Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structure and Functions: Steps
Uploaded by
Geetika KhuranaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structure and Functions: Steps
Uploaded by
Geetika KhuranaCopyright:
Available Formats
STEPS A T CY Progr am _________________________________________________________________________________
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11 12 13.
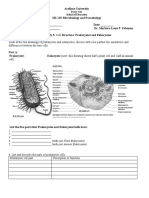
What is cell? What are the unicellular and multicellular organisms? Write the function of Flagella? What is the role of chloroplast in the plants? Name the material found in the nucleus. Differentiate between plant cell and animal cell. What is cell wall? Give its functions? Group the following organism into unicellular and multicellular organism. Amoeba, plants, paramecium, bacteria, human Draw a well labelled diagram of a typical cell. Give the average size of the following cells in the living organism. 1. Living red blood cell 2. Nerve cell 3. Green algae Chara 4. Ostrich egg Write a short note on plastids. Write short note on (A) Nucleus (B) Mitochondria Write a short note on protoplasm.
[1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [2] [2] [2] [3] [3] [3] [5] [5]
STEPS____________________________________________________________ 1
Get free notes for Class X and IX on www.tcyonline.com
STEPS A T C Y P rogr am _________________________________________________________________________________
SOLUTIONS
1. 2. Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organism. Unicellular organism Single celled organism are called unicellular organism. Multi cellular organism Multi cellular organism has millions of cells. Flagella help in the movement of the cell or the organisms. They help in the synthesis of food. Chromatin (1) Cell wall (2) Plastids (3) Vacuoles (4) Mitochondria 7. 8 9 Plant cell Present Present Large Present Animal cell Absent Absent Small Present
3. 4. 5. 6.
An outer rigid layer in plant cell called cell wall Function Cell wall give shape to the cell. Unicellular organism: Amoeba, paramecium and bacteria. Multi cellular organism: Human and plants.
Structure of a typical cell
10. 1. 9 m (9 106m) 2. more than a metre long 3. 10 cm 4. 170 mm in diameter 12 (A) Plastids are the particles found in plant cells. These contain pigments. The green plastids in the plants are celled chloroplasts. They help in the synthesis of food. The red colour plastid in tomato is due to the plastids with red pigments. Nucleus Most of the cell contain nucleus in the centre. However, it may also be in the periphery of the cell as in case of plant cell. The liquid protoplasm in the nucleus is called nucleoplasm, which is bound by nuclear membrane. Nucleus controls the activities of the cells.
11
2 STEPS____________________________________________________________ Get free notes for Class X and IX on www.tcyonline.com
STEPS A T CY Progr am _________________________________________________________________________________
It contains a network of fibrous material called chromatin. The condensed chromatin is the form of fibre like structures called chromosome, which helps in transfer of characters from the parents to next generation. (B) Mitochondria Mitochondria is rodshaped or spherical organelles. Each Mitochondria is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane. Mitochondria provide energy for the activities of the cell. Cell membrane encloses a liquid substance known as protoplasm. Protoplasm is made up of compounds of four elements, namely carbon, hydrogen nitrogen and oxygen. It also contains compound of other elements. Elements in different combination from compounds. Some of these compounds such as water, carbohydrate, protein, fats, nucleic aid and minerals salts which provide living nature to the protoplasm. Protoplasm contains several of smaller components of cell. Such as nucleus, chromatin, plastids, mitochondria etc.
13.
