g., sodium, potassium), gout, lupus Avoid prolonged sun exposure, tanning booths or sunlamps Laboratory and/or medical tests (e.g., kidney and liver function tests, uric acid, cholesterol levels, blood mineral levels such as potassium,) should be performed periodically to monitor your progress or check for side effects Have your blood pressure checked regularly while taking this medication
Nitroglyceri n 5g ACLU L x 16
Nitrostat, Nitr oqui ck, Nitr olin gual, Nitr oDur, Mini tran, Nitr oBid and Nitr al Patc h
Preferentially dilates
congestive heart failure associate d with myocardial infarction (heart attack) and high blood pressure
Some antidepressants;
some antipsychotics, quinidine (Quin aglute, Quinidex), procainamide(Pr onestyl, Procan-SR, Procanbid), benzodiazepine s such as diazepam (Valium) or opiates(morphine) Patients receiving nitroglycerin should be advised to drink alcoholic beverages with caution. Sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis) and vardenafil (Levitra) exaggerate the blood pressure lowering effects of nitroglycerin Ergot alkaloids can oppose the vasodilatory actions of nitroglycerin and may cause angina.
Persistent,
throbbing headache, flushing of the head and neck can occur with nitroglycerin therapy as can an increase in heart rate or palpitations, dizziness or weakness.
Before using this medication tell your doctor your medical history especially of: heart problems, head injury or surgery, glaucoma, thyroid conditions, anemia, alcohol usage, allergies (especially allergies to drugs or adhesives).
LABORATORY RESULTS Serum Test July 18, 2010 SERUM Glucose HDL RESULTS 6.11 mmol/L 0.6 mmol/L NORMAL 4.16-6.11 mmol/L 1.0- 1.6 mmol/L INDICATIONS Normal range considered a coronary heart disease risk factor independent of the level of total cholesterol Associated with arterial artherosclerosis
LDL
4.00 mmol/L
0.00-3.36 mmol/L
Serum Test July 18, 2010 SERUM Urea Crea Na K RESULTS 3.4 mmol/L 72.0 mmol/L 137.0 mmol/L 3.5 mmol/L NORMAL 3.2-7.1 mmol/L 58.0-110 mmol/L 137.0- 145 mmol/L 3.6- 5.0 mmol/L INDICATIONS Normal range Normal range Cardiac failure, Diuretics abuse Associated with corticosteroids & diuretics, drugs that may cause hypokalemia
Course in the ward
PRESENT HISTORY: 3 days PTA,the patient has(+)Cough with productive with yellowish phlegm;(+)Fever; (+)Easy fatigability. Took self medications with paracetamol, Cefalexin, Salbutamol,and Guiafenessin PAST HISTORY The patient has(+)Previous Hospitalization (Year2000) at QMMC with Dx: PUD; (+)HPN with (-)maintenace medication;(-)DM, BA, PTB;(-)FDA ;previous cigarette smoker D/C 2000,Alcoholic
EMERGENCY ROOM: 07-18-10(6:30am) Admitted a 49 y/o married male filipino client CC: DIFFICULTY OF BREATHING Secure consent for admission
ASSESSMENT FINDINGS
(+) Crackles lower base with occasional wheezes; SCE
DOB
Easy Fatigability NPO Temporarily LABORATORIES: CBC, APC, Na, K, BUN, Creatinine, CXR-PA, HDL,LDL
(+)HPN
(+) Fever
Chest Pain
Hold Nebulization for 15 mins, 60mg tab PO now
Combivent ml + PNSS 2cc x 3 doses c 15 mins interval, then q 2o
Given Calcibloc prn
Hooked to PNSS 1Llx 12o
Given O2 at 4Lpm Via NC
MEDICATIONS: Cefuroxime 1.5 g (-)ANST TIV now then 250 mg TIV prn Clarithrimycin 500mg if needed then BID Paracetamol 300g TIV
BP: 250/190 mmHg P: 107 bpm T: 38.5oC RR: 32 breaths
Results: Urea: 3.4 mmol/L; Crea:72.0mmmol/L; Na:137.0mmol(LO); K:3.5 mmol/L(LO)
on LSLF Diet
Shift IVF to D5W 500cc x KVO
Give Furosemide 40mg TIV nowCheck BP
Referral to Male Medicine Ward
Results: Medications: With 2 Continue Oon going SF 2DECHO with BP: 150/120 S/E by Dr. Duro LDL: 4.00mmol/L(HI) Clarithromycin 500 mg/cap IVF: PNSS 1L IVF PNSS 1L Conscious & x SF 2DECHO with support 3Lpm HDL: 0.6mmol/L(LO) DS-request breaths Paracetamol RR: MALE with orders carried MEDICINE WARD 07-18-10(4pm) MALE MEDICINE WARD 07-19-10(6am) Losartan 100mg/tab 36 o, AU, Applied Nitroglycerin x KVO at at HBR KVO at full Coherent WORKIND DIAGNOSIS: DS, UA, FBS, TC, Chest Pain Perform TSBADMITTING DIAGNOSIS: TIV Diet: o via NC FBS, TC, TG, HDL, 1amp T: 36.7 C by relative Transfer via stretcherpatch out CVD o GLUCOSE:6.11mmol/L(HI) via NC sodium On Moderate HBR HPNCVD; CAPT: 38.level CAP MR, Lpm CHF 2 LR With O2 2-3HAS 900cc 9oCefuroxime LDL 750mg TIV T: LSLF Diet level LSLF with SAP C HDL,LDL, 37.4 C CR: 108 bp
