Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 15 Section 1
Uploaded by
Autumn FingerOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 15 Section 1
Uploaded by
Autumn FingerCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 15 Section 1 Notes
Chapter 15 Section 1 The Idea of Evolution The development of new types of organisms from preexisting types of organisms over time is called evolution. Modern scientists also define evolution as a change in the characteristics within a population from one generation to the next. After visiting the Galapagos Islands and noticing the variety of animal species there, Charles Darwin wanted to present evidence that evolution occurred. Darwin's theory became the basis for future explanations of evolution
During the 18th century, most European scientists believed that all species were permanent and unchanging. Additionally, they believed that the Earth was only thousands of years old. However, new evidence was being found that suggested that species have changed overtime and that the Earth was much older than anyone had previously imagined
Ideas of Darwins Time
Ideas about Geology
Scientists in Europe had begun studying rock layers, also known as strata. They found that strata re formed as new layers of rock are deposited over time, inferring that lower strata were formed first. These scientists also discovered fossils of different organisms in the strata Georges Cuvier, a French anatomist, gave convincing evidence that some organisms in the past were vastly different that organisms of today, and that some of them had become extinct, and ceased to exist after a certain point in time. He also found that deeper and older strata hold organisms that are increasingly different from living species. He also found many sudden changes in the kinds of organisms found in one rock stratum compared to the next. Cuvier promoted the idea of catastrophism, which states that sudden geologic catastrophes caused the extinction of large groups of organisms in the past English geologist Charles Lyell thought that the geologic processes that have shaped Earth in the past continue to work in the same ways. His idea is called uniformtarianism. Charles Darwin read Lyells writings, excited to find how well Lyells ideas fit with his own observations and ideas
Lamarcks Ideas on Evolution
Jean Lamarck supported the idea that populations of organisms change overtime. He put forth a new idea to explain how evolution occurred he thought that simple organisms could arise from nonliving matter and that simple forms of life inevitably develop into more complex forms. He proposed that individuals could acquire traits during their lifetimes as a result of experience or behavior, and then pass on those traits to offspring. His idea is called the inheritance of acquired characteristics. However, his ideas are no longer accepted by scientists, since it has not been supported by modern scientific study
Darwin's Ideas Descent with Modification
Natural Selection
Darwin used the phrase descent with modification to describe the process of evolution. He reviewed the evidence that every species must have descended by reproduction from preexisting species and that species must be able to change overtime. While not the first person to put forward the idea of descent with modification, Darwin was the first to apply it to all species Animals of the Galapagos Islands were seen as evidence of descent with modification by Darwin. For example, the islands are home to thirteen different species. Each of these species has a beak that is best adapted for a certain kind of food. Darwin suspected that all thirteen species descended from the same ancestor, then diverged to better survive in the varied environments of the different islands. The theory of natural selection was proposed by Darwin as the mechanism for descent with modification. 1)Overproduction More offspring can be produced than can survive to maturity. Since each new organism needs food and is vulnerable to predators and disease, not all of them live for very long. Economist Thomas Malthus pointed out that human populations can increase more quickly than food supply, but that populations are limited by the environment. Darwin drew this part of his theory from Malthus idea, realizing that the environment limits the populations of all organisms by causing deaths or limiting births. 2)Genetic Variation Within a population, individuals have different traits. For example, some giraffes have longer necks than others. These variations can be inherited; giraffes with long necks tend to have offspring with long necks. New traits can appear in a population. 3)Struggle to Survive Individual must compete with each other in a struggle for existence. Some variations allow organisms to have a better chance of surviving and reproducing. For example, giraffes with longer necks will be able to reach more leaves on trees than those with shorter necks. An adaptation is a trait that makes an individual successful in its environment. 4)Differential Reproduction Darwin concluded that organisms with the best adaptations are most likely to survive and reproduce. Through inheritance, the adaptations will become more frequent in the population. Thus, populations may begin to differ if they become adapted to different environments, even if they descended from the same ancestors. The theory of natural selection proposes that nature changes species by selecting traits. The environment selects the traits that may increase in a population by selecting the parents for each new generation.
