Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bba Mis Topic 7
Uploaded by
Jebby VargheseOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bba Mis Topic 7
Uploaded by
Jebby VargheseCopyright:
Available Formats
Management Information Systems
By : Prof. Prakash M Soni
Topic No.: 7 MIS Design Approach
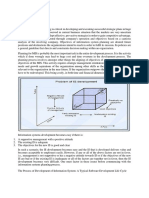
Introduction 1
The fundamental part of any MIS development process is PLAN & IMPLEMENTATION process of it. The major and very critical element of any MIS is the Inflow of Information with all attributes If this stage is in place, then it's just based on effective management activities to handle information. The control mechanism will take care of the usage of information to the user at different levels of the organization We need a management information system flexible enough to deal with the changing need of information in the organization. It should be Open System in working nature to provide support organization at appropriate time and level. Designing of such system is very complex and critical task. It can be achieved only if MIS is planned, keeping in mind the organization structure, information flow and effect of information on levels of organization MIS plan has to match with the organization plan and aim The development process should be focus on the strategic need and implementation of information on the levels of organization The plan of development of the MIS is linked with the steps of the implementation in a business development plan The system of information generation is so planned that strategic information is provided for the strategic planning, control information is for controlling process and short term planning and execution support to operation management team
Steps of MIS Development
Identify Business Goals Determine critical success factors Develop business strategy and IS strategies Identify critical business applications Make decision analysis and enumerate operational and strategic decisions Develop business performance indicators Identify information entities to decision support for business Determine IS structure to generate information to build MIS Build MIS superset as prescribed in general model of MIS
Development Process Model - 1
Study the business environment Study the organization and structure Identify mission and business goals Identify critical success factors Identify critical business applications
Queries? Email: profprakashsoni@gmail.com
Management Information Systems
By : Prof. Prakash M Soni
Ascertain the business strategy Identify business decisions needed to implement strategy Determine MIS goals supporting business goals Determine MISs support Develop key performance indicators to measure the business progress and performance Identify data and information needs meeting the MIS goals and business goals Develop IS and IT strategy to meet the goals Determine IS and IT support structure to meet data and information needs Link and map MISs and information outcome to business goals and strategy Design information reporting structure: Periodic, Exception and Control Reports Design KMS and BI System
Business Plan Vs MIS Plan
Business Plan
MIS Plan
Business Goals and Objective Business Plan and Strategy Strategy Planning and Decisions Management plan and execution and Control Operation plan for the execution
MIS, Objectives, Consistent to the business goals and objectives Information Strategy for the business plan implementation playing a supportive role Architecture of the MIS to support decisions System development schedule, matching the plan execution Hardware and Software plan for the procurement and the implementation
MIS Design Approaches
Once it's been decided to develop MIS, the next call is to formulate the strategies for designing, development and implementation of MIS in the organization The development approaches determines where to begin and in what sequence the development can take place with the sole objective of assuring the information support Types of MIS development approaches are: Prototype Approach Life Cycle Approach
Queries? Email: profprakashsoni@gmail.com
Management Information Systems
By : Prof. Prakash M Soni Prototype Approach
It is a process of progressively ascertaining the information needs, developing methodology, trying it out on a smaller scale with respect to the data and the complexity, ensuring that it satisfies the needs of the users and assess the problems of development and implementations Designers task becomes difficult with multi-user involvement It is information gathering process to get exact reactions, feedbacks, innovations, review plans of the system by the end users Its a trial and error based system It is based on Iteration Approach for exact development and implementations to meet organizational goal
Steps in Prototyping Approach
Situations for applicability of Prototyping
Unclear Requirements Complicated and Large System Illustrations of User Interface Unclear Solutions Throw Way Plans
Advantages Of Prototyping
User feedback Motivates User Early Error Handling Flexibility
Queries? Email: profprakashsoni@gmail.com
Management Information Systems
By : Prof. Prakash M Soni Disadvantages Of Prototyping