STEPS____________________________________________________________ 3
Get free notes for Class X and IX on www.tcyonline.com
You might also like
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Cell Organelles - Biology Class 11 - NEETDocument18 pagesCell Organelles - Biology Class 11 - NEETsanjNo ratings yet
- Class-8, Ch5,6Document2 pagesClass-8, Ch5,6Amit Kumar LalNo ratings yet
- Activity Worksheets: BiotechnologyDocument15 pagesActivity Worksheets: BiotechnologyTrinity MarieNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8Document6 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8Abhay rathorNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Module 4-c3 3Document6 pagesScience 8 Module 4-c3 3Naomi Margaret PetolanNo ratings yet
- Revision: Cell Division 20 MARCH 2013: Lesson DescriptionDocument19 pagesRevision: Cell Division 20 MARCH 2013: Lesson DescriptionKaylaNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organelles New - Answer KEY - FinalDocument9 pagesCells and Organelles New - Answer KEY - FinalMelyza Ann Pronebo50% (2)
- GEN BIO1 Q1M1 Subtopic Week 2 LectureDocument4 pagesGEN BIO1 Q1M1 Subtopic Week 2 LectureDonnalyn Mae EscrupoloNo ratings yet
- Cells Objectives For Exam #1Document6 pagesCells Objectives For Exam #1Nelsi Antonius Kala100% (1)
- Worksheet 2 Cell StructureDocument4 pagesWorksheet 2 Cell StructurenathanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cell AnatomyDocument5 pagesModule 2 Cell Anatomy10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- Cells: Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument8 pagesCells: Cells: The Building Blocks of Lifems_m_tan100% (8)
- SLM Biotech Wekk 1 2Document7 pagesSLM Biotech Wekk 1 2Petronila LumaguiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and Function WorksheetsDocument24 pagesCellular Structure and Function WorksheetsLouiseNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions of Cell Structure and Functions of Class 8 Science - Free PDF DownloadDocument5 pagesNCERT Solutions of Cell Structure and Functions of Class 8 Science - Free PDF DownloadLucky MishraNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell Membrane: Patricia Caldani MSDocument51 pagesCell and Cell Membrane: Patricia Caldani MSkittypattyNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesDelhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionSaket TNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 BioA 3201Document6 pagesAssign 2 BioA 3201Princess CabardoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1. The CellDocument7 pagesLesson 2.1. The CellGemma CabañasNo ratings yet
- Cell Lesson NotesDocument8 pagesCell Lesson NotesNikshita KNo ratings yet
- Dajana Lucaj - Cells & Their Organelles PDFDocument8 pagesDajana Lucaj - Cells & Their Organelles PDFdajanaNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure and Function Class 8 Notes: CellsDocument26 pagesCell - Structure and Function Class 8 Notes: CellsPrabal SinghNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument8 pagesActivity 5 - Cell Structure - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAdrian NenengNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts Functions WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Parts Functions WorksheetIan CausseauxNo ratings yet
- SLM Number 4-Grade 7 Science - 2nd-Quarter - Plant - and - Animalcell-2Document16 pagesSLM Number 4-Grade 7 Science - 2nd-Quarter - Plant - and - Animalcell-2Maria Fe Vibar100% (5)
- Cells and Organelles - 1Document6 pagesCells and Organelles - 1Izabayo philippeNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH IN MEDICINE 1 (Y đa khoa) -đã chuyển đổiDocument16 pagesENGLISH IN MEDICINE 1 (Y đa khoa) -đã chuyển đổiNguyễn Thị HiênNo ratings yet
- Edible Plant CellDocument4 pagesEdible Plant CellgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function ObjectivesDocument4 pagesCell Structure & Function ObjectivesNathan NkNo ratings yet
- Cells and OrganellesDocument8 pagesCells and OrganellesWilliam RyandinataNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsPrashant PatilNo ratings yet