END OF DUTY
EVALUATION
During the interview, nurse fined it hard to gather data that are necessary in their study. The patient was 49years old but having difficulty speaking due to cough. Even though there was a barrier on gathering information, the nurse was able to gather needed information because they had also interviewed the clients wife and daughter.
The doctors orders were all put into action by the nurse in charge just like the order for a 2DECHO. Other than that, there were some other laboratory tests that were undertaken by the client for further monitoring. There were many medications that were given to the client for different purposes like Furosemide, Clarithromycin, Losartan, and others.
Overall, the nurse thought t all of the interventions made by all health care providers were effective after the prescription to continue his medications. The nurse was able to implement necessary interventions like deep breathing exercise, coughing exercise as well as diet management for the client.
You might also like
- Manual Digital Therapy MachineDocument37 pagesManual Digital Therapy MachineEduardo Soares100% (1)
- Case Study: Congestive Heart FailureDocument7 pagesCase Study: Congestive Heart FailureXI-E / 21 / MARY TRIANANo ratings yet
- NCP Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument12 pagesNCP Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisScarlet ScarletNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation: by Michael ArmstrongDocument21 pagesCase Presentation: by Michael ArmstrongWirawan Amirul BahriNo ratings yet
- Nursing Case Presentation For A Patient With CABG: Subject: Medical Surgical Nursing-IIDocument10 pagesNursing Case Presentation For A Patient With CABG: Subject: Medical Surgical Nursing-IIanamika sharmaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PresentationDocument20 pagesPneumonia PresentationsetanpikulanNo ratings yet
- Right Sided Heart FailureDocument33 pagesRight Sided Heart FailurePaulNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Dinesh Kumar PDocument42 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: Dinesh Kumar PRiya Sweetsolitude100% (1)
- Exudative Pleural Effusions - UpToDateDocument2 pagesExudative Pleural Effusions - UpToDateAsif IqbalNo ratings yet
- Case AppendicitisDocument30 pagesCase AppendicitisSarahNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy My LectureDocument33 pagesCardiomyopathy My LectureAbraha HailuNo ratings yet
- IM - Heart Failure Concept Map - PathophysDocument5 pagesIM - Heart Failure Concept Map - PathophysTrisNo ratings yet
- IM Clinics History 2Document4 pagesIM Clinics History 2LucyellowOttemoesoeNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis 0232Document118 pagesCholelithiasis 0232Kz LonerNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument124 pagesCongenital Heart DiseasemulkanmustafaNo ratings yet
- AKI CASE NishaDocument64 pagesAKI CASE NishaSurkhali Bipana100% (1)
- Case Study PPT Patho NLNGDocument36 pagesCase Study PPT Patho NLNGKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Anal FistulaDocument26 pagesAnal FistulaBeverly PagcaliwaganNo ratings yet
- MIDocument22 pagesMIGagauz SiliviaNo ratings yet
- MICU Case Study PresentationDocument55 pagesMICU Case Study Presentationjmarc_21100% (4)
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument27 pagesIntestinal ObstructionAna AvilaNo ratings yet
- Case Study LeukemiaDocument8 pagesCase Study LeukemiaAlexander NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Cerebral HemorrhageDocument10 pagesCerebral HemorrhageJayd Lorenz Vicente ChuanNo ratings yet
- Acute Cholecystitis - PCP CPG 2003Document37 pagesAcute Cholecystitis - PCP CPG 2003Teng IbanezNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment ON Gastro Intestinal System: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument13 pagesHealth Assessment ON Gastro Intestinal System: Submitted To: Submitted byAnanthibalaNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain.Document53 pagesChest Pain.Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- ConceptMap AMLDocument1 pageConceptMap AMLnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- 22 Ventricular Septal DefectDocument26 pages22 Ventricular Septal Defectdhiraj parmarNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Critically Ill PatientDocument5 pagesAssessment of The Critically Ill PatientCris John RicoNo ratings yet