Need of Accurate Prototype Lack of Each Phase Review Lack of Documentations Lack of Recovery Extended Schedules Can Mislead Users
Life Cycle Approach
Every MIS System and sub-system have a defined life cycle of development & working. Sometimes it does comes sudden or structure or time rule based. Minor changes are the ongoing process with any MIS system but the major steps become the change-over reason for new development and application Such changes are within the sub-system and they become the root cause of such new development
SDLC Life Cycle
SDLC: Investigation
System Planning & Selection: Survey the organization to screen and select the system aspects which are based on formal and open information system Feasibility System: Based on the information generated about the system, now need to take call on feasibility of development Feasibility Report: Document and communicate the results of the feasibility study to end users and management
Queries? Email: profprakashsoni@gmail.com
Management Information Systems
By : Prof. Prakash M Soni SDLC: Analysis
Analysis of the organizational environment: Analyze in detail the information needs of an end user organization & its subsystem & environment systems Analysis of any present system: Analyze the resources, products & activities of any information system presently used System requirement analysis: determine the information system capabilities that will meet the information need of the users System requirements: Document & communicate the logical input, process, output storage & control requirements of system
SDLC: Design
Logical System Design: Develop general specifications for how input, processing, output storage & control activities will work Physical System Design: Develop detailed specifications for user interface products and methods, database structure & processing and control processes. Hardware and software specifications etc System Specifications: Document and communicate the detailed specifications of the proposed system to end users
SDLC: Implementation
Acquisition of Hardware, Software and Services: Evaluation of all System requirement proposals from vendors Software Testing: Trail and Error process End User Training: Educate and train management, end users, customers and other business stakeholders etc Documentation: Record and communicate process of usage and User Manual for references Conversion: Convert from the use of a present system to the operational of a new or improved system
SDLC: Maintenance
To correct Errors: Uncovering bugs in the programs or weaknesses in the design that were not detected during testing & correcting them To keep System Current: Over the time, changes occurs in the system environments that requires modifications in the current system To Improve the System: Continuous improvement in the system is required to meet user requirements but only feasible changes
Queries? Email: profprakashsoni@gmail.com
Management Information Systems
By : Prof. Prakash M Soni Project Management
MIS design can be easily thought of as Project Management and its important task is to designate the key project values of INFORMATION MIS designers will have to work upon the planning and controlling activities of management for PM. The controlling majorly focus on Cost & Time variables in PM But, Projects differs from Processes because they aims at Functional development rather than Procedural development
Project Management Steps
MIS Project Needs
The search for planning and operating problems The search for areas of recurring difficult decisions The search for company opportunities that depends upon expanded information system Prioritization of problems and opportunities Selection of projects whose payoff in terms of cost and limitations of resources is justified
Setting Project Objective
Financial and Accounting System Corporate management for competitors and opportunities Production and Inventory System with Purchasing system Online Information system for SCM with locations To control technical cost, work and schedules Better manpower planning New forecasting techniques Financial Reporting System on weekly basis
Queries? Email: profprakashsoni@gmail.com
Management Information Systems
By : Prof. Prakash M Soni
Project Proposal
Drafting proposal after identifying needs, objectives, preliminary definition of project work, scope, costs and benefits then seeking approval of management after evaluating and selection process Second option is MIS project is rolled out then the budgeting issues were discussed by management and its very time consuming process with less opportunity to evolve all aspects of management and information Project Proposal consists of introduction, management summary, a system description and costs estimates with schedules
Planning Techniques
Work Breakdown Structure: System to sub-system, Sub-system to task, task to sub-task, Subtask to work package etc Sequence Planning: Development of the system, it is necessary to determine what immediately preceding tasks must first be completed. Factors are time, cost, user involvement etc Master Program Schedule: The predetermined deadline dates set by management for overall development of MIS Budgeting: The establishment of cost and resource targets for a planned series of periods in advance is project planning. It covers only direct costs.