- Hum, An CellDocument6 pagesHum, An CellQlife KlinikNo ratings yet
- Cell Class 8Document3 pagesCell Class 8Diksha MehraNo ratings yet
- GR 8 3.1-3.2-3.3 FormativeDocument4 pagesGR 8 3.1-3.2-3.3 FormativeShaimaa SalamaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document13 pagesCell Organelles 2Sadeeq ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1, Cell BiologyDocument8 pagesChapter-1, Cell Biologyguptanirmal996No ratings yet
- 2022 Cells Revision AnswersDocument11 pages2022 Cells Revision Answersdantimtam33No ratings yet
- Biology: Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument5 pagesBiology: Cell Organelles WorksheetАлександър Антоан НиколовNo ratings yet
- Unit Cell. Organization of The Human Body: Organ SystemDocument11 pagesUnit Cell. Organization of The Human Body: Organ SystemАнастасия ФилипчукNo ratings yet
- 5 Cell Review PacketDocument4 pages5 Cell Review PacketWilliam Pettus100% (1)
- Iqbal Memorial High School Dooru Shahabad: Lesson No. 2 (The Cell) A. Subjective QuestionsDocument18 pagesIqbal Memorial High School Dooru Shahabad: Lesson No. 2 (The Cell) A. Subjective QuestionsUBAID YAQOOBNo ratings yet
- cell and its structure (разработка)Document8 pagescell and its structure (разработка)Ирина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Ap BiologyDocument11 pagesAp BiologyChandra NekkantiNo ratings yet
- Unit Cell. Organization of The Human Body: Organ SystemDocument11 pagesUnit Cell. Organization of The Human Body: Organ SystemVlad PopaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 3rd Edition AlbertsDocument16 pagesCH 1 Test Bank For Essential Cell Biology 3rd Edition AlbertsRokia GhariebNo ratings yet
- Lesson No & Name: 8 - : Cell-Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesLesson No & Name: 8 - : Cell-Structure and FunctionUzair MaqdoomNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Cell StructureDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 - Cell StructureRonel Mendoza50% (2)
- Unit Cell. Organization of The Human Body: Organ SystemDocument11 pagesUnit Cell. Organization of The Human Body: Organ SystemГорькое ДноNo ratings yet
- Complete TB Essential Cell Biology by Alberts 3rd Ed PDFDocument346 pagesComplete TB Essential Cell Biology by Alberts 3rd Ed PDFHusein Dharas95% (19)
- Botany Chapter 3 Review QuestionsDocument5 pagesBotany Chapter 3 Review QuestionsMia MistypuffNo ratings yet
- Key Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellDocument14 pagesKey Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellShweta ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Structurelingesh tamizhanNo ratings yet
- G10 PB WE CELL STRUCTURE BIO Fixx Bangettt Banget YaaaaDocument7 pagesG10 PB WE CELL STRUCTURE BIO Fixx Bangettt Banget YaaaaLia lylNo ratings yet
- ds45 Intro To Cellular OrganellesDocument10 pagesds45 Intro To Cellular Organellesapi-110789702No ratings yet
- OliverosChristian Laboratory Activity No. 2Document11 pagesOliverosChristian Laboratory Activity No. 2Christian OliverosNo ratings yet
- Cell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1Document7 pagesCell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Animal CellsDocument29 pagesAnimal Cellschinatu4No ratings yet
- Session No. 1.2. Cell Types and ModificationsDocument48 pagesSession No. 1.2. Cell Types and ModificationsShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Class X Maths Sample Paper1Document12 pagesClass X Maths Sample Paper1Tata V DixitNo ratings yet
- Dav Solved Question Paper 2017-18Document381 pagesDav Solved Question Paper 2017-18Geetika Khurana0% (1)
- Comp 1Document89 pagesComp 1Geetika KhuranaNo ratings yet
- X Practice Paper 1Document35 pagesX Practice Paper 1Geetika KhuranaNo ratings yet
- 10th 1040117 - C2 Mathematics QPDocument13 pages10th 1040117 - C2 Mathematics QPVishnupriya NikhilNo ratings yet
- 2013 10 SP Mathematics Sa2 04Document10 pages2013 10 SP Mathematics Sa2 04Geetika KhuranaNo ratings yet
- 2081 SS QPDocument10 pages2081 SS QPGeetika KhuranaNo ratings yet