- Choledocholithiasis: A Case Study ofDocument5 pagesCholedocholithiasis: A Case Study ofJanelle Kate SaleNo ratings yet
- Men in NursingDocument2 pagesMen in NursingMark JosephNo ratings yet
- LA Myxoma Case PresentationDocument34 pagesLA Myxoma Case PresentationWiwik Puji LestariNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Distension: Common Causes: - (Five F'S) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. History of Present Illness 1Document3 pagesAbdominal Distension: Common Causes: - (Five F'S) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. History of Present Illness 1Maxamed DananNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation - GASTRODocument46 pagesCase Presentation - GASTROalidudeNo ratings yet
- How To Define CardiomegalyDocument2 pagesHow To Define CardiomegalyKjean De Vera MelendezNo ratings yet
- UGIBDocument5 pagesUGIBdwyane0033100% (1)
- Case Presentation On Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument64 pagesCase Presentation On Supraventricular TachycardiaHazel AsperaNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 (Case 1)Document53 pagesCovid 19 (Case 1)cendy andestriaNo ratings yet
- Case Stydy Angina PectorisDocument46 pagesCase Stydy Angina PectorissharenNo ratings yet
- BPHDocument81 pagesBPHFlo Neri BerondoNo ratings yet
- HemiplegiaDocument11 pagesHemiplegiaFares EL DeenNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On Copd: By, Thomas Eipe Pharm D InternDocument32 pagesCase Presentation On Copd: By, Thomas Eipe Pharm D InternThomas EipeNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation - HerniaDocument19 pagesCase Presentation - HerniaElvin Louie Lisondra100% (1)
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Bello, Mickaela Bianca A. Gumiran, NomerDocument37 pagesCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia: Bello, Mickaela Bianca A. Gumiran, NomerKristine-Joy Legaspi FrancoNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument15 pagesCase PresentationMarianne Del Rosario AndayaNo ratings yet
- Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument10 pagesRenal Cell Carcinoma'asyura Mohd RezaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonaryembolism 150329161109 Conversion Gate01Document60 pagesPulmonaryembolism 150329161109 Conversion Gate01Rafika RaraNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument39 pagesAsthmamits98No ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Patient Chart - Mary JohnsonDocument12 pagesCase Presentation: Patient Chart - Mary Johnsonivoneeh_16100% (1)
- MR Elamin ShockDocument70 pagesMR Elamin ShockMohammed Abd AlgadirNo ratings yet
- Case StudyNursing AssessmentDocument7 pagesCase StudyNursing AssessmentArindomNo ratings yet
- Asthma2 Case StudyDocument8 pagesAsthma2 Case StudyGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- PBL PgamboaDocument6 pagesPBL PgamboaLeanne Princess GamboaNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Distress SyndromDocument38 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress SyndrompatriaindraNo ratings yet
- IM AdconDocument28 pagesIM AdconCla SantosNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument11 pagesPericarditisrbarcellonaNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument35 pagesPleural Effusionkhikmatul mu'jizahNo ratings yet
- Cva Case PDFDocument39 pagesCva Case PDFEmsy Ni ThelayNo ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- 4 E - KYM 2011 - Detection of Counterfeit Currency SINGAPOREDocument5 pages4 E - KYM 2011 - Detection of Counterfeit Currency SINGAPOREJhune VillegasNo ratings yet
- OJT Attendance FormDocument1 pageOJT Attendance FormJhune Villegas100% (1)
- 21 GunsDocument2 pages21 GunsJhune VillegasNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Monitoring at HomeDocument11 pagesBlood Pressure Monitoring at HomeJhune VillegasNo ratings yet