Reporting & Controlling
Control of the project means control of Performances, Cost and Time variables The reporting format of any control mechanism should consists PCT elements together with full scope Control of PCT elements is from the project concept development phase till the final rolling out and evolution of the project of MIS based on organization structure and level of information involved
Implementation of MIS
MIS Implementation Procedure Planning the implementation Acquisition of facilities Procedure development Generation Files and Folders Testing of System Evaluation & Maintenance of System
Queries? Email: profprakashsoni@gmail.com
You might also like
- Fixed Cost: Marginal CostingDocument6 pagesFixed Cost: Marginal CostingJebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Fixed Cost: Marginal CostingDocument6 pagesFixed Cost: Marginal CostingJebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Zero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionFrom EverandZero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionNo ratings yet
- MB0031 Management Information SystemDocument20 pagesMB0031 Management Information Systempranay srivastavaNo ratings yet
- JAMES A. HALL - Accounting Information System Chapter 13Document45 pagesJAMES A. HALL - Accounting Information System Chapter 13Joe VaTaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual DesignDocument8 pagesConceptual DesignPallavi SacharNo ratings yet
- Mis Mba Full NoteDocument41 pagesMis Mba Full NoteShinu Joseph Kavalam83% (6)
- Automatic Speaker VerificationDocument24 pagesAutomatic Speaker VerificationJagadish KakkireniNo ratings yet
- R12 Uploading A Journal Using Web ADI - Step by Step - Oracle Techno & FunctionalDocument18 pagesR12 Uploading A Journal Using Web ADI - Step by Step - Oracle Techno & FunctionalMadhavi SinghNo ratings yet
- Software Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSoftware Testing Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- IT Alignment StrategiesDocument5 pagesIT Alignment StrategiesMuhammad SadiqNo ratings yet
- SAPSCRIPT To PDFDocument15 pagesSAPSCRIPT To PDFssurisetty83% (6)
- Flow DWDocument200 pagesFlow DWPino Watson PisoloNo ratings yet
- Company ListDocument5 pagesCompany ListDheeraj50% (2)
- Development of Management Information SystemDocument7 pagesDevelopment of Management Information Systemsunitamanro100% (1)
- Unit-3 MisDocument17 pagesUnit-3 Misuttkarshpandey0018No ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument30 pagesManagement Information SystemMohsin KhanNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument36 pagesManagement Information SystemShubham JainNo ratings yet
- Development of Long Rate Plans of The MISDocument10 pagesDevelopment of Long Rate Plans of The MISDeepak MauryaNo ratings yet
- Mis 3Document5 pagesMis 3peterNo ratings yet
- Information System PlansDocument10 pagesInformation System PlansAhmed GulzarNo ratings yet
- MIS Notes Unit 4Document9 pagesMIS Notes Unit 4Sanjeev Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Need For Information SystemDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Need For Information Systemmaryallaine02No ratings yet
- MIS Slides Module 4Document85 pagesMIS Slides Module 4priyanka_5sNo ratings yet
- MIS DevelopmentDocument6 pagesMIS DevelopmentSonia LawsonNo ratings yet
- MIS - Development Process - TutorialspointDocument6 pagesMIS - Development Process - Tutorialspointtusharsinghal94No ratings yet
- Unit Iii Developing Information SystemDocument14 pagesUnit Iii Developing Information SystemMala niveNo ratings yet
- Class 5Document15 pagesClass 5Swastik SahooNo ratings yet
- Themes in Information System DevelopmentDocument14 pagesThemes in Information System DevelopmentMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Mis Planning and Development BY Ankur MittalDocument30 pagesMis Planning and Development BY Ankur Mittalankurmittal2112No ratings yet