- 041 X Sa2 01 c1 QP MathematicsDocument12 pages041 X Sa2 01 c1 QP MathematicsGeetika KhuranaNo ratings yet
- I SA Class VI English 2011Document5 pagesI SA Class VI English 2011Geetika KhuranaNo ratings yet
- 1001 Ma QPDocument9 pages1001 Ma QPGeetika KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Leaky Blood Vessels - An Unknown Danger of COVID-19 Vaccination - Doctors For COVID EthicsDocument2 pagesLeaky Blood Vessels - An Unknown Danger of COVID-19 Vaccination - Doctors For COVID EthicsHansley Templeton CookNo ratings yet
- Principles of Nerual ScienceDocument28 pagesPrinciples of Nerual ScienceRaunak MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Advances in Parasit OlogyDocument321 pagesAdvances in Parasit Ologyintanhardianti7No ratings yet
- IB DP Biology 1.4 Membrane Transport QuestionDocument19 pagesIB DP Biology 1.4 Membrane Transport QuestionikaNo ratings yet
- Amparo Torreblanca UvegDocument28 pagesAmparo Torreblanca Uvegapi-238489868No ratings yet
- (Methods in Molecular Biology 823) Stacy M. Cowherd (Auth.), Virginia Espina, Lance A. Liotta (Eds.) - Molecular Profiling - Methods and Protocols (2012, Humana Press)Document462 pages(Methods in Molecular Biology 823) Stacy M. Cowherd (Auth.), Virginia Espina, Lance A. Liotta (Eds.) - Molecular Profiling - Methods and Protocols (2012, Humana Press)ashutosh pandey100% (1)
- Pglo Lab ReportDocument4 pagesPglo Lab Reportapi-345256671No ratings yet
- Biology 11 NotesDocument219 pagesBiology 11 NotesShitalPatilNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 4 2007 Jan MSDocument10 pagesBiology Unit 4 2007 Jan MSnaim118No ratings yet
- AGM 301 - Mid Sem QPDocument15 pagesAGM 301 - Mid Sem QPshubham100% (1)
- Norditropin PresentationDocument5 pagesNorditropin PresentationCaralee Nelson HarpsøeNo ratings yet
- Etextbook 978 0077837280 Ecology Concepts and Applications 7th EditionDocument61 pagesEtextbook 978 0077837280 Ecology Concepts and Applications 7th Editioncarolee.kuehl851100% (50)
- Denaturation of ProteinsDocument16 pagesDenaturation of ProteinsLineah Untalan100% (2)
- Plant Transport Multiple Choice Qs PDFDocument7 pagesPlant Transport Multiple Choice Qs PDFMathula MuhundanNo ratings yet
- Biology Ncert Revision-BiomoleculesDocument12 pagesBiology Ncert Revision-BiomoleculesRITANKAR dASNo ratings yet
- Hope - 1 Grade 11: Exercise For FitnessDocument11 pagesHope - 1 Grade 11: Exercise For FitnessMark Johnson San JuanNo ratings yet
- The Importance of A Balanced DietDocument4 pagesThe Importance of A Balanced DietdimdamflyNo ratings yet
- TN - Gram Positive Vs Gram Negative - Article - JL - V2ksDocument5 pagesTN - Gram Positive Vs Gram Negative - Article - JL - V2ksNGÂN NGUYỄN HOÀNG TRÚCNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom PowernotesDocument3 pagesPlant Kingdom Powernotessheikhanzar643No ratings yet
- Osmosis LabDocument12 pagesOsmosis Labapi-319060025No ratings yet
- Meselson and Stahl Experiment DeterminedDocument1 pageMeselson and Stahl Experiment DeterminedCarolina RelvaNo ratings yet
- Latihan MitosisDocument7 pagesLatihan MitosisChe Mahani HussainNo ratings yet
- Scaling Test - JawaharDocument12 pagesScaling Test - JawaharJawahar JawaharNo ratings yet
- Diversity and Endemicity of Chilimo Forest, Central EthiopiaDocument4 pagesDiversity and Endemicity of Chilimo Forest, Central Ethiopiaasmeraamde21No ratings yet
- History of Genetics - BargayoDocument14 pagesHistory of Genetics - BargayoDarling Jen Saranillo BargayoNo ratings yet
- ENS ReportDocument13 pagesENS ReportAirastormNo ratings yet
- PiXL Knowledge Test QUESTIONS - AQA B1 CORE Science - Legacy (2016 and 2017)Document6 pagesPiXL Knowledge Test QUESTIONS - AQA B1 CORE Science - Legacy (2016 and 2017)Mrs S BakerNo ratings yet
- The Skeleton System Book 2 Book 2Document30 pagesThe Skeleton System Book 2 Book 2MortezaNo ratings yet
- Hea 1 PERSONAL AND COMMUNITY HEALTHDocument4 pagesHea 1 PERSONAL AND COMMUNITY HEALTHvaneknekNo ratings yet
- Mantle Cell LymphomaDocument9 pagesMantle Cell Lymphomavam buddhaNo ratings yet