Darwin also used the phrase survival of the fittest to describe his theory of natural selection. Fitness is a measure of an individuals hereditary contribution to the next generation to be fit, an individual must have offspring that also live long enough to reproduce in a given environment. If a certain trait increases an organisms fitness, the proportion of organisms with that trait is likely to increase over time. In conclusion, adaptations are traits that increase the fitness of individuals, and populations tend to be well adapted to survive the conditions in which they live Adaptation is also used to describe changes in traits in populations over time, and is different from short-term adaptation by an individual to a temporary condition. Acclimatization is a short-term process in which physiological changes take place in an individual in its own lifetime growing thicker fur in a cold climate. This is different from the adaptations discussed previously because this is not a variation caused by genetics.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Bhalaaji - Art and Science of Orthodontics WordDocument578 pagesBhalaaji - Art and Science of Orthodontics WordBudi AthAnza Suhartono85% (13)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Aoun, Lucas (2021) BOOST YOUR BRAIN - A Beginner's Guide To Leverage The Power of Nootropics For Ultimate Brain EnhancementDocument49 pagesAoun, Lucas (2021) BOOST YOUR BRAIN - A Beginner's Guide To Leverage The Power of Nootropics For Ultimate Brain EnhancementJordan67% (3)
- DBQ FOCUS: Columbian Exchange: Document-Based Question FormatDocument5 pagesDBQ FOCUS: Columbian Exchange: Document-Based Question Formatbaruc barranco50% (2)
- Hydroponics - Introduction To HydroponicsDocument91 pagesHydroponics - Introduction To HydroponicscorradiniaNo ratings yet
- Ipdoaj MS Id 000113Document3 pagesIpdoaj MS Id 000113Ayu DamayNo ratings yet
- Wrist Pivot Method of TMJ Dislocation ReductionDocument4 pagesWrist Pivot Method of TMJ Dislocation ReductionRomzi HanifNo ratings yet
- 7 Activities in Sciencewithout ProceduresDocument5 pages7 Activities in Sciencewithout ProceduresRhenier Ruiz GustiloNo ratings yet
- ManuskripDocument156 pagesManuskripFarhan FaturrohmanNo ratings yet
- UB HSPED Differential Diagnosis of Lower Back PainDocument62 pagesUB HSPED Differential Diagnosis of Lower Back PainJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis and HomoeopathyDocument18 pagesDermatitis and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (1)
- 11 Oxirane GC MSDocument6 pages11 Oxirane GC MSCHRISTIAN FELIPE JIMENEZ MURILLONo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Gas ExchangeDocument7 pagesLesson 3 Gas ExchangeBrent PatarasNo ratings yet
- Screening For Colorectal CancerDocument6 pagesScreening For Colorectal CancerDiana BlanaruNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Childhood Cancer On Family FunctioningDocument13 pagesThe Impact of Childhood Cancer On Family Functioningapi-585969205No ratings yet
- Script For Head To NeckDocument7 pagesScript For Head To NeckSydney Joy Abaca100% (1)
- E2870-13 Standard Test Method For Evaluating RelativDocument6 pagesE2870-13 Standard Test Method For Evaluating RelativA MusaverNo ratings yet
- High - Risk Labor and Delivery 2Document106 pagesHigh - Risk Labor and Delivery 2Charmaine Louie Macalanda Lopez-Soriano100% (2)
- Scaling and Root Planing Presentation - DR - Naaz GillDocument37 pagesScaling and Root Planing Presentation - DR - Naaz GillNaazGill100% (1)
- Round Cell Tumors - Classification and ImmunohistochemistryDocument13 pagesRound Cell Tumors - Classification and ImmunohistochemistryRuth SalazarNo ratings yet
- PSM 2 PypDocument186 pagesPSM 2 PypsuriNo ratings yet
- Power in The Group 95 5 Wellness Solution GuideDocument33 pagesPower in The Group 95 5 Wellness Solution GuideSanjaMilićevNo ratings yet
- Alkalizing Nutritional Therapy in The Prevention and Treatment of Any Cancerous Condition by Robert Young Galina Migalko (Young, Robert Migalko, Galina)Document51 pagesAlkalizing Nutritional Therapy in The Prevention and Treatment of Any Cancerous Condition by Robert Young Galina Migalko (Young, Robert Migalko, Galina)Maria S100% (1)
- Maw Soundbridge ArticleDocument11 pagesMaw Soundbridge ArticleSarah MacNo ratings yet
- In The Context of Nepal, Most of The Studies Have Identi Ed Iron de Ciency Anemia Only Based On Hemoglobin Level in The Context of Nepal, Most of The Studies Have Identi EdDocument10 pagesIn The Context of Nepal, Most of The Studies Have Identi Ed Iron de Ciency Anemia Only Based On Hemoglobin Level in The Context of Nepal, Most of The Studies Have Identi EdAshma KhulalNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Clinical SignificanceDocument10 pagesCarbohydrates Clinical SignificanceMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
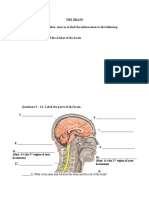
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument3 pagesNervous System WorksheetaNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument22 pagesCase PresentationManjunath ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Ru 638 2 in 1 Beauty Instrument ManualDocument4 pagesRu 638 2 in 1 Beauty Instrument Manualyeny8001No ratings yet
- Covid CertificateDocument1 pageCovid CertificatesrilaksvelacheryNo ratings yet
- The Witch Trials of Finnmark, Northern NorwayDocument14 pagesThe Witch Trials of Finnmark, Northern NorwaythestylerhimselfNo ratings yet