- AsteroidsDocument3 pagesAsteroidsJhune VillegasNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument4 pagesAnemiaJhune VillegasNo ratings yet
- Ofw ClinicsDocument19 pagesOfw Clinicsnum_lock_erNo ratings yet
- Educational DiagnosisDocument2 pagesEducational DiagnosisJhune VillegasNo ratings yet
- EuthanasiaDocument1 pageEuthanasiaJhune VillegasNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Clinical Case StudyDocument5 pagesMental Health Clinical Case Studyapi-546156641No ratings yet
- SCD and Hydroxyurea TherapyDocument29 pagesSCD and Hydroxyurea Therapysamuel waiswaNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 - Lesson 3 (Pulmonary Embolism)Document4 pagesNCM 118 - Lesson 3 (Pulmonary Embolism)Bobby Christian DuronNo ratings yet
- 6 Depression in ChildrenDocument4 pages6 Depression in ChildrenMirza ShaplaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Prevention and ControlDocument19 pagesHepatitis B Prevention and Controlcolltfrank100% (1)
- Cross Sectional Studies Hemed 2015Document12 pagesCross Sectional Studies Hemed 2015delovinaNo ratings yet
- American Indian Reservations: The First Underclass Areas?: Brief History of The Reservation SystemDocument5 pagesAmerican Indian Reservations: The First Underclass Areas?: Brief History of The Reservation SystemtheactioneerNo ratings yet
- CATCH UP FRIDAY - March 22 2024Document2 pagesCATCH UP FRIDAY - March 22 2024jeffersonmanalo787No ratings yet
- Regulatory Bodies of Nursing in India: Dr. Maheswari JaikumarDocument75 pagesRegulatory Bodies of Nursing in India: Dr. Maheswari Jaikumarkalla sharonNo ratings yet
- Coccaro 2016Document22 pagesCoccaro 2016Umar RachmatNo ratings yet
- Things Inside The First Aid Kit: Name: Emplamado, RG B. Course and Section: BS Accountancy - 1BDocument4 pagesThings Inside The First Aid Kit: Name: Emplamado, RG B. Course and Section: BS Accountancy - 1BArgNo ratings yet
- HypnosisDocument328 pagesHypnosisPabloAPacheco93% (14)
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and DiagnosisDocument9 pagesPosttraumatic Stress Disorder Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and Diagnosisisa_horejsNo ratings yet
- Cure For Cancer or Placebo Effect!Document3 pagesCure For Cancer or Placebo Effect!samantha willisNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: F112 Surfactant F112Document8 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: F112 Surfactant F112sajad gohariNo ratings yet
- Healthy Neighborhoods GuidebookDocument102 pagesHealthy Neighborhoods GuidebookSuci Dika UtariNo ratings yet
- Johanna BudwigDocument4 pagesJohanna Budwigjcoppala44760% (1)
- SulfonylureasDocument3 pagesSulfonylureasarsalanzahid1No ratings yet
- InBody 270Document27 pagesInBody 270lee CeeNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications in Najaf City, IraqDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitus and Its Complications in Najaf City, IraqYaman HassanNo ratings yet
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDocument13 pagesAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- 5 Parts and Questionnaire EditDocument11 pages5 Parts and Questionnaire EditMichael Oblefias SorongonNo ratings yet
- FARC-01 - Senior First Aid (Occupational First Aid Course OFAC)Document2 pagesFARC-01 - Senior First Aid (Occupational First Aid Course OFAC)Ewien Vars SianturieNo ratings yet
- Cor PulmonaleDocument21 pagesCor Pulmonalemaibejose100% (1)
- Adult Survivors of Childhood Trauma: Complex Trauma, Complex NeedsDocument9 pagesAdult Survivors of Childhood Trauma: Complex Trauma, Complex NeedsPhy MedNo ratings yet
- June 23 2022 Owosso Job Fair Flyer GSTDocument4 pagesJune 23 2022 Owosso Job Fair Flyer GSTCaleb HollowayNo ratings yet
- Childhood Glaucoma: by Kelli OrdakowskiDocument16 pagesChildhood Glaucoma: by Kelli OrdakowskikmordakowskiNo ratings yet
- Proximal Femur Fractures: Sulita Turaganiwai s130364Document26 pagesProximal Femur Fractures: Sulita Turaganiwai s130364Wālē NandNo ratings yet
- Laws Affecting Nursing PracticeDocument52 pagesLaws Affecting Nursing Practiceapi-3731845100% (3)