- Mb0047 Unit 05-SlmDocument24 pagesMb0047 Unit 05-SlmBibin JoyNo ratings yet
- Assignment of MISDocument9 pagesAssignment of MISPranav GoyalNo ratings yet
- Mis Design FinaDocument19 pagesMis Design FinargaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology On System Analysis and DesignDocument17 pagesResearch Methodology On System Analysis and Designstarvamsi123No ratings yet
- Survch 1Document9 pagesSurvch 1Doaa RezkNo ratings yet
- Mis Assignment 2 FinalDocument7 pagesMis Assignment 2 Finaleyob yohannesNo ratings yet
- I. Information Systems PlanningDocument28 pagesI. Information Systems Planningtricia quilangNo ratings yet
- I. Information Systems PlanningDocument8 pagesI. Information Systems Planningtricia quilangNo ratings yet
- Employee Survey Feedback System 201: 1.1. ObjectiveDocument32 pagesEmployee Survey Feedback System 201: 1.1. ObjectiveAbhijeet NigoskarNo ratings yet
- Module 03Document48 pagesModule 03CGASTUFFNo ratings yet
- The Systems Development Environment Information Systems Analysis and DesignDocument10 pagesThe Systems Development Environment Information Systems Analysis and Designsuryavamshirakesh1No ratings yet
- MisDocument13 pagesMisFish de Paie0% (1)
- SDLCDocument37 pagesSDLCYna SarrondoNo ratings yet
- Conceptual System Design OverviewDocument3 pagesConceptual System Design OverviewSuresh Kumar100% (2)
- MIS Session 5 2011Document53 pagesMIS Session 5 2011avinash00000No ratings yet
- UNIT - 3 Bba VI MISDocument5 pagesUNIT - 3 Bba VI MISTIBNA SAYYEDNo ratings yet
- Lovely Professional University Home Work: #1 Architecture School: LSECADocument5 pagesLovely Professional University Home Work: #1 Architecture School: LSECAParveen PaulNo ratings yet
- Systems Development Investigation and AnalysisDocument15 pagesSystems Development Investigation and AnalysisAditya Singh100% (1)
- Sad Notes Unit ThreeDocument9 pagesSad Notes Unit ThreeNaresh PatelNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS - System Planning & Initial InvestigationDocument10 pagesANALYSIS - System Planning & Initial InvestigationEru100% (2)
- Management Information System - Planning, Designing and Implementation of MisDocument12 pagesManagement Information System - Planning, Designing and Implementation of Miscompiler&automataNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Lecture No. 05Document5 pagesUnit 01 Lecture No. 05Jayshri SachdevNo ratings yet
- BB0007 Management Information SystemsDocument29 pagesBB0007 Management Information SystemsAshraf HussainNo ratings yet
- Obrien13e Chap010Document82 pagesObrien13e Chap010Sohail MerchantNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Management Information SystemsDocument14 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Management Information SystemsvinuoviyanNo ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration-MBA Semester II (Assignment Set-1 (60 Marks)Document17 pagesMaster of Business Administration-MBA Semester II (Assignment Set-1 (60 Marks)Shiv KumarNo ratings yet
- Management:: DefinitionDocument12 pagesManagement:: Definitionkapiljangra25No ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument25 pagesManagement Information SystemHamud Husein Du'aleNo ratings yet
- MIS Unit-1Document15 pagesMIS Unit-1Ranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- College Info and SolutionDocument47 pagesCollege Info and SolutionNilesh Kumar ParjapatiNo ratings yet
- Introduction of ProjectDocument38 pagesIntroduction of ProjectAndrew MeyerNo ratings yet
- MIS Development ProcessDocument19 pagesMIS Development ProcessAnchal MishraNo ratings yet
- Management Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4From EverandManagement Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4No ratings yet
- MIS Topic No 08Document13 pagesMIS Topic No 08Jebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- POM ImportancedDocument1 pagePOM ImportancedJebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- MIS Analysis 2012Document1 pageMIS Analysis 2012Jebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Bba Mis Topic 6Document3 pagesBba Mis Topic 6Jebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Plant LayoutDocument60 pagesPlant LayoutJebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Bba Mis Topic 5Document2 pagesBba Mis Topic 5Jebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Bba Mis Topic 2Document2 pagesBba Mis Topic 2Jebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Mis BbaDocument2 pagesMis BbaJebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Bba Mis Topic 4Document6 pagesBba Mis Topic 4Jebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Bba Mis Topic 3Document5 pagesBba Mis Topic 3Jebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Budget Imp..Document5 pagesBudget Imp..lavanya2401No ratings yet
- Bba Mis Topic 1Document3 pagesBba Mis Topic 1Jebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Statement: Position of A Firm. Cash and Relevant Terms As Per AS-3 (Revised)Document17 pagesCash Flow Statement: Position of A Firm. Cash and Relevant Terms As Per AS-3 (Revised)Jebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Fund Flow STDocument6 pagesFund Flow STJebby VargheseNo ratings yet
- Web Image Re-Ranking Using Query-Specific Semantic SignaturesDocument14 pagesWeb Image Re-Ranking Using Query-Specific Semantic Signaturesphilo minaNo ratings yet
- Personal Systems Reference Lenovo Thinkcentre Desktops: October 2009 - Version 364Document100 pagesPersonal Systems Reference Lenovo Thinkcentre Desktops: October 2009 - Version 364Jacob JouNo ratings yet
- 190226155747MHADA Nashik Booklet 2019 PDFDocument90 pages190226155747MHADA Nashik Booklet 2019 PDFChaitanya M MundheNo ratings yet
- Getting Started in MicroStationDocument59 pagesGetting Started in MicroStationnurul_suhariNo ratings yet
- Programming Concepts: by RamanamurthyDocument10 pagesProgramming Concepts: by RamanamurthyRamanamurthy SaripalliNo ratings yet
- LectureNotes - 20170410-1 - Introduction To EHMIDocument19 pagesLectureNotes - 20170410-1 - Introduction To EHMINam Vũ0% (1)
- Accurately Identify Tortuosity From Spud To Total Depth: Microguide™Document2 pagesAccurately Identify Tortuosity From Spud To Total Depth: Microguide™Jose Manuel Lezama SantaellaNo ratings yet
- HCF and LCMDocument4 pagesHCF and LCMSureJobsPlacementsNo ratings yet
- Interbase Language Reference PDFDocument292 pagesInterbase Language Reference PDFdanielbg817No ratings yet
- Railway Reservation System Er DiagramDocument4 pagesRailway Reservation System Er DiagramPenki Sarath67% (3)
- Java Coding GuidelineDocument26 pagesJava Coding GuidelineNazmul KarimNo ratings yet
- S0 HandoutDocument4 pagesS0 HandoutJ Reach (JR3ach)No ratings yet
- Mail Enable Enterprise GuideDocument135 pagesMail Enable Enterprise Guideapi-3830738100% (1)
- Book Shop Management SystemDocument20 pagesBook Shop Management Systemkabatahjohn100% (2)
- Project Report Submitted To For ExampleDocument10 pagesProject Report Submitted To For ExampleKrishnanand AnvekarNo ratings yet
- 8086 Development ToolsDocument7 pages8086 Development ToolsJashuva Chukka0% (1)
- CAD IntegrationDocument132 pagesCAD IntegrationSuri Kens MichuaNo ratings yet
- HW2 JARNIR2 Rozita 5116201037Document7 pagesHW2 JARNIR2 Rozita 5116201037Rozita RahmanNo ratings yet
- OmniSwitch - Router User Manual R4-5Document1,100 pagesOmniSwitch - Router User Manual R4-5HeriNo ratings yet
- Power ViewDocument2 pagesPower ViewcerebroNo ratings yet
- 5 - Integration - Partial FractionsDocument2 pages5 - Integration - Partial FractionsDudeNo ratings yet
- Bus Pass BharatDocument2 pagesBus Pass BharatRakNo ratings yet
- "Parasitic Computing": Seminar Report ByDocument10 pages"Parasitic Computing": Seminar Report ByKanumuru KushalNo ratings yet
- Bolt Pattern OptimizationDocument20 pagesBolt Pattern OptimizationNitin Chandra0% (1)